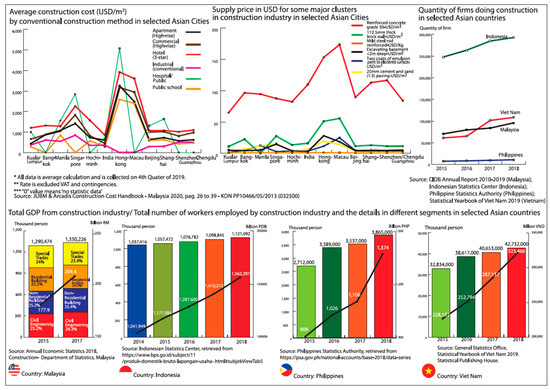
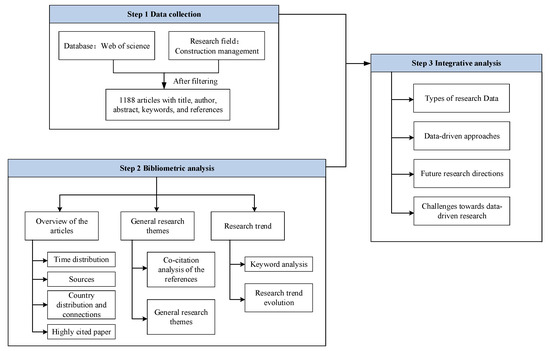
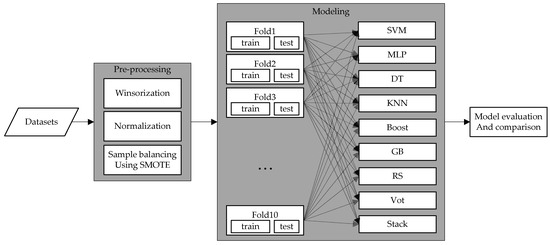
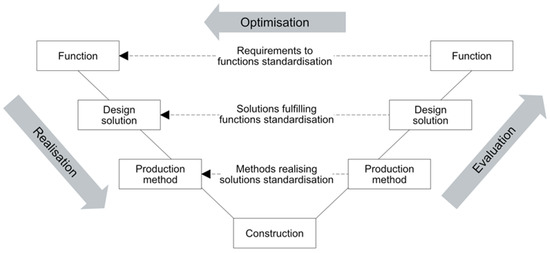
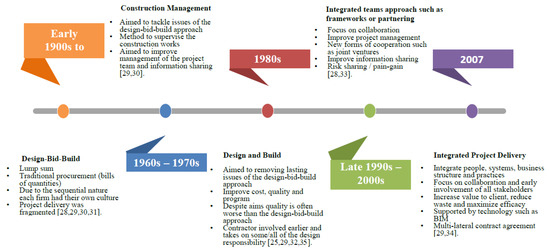
Construction Management – Future Innovations, Methods, Techniques and Technologies
A topical collection in Buildings (ISSN 2075-5309). This collection belongs to the section "Construction Management, and Computers & Digitization".
Viewed by 250149Editors
Interests: supporting decisions in construction; delays in construction projects; risk assessment in construction; project cost estimation; tendering and bidding in construction; using artificial neural networks in construction management; building procurement
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: construction cost estimation; building information modelling technology; design and build and integrated project delivery; activity of developer companies; evaluation of investment efficiency; sustainable construction and using case-based reasoning and fuzzy logic in construction management
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
The management of construction projects can be a very complicated process, especially when there are too many construction companies and various parties involved. The progress of information technology, as well as decision support methods, in the fields of cost planning and time and risk management systematically pushes the limits of possibilities in the construction industry and the range of impact on the entire construction industry.
The implementation of the latest solutions is necessary for construction companies to achieve success in the industry and remain competitive in the global market. As advanced technologies developed, the integration of technologies has been adopted for promoting new technologies and methods in construction in recent years, such as building information modeling (BIM), simulation-based methods, or mathematical methods supporting decision-making.
It is necessary to use new trends and ideas in many areas of construction project management, such as costing, scheduling, safety at the construction site, and human resource management in various types of construction projects in all phases.
The aim of this Topical Collection is to provide a platform to explore the state-of-the-art knowledge, practical implementation, and cutting-edge innovations in the area of construction management in construction industry.
Survey and theoretical articles, as well as application papers, are welcome.
Prof. Dr. Agnieszka Leśniak
Dr. Krzysztof Zima
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Buildings is an international peer-reviewed open access monthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2600 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- BIM technology
- construction procurement
- cost management
- demolition and disposal
- health and safety
- information technologies
- project scheduling problems
- risk management
- simulation-based methods
- supporting decision-making