-
 The Role of the Myokine Irisin in the Protection and Carcinogenesis of the Gastrointestinal Tract
The Role of the Myokine Irisin in the Protection and Carcinogenesis of the Gastrointestinal Tract -
 Screening for Metal-Chelating Activity in Potato Protein Hydrolysates Using Surface Plasmon Resonance and Peptidomics
Screening for Metal-Chelating Activity in Potato Protein Hydrolysates Using Surface Plasmon Resonance and Peptidomics -
 Evaluation of Sample Size Influence on Chemical Characterization and In Vitro Antioxidant Properties of Flours Obtained from Mushroom Stems Coproducts
Evaluation of Sample Size Influence on Chemical Characterization and In Vitro Antioxidant Properties of Flours Obtained from Mushroom Stems Coproducts -
 Mitochondria Dysfunction and Neuroinflammation in Neurodegeneration: Who Comes First?
Mitochondria Dysfunction and Neuroinflammation in Neurodegeneration: Who Comes First? -
 Cyanide Insensitive Oxidase Confers Hydrogen Sulfide and Nitric Oxide Tolerance to Pseudomonas aeruginosa Aerobic Respiration
Cyanide Insensitive Oxidase Confers Hydrogen Sulfide and Nitric Oxide Tolerance to Pseudomonas aeruginosa Aerobic Respiration
Journal Description
Antioxidants
Antioxidants
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal, published monthly online by MDPI. The International Coenzyme Q10 Association (ICQ10A), Israel Society for Oxygen and Free Radical Research (ISOFRR) and European Academy for Molecular Hydrogen Research (EAMHR) are affiliated with Antioxidants and their members receive discounts on the article processing charge.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE (Web of Science), PubMed, PMC, FSTA, PubAg, CAPlus / SciFinder, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q1 (Food Science & Technology) / CiteScore - Q1 (Food Science)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 13.9 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.6 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2023).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
- Testimonials: See what our editors and authors say about Antioxidants.
- Companion journal: Oxygen.
Impact Factor:
7.0 (2022);
5-Year Impact Factor:
7.3 (2022)
Latest Articles
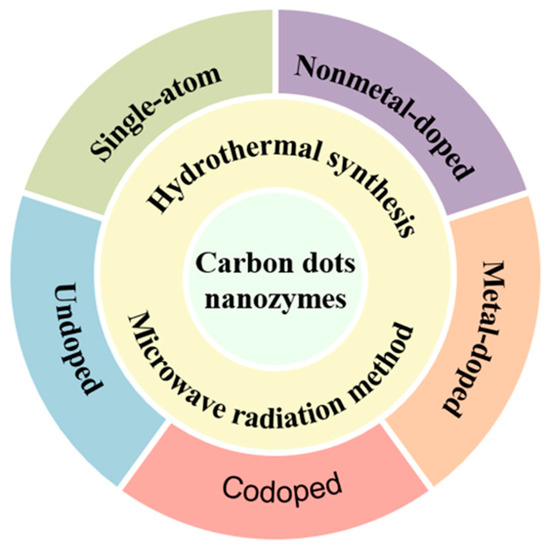
Preparation and Application of Carbon Dots Nanozymes
Antioxidants 2024, 13(5), 535; https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox13050535 (registering DOI) - 27 Apr 2024
Abstract
►
Show Figures
Carbon dot (CD) nanozymes have enzyme-like activity. Compared with natural enzymes, CD nanozymes offer several advantages, including simple preparation, easy preservation, good stability and recycling, which has made them a popular research topic in various fields. In recent years, researchers have prepared a
[...] Read more.
Carbon dot (CD) nanozymes have enzyme-like activity. Compared with natural enzymes, CD nanozymes offer several advantages, including simple preparation, easy preservation, good stability and recycling, which has made them a popular research topic in various fields. In recent years, researchers have prepared a variety of CD nanozymes for biosensing detection, medicine and tumor therapy, and many of them are based on oxidative stress regulation and reactive oxygen species clearance. Particularly to expand their potential applications, elemental doping has been utilized to enhance the catalytic capabilities and other properties of CD nanozymes. This review discusses the prevalent techniques utilized in the synthesis of CD nanozymes and presents the diverse applications of CD nanozymes based on their doping characteristics. Finally, the challenges encountered in the current utilization of CD nanozymes are presented. The latest research progress of synthesis, application and the challenges outlined in the review can help and encourage the researchers for the future research on preparation, application and other related researches of CD nanozymes.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
LanCL2 Implicates in Testicular Redox Homeostasis and Acrosomal Maturation
by
Yanling Zhao, Jichen Wang, Shuai Shi, Xinting Lan, Xiangyu Cheng, Lixia Li, Yuanfeng Zou, Lanlan Jia, Wentao Liu, Qihui Luo, Zhengli Chen and Chao Huang
Antioxidants 2024, 13(5), 534; https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox13050534 (registering DOI) - 27 Apr 2024
Abstract
Redox balance plays an important role in testicular homeostasis. While lots of antioxidant molecules have been identified as widely expressed, the understanding of the critical mechanisms for redox management in male germ cells is inadequate. This study identified LanCL2 as a major male
[...] Read more.
Redox balance plays an important role in testicular homeostasis. While lots of antioxidant molecules have been identified as widely expressed, the understanding of the critical mechanisms for redox management in male germ cells is inadequate. This study identified LanCL2 as a major male germ cell-specific antioxidant gene that is important for testicular homeostasis. Highly expressed in the brain and testis, LanCL2 expression correlates with testicular maturation and brain development. LanCL2 is enriched in spermatocytes and round spermatids of the testis. By examining LanCL2 knockout mice, we found that LanCL2 deletion did not affect postnatal brain development but injured the sperm parameters of adult mice. With histopathological analysis, we noticed that LanCL2 KO caused a pre-maturation and accelerated the self-renewal of spermatogonial stem cells in the early stage of spermatogenesis. In contrast, at the adult stage, LanCL2 KO damaged the acrosomal maturation in spermiogenesis, resulting in spermatogenic defects with a reduced number and motility of spermatozoa. Furthermore, we show that this disruption of testicular homeostasis in the LanCL2 KO testis was due to dysbalanced testicular redox homeostasis. This study demonstrates the critical role of LanCL2 in testicular homeostasis and redox balance.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Effect of Oxidative Stress on Reproduction and Development—2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures
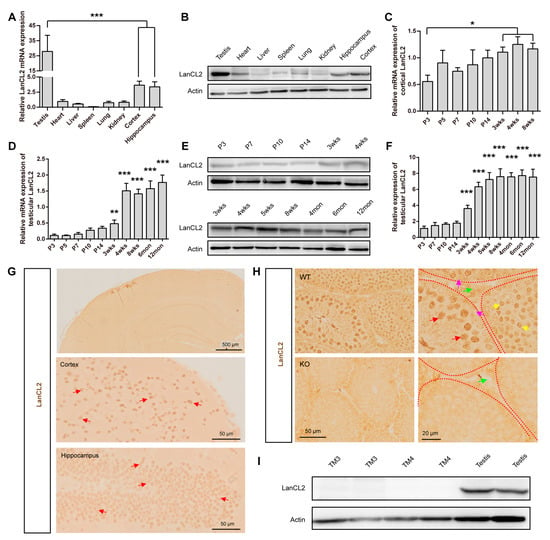
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Microbe-Derived Antioxidants Protect IPEC-1 Cells from H2O2-Induced Oxidative Stress, Inflammation and Tight Junction Protein Disruption via Activating the Nrf2 Pathway to Inhibit the ROS/NLRP3/IL-1β Signaling Pathway
by
Cheng Shen, Zhen Luo, Sheng Ma, Chengbing Yu, Ting Lai, Shangshang Tang, Hongcai Zhang, Jing Zhang, Weina Xu and Jianxiong Xu
Antioxidants 2024, 13(5), 533; https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox13050533 (registering DOI) - 27 Apr 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Oxidative stress can induce inflammation and tight junction disruption in enterocytes. The initiation of inflammation is thought to commence with the activation of the ROS/NLRP3/IL-1β signaling pathway, marking a crucial starting point in the process. In our previous studies, we found that microbe-derived
[...] Read more.
Oxidative stress can induce inflammation and tight junction disruption in enterocytes. The initiation of inflammation is thought to commence with the activation of the ROS/NLRP3/IL-1β signaling pathway, marking a crucial starting point in the process. In our previous studies, we found that microbe-derived antioxidants (MAs) showed significant potential in enhancing both antioxidant capabilities and anti-inflammatory effects. The main aim of this research was to investigate the ability of MAs to protect cells from oxidative stress caused by H2O2, to reduce inflammatory responses, and to maintain the integrity of tight junction proteins by modulating the ROS/NLRP3/IL-1β signaling pathway. IPEC-1 cells (1 × 104 cells/well) were initially exposed to 100 mg/L of MAs for 12 h, after which they were subjected to 1 mM H2O2 treatment for 1 h. We utilized small interfering RNA (siRNA) to inhibit the expression of NLRP3 and Nrf2. Inflammatory factors such as IL-1β and antioxidant enzyme activity levels were detected by ELISA. Oxidative stress marker ROS was examined by fluorescence analysis. The NLRP3/IL-1β signaling pathway, Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway and tight junction proteins (ZO-1 and Occludin) were detected by RT-qPCR or Western blotting. In our research, it was observed that MA treatment effectively suppressed the notable increase in H2O2-induced inflammatory markers (TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-18), decreased ROS accumulation, mitigated the expression of NLRP3, ASC, and caspase-1, and promoted the expression of ZO-1 and Occludin. After silencing the NLRP3 gene with siRNA, the protective influence of MAs was observed to be linked with the NLRP3 inflammasome. Additional investigations demonstrated that the treatment with MAs triggered the activation of Nrf2, facilitating its translocation into the nucleus. This process resulted in a notable upregulation of Nrf2, NQO1, and HO-1 expression, along with the initiation of the Nrf2-HO-1 signaling pathway. Consequently, there was an enhancement in the activities of antioxidant enzymes like SOD, GSH-Px, and CAT, which effectively mitigated the accumulation of ROS, thereby ameliorating the oxidative stress state. The antioxidant effectiveness of MAs was additionally heightened in the presence of SFN, an activator of Nrf2. The antioxidant and anti-inflammatory functions of MAs and their role in regulating intestinal epithelial tight junction protein disruption were significantly affected after siRNA knockdown of the Nrf2 gene. These findings suggest that MAs have the potential to reduce H2O2-triggered oxidative stress, inflammation, and disruption of intestinal epithelial tight junction proteins in IPEC-1 cells. This reduction is achieved by blocking the ROS/NLRP3/IL-1β signaling pathway through the activation of the Nrf2 pathway.
Full article
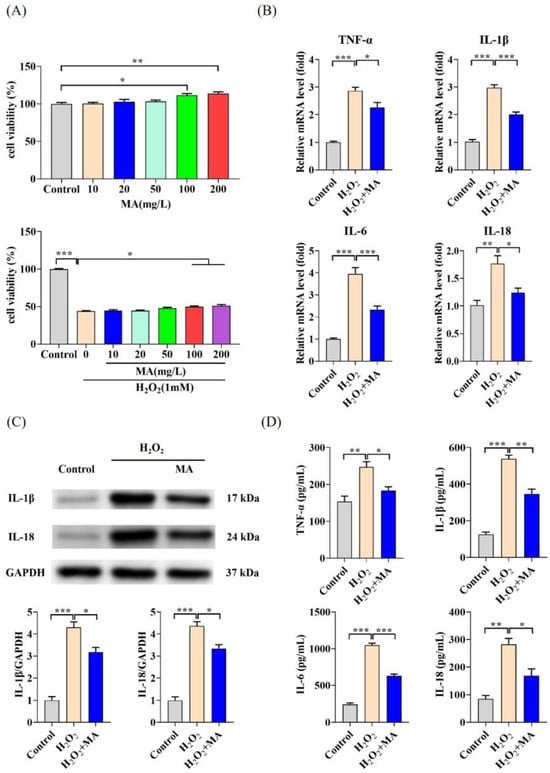
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Antioxidant Activities in Kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus) Shoots during Growth Stages and Destination of Chlorogenic Acid and Kaempferol Glycosides
by
Shucheng Duan, Soon-Jae Kwon, Da Yun Jeong, Ji Hye Kim, You Rang Park, Chang Kyu Kim, Jae-Hee Kim and Seok Hyun Eom
Antioxidants 2024, 13(5), 532; https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox13050532 - 26 Apr 2024
Abstract
Apart from being utilized as a commercial fiber at maturity, kenaf shoots have potential as a food and feed source because of their diverse bioactivities. Previous studies have focused on mature stems because of their high biomass, whereas the antioxidant activities (AA) and
[...] Read more.
Apart from being utilized as a commercial fiber at maturity, kenaf shoots have potential as a food and feed source because of their diverse bioactivities. Previous studies have focused on mature stems because of their high biomass, whereas the antioxidant activities (AA) and the destination of AA contributors of kenaf stems and their high-yielding byproduct leaves during the growth stage have rarely been studied. Therefore, we investigated changes in AA and its relative components in kenaf leaves and stems during the four vital growth stages. Higher ABTS radical cation and DPPH radical scavenging abilities and ferric reducing antioxidant power, total phenolic content, total flavonoid content, and total polysaccharide content were observed at all leaf stages and in the late stem stages. Chlorogenic acid (CGA) and kaempferol glycosides, especially kaempferitrin (Kfr), were identified as representative phenolic acids and flavonoids in both kenaf leaves and stems. The content of CGA in both leaves and stems increased corresponding to the plant’s growth stage, whereas kaempferol glycosides were enhanced in leaves but declined in stems. The highest correlation was observed between TPC and AA in all organs. Further evaluation of CGA and Kfr verified that CGA was the predominant contributor to AA, surpassing Kfr. These findings suggest that kenaf leaves increase antioxidant levels as they grow and can be a useful source of stem harvesting byproducts.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Plant Matrices of Bioactive Compounds as Strong Antioxidants with Health-Promoting Properties)
Open AccessArticle
Exploring Iodide and Hydrogen Sulfide as ROS Scavengers to Delay Acute Rejection in MHC-Defined Vascularized Composite Allografts
by
Philipp Tratnig-Frankl, Alec R. Andrews, Yanis Berkane, Claire Guinier, Marion Goutard, Elise Lupon, Hyshem H. Lancia, Michael L. Morrison, Mark B. Roth, Mark A. Randolph, Curtis L. Cetrulo, Jr. and Alexandre G. Lellouch
Antioxidants 2024, 13(5), 531; https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox13050531 - 26 Apr 2024
Abstract
Vascularized composite allografts (VCA) face ischemic challenges due to their limited availability. Reperfusion following ischemia triggers oxidative stress and immune reactions, and scavenger molecules could mitigate ischemia–reperfusion injuries and, therefore, immune rejection. We compared two scavengers in a myocutaneous flap VCA model. In
[...] Read more.
Vascularized composite allografts (VCA) face ischemic challenges due to their limited availability. Reperfusion following ischemia triggers oxidative stress and immune reactions, and scavenger molecules could mitigate ischemia–reperfusion injuries and, therefore, immune rejection. We compared two scavengers in a myocutaneous flap VCA model. In total, 18 myocutaneous flap transplants were performed in Major histocompatibility complex (MHC)-defined miniature swine. In the MATCH group (n = 9), donors and recipients had minor antigen mismatch, while the animals were fully mismatched in the MISMATCH group (n = 9). Grafts were pretreated with saline, sodium iodide (NaI), or hydrogen sulfide (H2S), stored at 4 °C for 3 h, and then transplanted. Flaps were monitored until clinical rejection without immunosuppression. In the MATCH group, flap survival did not significantly differ between the saline and hydrogen sulfide treatments (p = 0.483) but was reduced with the sodium iodide treatment (p = 0.007). In the MISMATCH group, survival was similar between the saline and hydrogen sulfide treatments (p = 0.483) but decreased with the sodium iodide treatment (p = 0.007). Rhabdomyolysis markers showed lower but non-significant levels in the experimental subgroups for both the MATCH and MISMATCH animals. This study provides insightful data for the field of antioxidant-based approaches in VCA and transplantation.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Oxidative Stress in Ischemia–Reperfusion Injury)
►▼
Show Figures
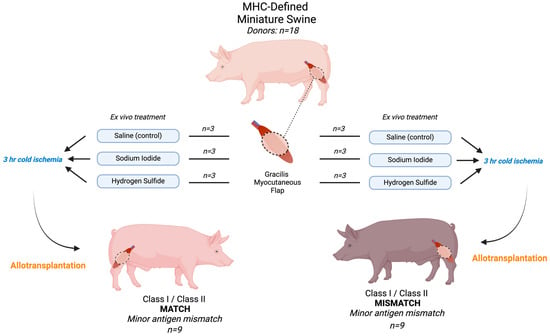
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Efficacy and Safety of Coenzyme Q10 Supplementation in Neonates, Infants and Children: An Overview
by
David Mantle and Iain Parry Hargreaves
Antioxidants 2024, 13(5), 530; https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox13050530 - 26 Apr 2024
Abstract
To date, there have been no review articles specifically relating to the general efficacy and safety of coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) supplementation in younger subjects. In this article, we therefore reviewed the efficacy and safety of CoQ10 supplementation in neonates (less than 1 month
[...] Read more.
To date, there have been no review articles specifically relating to the general efficacy and safety of coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) supplementation in younger subjects. In this article, we therefore reviewed the efficacy and safety of CoQ10 supplementation in neonates (less than 1 month of age), infants (up to 1 year of age) and children (up to 12 years of age). As there is no rationale for the supplementation of CoQ10 in normal younger subjects (as there is in otherwise healthy older subjects), all of the articles in the medical literature reviewed in the present article therefore refer to the supplementation of CoQ10 in younger subjects with a variety of clinical disorders; these include primary CoQ10 deficiency, acyl CoA dehydrogenase deficiency, Duchenne muscular dystrophy, migraine, Down syndrome, ADHD, idiopathic cardiomyopathy and Friedreich’s ataxia.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Antioxidant Enzyme Systems)
Open AccessArticle
Oral Supplementation of Ozonated Sunflower Oil Augments Plasma Antioxidant and Anti-inflammatory Abilities with Enhancement of High-Density Lipoproteins Functionality in Rats
by
Kyung-Hyun Cho, Ji-Eun Kim, Myeong-Sung Lee and Ashutosh Bahuguna
Antioxidants 2024, 13(5), 529; https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox13050529 - 26 Apr 2024
Abstract
Research on ozonated sunflower oil (OSO) is mostly restricted to its topical application, whereas the functional and toxicological assessment of oral OSO consumption is yet to be solved. Herein, OSO was orally supplemented in rats to assess the impact on plasma antioxidant status,
[...] Read more.
Research on ozonated sunflower oil (OSO) is mostly restricted to its topical application, whereas the functional and toxicological assessment of oral OSO consumption is yet to be solved. Herein, OSO was orally supplemented in rats to assess the impact on plasma antioxidant status, low-density lipoproteins (LDL), and high-density lipoproteins (HDL). Also, the functionality of HDL from the OSO-supplemented rats (OSO-HDL) was tested against carboxymethyl-lysine (CML)- induced hyperinflammation in embryo and adult zebrafish. The results revealed that four weeks of OSO supplementation (3 g/kg BW/day) had no adverse effect on rats’ hematological and blood biochemical profiles. Nonetheless, decreased interleukin (IL)-6, and LDL-C levels, along with enhanced ferric ion reduction ability (FRA) and sulfhydryl content, were observed in the plasma of OSO-supplemented rats compared to the control and sunflower oil (SO) supplemented group. In addition, OSO supplementation stabilized apoA-I/HDL and augmented HDL-allied paraoxonase (PON)-1 activity. The microinjection of OSO-HDL (10 nL, 2 mg/mL) efficiently prevented the CML (500 ng)-induced zebrafish embryo mortality and developmental deformities. Similarly, OSO-HDL thwarted CML-posed neurotoxicity and demonstrated a significant hepatoprotective effect against CML-induced fatty liver changes, hepatic inflammation, oxidative stress, and apoptosis, as well as exhibiting a noticeable influence to revert CML-induced dyslipidemia. Conclusively, OSO supplementation demonstrated no toxic effects on rats, ameliorated plasma antioxidant status, and positively influenced HDL stability and functionality, leading to a protective effect against CML-induced toxicity in zebrafish.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Impact of Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Functions of HDL in Diseases—2nd Edition)
Open AccessArticle
Hispidulin Alleviates Mast Cell-Mediated Allergic Airway Inflammation through FcεR1 and Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling Pathway
by
Seungwon Jeong, Yeon-Yong Kim, Dongwon Lee, Sang-Hyun Kim and Soyoung Lee
Antioxidants 2024, 13(5), 528; https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox13050528 - 26 Apr 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Allergic asthma is a type 2 immune-response-mediated chronic respiratory disease. Mast cell activation influences the pathogenesis and exacerbation of allergic asthma. Therefore, the development of mast cell-targeting pharmacotherapy is important for managing allergic airway inflammation. We investigated the efficacy of hispidulin (HPD), natural
[...] Read more.
Allergic asthma is a type 2 immune-response-mediated chronic respiratory disease. Mast cell activation influences the pathogenesis and exacerbation of allergic asthma. Therefore, the development of mast cell-targeting pharmacotherapy is important for managing allergic airway inflammation. We investigated the efficacy of hispidulin (HPD), natural flavone, in a mast-cell-mediated ovalbumin (OVA)-induced allergic airway inflammation model. HPD alleviated symptoms of allergic asthma and decreased the levels of immunoglobulin (Ig) E, type 2 inflammation, immune cell infiltration, and mast cell activation in the lung. Furthermore, in vivo analysis confirmed the efficacy of HPD through the evaluation of IgE-mediated allergic responses in a mast cell line. HPD treatment inhibited mast cell degranulation through inhibition of the FcεR1 signaling pathway and suppressed the expression of inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-4, IL-6, and IL-13) through suppression of the NF-κB signaling pathway. The antioxidant effects of HPD in activated mast cells were identified through modulation of antioxidant enzymes and the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. In conclusion, HPD may be a potential therapeutic candidate for allergic airway inflammation of asthma and acts by suppressing mast cell activation and oxidative stress.
Full article
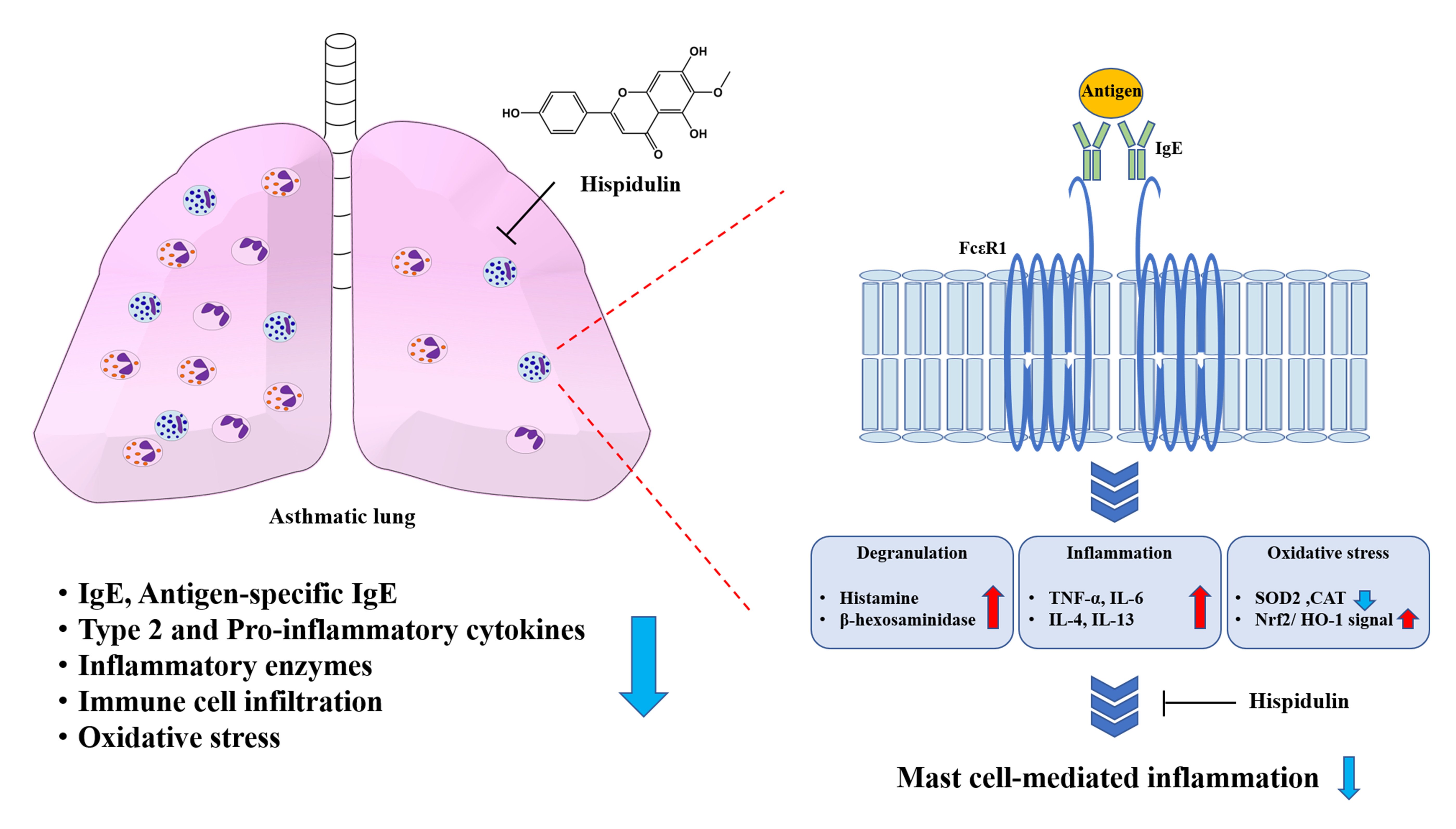
Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Unravelling the Role of Candida albicans Prn1 in the Oxidative Stress Response through a Proteomics Approach
by
Victor Arribas, Lucia Monteoliva, María Luisa Hernáez, Concha Gil and Gloria Molero
Antioxidants 2024, 13(5), 527; https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox13050527 - 26 Apr 2024
Abstract
Candida albicans Prn1 is a protein with an unknown function similar to mammalian Pirin. It also has orthologues in other pathogenic fungi, but not in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Prn1 highly increases its abundance in response to H2O2 treatment; thus, to
[...] Read more.
Candida albicans Prn1 is a protein with an unknown function similar to mammalian Pirin. It also has orthologues in other pathogenic fungi, but not in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Prn1 highly increases its abundance in response to H2O2 treatment; thus, to study its involvement in the oxidative stress response, a C. albicans prn1∆ mutant and the corresponding wild-type strain SN250 have been studied. Under H2O2 treatment, Prn1 absence led to a higher level of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and a lower survival rate, with a higher percentage of death by apoptosis, confirming its relevant role in oxidative detoxication. The quantitative differential proteomics studies of both strains in the presence and absence of H2O2 indicated a lower increase in proteins with oxidoreductase activity after the treatment in the prn1∆ strain, as well as an increase in proteasome-activating proteins, corroborated by in vivo measurements of proteasome activity, with respect to the wild type. In addition, remarkable differences in the abundance of some transcription factors were observed between mutant and wild-type strains, e.g., Mnl1 or Nrg1, an Mnl1 antagonist. orf19.4850, a protein orthologue to S. cerevisiae Cub1, has shown its involvement in the response to H2O2 and in proteasome function when Prn1 is highly expressed in the wild type.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Redox in Microorganisms, 2nd Edition)
Open AccessArticle
Profiling of Metabolites in Organically Grown Plums from Norway: Does Location or Cultivar Matter?
by
Mekjell Meland, Dragana Dabić Zagorac, Mihajlo Jakanovski, Milica Sredojević, Maja Natić, Marko Kitanović and Milica Fotirić Akšić
Antioxidants 2024, 13(5), 526; https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox13050526 - 26 Apr 2024
Abstract
The aim of this work was to investigate the influence of two locations and seven cultivars on the profiling of metabolites in organically grown plums (Prunus domestica L.) fruit in Norway. P, K, and Ca were most abundant in the studied fruits,
[...] Read more.
The aim of this work was to investigate the influence of two locations and seven cultivars on the profiling of metabolites in organically grown plums (Prunus domestica L.) fruit in Norway. P, K, and Ca were most abundant in the studied fruits, while Ba and Sr formed a clear line between the locations. The most abundant sugars were glucose, fructose, sucrose, and sorbitol, which together accounted for up to 97.00%. Quinic acid and malic acid were the predominant organic acids, while chlorogenic acid, rutin, and kaempferol-3-O-glucoside were the most abundant polyphenols. Plums from Ullensvang were characterized by a higher content of minerals, sugars, organic acids, total polyphenol content (TPC), and radical scavenging activity (RSA), while plums from Telemark had a higher content of quantified polyphenols. The cultivar ‘Mallard’ had the highest mineral and radical scavenging activity, ‘Opal’ had the sweetest fruit, ‘Jubileum’ had the highest acidity, ‘Excalibur’ had the highest TPC content, and ‘Valor’ stored the highest content of quantified polyphenols, especially chlorogenic acid. These results provide comprehensive information on the chemical profiles of selected plum cultivars, suggesting that organic plums are a rich source of beneficial compounds that can have a positive impact on human health.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Natural and Synthetic Antioxidants)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Luteolin Alleviates Cadmium-Induced Kidney Injury by Inhibiting Oxidative DNA Damage and Repairing Autophagic Flux Blockade in Chickens
by
Kanglei Zhang, Jiahui Li, Wenxuan Dong, Qing Huang, Xueru Wang, Kai Deng, Waseem Ali, Ruilong Song, Hui Zou, Di Ran, Gang Liu and Zongping Liu
Antioxidants 2024, 13(5), 525; https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox13050525 - 26 Apr 2024
Abstract
Chickens are a major source of meat and eggs in human food and have significant economic value. Cadmium (Cd) is a common environmental pollutant that can contaminate feed and drinking water, leading to kidney injury in livestock and poultry, primarily by inducing the
[...] Read more.
Chickens are a major source of meat and eggs in human food and have significant economic value. Cadmium (Cd) is a common environmental pollutant that can contaminate feed and drinking water, leading to kidney injury in livestock and poultry, primarily by inducing the generation of free radicals. It is necessary to develop potential medicines to prevent and treat Cd-induced nephrotoxicity in poultry. Luteolin (Lut) is a natural flavonoid compound mainly extracted from peanut shells and has a variety of biological functions to defend against oxidative damage. In this study, we aimed to demonstrate whether Lut can alleviate kidney injury under Cd exposure and elucidate the underlying molecular mechanisms. Renal histopathology and cell morphology were observed. The indicators of renal function, oxidative stress, DNA damage and repair, NAD+ content, SIRT1 activity, and autophagy were analyzed. In vitro data showed that Cd exposure increased ROS levels and induced oxidative DNA damage and repair, as indicated by increased 8-OHdG content, increased
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Crosstalk between Autophagy and Oxidative Stress)
►▼
Show Figures
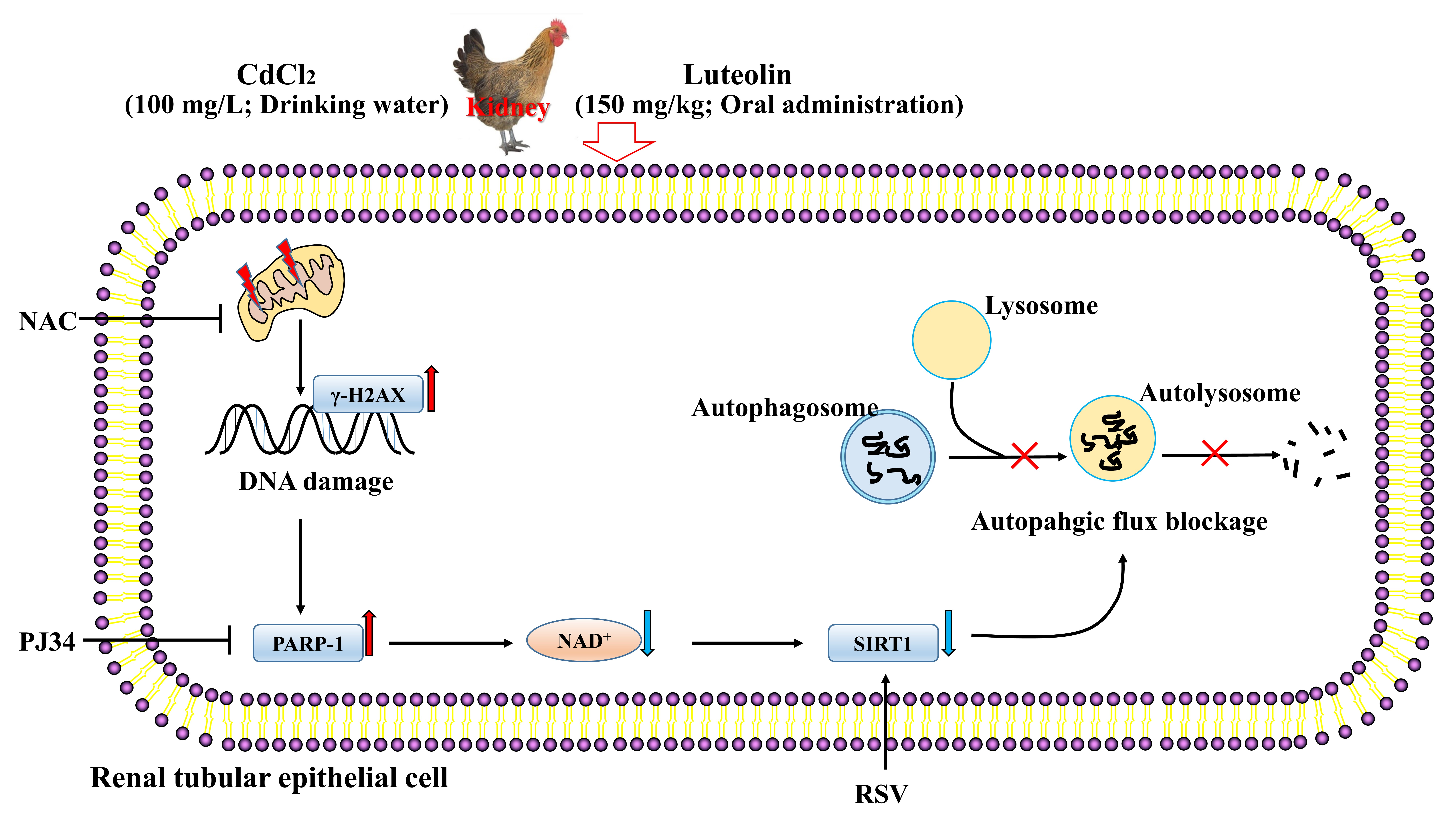
Graphical abstract
Open AccessBrief Report
H2O2-Induced Oxidative Stress Responses in Eriocheir sinensis: Antioxidant Defense and Immune Gene Expression Dynamics
by
Qinghong He, Wenrong Feng, Xue Chen, Yuanfeng Xu, Jun Zhou, Jianlin Li, Pao Xu and Yongkai Tang
Antioxidants 2024, 13(5), 524; https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox13050524 - 26 Apr 2024
Abstract
Eriocheir sinensis, a key species in China’s freshwater aquaculture, is threatened by various diseases, which were verified to be closely associated with oxidative stress. This study aimed to investigate the response of E. sinensis to hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)-induced
[...] Read more.
Eriocheir sinensis, a key species in China’s freshwater aquaculture, is threatened by various diseases, which were verified to be closely associated with oxidative stress. This study aimed to investigate the response of E. sinensis to hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)-induced oxidative stress to understand the biological processes behind these diseases. Crabs were exposed to different concentrations of H2O2 and their antioxidant enzyme activities and gene expressions for defense and immunity were measured. Results showed that activities of antioxidant enzymes—specificallysuperoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), total antioxidant capacity(T-AOC), glutathione (GSH), and glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px)—varied with exposure concentration and duration, initially increasing then decreasing. Notably, SOD, GSH-Px, and T-AOC activities dropped below control levels at 96 h. Concurrently, oxidative damage markers, including malondialdehyde (MDA), H2O2, and 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG) levels, increased with exposure duration. The mRNA expression of SOD, CAT, and GSH-Px also showed an initial increase followed by a decrease, peaking at 72 h. The upregulation of phenoloxidaseloxidase (proPO) and peroxinectin (PX) was also detected, but proPO was suppressed under high levels of H2O2. Heat shock protein 70 (HSP70) expression gradually increased with higher H2O2 concentrations, whereas induced nitrogen monoxide synthase (iNOS) was upregulated but decreased at 96 h. These findings emphasize H2O2’s significant impact on the crab’s oxidative and immune responses, highlighting the importance of understanding cellular stress responses for disease prevention and therapy development.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Natural Antioxidants and Aquatic Animal Health)
►▼
Show Figures
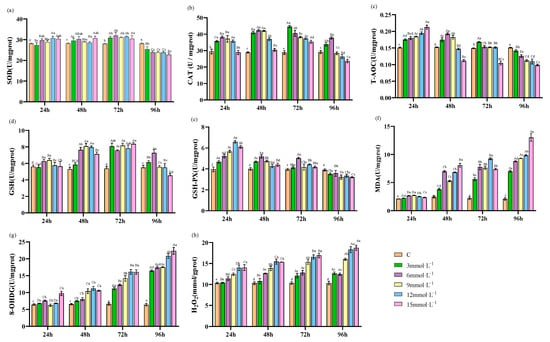
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Lysyl Oxidase in Ectopic Cardiovascular Calcification: Role of Oxidative Stress
by
Carme Ballester-Servera, Judith Alonso, Laia Cañes, Paula Vázquez-Sufuentes, Ana B. García-Redondo, Cristina Rodríguez and José Martínez-González
Antioxidants 2024, 13(5), 523; https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox13050523 - 26 Apr 2024
Abstract
Lysyl oxidase (LOX)-mediated extracellular matrix crosslinking modulates calcification in atherosclerosis and aortic valve disease; however, this enzyme also induces oxidative stress. We addressed the contribution of LOX-dependent oxidative stress to cardiovascular calcification. LOX is upregulated in human-calcified atherosclerotic lesions and atheromas from atherosclerosis-challenged
[...] Read more.
Lysyl oxidase (LOX)-mediated extracellular matrix crosslinking modulates calcification in atherosclerosis and aortic valve disease; however, this enzyme also induces oxidative stress. We addressed the contribution of LOX-dependent oxidative stress to cardiovascular calcification. LOX is upregulated in human-calcified atherosclerotic lesions and atheromas from atherosclerosis-challenged LOX transgenic mice (TgLOXVSMC) and colocalized with a marker of oxidative stress (8-oxo-deoxyguanosine) in vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs). Similarly, in calcific aortic valves, high LOX expression was detected in valvular interstitial cells (VICs) positive for 8-oxo-deoxyguanosine, while LOX and LOXL2 expression correlated with osteogenic markers (SPP1 and RUNX2) and NOX2. In human VICs, mito-TEMPO and TEMPOL attenuated the increase in superoxide anion levels and the mineralization induced by osteogenic media (OM). Likewise, in OM-exposed VICs, β-aminopropionitrile (a LOX inhibitor) ameliorated both oxidative stress and calcification. Gain- and loss-of-function approaches in VICs demonstrated that while LOX silencing negatively modulates oxidative stress and calcification induced by OM, lentiviral LOX overexpression exacerbated oxidative stress and VIC calcification, effects that were prevented by mito-TEMPO, TEMPOL, and β-aminopropionitrile. Our data indicate that LOX-induced oxidative stress participates in the procalcifying effects of LOX activity in ectopic cardiovascular calcification, and highlight the multifaceted role played by LOX isoenzymes in cardiovascular diseases.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Oxidative Stress and Atherosclerosis)
►▼
Show Figures
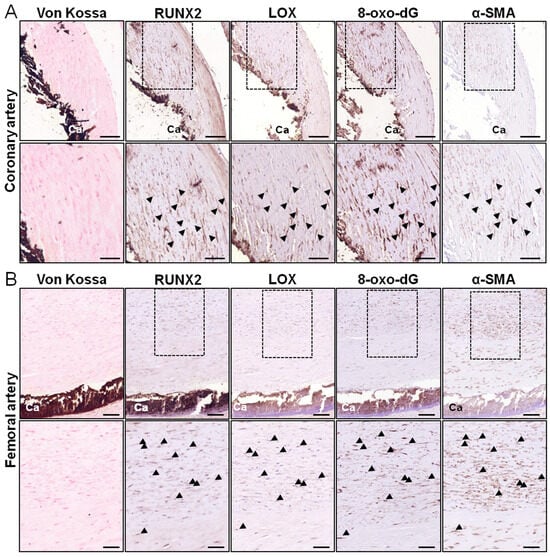
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Dietary Astaxanthin Can Promote the Growth and Motivate Lipid Metabolism by Improving Antioxidant Properties for Swimming Crab, Portunus trituberculatus
by
Yao Deng, Shichao Xie, Wenhao Zhan, Hongyu Peng, Haiqing Cao, Zheng Tang, Yinqiu Tian, Tingting Zhu, Min Jin and Qicun Zhou
Antioxidants 2024, 13(5), 522; https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox13050522 - 26 Apr 2024
Abstract
This study aimed to assess the influence of varying dietary levels of astaxanthin (AST) on the growth, antioxidant capacity and lipid metabolism of juvenile swimming crabs. Six diets were formulated to contain different AST levels, and the analyzed concentration of AST in experimental
[...] Read more.
This study aimed to assess the influence of varying dietary levels of astaxanthin (AST) on the growth, antioxidant capacity and lipid metabolism of juvenile swimming crabs. Six diets were formulated to contain different AST levels, and the analyzed concentration of AST in experimental diets were 0, 24.2, 45.8, 72.4, 94.2 and 195.0 mg kg−1, respectively. Juvenile swimming crabs (initial weight 8.20 ± 0.01 g) were fed these experimental diets for 56 days. The findings indicated that the color of the live crab shells and the cooked crab shells gradually became red with the increase of dietary AST levels. Dietary 24.2 mg kg−1 astaxanthin significantly improved the growth performance of swimming crab. the lowest activities of glutathione (GSH), total antioxidant capacity (T-AOC), superoxide dismutase (SOD) and peroxidase (POD) were found in crabs fed without AST supplementation diet. Crabs fed diet without AST supplementation showed lower lipid content and the activity of fatty acid synthetase (FAS) in hepatopancreas than those fed diets with AST supplementation, however, lipid content in muscle and the activity of carnitine palmitoyl transferase (CPT) in hepatopancreas were not significantly affected by dietary AST levels. And it can be found in oil red O staining that dietary 24.2 and 45.8 mg kg−1 astaxanthin significantly promoted the lipid accumulation of hepatopancreas. Crabs fed diet with 195.0 mg kg−1 AST exhibited lower expression of ampk, foxo, pi3k, akt and nadph in hepatopancreas than those fed the other diets, however, the expression of genes related to antioxidant such as cMn-sod, gsh-px, cat, trx and gst in hepatopancreas significantly down-regulated with the increase of dietary AST levels. In conclusion, dietary 24.2 and 45.8 mg kg−1 astaxanthin significantly promoted the lipid accumulation of hepatopancreas and im-proved the antioxidant and immune capacity of hemolymph.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Use of Antioxidant Supplementation in Aquaculture: Impact on Growth, Health, and Product Quality)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Chitosan Oligosaccharides Mitigate Flooding Stress Damage in Rice by Affecting Antioxidants, Osmoregulation, and Hormones
by
Haoyu Lu, Mei Wang, Shangfeng Zhou, Ke Chen, Lifeng Wang, Zhenxie Yi, Lianyang Bai and Yuzhu Zhang
Antioxidants 2024, 13(5), 521; https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox13050521 - 26 Apr 2024
Abstract
Rice (Oryza sativa L.) is one of the most important food crops worldwide. However, during direct seeding, rice is extremely vulnerable to flooding stress, which impairs rice’s emergence and seedling growth and results in a significant yield loss. According to our research,
[...] Read more.
Rice (Oryza sativa L.) is one of the most important food crops worldwide. However, during direct seeding, rice is extremely vulnerable to flooding stress, which impairs rice’s emergence and seedling growth and results in a significant yield loss. According to our research, chitosan oligosaccharides have the potential to be a chemical seed-soaking agent that greatly increases rice’s resistance to flooding. Chitosan oligosaccharides were able to enhance seed energy supply, osmoregulation, and antioxidant capacity, according to physiological index assessments. Using transcriptome and metabolomic analysis, we discovered that important differential metabolites and genes were involved in the signaling pathway for hormone synthesis and antioxidant capacity. Exogenous chitosan oligosaccharides specifically and significantly inhibit genes linked to auxin, jasmonic acid, and abscisic acid. This suggested that applying chitosan oligosaccharides could stabilize seedling growth and development by controlling associated hormones and reducing flooding stress by enhancing membrane stability and antioxidant capacity. Finally, we verified the effectiveness of exogenous chitosan oligosaccharides imbibed in seeds by field validation, demonstrating that they can enhance rice seedling emergence and growth under flooding stress.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Antioxidant Mechanisms and Redox Signalling in Seeds)
►▼
Show Figures
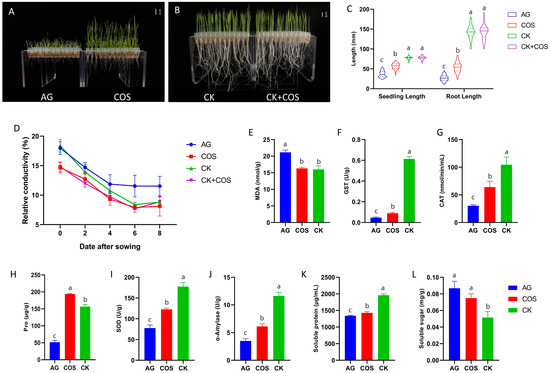
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
In Vitro Gastrointestinal Digestion of Various Sweet Potato Leaves: Polyphenol Profiles, Bioaccessibility and Bioavailability Elucidation
by
Junren Wen, Yong Sui, Jianbin Shi, Sha Cai, Tian Xiong, Fang Cai, Lei Zhou, Shuyi Li and Xin Mei
Antioxidants 2024, 13(5), 520; https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox13050520 - 26 Apr 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The chemical composition discrepancies of five sweet potato leaves (SPLs) and their phenolic profile variations during in vitro digestion were investigated. The results indicated that Ecaishu No. 10 (EC10) provided better retention capacity for phenolic compounds after drying. Furthermore, polyphenols were progressively released
[...] Read more.
The chemical composition discrepancies of five sweet potato leaves (SPLs) and their phenolic profile variations during in vitro digestion were investigated. The results indicated that Ecaishu No. 10 (EC10) provided better retention capacity for phenolic compounds after drying. Furthermore, polyphenols were progressively released from the matrix as the digestion process proceeded. The highest bioaccessibility of polyphenols was found in EC10 intestinal chyme at 48.47%. For its phenolic profile, 3-, 4-, and 5-monosubstituted caffeoyl quinic acids were 9.75%, 57.39%, and 79.37%, respectively, while 3,4-, 3,5-, and 4,5-disubstituted caffeoyl quinic acids were 6.55, 0.27 and 13.18%, respectively. In contrast, the 3,4-, 3,5-, 4,5-disubstituted caffeoylquinic acid in the intestinal fluid after dialysis bag treatment was 62.12%, 79.12%, and 62.98%, respectively, which resulted in relatively enhanced bioactivities (DPPH, 10.51 μmol Trolox/g; FRAP, 8.89 μmol Trolox/g; ORAC, 7.32 μmol Trolox/g; IC50 for α-amylase, 19.36 mg/g; IC50 for α-glucosidase, 25.21 mg/g). In summary, desirable phenolic acid release characteristics and bioactivity of EC10 were observed in this study, indicating that it has potential as a functional food ingredient, which is conducive to the exploitation of the sweet potato processing industry from a long-term perspective.
Full article
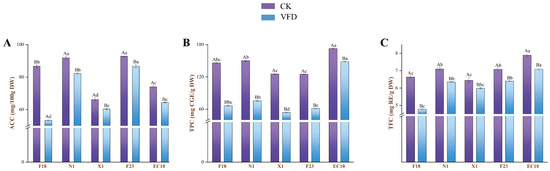
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Development of Coated PLA Films Containing a Commercial Olive Leaf Extract for the Food Packaging Sector
by
Cecilia Fiorentini, Giulia Leni, Elena Díaz de Apodaca, Laura Fernández-de-Castro, Gabriele Rocchetti, Claudia Cortimiglia, Giorgia Spigno and Andrea Bassani
Antioxidants 2024, 13(5), 519; https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox13050519 - 26 Apr 2024
Abstract
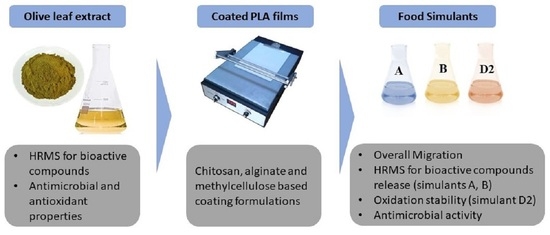
A commercial olive leaf extract (OL), effective against Salmonella enterica, Escherichia coli, Listeria monocytogenes, and Staphylococcus aureus, was added to three different coating formulations (methylcellulose, MC; chitosan, CT; and alginate, ALG) to produce active polylactic acid (PLA) coated films.
[...] Read more.
A commercial olive leaf extract (OL), effective against Salmonella enterica, Escherichia coli, Listeria monocytogenes, and Staphylococcus aureus, was added to three different coating formulations (methylcellulose, MC; chitosan, CT; and alginate, ALG) to produce active polylactic acid (PLA) coated films. Evaluation of these coated PLA films revealed significant inhibition of S. aureus growth, particularly with the MC and CT formulations exhibiting the highest inhibition rates (99.7%). The coated films were then tested for food contact compatibility with three food simulants (A: 10% ethanol; B: 3% acetic acid; D2: olive oil), selected to assess their suitability for pre-cut hams and ready-to-eat vegetables in relation to overall migration. However, coated films with active functions exhibited migration values in simulants A and B above legal limits, while promising results were obtained for simulant D2, highlighting the need to deeply investigate these coatings’ impact on a real food system. Untargeted metabolomics revealed that the type of coating influenced the selective release of certain phenolic classes based on the food simulant tested. The Oxitest analysis of simulant D2 demonstrated that the MC and ALG-coated PLA films slightly slowed down the oxidation of this food simulant, which is an edible vegetable oil.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Antimicrobial and Antioxidants Capacities: Application in Food Packaging)
►▼
Show Figures
Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Studying the Changes in Physical Functioning and Oxidative Stress-Related Molecules in People Living with HIV after Switching from Triple to Dual Therapy
by
Jessica Cusato, Anna Mulasso, Micol Ferrara, Alessandra Manca, Miriam Antonucci, Guido Accardo, Alice Palermiti, Gianluca Bianco, Francesco Chiara, Jacopo Mula, Maria Grazia Maddalone, Maria Cristina Tettoni, Simone Cuomo, Giulia Trevisan, Stefano Bonora, Giovanni Di Perri, Corrado Lupo, Alberto Rainoldi and Antonio D’Avolio
Antioxidants 2024, 13(5), 518; https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox13050518 - 26 Apr 2024
Abstract
Background: Physical activity could increase the production of oxidative stress biomarkers, affecting the metabolism and excretion of antiretroviral drugs and, consequently, the clinical outcome. Nowadays, people living with HIV (PLWH) are mostly switching from triple to dual therapy, but no data are available
[...] Read more.
Background: Physical activity could increase the production of oxidative stress biomarkers, affecting the metabolism and excretion of antiretroviral drugs and, consequently, the clinical outcome. Nowadays, people living with HIV (PLWH) are mostly switching from triple to dual therapy, but no data are available in terms of physical functioning and oxidative stress. The aim of this study was to evaluate if some antioxidant biomarkers and physical functioning tests could be different according to triple or dual antiretroviral therapy. Methods: PLWH were evaluated at baseline (BL), while treated with three drugs, and six months after the switch to dual therapy. Physical functioning was quantified using validated tools. Mitochondrial and cytosol antioxidant molecules were evaluated through liquid chromatography. Results: Twenty-five patients were analyzed. A statistically significant difference between triple and dual therapy was found for mitochondrial glutathione, but not for physical tests. Evaluating differences between physically active and inactive individuals, the following statistically significant differences were suggested, considering triple therapy (mitochondrial n-formyl-methionine p = 0.022, triglycerides p = 0.023) and double therapy (mitochondrial glycine p = 0.035, cytosol glutamic acid p = 0.007, cytosol s-adenosylmethionine p = 0.021). Conclusions: For the first time, this study suggests possible differences in terms of antioxidant molecules and physical functioning in PLWH switching from triple to dual therapy.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Antioxidants and Oxidative Stress in the Development of Diseases and Therapy)
►▼
Show Figures
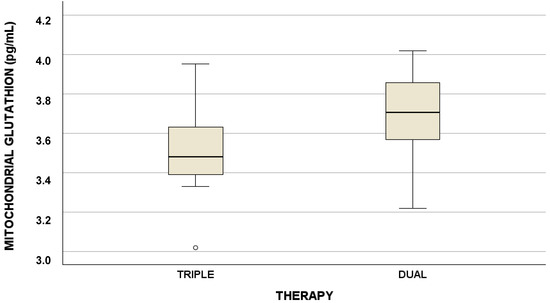
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
UV Radiation and Protein Hydrolysates in Bio-Based Films: Impacts on Properties and Italian Salami Preservation
by
Viviane Patrícia Romani, Paola Chaves Martins, Meritaine da Rocha, Maria Carolina Salum Bulhosa, Felipe Kessler and Vilásia Guimarães Martins
Antioxidants 2024, 13(5), 517; https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox13050517 - 26 Apr 2024
Abstract
UV radiation was combined with the incorporation of fish protein hydrolysates to improve the performance of active bio-based films for food packaging. UV radiation was not used previously to enhance the packaging performance of blend films of starch/protein, and fish protein hydrolysates were
[...] Read more.
UV radiation was combined with the incorporation of fish protein hydrolysates to improve the performance of active bio-based films for food packaging. UV radiation was not used previously to enhance the packaging performance of blend films of starch/protein, and fish protein hydrolysates were not incorporated in bio-based polymer surfaces previously. Rice starch and fish proteins (from Whitemouth croaker muscle) were utilized to prepare films by the casting technique, which were UV-radiated under different exposure times (1, 5, and 10 min). The packaging performance of the films was determined according to the mechanical and barrier performance, solubility, and color. Fish protein hydrolysates (from Argentine croaker muscle) were then incorporated into the films (bulk structure or surface). The results showed that UV radiation for 1 min increased the tensile strength and modified the optical properties of films. It also altered the structure of the polymeric matrix, as demonstrated by the microstructure and thermal analysis, in agreement with the data obtained in packaging properties. The evaluation of antioxidant capacity through 2,2-azino-bis-3-ethylbenzthiazoline-6-sulphonic acid (ABTS) and reducing power indicated that incorporating fish protein hydrolysates either in the films’ bulk structure or film surface promoted antioxidant properties; control films (produced with rice starch/fish proteins without hydrolysates) also presented antioxidant potential. According to the peroxide value and thiobarbituric acid reactive substance (TBARS) assays, control films and the films containing hydrolysates in their bulk structure or on the surface could prevent the lipid oxidation of Italian salami. Thus, combining UV radiation to shape the characteristics of bio-based materials with fish protein hydrolysates to reduce lipid oxidation contributes to the performance of active bio-based films for food packaging.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Antimicrobial and Antioxidants Capacities: Application in Food Packaging)
►▼
Show Figures
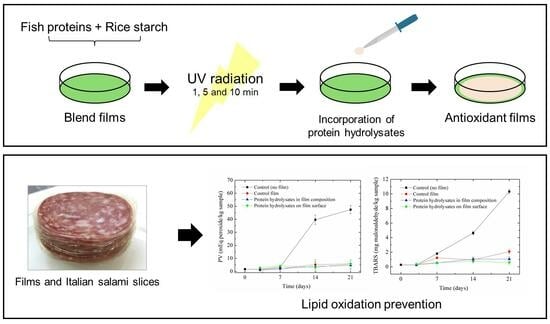
Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Comparative Physio-Biochemical and Transcriptome Analyses Reveal Contrasting Responses to Magnesium Imbalances in Leaves of Mulberry (Morus alba L.) Plants
by
Yisu Shi, Xin Jin, Michael Ackah, Frank Kwarteng Amoako, Jianbin Li, Victor Edem Tsigbey, Haonan Li, Zipei Cui, Longwei Sun, Chengfeng Zhao and Weiguo Zhao
Antioxidants 2024, 13(5), 516; https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox13050516 - 25 Apr 2024
Abstract
Magnesium (Mg) deficiency is a major factor limiting the growth and development of plants. Mulberry (Morus alba L.) is an important fruit tree crop that requires Mg for optimal growth and yield, especially in acid soils. However, the molecular mechanism of Mg
[...] Read more.
Magnesium (Mg) deficiency is a major factor limiting the growth and development of plants. Mulberry (Morus alba L.) is an important fruit tree crop that requires Mg for optimal growth and yield, especially in acid soils. However, the molecular mechanism of Mg stress tolerance in mulberry plants remains unknown. In this study, we used next-generation sequencing technology and biochemical analysis to profile the transcriptome and physiological changes of mulberry leaves under different Mg treatments (deficiency: 0 mM, low: 1 mM, moderate low: 2 mM, sufficiency: 3 mM, toxicity: 6 mM, higher toxicity: 9 mM) as T1, T2, T3, CK, T4, T5 treatments, respectively, for 20 days. The results showed that Mg imbalance altered the antioxidant enzymatic activities, such as catalase (CAT), peroxidase (POD), and superoxide dismutase (SOD), and non-enzymatic, including soluble protein, soluble sugar, malondialdehyde (MDA), and proline (PRO), contents of the plant. The Mg imbalances disrupted the ultrastructures of the vital components of chloroplast and mitochondria relative to the control. The transcriptome data reveal that 11,030 genes were differentially expressed (DEGs). Genes related to the photosynthetic processes (CAB40, CAB7, CAB6A, CAB-151, CAP10A) and chlorophyll degradation (PAO, CHLASE1, SGR) were altered. Antioxidant genes such as PER42, PER21, and PER47 were downregulated, but DFR was upregulated. The carbohydrate metabolism pathway was significantly altered, while those involved in energy metabolism processes were perturbed under high Mg treatment compared with control. We also identified several candidate genes associated with magnesium homeostasis via RT-qPCR validation analysis, which provided valuable information for further functional characterization studies such as promoter activity assay or gene overexpression experiments using transient expression systems.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue The Roles of Environmental Factors in Regulation of Oxidative Stress in Plants)

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Antioxidants Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Society Collaborations
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Antioxidants, IJPB, Molecules, Pharmaceuticals, Plants
Plants Volatile Compounds
Topic Editors: Dario Kremer, Igor Jerković, Valerija DunkićDeadline: 30 April 2024
Topic in
Analytica, Antioxidants, Biomedicines, Nutrients, Separations
Discovery of Bioactive Compounds from Natural Organisms and Their Molecular Mechanisms against Diseases
Topic Editors: Jun Dang, Tengfei Ji, Xinxin ZhangDeadline: 31 July 2024
Topic in
Analytica, Antioxidants, Applied Sciences, Molecules, Separations
New Analytical Methods in Plant Active Components Analysis
Topic Editors: Filomena Lelario, Giuliana Bianco, Radosław KowalskiDeadline: 31 October 2024
Topic in
Antioxidants, Biomolecules, Molecules, Pharmaceutics, Separations
Application of Analytical Chemistry in Exercise Physiology and Pharmacology
Topic Editors: Andrzej Pokrywka, Dorota KwiatkowskaDeadline: 15 November 2024

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Antioxidants
Advances for the NO/NOS System
Guest Editors: Adriana Bulboaca, Sorana D. BolboacăDeadline: 30 April 2024
Special Issue in
Antioxidants
Oxidative Stress and NRF2 in Health and Disease
Guest Editor: Lidija MilkovićDeadline: 20 May 2024
Special Issue in
Antioxidants
Antioxidant Activity of Fermented Foods and Food Microorganisms
Guest Editor: Myung-Ji SeoDeadline: 31 May 2024
Special Issue in
Antioxidants
Beneficial Effects on Oxidative Stress and Human Health by Dietary Polyphenols
Guest Editor: Arianna VigniniDeadline: 20 June 2024
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Antioxidants
Advances in Antioxidant Ingredients from Natural Products
Collection Editors: Carla Susana Correia Pereira, Lillian Barros