Journal Description
Uro
Uro
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on all aspects of urology and andrology, including oncology, endourology, sexual dysfunction, fertility, and infertility, published quarterly online by MDPI. The Italian Society of Andrology (SIA) is affiliated to Uro, and its members receive a discount on the article processing charges.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 14.1 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 9 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2023).
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
- Uro is a companion journal of JCM.
Latest Articles
The Clinical Management of Leukocytospermia in Male Infertility: A Narrative Review
Uro 2024, 4(2), 36-49; https://doi.org/10.3390/uro4020004 - 19 Apr 2024
Abstract
A major global health concern, male infertility affects 8–12% of couples globally. Leukocytospermia is a complicated illness that is distinguished from other reasons causing male infertility by having high white blood cell counts in semen. The complex mechanisms behind leukocytospermia’s effects on sperm
[...] Read more.
A major global health concern, male infertility affects 8–12% of couples globally. Leukocytospermia is a complicated illness that is distinguished from other reasons causing male infertility by having high white blood cell counts in semen. The complex mechanisms behind leukocytospermia’s effects on sperm function and fertility are examined in this review. Leukocytospermia induces oxidative stress and reactive oxygen species (ROS) that impair DNA integrity, mitochondrial function, cytoplasmic extrusion, and sperm quality overall. Leukocytospermia is exacerbated by non-infectious factors, such as substance abuse and varicocele, even though genital tract infections are a common cause. The usefulness and dependability of diagnostic techniques range from immunochemistry to direct counting. Although there is still disagreement on the most effective course of action, clinical-care techniques, such as antioxidant supplementation and antibiotic therapy, attempt to address underlying causes and reduce ROS-induced damage. Prospectively, the combination of artificial intelligence with the latest developments in artificial reproductive technologies presents opportunities for more precise diagnosis and customized treatments.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Male Infertility—Diagnosis and Treatment)
Open AccessReview
The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Male Infertility: Evaluation and Treatment: A Narrative Review
by
Nikit Venishetty, Marwan Alkassis and Omer Raheem
Uro 2024, 4(2), 23-35; https://doi.org/10.3390/uro4020003 - 25 Mar 2024
Abstract
Male infertility has affected an increasingly large population over the past few decades, affecting over 186 million people globally. The advent of assisted reproductive technologies (ARTs) and artificial intelligence (AI) has changed the landscape of diagnosis and treatment of male infertility. Through an
[...] Read more.
Male infertility has affected an increasingly large population over the past few decades, affecting over 186 million people globally. The advent of assisted reproductive technologies (ARTs) and artificial intelligence (AI) has changed the landscape of diagnosis and treatment of male infertility. Through an extensive literature review encompassing the PubMed, Google Scholar, and Scopus databases, various AI techniques such as machine learning (ML), artificial neural networks (ANNs), deep learning (DL), and natural language processing (NLP) were examined in the context of evaluating seminal quality, predicting fertility potential, and improving semen analysis. Research indicates that AI models can accurately estimate the quality of semen, diagnose problems with sperm, and provide guidance on reproductive health decisions. In addition, developments in smartphone-based semen analyzers and computer-assisted semen analysis (CASA) are indicative of initiatives to improve the price, portability, and accuracy of results. Future directions point to possible uses for AI in ultrasonography assessment, microsurgical testicular sperm extraction (microTESE), and home-based semen analysis. Overall, AI holds significant promise in revolutionizing the diagnosis and treatment of male infertility, offering standardized, objective, and efficient approaches to addressing this global health challenge.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Male Infertility—Diagnosis and Treatment)
Open AccessArticle
Patient Factors and Their Effect on Operating Room Time for Urologic Procedures
by
Wei-Shin Lu, Ali Zia, Nagalakshmi Nadiminty, Barbara Saltzman, Andrew B. Casabianca and Puneet Sindhwani
Uro 2024, 4(1), 12-22; https://doi.org/10.3390/uro4010002 - 04 Mar 2024
Abstract
Introduction: We examined three patient characteristics: body mass index (BMI), the American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) status, and pre-admission testing (PAT), and their effect on total operating room (OR) time for six urologic procedures, including ureteroscopy, transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP), transurethral
[...] Read more.
Introduction: We examined three patient characteristics: body mass index (BMI), the American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) status, and pre-admission testing (PAT), and their effect on total operating room (OR) time for six urologic procedures, including ureteroscopy, transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP), transurethral resection of bladder tumor (TURBT), prostatectomy, nephrectomy, and kidney transplants. Methods: We investigated the effect of these patient factors on OR time using linear regression for urologic procedures from The University of Toledo Medical Center from 2015 to 2020. Results: An increase in BMI was found to correlate with a statistically significant increase in total OR time for ureteroscopy, prostatectomy, and kidney transplant. The PAT showed a decrease in OR time for TURBT cases and an increase for kidney transplant cases. We found no correlation between the ASA status and changes in the total OR time. Conclusions: A higher BMI significantly increases the total OR time for robotic-assisted prostatectomy and kidney transplant but has a minimal effect on endoscopic procedures. Our results do not support ASA status as a predictor of total OR time. Due to the lack of consistency in results for PAT for the different procedures analyzed, further exploration of the effect of this patient factor on OR efficiency is needed.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
An Exploratory Study of Early Immune Response Markers for Pembrolizumab in Urothelial Tract Cancer
by
Dag Rune Stormoen, Lise Høj Omland, Kent William Mouw, Zoltan Szallasi, Sisse Rye Ostrowski, Susanne Dam Nielsen and Helle Pappot
Uro 2024, 4(1), 1-11; https://doi.org/10.3390/uro4010001 - 12 Jan 2024
Abstract
Background: This prospective pilot study explored the potential of the innate immune system’s response to cancer-related immuno-stimulants as a predictive biomarker for Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor (ICI) effectiveness, using pembrolizumab-treated metastatic urothelial tract cancer (mUTC) patients as the study population. Methods: We included ten
[...] Read more.
Background: This prospective pilot study explored the potential of the innate immune system’s response to cancer-related immuno-stimulants as a predictive biomarker for Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor (ICI) effectiveness, using pembrolizumab-treated metastatic urothelial tract cancer (mUTC) patients as the study population. Methods: We included ten mUTC patients and assessed their innate immune responses before the first and second pembrolizumab cycles with the TruCulture® immunoassay. We also executed survival analysis and compared cytokine release. Results: R848-induced IFNα and HKCA-induced IL-10 values decreased in patients with disease progression (n = 7), while these values increased in non-progressing patients (n = 3), denoting a significant difference (p = 0.00192 and p = 0.00343, respectively). Further, an increased R848-induced IFNα response correlated with extended survival (log-rank p-value of 0.048). Conclusion: Our small study identified distinct immune response patterns following pembrolizumab’s first cycle in mUTC patients, hypothesizing the potential of an increased R848-induced IFNα response for improved survival outcomes. Further confirmatory studies are in progress.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Urologic Oncology: Analysis and Treatment)
►▼
Show Figures
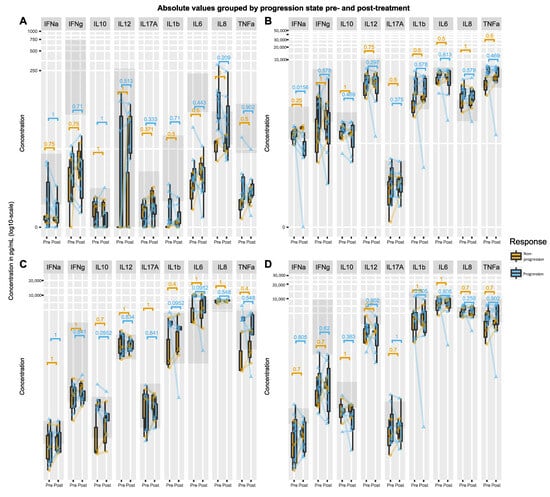
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Understanding Renal Failure Mortality Trends and Determinants in the US (1999–2020): Impacts of the Affordable Care Act, Advancements, Disparities, and Challenges
by
Oscar Salichs, Sishir Doddi, Taryn Hibshman, Jama Hersi and Puneet Sindhwani
Uro 2023, 3(4), 271-281; https://doi.org/10.3390/uro3040027 - 18 Dec 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Introduction: Renal failure, encompassing both acute and chronic forms, stands as a formidable public health challenge with far-reaching consequences for individual well-being and healthcare systems. This study delves into the mortality rates of renal failure in the United States over two transformative decades,
[...] Read more.
Introduction: Renal failure, encompassing both acute and chronic forms, stands as a formidable public health challenge with far-reaching consequences for individual well-being and healthcare systems. This study delves into the mortality rates of renal failure in the United States over two transformative decades, from 1999 to 2020. Renal failure’s significance arises from its escalating prevalence, substantial healthcare costs, and the imperative to understand the multifaceted factors that influence its outcomes. Objectives: The primary objectives of this research are to analyze temporal trends in renal failure mortality rates, explore the impact of the Affordable Care Act (ACA) and advancements in renal care practices on mortality rates, and assess demographic disparities in mortality outcomes. Methods: Utilizing CDC WONDER’s multi-cause mortality data, we assessed mortality due to renal failure (ICD-10 Codes: N17–N19). Age-adjusted mortality rates (AAMRs) were collected and stratified by sex and race. The Joinpoint Regression Program analyzed trends, calculating annual percent change (APC) and significant average annual percent change (AAPC) from 1999 to 2020. Segmented line regression models were employed for parallel pairwise comparisons. Results: Renal failure mortality rates decreased for both sexes during the late 2000s. The ACA’s enactment in 2010 coincided with improved access to healthcare, possibly contributing to the decline. Demographic disparities highlighted variations in mortality rates across racial and gender groups. Advancements in renal care practices were evident, which were driven by innovations in treatment modalities and disease management. Significant temporal trends were observed by race, with varying periods of decrease or uptrend. Conclusions: The decline in renal failure mortality rates during the late 2000s was potentially influenced by the ACA and advances in renal care practices. Demographic disparities emphasize the need for equitable healthcare access and interventions. These findings underscore the significance of healthcare policies and medical advancements in reducing renal failure mortality rates and addressing disparities. Persistent efforts to mitigate challenges such as healthcare access, cost barriers, and disparities remain crucial to enhancing renal failure outcomes.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessBrief Report
Efficacy of Fosfomycin against Extended Spectrum Beta-Lactamase-Producing Escherichia coli Isolated from Patient Urinary Cultures in the General Reference Hospital of Niamey, Niger
by
Alassane Halawen Mohamed, René Dembélé, Alio Mahamadou Fody, Alix Bénédicte Kagambèga, Hiliassa Coulibaly, Frédéric François Bado, Chaibou Salaou, Laouali Boubou, Alkassoum Ibrahim, Eric Adehossi Omar and Nicolas Barro
Uro 2023, 3(4), 262-270; https://doi.org/10.3390/uro3040026 - 04 Dec 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Urinary tract infection (UTI) is a common patient infection and a major public health problem today. The rapid spread of antibiotic resistance genes in Enterobacterales, particularly in Extended-spectrum beta-lactamases producing Escherichia coli (ESBL-E. coli), is compromising treatment with the
[...] Read more.
Urinary tract infection (UTI) is a common patient infection and a major public health problem today. The rapid spread of antibiotic resistance genes in Enterobacterales, particularly in Extended-spectrum beta-lactamases producing Escherichia coli (ESBL-E. coli), is compromising treatment with the antibiotics that are normally used. The aim of this study was to evaluate the level of susceptibility of uropathogenic ESBL-producing E. coli to fosfomycin as an alternative treatment. A total of 3369 samples of urine were received and processed in the Bacteriology Laboratory of the Niamey General Reference Hospital (NGRH) throughout 2021. Synergy testing was performed for phenotypic detection of ESBLs, and fosfomycin sensibility of ESBLs-producing uropathogenic E. coli isolates were determined using the Viteck-2 system. Of the 280 enterobacteria identified in the urine samples, 104 Escherichia coli isolates were positive to the synergy test. The average age of the patients was 54 ± 17. The age range of 46–65 years was the most affected by these infections. The female patients predominated over the male ones, with a prevalence of 51.90%, a sex ratio of 1.08. The ESBL-producing E. coli isolates were 0.97% resistant to fosfomycin. Fosfomycin is highly effective against uropathogenic ESBL-producing E. coli isolates. It could be used as an alternative treatment for both uncomplicated and complicated urinary tract infections.
Full article
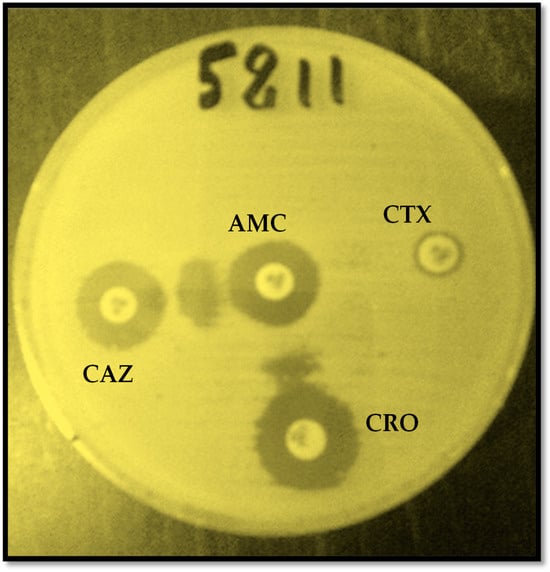
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Prophylactic Lymphadenectomy in Patients with Penile Cancer: Is Sooner Better?
by
Tommaso Cai, Marco Capece, Maria Grazia Zorzi, Alessandro Palmieri, Gabriella Nesi, Mattia Barbareschi and Truls E. Bjerklund Johansen
Uro 2023, 3(4), 251-261; https://doi.org/10.3390/uro3040025 - 09 Nov 2023
Abstract
Background: Management of penile cancer patients has its grey zones. In particular, no strong evidence or recommendations exist regarding the timing of prophylactic lymphadenectomy. Here, we aim to review the impact that the timing of inguinal and pelvic prophylactic lymph node dissection
[...] Read more.
Background: Management of penile cancer patients has its grey zones. In particular, no strong evidence or recommendations exist regarding the timing of prophylactic lymphadenectomy. Here, we aim to review the impact that the timing of inguinal and pelvic prophylactic lymph node dissection has on patient outcome. Methods: All relevant databases were searched following the preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analysis guidelines. A narrative review of indications for lymph node dissection and pathological considerations precede a systematic review of the impact of prophylactic lymph node dissection timing on prognosis. The primary endpoint is disease-free and overall survival in patients undergoing early or late lymph node dissection after penile cancer diagnosis. Results: Four clinical trials, all focusing on the role of inguinal lymph node dissection, are included. Despite the lack of randomized and controlled trials, this review suggests that lymph node dissection should be performed as soon as possible after diagnosis, with 3 months as a realistic cut-off. Conclusions: Survival of penile cancer patients is strictly related to the timing of prophylactic pelvic lymph node dissection. All patients at high risk of nodal metastasis should be offered lymph node dissection within three months of diagnosis, until new predicting tools are validated.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Andrology and Reproductive Health)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1
Open AccessFeature PaperReview
Fertility Preservation Options for Transgender Patients: An Overview
by
Natalie Mainland, Dana A. Ohl, Ahmed R. Assaly, Nabila Azeem, Amber Cooper, Angie Beltsos, Puneet Sindhwani and Tariq A. Shah
Uro 2023, 3(4), 239-250; https://doi.org/10.3390/uro3040024 - 08 Oct 2023
Abstract
Fertility preservation technologies have existed for decades, and the field is rapidly advancing; limited data exist regarding the use of these technologies by transgender patients. Many options are available for transgender patients who wish to preserve fertility before transitioning. These options include the
[...] Read more.
Fertility preservation technologies have existed for decades, and the field is rapidly advancing; limited data exist regarding the use of these technologies by transgender patients. Many options are available for transgender patients who wish to preserve fertility before transitioning. These options include the cryopreservation of gametes, embryos, or ovarian tissue. Currently, ejaculated, or testicular sperm, immature oocytes, and ovarian tissue can be preserved for later use, but no such use option exists for immature testicular tissue. Many financial, sociological, and legal barriers and a lack of awareness among physicians and patients also hinders the utilization of these fertility preservation services. While options are abundant, usage rates are relatively low. The initial data regarding the successful use of preserved tissues appears promising, with birth rates not dissimilar to non-transgender patients. Further investigations into this area are needed. In addition, counseling regarding fertility preservation options should become a significant part of the provider-patient conversation before transitioning therapies.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Andrology and Reproductive Health)
Open AccessReview
Urinary Artificial Sphincter in Male Stress Urinary Incontinence: Where Are We Today? A Narrative Review
by
Anna Ricapito, Matteo Rubino, Pasquale Annese, Vito Mancini, Ugo Falagario, Luigi Cormio, Giuseppe Carrieri, Gian Maria Busetto and Carlo Bettocchi
Uro 2023, 3(3), 229-238; https://doi.org/10.3390/uro3030023 - 06 Sep 2023
Abstract
Introduction: Urinary incontinence is a prevalent condition, especially in elderly men, with stress urinary incontinence (SUI) being a common cause after radical prostatectomy. The artificial urinary sphincter (AUS), particularly the AMS 800™ device, has been the gold-standard treatment for moderate-severe male SUI for
[...] Read more.
Introduction: Urinary incontinence is a prevalent condition, especially in elderly men, with stress urinary incontinence (SUI) being a common cause after radical prostatectomy. The artificial urinary sphincter (AUS), particularly the AMS 800™ device, has been the gold-standard treatment for moderate-severe male SUI for decades. Despite some technical advancements and alternative devices like ZSI-375, Victo, and BR-SL-AS 904 being introduced, there is limited literature comparing their effectiveness to the AMS 800™. Methods: This literature review compares the AMS 800™ to the newer technologies in the management of SUI. We reviewed the current literature on urinary sphincter implant in male stress incontinence, including AMS 800™, ZSI-375, Victo, and BR-SL-AS 904. Findings: The AMS 800™ is a sophisticated system consisting of an inflatable cuff, a pressure-regulating balloon, and a control pump. Studies show continence rates ranging from 61% to 100% with AMS 800™ implants, with low infection rates and significant improvement in patients’ quality of life. The ZSI-375 sphincter is a unique single-piece cuff without an abdominal reservoir, simplifying implantation. Preliminary data show a social continence rate of 73% at six months, with lower complication rates than the AMS 800™. The VICTO® device offers adjustable pressure and a stress relief mechanism, providing conditional occlusion of the urethra. Early studies report a satisfaction rate of up to 94.2% and a complication rate of 17.6%. BR-SL-AS 904 is a newly proposed urinary sphincter, but due to the limited number of cases and a single study, its efficacy and complication rates remain uncertain. Conclusions: Overall, AMS 800™ remains the gold-standard treatment for SUI after radical prostatectomy. Alternative devices like ZSI-375 and VICTO® show promising results, but longer studies and more data are needed to establish their effectiveness and safety compared with the AMS 800™. Further research and ongoing monitoring are essential to address mechanical issues associated with AUS implants.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Lower Urinary Tract Research: Rationale, Feasibility, and Design)
Open AccessReview
Effectiveness of Silymarin, Sulforaphane, Lycopene, Green Tea, Tryptophan, Glutathione, and Escin on Human Health: A Narrative Review
by
Francesco Sebastiani, Carlo D’Alterio, Cristina Vocca, Luca Gallelli, Fabrizio Palumbo, Tommaso Cai and Alessandro Palmieri
Uro 2023, 3(3), 208-228; https://doi.org/10.3390/uro3030022 - 09 Aug 2023
Abstract
Background: Recently, the role of nutraceutical compounds in the prevention of human diseases has been rapidly increasing. Here, we aim to evaluate the beneficial effect of dietary supplementation with seven active principles, i.e., lycopene, sulforaphane, silymarin, glutathione, escin, tryptophan, and green tea catechins,
[...] Read more.
Background: Recently, the role of nutraceutical compounds in the prevention of human diseases has been rapidly increasing. Here, we aim to evaluate the beneficial effect of dietary supplementation with seven active principles, i.e., lycopene, sulforaphane, silymarin, glutathione, escin, tryptophan, and green tea catechins, on human health. Methods: An extensive search of PubMed and Medline database was performed with the following keywords: “silymarin”, “sulforaphane”, “lycopene”, “green tea catechins”, “tryptophan”, “glutathione” and “escin” accompanied by the keywords “supplement”, “supplementation”, and “nutraceutics”. All preclinical and clinical trials were considered for this review. Results: One hundred and eighteen full-text articles were eligible for inclusion in this review. The papers examined presented considerable variability due to the wide heterogeneity of dosages administered, population involved, and outcomes pursued. Conclusion: Nutritional supplementation with lycopene, sulforaphane, silymarin, glutathione, escin, tryptophan, and green tea catechins appears to exert a wide range of benefits on human health, ranging from mood and cognition to cardiovascular health, fertility, metabolism, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory capabilities, as well as potential anticancer effects. Further studies are required to better define the potential synergic effect, optimal dosage, mechanism of action, and tolerability profiles of these substances.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Andrology and Reproductive Health)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Efficacy and Safety of a Natural Supplement Containing Serenoa Repens, Solanum Lycopersicum, Lycopene, and Bromelain in Reducing Symptoms of Chronic Prostatitis/Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome: A Prospective Cohort Study in 250 Patients
by
Luca Lambertini, Alessandro Sandulli, Vincenzo Salamone, Mara Bacchiani, Sofia Giudici, Eleana Massaro, Anna Cadenar, Riccardo Mariottini, Simone Coco, Laia Bardina, Elena Ciaralli, Marco Saladino, Andrea Romano, Francesca Valastro, Antonio Andrea Grosso, Fabrizio Di Maida, Giampaolo Siena, Sabino Scelzi and Andrea Mari
Uro 2023, 3(3), 199-207; https://doi.org/10.3390/uro3030021 - 20 Jul 2023
Abstract
Background: Chronic Prostatitis/Chronic Pelvic Pain syndrome NIH-class III is a widespread condition affecting men universally, with existing treatments showing limited success. This study evaluated the efficacy and safety of a natural supplement, composed of Serenoa repens, Solanum lycopersicum, lycopene, and bromelain, in managing
[...] Read more.
Background: Chronic Prostatitis/Chronic Pelvic Pain syndrome NIH-class III is a widespread condition affecting men universally, with existing treatments showing limited success. This study evaluated the efficacy and safety of a natural supplement, composed of Serenoa repens, Solanum lycopersicum, lycopene, and bromelain, in managing symptoms of this condition among a substantial patient group. Methods: In this prospective study, 245 patients diagnosed with Chronic Prostatitis/Chronic Pelvic Pain syndrome NIH-class III were treated with the aforementioned supplement, alongside lifestyle alterations, such as refraining from spicy foods, alcohol, caffeine, and cycling, for a duration of three months. Patients’ progress was assessed at one and three months using the National Institutes of Health Chronic Prostatitis Symptom Index (NIH-CPSI), the International Prostate Symptom Index (IPSS), quality of life (QoL) scores, and changes in total prostate-specific antigen (PSA) levels. Results: The supplement was well received with no serious adverse events reported. Significant improvements were observed in NIH-CPSI scores, IPSS, QoL scores, and a substantial decrease in total PSA levels at three months compared to baseline, with a positive trend noted from one-month to three-month evaluations. This was consistent in either patients with predominantly voiding or storage urinary symptoms. Conclusions: Our results suggest that this natural supplement in conjunction with lifestyle changes could offer a safe and effective alternative treatment for patients suffering from Chronic Prostatitis/Chronic Pelvic Pain syndrome NIH-class III. However, these findings require validation through further large-scale randomized controlled trials.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Andrology and Reproductive Health)
►▼
Show Figures
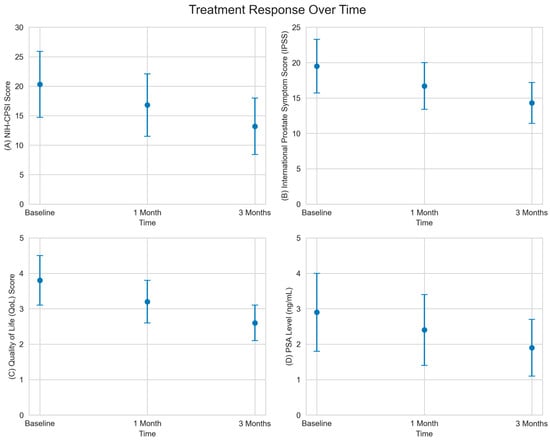
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Deceased Transplant Recipients: A Forgotten Source of Organ Donors
by
Dai D. Nghiem
Uro 2023, 3(3), 187-198; https://doi.org/10.3390/uro3030020 - 03 Jul 2023
Abstract
Background: Organ transplantation is the most successful therapy for end-stage organ disease since it increases the quality of life and life expectancy. For these reasons, over 107,000 patients were on the waitlist in the United States for a transplant in 2022. Unfortunately, only
[...] Read more.
Background: Organ transplantation is the most successful therapy for end-stage organ disease since it increases the quality of life and life expectancy. For these reasons, over 107,000 patients were on the waitlist in the United States for a transplant in 2022. Unfortunately, only 42,887 transplants were performed, and annually, over 7000 patients on the kidney list die or are too sick to transplant. To solve this severe organ shortage, the use of the deceased transplant recipients with functioning organs, whether transplanted or native, is explored as a new source of organ donors. Methods: To assess the feasibility of this option, first, we will review the rate of kidney transplant recipients dying with functioning grafts (DWGF), their re-use, the organ allocation system, the technical aspects of the organ procurement, and the transplantation of the DWGF kidneys. Then, we will consider the larger group of all deceased transplant recipients as potential donors for all functioning, native, or transplanted organs. Conclusions: (1). All functioning kidney transplants explanted from the deceased transplant recipients have excellent long-term function after re-transplantation. (2). The other functioning organs constitute a large unrecognized pool of transplantable organs. (3). The intensivists and the transplant community should be educated about these new options to improve the organ shortage.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Current Concepts in Transplantation)
►▼
Show Figures
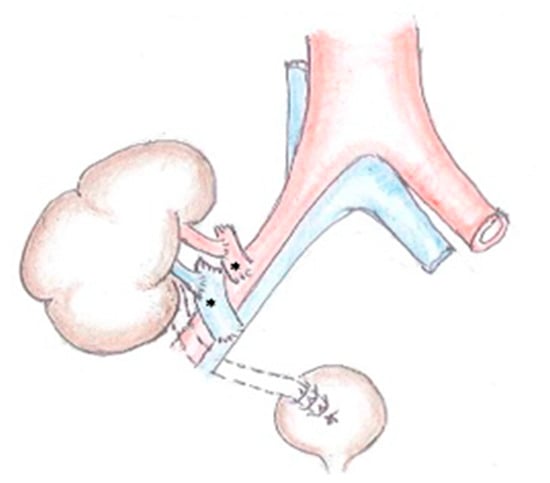
Figure 1
Open AccessCase Report
Adult-Type Granulosa Cell Tumor of the Testis: A Report of a Case and a Discussion of the Literature
by
Georgios Zervopoulos, Nikolaos Mitsimponas, Filippos Venetsanos and Athanasios Papathanasis
Uro 2023, 3(3), 177-186; https://doi.org/10.3390/uro3030019 - 03 Jul 2023
Abstract
Testicular granulosa cell tumors (TGCTs) are rare tumors of sex cord-stromal origin. TGCTs are classified into two main categories, the adult type and the juvenile type. The adult type is extremely rare, with only 93 known cases reported in the literature. Herein, we
[...] Read more.
Testicular granulosa cell tumors (TGCTs) are rare tumors of sex cord-stromal origin. TGCTs are classified into two main categories, the adult type and the juvenile type. The adult type is extremely rare, with only 93 known cases reported in the literature. Herein, we present a report of a case of a 30-year-old male patient who presented with a testicular mass and underwent radical inguinal orchiectomy; the pathology examination revealed an adult-type granulosa tumor. Additionally, we review the literature to summarize the scientific knowledge of an entity barely described worldwide.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Uro-Oncology: Treatment and Future Directions)
Open AccessArticle
Targeted Antimicrobial Prophylaxis with Cefmetazole Based on Presence of Fluoroquinolone-Resistant Isolates to Prevent Post-Prostate Biopsy Infectious Complications
by
Shinichiro Higashi, Yuko Yoshio, Hideki Kanda, Taketomo Nishikawa, Momoko Kato, Yusuke Sugino, Takeshi Sasaki, Manabu Kato, Satoru Masui, Kouhei Nishikawa and Takahiro Inoue
Uro 2023, 3(2), 168-176; https://doi.org/10.3390/uro3020018 - 09 Jun 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Fluoroquinolones (FQs) have been traditionally used for prophylaxis against bacterial infection. However, the rapid emergence of FQ-resistant Escherichia coli due to overuse and misuse have resulted in an increase in post-biopsy infections. We requested 723 patients undergoing transrectal or transrectal plus transperineal targeted
[...] Read more.
Fluoroquinolones (FQs) have been traditionally used for prophylaxis against bacterial infection. However, the rapid emergence of FQ-resistant Escherichia coli due to overuse and misuse have resulted in an increase in post-biopsy infections. We requested 723 patients undergoing transrectal or transrectal plus transperineal targeted prostate biopsy to provide preprocedure rectal swabs. The rectal swabs were plated onto deoxycholate hydrogen sulfate lactose agar culture and FQ resistance tests were conducted using the disc diffusion method following the guidelines of the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. All patients undergoing biopsy were given a 1.0 g intravenous injection of cefmetazole (CMZ) 30 min before and 12 h after biopsy. Patients with FQ-resistant organisms received an additional 1.0 g intravenous injection of CMZ every 12 h for an additional 1.5 days, while those without FQ-resistant organisms received levofloxacin 500 mg for 4 days. We evaluated infectious symptoms during the 30 days after the biopsy. We also evaluated the incidence of acute prostatitis within 7 days after the biopsy and isolation rates of FQ-resistant strains. A total of 289 patients (40%) had FQ-resistant isolates on rectal swabs. The overall infectious complication rate was 0.69%. Two patients with FQ-resistant isolates and three patients without them experienced infectious episodes. One patient with FQ-resistant isolates and two patients without them suffered acute prostatitis. The difference in the rates of infectious complication and acute prostatitis rates between FQ-resistant and FQ-susceptible carriers were not significant (p = 1.0 and 1.0, respectively). Post-biopsy sepsis was identified in one patient (0.14%) who had FQ-resistant Escherichia coli. Targeted antimicrobial prophylaxis with cefmetazole based on presence of FQ-resistant isolates on rectal swabs may prevent post-prostate biopsy infectious complications, especially in geographic lesions with a high incidence of FQ-resistant strains in rectal flora.
Full article
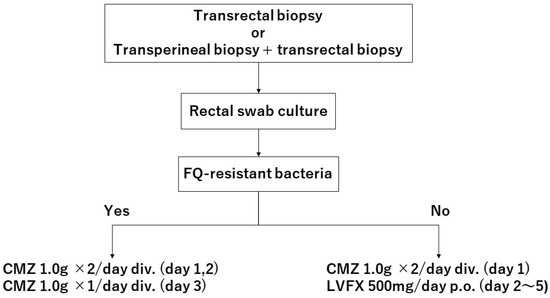
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Current Evidence on the Use of Hyaluronic Acid as Nonsurgical Option for the Treatment of Peyronie’s Disease: A Contemporary Review
by
Marco Capece, Giuseppe Celentano and Roberto La Rocca
Uro 2023, 3(2), 160-167; https://doi.org/10.3390/uro3020017 - 01 Jun 2023
Abstract
Peyronie’s disease is a condition characterized by the formation of fibrous plaques in the tunica albuginea, which can cause pain, curvature, and erectile dysfunction. Preclinical studies have demonstrated the potential benefits of hyaluronic acid in treating Peyronie’s disease, including antifibrotic, anti-inflammatory, and proangiogenic
[...] Read more.
Peyronie’s disease is a condition characterized by the formation of fibrous plaques in the tunica albuginea, which can cause pain, curvature, and erectile dysfunction. Preclinical studies have demonstrated the potential benefits of hyaluronic acid in treating Peyronie’s disease, including antifibrotic, anti-inflammatory, and proangiogenic effects, although more research is needed to fully understand its mechanisms of action. Clinical studies have shown promising results, with hyaluronic acid injections leading to improvements in plaque size, penile curvature, and erectile function, and being well tolerated by patients. The findings suggest that HA injections could be a viable and safe treatment option for Peyronie’s disease, particularly in the early stages of the disease. However, more research is needed to determine the optimal dosage and treatment duration for HA injections, and to confirm its efficacy in the stable phase of Peyronie’s disease. Overall, hyaluronic acid is a potentially effective therapy for Peyronie’s disease, with the ability to inhibit fibrosis and promote angiogenesis, and low risk of adverse effects, making it an attractive option for patients who are unable or unwilling to undergo surgery.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Andrology and Reproductive Health)
Open AccessFeature PaperReview
From the Triangulation Technique to the Use of the Donor Aorta and Vena Cava for Kidney Transplantation: Lessons from the Past and Path to the Future of Xenotransplantation
by
Dai D. Nghiem
Uro 2023, 3(2), 151-159; https://doi.org/10.3390/uro3020016 - 26 May 2023
Abstract
Revascularization of the kidney transplant is classically performed by anastomosing the renal vessels to the recipient iliac vessels. This technique is not applicable when the renal vessels are very small, numerous or anomalous and aberrant. In these instances, the donor aorta and the
[...] Read more.
Revascularization of the kidney transplant is classically performed by anastomosing the renal vessels to the recipient iliac vessels. This technique is not applicable when the renal vessels are very small, numerous or anomalous and aberrant. In these instances, the donor aorta and the vena cava have to be used for vascular anastomosis. It would be useful to briefly review the development and the use of the donor aorta and cava in renal transplantation during the last century and discuss the potential clinical application of this technique in xenotransplantation of the porcine kidneys in humans at the dawn of the 21st century.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Current Concepts in Transplantation)
Open AccessArticle
A Decade of Pancreas Transplantation—A Registry Report
by
Angelika C. Gruessner
Uro 2023, 3(2), 132-150; https://doi.org/10.3390/uro3020015 - 25 May 2023
Cited by 3
Abstract
Since the first pancreas transplant in 1966, over 67,000 pancreas transplants have been performed worldwide and the number is growing. While the number of transplants in the US has changed only slightly over the past decade, many countries outside the US have shown
[...] Read more.
Since the first pancreas transplant in 1966, over 67,000 pancreas transplants have been performed worldwide and the number is growing. While the number of transplants in the US has changed only slightly over the past decade, many countries outside the US have shown strong growth in transplant numbers. The worldwide growth in numbers is due to the increasing number of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus receiving a pancreas transplant. Only during the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020 and 2021 did transplant numbers decline, but they started to recover in 2022. The decline was especially noted for solitary transplants. This development over time was due to excellent patient and graft survival after simultaneous pancreas and kidney transplant (SPK). Patient survival at three years was >90% in SPK as well as in solitary transplants. At 3 years post-transplant, SPK pancreas graft survival was over 86% and SPK kidney graft survival over 90%. In pancreas transplants alone (PTA) and in pancreas after kidney transplants, the 3-year graft function reached 75%. The main reasons for advancement in outcome were reductions in technical failures and immunological graft losses. These improvements were due to better patient and donor selection, standardization of surgical techniques, and superior immunosuppressive protocols.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Current Concepts in Transplantation)
►▼
Show Figures
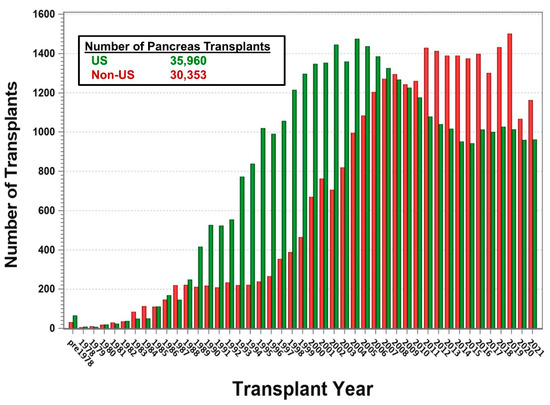
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Evolving Treatment Options for Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma (mRCC)
by
Eun-mi Yu, Mythri Mudireddy, Ishan Patel and Jeanny B. Aragon-Ching
Uro 2023, 3(2), 117-131; https://doi.org/10.3390/uro3020014 - 01 Apr 2023
Cited by 2
Abstract
Approximately a third of patients diagnosed with kidney cancer in the United States present with advanced disease and those who present with distant metastases historically had dismal 5-year relative survival. However, over the last several years, advancements have led to improved life expectancy
[...] Read more.
Approximately a third of patients diagnosed with kidney cancer in the United States present with advanced disease and those who present with distant metastases historically had dismal 5-year relative survival. However, over the last several years, advancements have led to improved life expectancy and patient outcomes in those who develop advanced renal cell carcinoma. Metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma (mccRCC) treatment has rapidly evolved with multiple drug approvals since 2006. Moreover, multiple combination regimens including a vascular endothelial growth factor tyrosine kinase inhibitor (VEGF-TKI) plus immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) and the combination of ipilimumab plus nivolumab have supplanted first-line VEGF-TKI monotherapy. Thus, the insights we gained from prospective randomized controlled trials focusing on systemic therapy beyond first-line therapy in mRCC patients treated in the TKI monotherapy era quickly became less relevant with the adoption of contemporary first-line combination regimens. Herein, we will review contemporary first- and second-line therapies for mccRCC, as well as highly anticipated clinical trials looking into novel regimens beyond first-line therapy in patients who have received combination therapy.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Uro-Oncology: Treatment and Future Directions)
►▼
Show Figures
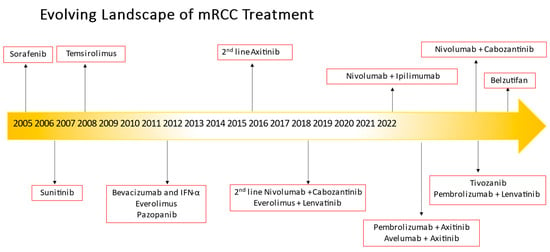
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Current Knowledge on Radiation-Therapy-Induced Erectile Dysfunction in Prostate-Cancer Patients: A Narrative Review
by
Connie Labate, Andrea Panunzio, Francesco De Carlo, Federico Zacheo, Sara De Matteis, Maria Cristina Barba, Umberto Carbonara, Floriana Luigina Rizzo, Silvana Leo, Saverio Forte, Pasquale Ditonno, Alessandro Tafuri and Vincenzo Pagliarulo
Uro 2023, 3(2), 104-116; https://doi.org/10.3390/uro3020013 - 01 Apr 2023
Abstract
Prostate cancer is the most frequently diagnosed cancer in men in the United States. Among the different available treatment options, radiation therapy is recommended for localized or even advanced disease. Erectile dysfunction (ED) often occurs after radiation therapy due to neurological, vascular, and
[...] Read more.
Prostate cancer is the most frequently diagnosed cancer in men in the United States. Among the different available treatment options, radiation therapy is recommended for localized or even advanced disease. Erectile dysfunction (ED) often occurs after radiation therapy due to neurological, vascular, and endocrine mechanisms resulting in arterial tone alteration, pudendal-nerve neuropraxia, and lastly fibrosis. Considering the influence of quality of life on patients’ treatment choice, radiation-therapy-induced ED prevention and treatment are major issues. In this narrative review, we briefly summarize and discuss the current state of the art on radiation-therapy-induced ED in PCa patients in terms of pathophysiology and available treatment options.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Prostate Cancer and Erectile Disfunction)
►▼
Show Figures
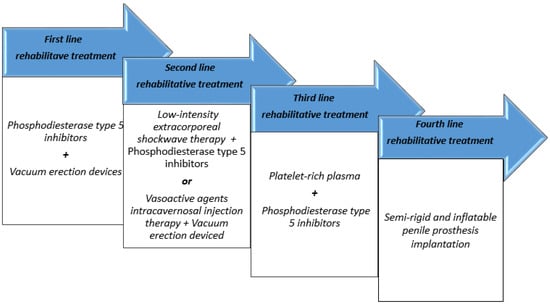
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Prostate Cancer: Advances in Genetic Testing and Clinical Implications
by
Ahmad S. Abdelrazek, Khaled Ghoniem, Mohamed E. Ahmed, Vidhu Joshi, Ahmed M. Mahmoud, Nader Saeed, Nazih Khater, Mohammed S. Elsharkawy, Ahmed Gamal, Eugene Kwon and Ayse Tuba Kendi
Uro 2023, 3(2), 91-103; https://doi.org/10.3390/uro3020012 - 24 Mar 2023
Cited by 1
Abstract
The demand for genetic testing (GT) for prostate cancer (PCa) is expanding, but there is limited knowledge about the genetic counseling (GC) needs of men. A strong-to-moderate inherited genetic predisposition causes approximately 5–20% of prostate cancer (PCa). In men with prostate cancer, germline
[...] Read more.
The demand for genetic testing (GT) for prostate cancer (PCa) is expanding, but there is limited knowledge about the genetic counseling (GC) needs of men. A strong-to-moderate inherited genetic predisposition causes approximately 5–20% of prostate cancer (PCa). In men with prostate cancer, germline testing may benefit the patient by informing treatment options, and if a mutation is noticed, it may also guide screening for other cancers and have family implications for cascade genetic testing (testing of close relatives for the same germline mutation). Relatives with the same germline mutations may be eligible for early cancer detection strategies and preventive measures. Cascade family testing can be favorable for family members, but it is currently unutilized, and strategies to overcome obstacles like knowledge deficiency, family communication, lack of access to genetic services, and testing expenses are needed. In this review, we will look at the genetic factors that have been linked to prostate cancer, as well as the role of genetic counseling and testing in the early detection of advanced prostate cancer.
Full article
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Uro
Prostate Cancer and Erectile Disfunction
Guest Editor: Alessandro TafuriDeadline: 15 May 2024
Special Issue in
Uro
Urologic Oncology: Analysis and Treatment
Guest Editor: Haoyue ShengDeadline: 15 July 2024



