-
 Estimating Forest Variables for Major Commercial Timber Plantations in Northern Spain Using Sentinel-2 and Ancillary Data
Estimating Forest Variables for Major Commercial Timber Plantations in Northern Spain Using Sentinel-2 and Ancillary Data -
 Aspen and Spruce Densities Affect Tree Size, Future Stand Volume, and Aboveground Carbon Following Precommercial Thinning
Aspen and Spruce Densities Affect Tree Size, Future Stand Volume, and Aboveground Carbon Following Precommercial Thinning -
 Driving Efficiency and Competitiveness: Trends and Innovations in ERP Systems for the Wood Industry
Driving Efficiency and Competitiveness: Trends and Innovations in ERP Systems for the Wood Industry -
 Cost–Benefit Analysis of Monitoring Insect Pests and Aerial Spraying of Insecticides
Cost–Benefit Analysis of Monitoring Insect Pests and Aerial Spraying of Insecticides -
 Policy and Regulations for Mobile Biochar Production in the United States of America
Policy and Regulations for Mobile Biochar Production in the United States of America
Journal Description
Forests
Forests
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on forestry and forest ecology published monthly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE (Web of Science), Ei Compendex, GEOBASE, PubAg, AGRIS, PaperChem, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q1 (Forestry) / CiteScore - Q1 (Forestry)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 16.9 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.8 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2023).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
- Testimonials: See what our editors and authors say about Forests.
Impact Factor:
2.9 (2022);
5-Year Impact Factor:
3.0 (2022)
Latest Articles
Substitution of Inorganic Fertilizer with Organic Fertilizer Influences Soil Carbon and Nitrogen Content and Enzyme Activity under Rubber Plantation
Forests 2024, 15(5), 756; https://doi.org/10.3390/f15050756 (registering DOI) - 25 Apr 2024
Abstract
Conventional fertilization practices can lead to many ecological problems, such as nutrient imbalance, soil acidity, and reduced soil fertility, in natural rubber plantations. To address these challenges, a field investigation was strategically carried out to substitute inorganic fertilizer with organic fertilizer, consisting of
[...] Read more.
Conventional fertilization practices can lead to many ecological problems, such as nutrient imbalance, soil acidity, and reduced soil fertility, in natural rubber plantations. To address these challenges, a field investigation was strategically carried out to substitute inorganic fertilizer with organic fertilizer, consisting of six treatments: no fertilization (CK), inorganic fertilizer (NPK), 25% replacement of inorganic through organic (25% manure (M)), 50% replacement of inorganic through organic (50% manure (M)), 75% replacement of inorganic through organic (75% manure (M)), and 100% organic fertilizer (100% manure). The soil physicochemical properties (soil organic carbon (SOC), total nitrogen (TN), mineral nitrogen (N), ammonium nitrogen (NH4+-N), and nitrate nitrogen (NO3−-N)), C:N, pH, and the carbon- and nitrogen-converting enzymes β-1,4-glucosidase (BG), N-acetylglucosaminidase (NAG) and L-leucine aminopeptidase (LAP) were all determined. The partial substitution of inorganic fertilizer with organic fertilizer (i.e., 75% M at surface soil layer) showed higher SOC (14.52 g·kg−1), TN (1.06 g·kg−1), N (20.07 mg·kg−1), C:N (14.63), NH4+-N (10.63 mg·kg−1), and NO3−-N (11.06 mg·kg−1) than NPK and CK. This increase in physicochemical properties after partial replacement of inorganic with organic fertilizer resulted from higher carbon and nitrogen enzyme activities (BG (143.17·nmol·g−1·h−1), NAG (153.96 nmol·g−1·h−1), and LAP (153.48 nmol·g−1·h−1)) compared to NPK and CK. Further, the Pearson correlation and redundancy analysis (RDA) analyses confirmed a significant positive correlation between SOC, N, and soil enzymes. This study presents a new strategy for assessing the impact of partially replacing inorganic fertilizer with organic fertilizer in rubber plantations in tropical regions, mainly by modifying the soil nutrient composition.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Sustainable Forest Fertilization Strategies: Impact on Soil Quality, Ecosystem Health and Productivity)
Open AccessArticle
A Deep Learning Method for Log Diameter Measurement Using Wood Images Based on Yolov3 and DeepLabv3+
by
Zhenglan Lu, Huilu Yao, Yubiao Lyu, Sheng He, Heng Ning, Yuhui Yu, Lixia Zhai and Lin Zhou
Forests 2024, 15(5), 755; https://doi.org/10.3390/f15050755 (registering DOI) - 25 Apr 2024
Abstract
Wood volume is an important indicator in timber trading, and log diameter is one of the primary parameters used to calculate wood volume. Currently, the most common methods for measuring log diameters are manual measurement or visual estimation by log scalers, which are
[...] Read more.
Wood volume is an important indicator in timber trading, and log diameter is one of the primary parameters used to calculate wood volume. Currently, the most common methods for measuring log diameters are manual measurement or visual estimation by log scalers, which are laborious, time consuming, costly, and error prone owing to the irregular placement of logs and large numbers of roots. Additionally, this approach can easily lead to misrepresentation of data for profit. This study proposes a model for automatic log diameter measurement that is based on deep learning and uses images to address the existing problems. The specific measures to improve the performance and accuracy of log-diameter detection are as follows: (1) A dual network model is constructed combining the Yolov3 algorithm and DeepLabv3+ architecture to adapt to different log-end color states that considers the complexity of log-end faces. (2) AprilTag vision library is added to estimate the camera position during image acquisition to achieve real-time adjustment of the shooting angle and reduce the effect of log-image deformation on the results. (3) The backbone network is replaced with a MobileNetv2 convolutional neural network to migrate the model to mobile devices, which reduces the number of network parameters while maintaining detection accuracy. The training results show that the mean average precision of log-diameter detection reaches 97.28% and the mean intersection over union (mIoU) of log segmentation reaches 92.22%. Comparisons with other measurement models demonstrate that the proposed model is accurate and stable in measuring log diameter under different environments and lighting conditions, with an average accuracy of 96.26%. In the forestry test, the measurement errors for the volume of an entire truckload of logs and a single log diameter are 1.20% and 0.73%, respectively, which are less than the corresponding error requirements specified in the industry standards. These results indicate that the proposed method can provide a viable and cost-effective solution for measuring log diameters and offering the potential to improve the efficiency of log measurement and promote fair trade practices in the lumber industry.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Wood Science and Forest Products)
Open AccessArticle
Monitoring Forest Dynamics and Conducting Restoration Assessment Using Multi-Source Earth Observation Data in Northern Andes, Colombia
by
Carlos Pedraza, Nicola Clerici, Marcelo Villa, Milton Romero, Adriana Sarmiento Dueñas, Dallan Beltrán Rojas, Paola Quintero, Harold Mauricio Martínez and Josef Kellndorfer
Forests 2024, 15(5), 754; https://doi.org/10.3390/f15050754 (registering DOI) - 25 Apr 2024
Abstract
Examining the efficacy of current assessment methodologies for forest conservation and restoration initiatives to align with global and national agendas to combat deforestation and facilitate restoration efforts is necessary to identify efficient and robust approaches. The objective of this study is to understand
[...] Read more.
Examining the efficacy of current assessment methodologies for forest conservation and restoration initiatives to align with global and national agendas to combat deforestation and facilitate restoration efforts is necessary to identify efficient and robust approaches. The objective of this study is to understand forest dynamics (1996–2021) and assess restoration implementations at the Urra’s supplying basin hydroelectric reservoir in Colombia. The processing approach integrates optical and radar Earth Observation (EO) data from Sentinel-2 and Landsat for forest mapping and multi-temporal forest change assessment (1996–2021), and a Sentinel-1 backscatter time-series analysis is conducted to assess the state of forest restoration implementations. The processing chain was scaled in a cloud-based environment using the Nebari and SEPPO software and the Python language. The results demonstrate an overall substantial decrease in forested areas in the 1996–2000 period (37,763 ha). An accuracy assessment of multi-temporal forest change maps showed a high precision in detecting deforestation events, while improvements are necessary for accurately representing non-forested areas. The forest restoration assessment suggests that the majority of the 270 evaluated plots are in the intermediate growth state (82.96%) compared to the reference data. This study underscores the need for robust and continuous monitoring systems that integrate ground truth data with EO techniques for enhanced accuracy and effectiveness in forest restoration and conservation endeavors.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Remote Sensing for Forestry: Theory, Methods, Applications, and Validation)
►▼
Show Figures
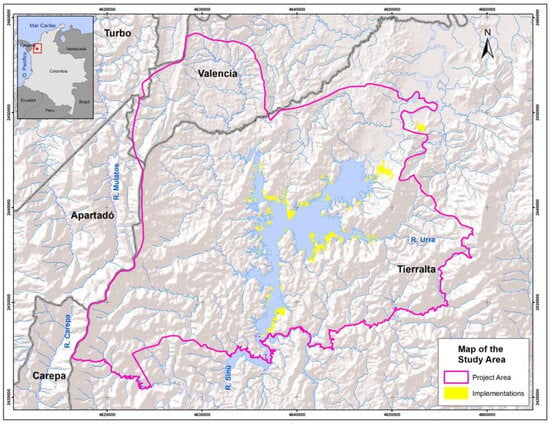
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Response of Soil CO2 Emission to Addition of Biochar and Dissolved Organic Carbon along a Vegetation Restoration Gradient of Subtropical China
by
Yulin Zhu, Xinghao Tang, Yunpeng Huang, Jing Jiang and Xiong Fang
Forests 2024, 15(5), 753; https://doi.org/10.3390/f15050753 (registering DOI) - 25 Apr 2024
Abstract
Biochar, as a soil amendment, has been widely confirmed to increase soil carbon sequestration. However, how biochar addition affects soil carbon changes during the vegetation restoration process is still unclear, which constrains our ability to explore biochar’s application in the technology of soil
[...] Read more.
Biochar, as a soil amendment, has been widely confirmed to increase soil carbon sequestration. However, how biochar addition affects soil carbon changes during the vegetation restoration process is still unclear, which constrains our ability to explore biochar’s application in the technology of soil carbon sequestration in forests. We conducted an incubation experiment on biochar and dissolved organic matter (DOM) addition to soil at three stages of revegetation (degraded land (DS), plantation forest (PS), and secondary natural forest (NS) in Changting County in Fujian province, China) to investigate the effects of vegetation restoration, biochar, DOM, and their interaction on soil CO2 emission and its relative mechanisms. We found that the accumulative release of CO2-C in the NS and PS soils was 7.6 and 6.8 times higher, respectively, in comparison to that from the DS soil. In the DS, biochar addition significantly increased the accumulative release of CO2-C, soil pH, NH4+-N content, qCO2, phenol oxidase, and peroxidase activities. Peroxidase activities were positively correlated with the accumulative release of CO2-C, and oxidase was the most important direct factor influencing the accumulative release of CO2-C in the DS. However, the accumulative release of CO2-C, soil NH4+-N content, qCO2, β-glucosidase, and N-acetylglucosaminidase activities was significantly reduced after the application of biochar in the PS and NS. These two hydrolases were positively associated with the accumulative release of CO2-C, and hydrolase was the most vital direct factor influencing the accumulative release of CO2-C from the PS and NS soils. The positive effect of DOM addition on CO2 emission under biochar application declined with a vegetation restoration age increase. Our results indicated that biochar could alter microbial physiological processes, inhibit qCO2 and hydrolase activities, and further decrease CO2 emission in relatively fertile soil from the PS and NS; but in the relatively barren soil from the DS, biochar might promote CO2 emission by stimulating microorganisms to enhance qCO2 and oxidase activities.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Soil Organic Matter and Soil Multifunctionality in Forest Ecosystems)
►▼
Show Figures
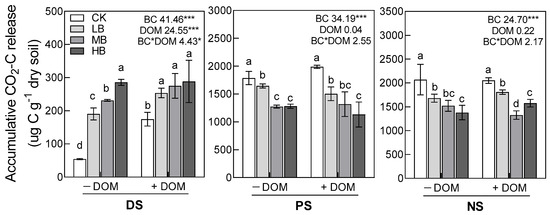
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Seasonal and Depth Dynamics of Soil Moisture Affect Trees on the Tibetan Plateau
by
Qian Li, Liang Jiao, Ruhong Xue, Xichen Che, Peng Zhang, Xuge Wang and Xin Yuan
Forests 2024, 15(5), 752; https://doi.org/10.3390/f15050752 (registering DOI) - 25 Apr 2024
Abstract
The soil moisture (SM) influences tree growth with climate change. However, the spatial and temporal dynamics of tree water use strategies in climate-sensitive areas remain uncertain. Therefore, we collected the tree-ring oxygen isotope (δ18OTR) chronologies and divided the wet–dry
[...] Read more.
The soil moisture (SM) influences tree growth with climate change. However, the spatial and temporal dynamics of tree water use strategies in climate-sensitive areas remain uncertain. Therefore, we collected the tree-ring oxygen isotope (δ18OTR) chronologies and divided the wet–dry gradients according to the precipitation on the Tibetan Plateau (TP). Further, the relationship between the δ18OTR and environmental factors was analyzed across different gradients. We found the following: (1) The SM during the growing season was the most important factor for δ18OTR. (2) The response of the δ18OTR to the SM had a lag in arid areas than in humid areas. (3) Trees absorbed the SM on the surface in humid areas (r = −0.49 to −0.41, p < 0.01), while trees absorbed the SM from deep in the soil in arid areas (r = −0.48 to −0.29, p < 0.01). The results demonstrated that trees were better able to cope with drought stress in arid regions because they used more stable deep soil water than in humid regions. Therefore, the findings will provide a scientific basis for water use of trees using the δ18OTR in complex environmental contexts. Trees with single water use strategies should be given more attention to keep ecosystems healthy.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Forest Soil)
►▼
Show Figures
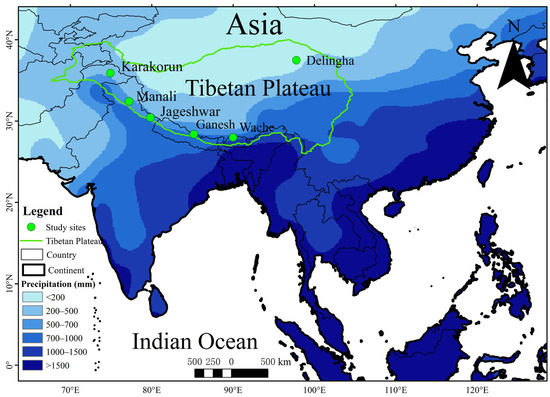
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Satellite Image Fusion Airborne LiDAR Point-Clouds-Driven Machine Learning Modeling to Predict the Carbon Stock of Typical Subtropical Plantation in China
by
Guangpeng Fan, Binghong Zhang, Jialing Zhou, Ruoyoulan Wang, Qingtao Xu, Xiangquan Zeng, Feng Lu, Weisheng Luo, Huide Cai, Yongguo Wang, Zhihai Dong and Chao Gao
Forests 2024, 15(5), 751; https://doi.org/10.3390/f15050751 (registering DOI) - 25 Apr 2024
Abstract
In the current context of carbon neutrality, afforestation is an effective means of absorbing carbon dioxide. Stock can be used not only as an economic value index of forest wood resources but also as an important index of biomass and carbon storage estimation
[...] Read more.
In the current context of carbon neutrality, afforestation is an effective means of absorbing carbon dioxide. Stock can be used not only as an economic value index of forest wood resources but also as an important index of biomass and carbon storage estimation in forest emission reduction project evaluation. In this paper, we propose a data-driven machine learning framework and method for predicting plantation stock based on airborne LiDAR + satellite remote sensing, and carried out experimental verification at the site of the National Forest emission reduction project in Southern China. We used step-up regression and random forest (RF) to screen LiDAR and Landsat 8 OLI multispectral indicators suitable for the prediction of plantation stock, and constructed a plantation stock model based on machine learning (support vector machine regression, RF regression). Our method is compared with traditional statistical methods (stepwise regression and partial least squares regression). Through the verification of 57 plantation field survey data, the accuracy of the stand estimation model constructed using the RF method is generally better (ΔR2 = 0.01~0.27, ΔRMSE = 1.88~13.77 m3·hm−2, ΔMAE = 1.17~13.57 m3·hm−2). The model evaluation accuracy based on machine learning is higher than that of the traditional statistical method, and the fitting R2 is greater than 0.91, while the fitting R2 of the traditional statistical method is 0.85. The best fitting models were all support vector regression models. The combination of UAV point clouds and satellite multi-spectral images has the best modeling effect, followed by LiDAR point clouds and Landsat 8. At present, this method is only applicable to artificial forests; further verification is needed for natural forests. In the future, the density and quality of higher clouds could be increased. The validity and accuracy of the method were further verified. This paper provides a method for predicting the accumulation of typical Chinese plantations at the forest farm scale based on the “airborne LiDAR + satellite remote sensing” data-driven machine learning modeling, which has potential application value for the current carbon neutrality goal of the southern plantation forest emission reduction project.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Forest Productivity, Carbon Dynamics and Eco-Environmental Response: Potential, Development and Challenges)
Open AccessArticle
Dynamic Estimation of Mangrove Carbon Storage in Hainan Island Based on the InVEST-PLUS Model
by
Xian Shi, Lan Wu, Yinqi Zheng, Xiang Zhang, Yijia Wang, Quan Chen, Zhongyi Sun and Tangzhe Nie
Forests 2024, 15(5), 750; https://doi.org/10.3390/f15050750 (registering DOI) - 25 Apr 2024
Abstract
Mangrove ecosystems are pivotal to the global carbon budget. However, there is still a dearth of research addressing the impact of regional mangrove land use and land cover change (LUCC) on carbon sequestration and its associated spatial distribution patterns. To investigate the impact
[...] Read more.
Mangrove ecosystems are pivotal to the global carbon budget. However, there is still a dearth of research addressing the impact of regional mangrove land use and land cover change (LUCC) on carbon sequestration and its associated spatial distribution patterns. To investigate the impact of different development scenarios on the carbon storage capacity of mangrove ecosystems, we focused on Hainan Island. We used LUCC data from 2010 to 2020 from mangrove-inhabited regions. The Markov-PLUS model was applied to predict the spatiotemporal dynamics of mangrove coverage under the natural increase scenario (NIS) and the mangrove protection scenario (MPS) over the next 40 years. Carbon storage was estimated using the InVEST model based on field-measured carbon density data. The outcomes show the following: (1) The Markov-PLUS model, with an overall accuracy of 0.88 and a Kappa coefficient of 0.82, is suitable for predicting mangrove distribution patterns on Hainan Island. (2) Environmental factors were the main drivers of historical mangrove changes on Hainan Island, explaining 54% of the variance, with elevation, temperature, and precipitation each contributing over 13%. (3) From 2025 to 2065, the mangrove area on Hainan Island is projected to increase by approximately 12,505.68 ha, mainly through conversions from forest land (12.73% under NIS and 12.37% under MPS) and agricultural land (39.72% under NIS and 34.53% under MPS). (4) The carbon storage increment within Hainan Island’s mangroves is projected at 2.71 TgC over the whole island, with notable increases expected in the eastern, northern, and northwestern regions, and modest gains in other areas. In this study, we comprehensively investigated the spatiotemporal dynamics and future trends of carbon storage in the mangroves of Hainan Island, offering invaluable guidance for the long-term management of mangrove ecosystems and the realization of carbon neutrality goals by 2060.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Aboveground and Belowground Interaction and Forest Carbon Cycling—Volume II)
►▼
Show Figures
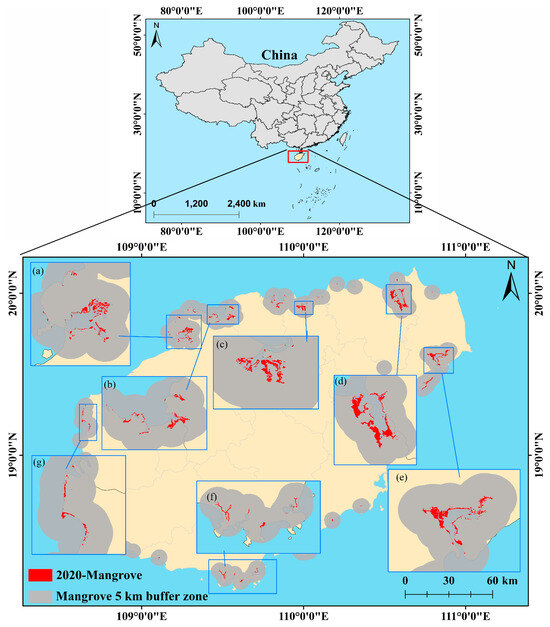
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Tree Radial Growth Responses to Climate and Reservoir Impoundment in Valleys in Southwestern China
by
Lian Sun, Wangke Ding, Yang Zhou, Jiejun Wang, Xingyue Ouyang, Zijun Fan, Youru Yao and Chonghong Zhang
Forests 2024, 15(5), 749; https://doi.org/10.3390/f15050749 (registering DOI) - 25 Apr 2024
Abstract
Southwestern China is a critical biodiversity hotspot area, and many large hydroelectric projects have been established in the valleys in the region. Tree growth in the valleys will be affected by both regional climate and reservoir impoundment. However, it remains unknown whether the
[...] Read more.
Southwestern China is a critical biodiversity hotspot area, and many large hydroelectric projects have been established in the valleys in the region. Tree growth in the valleys will be affected by both regional climate and reservoir impoundment. However, it remains unknown whether the radial growth of trees in the valleys has a common response pattern to the regional climate, and it is also unclear whether the response of radial growth to reservoir impoundment can be detected. In this study, we developed tree-ring width chronologies of Pinus yunnanensis Franch. collected at 11 sites with vertical and horizontal gradients to three hydroelectric reservoirs in three riverine valleys in southwestern China. We analyzed the radial growth responses to the regional climate from 1986 to 2017 by correlation with instrumental meteorological data. Tree growth responses to reservoir impoundment were investigated through spatial and temporal comparisons using the change in the Euclidean distance and difference test. We also distinguished their responses at tree-ring sites without influenced by reservoir impoundment including two sites in the valleys and seven sites at high elevations. The results showed that the climate conditions in May and the dry season before the growth season significantly limit the radial growth in the valleys, which is different to that at high-elevation areas in southwestern China. Growth variations in the valleys are related to elevations and the trees in similar slopes positions exhibit similar responses. For trees in the low slope positions, both variance and mean values of radial growth are affected by reservoir impoundment. Trees at relatively low sites (i.e., sites M2, R2, L2), rather than the trees close to the reservoirs (i.e., sites M1, R1, L1), respond more sensitively to reservoir impoundment.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Dendrochronology beyond the Ordinary: Understanding the Wood Formation and Climate Change)
►▼
Show Figures
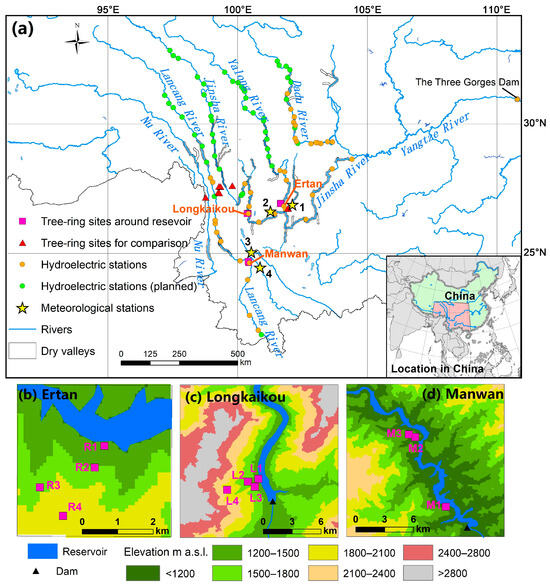
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A Study of the Effects of Stimulants on Resin Yield, Resin Duct and Turpentine Chemical Composition in Pinus kesiya var. langbianensis
by
Huanxin Yang, Junjie Shi, Lin Chen, Chunwang Yang, Changzhao Li, Yuxi Huang and Jian Qiu
Forests 2024, 15(5), 748; https://doi.org/10.3390/f15050748 (registering DOI) - 25 Apr 2024
Abstract
This study presents a comprehensive examination of Pinus kesiya var. langbianensis (Pinus kesiya var. langbianensis), the primary resin-extraction tree species in Yunnan Province, China. In this study, we formulated different concentration gradients of 0.25%, 0.5%, 1%, and 2% of diquat solution
[...] Read more.
This study presents a comprehensive examination of Pinus kesiya var. langbianensis (Pinus kesiya var. langbianensis), the primary resin-extraction tree species in Yunnan Province, China. In this study, we formulated different concentration gradients of 0.25%, 0.5%, 1%, and 2% of diquat solution as tapping stimulant to test the effect of different concentrations on the resin gain rate of Pinus kesiya, and analyzed the relationship between anatomical structure, major chemical composition of turpentine and resin yield by methods such as wood anatomy and chemical composition analysis of turpentine. The primary focus of the investigation was on exploring the interrelationships among resin-tapping stimulants, anatomical structures, turpentine components, and resin yield. Research findings demonstrate a significant enhancement in resin production due to the application of stimulants, with the highest increase rate reaching 55% in a specific group, while others achieved approximately 30% increments. Moreover, measurement data about resin duct dimensions indicate a noteworthy increase in resin duct area for the stimulant-treated group compared to the control group. However, it should be noted that the impact on resin duct area by varying stimulant concentrations was relatively minor. Furthermore, continuous observation of resin extraction from different resin-yield classes of P. kesiya revealed insignificant variation in resin yield over time for the low and moderate resin-yield groups. In contrast, the high resin-yield group exhibited a gradual increase in resin production. Interestingly, the high resin-yield group exhibited the smallest resin duct area, but the highest resin duct density, indicating an interconnectedness of resin duct-related data that influences resin yield. Additionally, correlative investigations between anatomical structures and resin yield demonstrate a positive correlation between resin duct area and resin yield, total resin production, and average resin yield. This underscores the importance of resin duct area as a significant factor in resin production. On the other hand, the influence of stimulant concentrations on the turpentine components was found to be negligible. Overall, the correlation results suggest that turpentine components cannot reliably predict or differentiate between high and low resin-yield trees. This study provides a comprehensive analysis of the interrelationships among stimulants, anatomical structures, and turpentine components, offering a theoretical foundation for the resin extraction and resin processing industries in Yunnan Province.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Forest Ecophysiology and Biology)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Assessing the Productivity of the Matang Mangrove Forest Reserve: Review of One of the Best-Managed Mangrove Forests
by
Waseem Razzaq Khan, Mohammad Nazre, Seemab Akram, Shoaib Ahmad Anees, Kaleem Mehmood, Faridah Hanum Ibrahim, Syeed SaifulAzry Osman Al Edrus, Abdul Latiff, Zohari Ahmad Fitri, Muhammad Yaseen, Ping Li and Xiaoshan Zhu
Forests 2024, 15(5), 747; https://doi.org/10.3390/f15050747 (registering DOI) - 25 Apr 2024
Abstract
Mangrove ecosystems are crucial for biodiversity and coastal protection but face threats from climate change and human activities. This review assesses the productivity of the Matang Mangrove Forest Reserve (MMFR) in Malaysia, which is recognised as one of the best-managed mangrove forests, while
[...] Read more.
Mangrove ecosystems are crucial for biodiversity and coastal protection but face threats from climate change and human activities. This review assesses the productivity of the Matang Mangrove Forest Reserve (MMFR) in Malaysia, which is recognised as one of the best-managed mangrove forests, while also addressing challenges such as deforestation and climate change-induced factors. This review explores the concept of productivity in mangrove forests, highlighting their role in carbon sequestration and discussing litterfall measurements as fundamental metrics for assessing primary productivity. An analysis of historical changes in MMFR’s biomass and productivity revealed fluctuations influenced by logging, reforestation, and climatic conditions. Trends in MMFR productivity indicate a concerning decline attributed to anthropogenic activities such as aquaculture and industrial projects. A regression analysis conducted on Rhizophora apiculata data with age as the predictor and AGB as the response variable indicated a positive trend (slope = 3.61, R-squared = 0.686), suggesting a quantitative increase in AGB with age. Further analysis revealed a significant negative trend in MMFR’s overall productivity over years (coefficient = −3.974, p < 0.05) with a strong inverse relationship (rho = −0.818, p < 0.05), indicating declining AGB trends. Despite these challenges, this review underscores the significance of sustainable management practices, effective conservation efforts, and community engagement in maintaining mangrove ecosystem health and productivity. In conclusion, sharing management lessons from MMFR can contribute to global conservation and sustainable mangrove forest management efforts, fostering resilience in these vital ecosystems.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Biodiversity, Health, and Ecosystem Services of Mangroves)
►▼
Show Figures
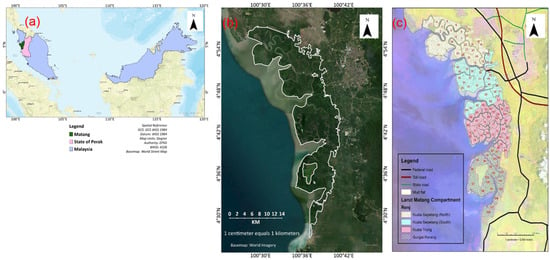
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Dynamic Change and Attribution Regarding Fractional Vegetation Coverage in Mengdong River Basin
by
Dan Cao and Shizhi Wen
Forests 2024, 15(5), 746; https://doi.org/10.3390/f15050746 (registering DOI) - 24 Apr 2024
Abstract
The situation of rocky desertification in the southwestern part of China is very serious and has been included as one of three major ecological problems. In this study, using Landsat images as the data sources, we estimated the fractional vegetation coverage (FVC
[...] Read more.
The situation of rocky desertification in the southwestern part of China is very serious and has been included as one of three major ecological problems. In this study, using Landsat images as the data sources, we estimated the fractional vegetation coverage (FVC) in the Mengdong River Basin in the Hunan Province over the past 40 years, analyzed its spatio-temporal variation characteristics, and explored the driving mechanism (climate and anthropogenic) using the Mann–Kendall, Hurst index, and partial correlation methods. Specifically, the impact of ecological engineering on the recovery of vegetation cover in rocky desertification areas was analyzed and discussed in this study. The results demonstrate the following: (1) The changes in FVC in the study area before and after the rocky desertification management ecological project differed significantly, with a very small change in the rate of change in the mean value of FVC between 1987 and 1999 (<0.1%), while the FVC had a significant linear growth trend between 2000 and 2022 (>0.9%). (2) The Hurst index of FVC ranged from −0.233 to 2.476, with an average value of 0.864. The area with an H value greater than 0.75 accounted for 80.12%, indicating that the future trend in the vast majority of regions will develop in accordance with the current change trend. (3) The average partial correlation coefficients between FVC and precipitation and between FVC and temperature were −0.02 and 0.27, respectively, showing that FVC is more sensitive to temperature than precipitation. The combination of climate change and human activities is the main cause of FVC change. The contributions of climate change (precipitation and temperature) and human activities to FVC variation are about 30% and 70%, respectively. Ecological restoration projects have a significant positive effect on the recovery of vegetation in rocky desertification areas. The results of this study are intended to provide a scientific basis for analyzing the characteristics of vegetation restoration in existing rocky desertification areas and ecological management in future rocky desertification areas.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Forest Inventory, Modeling and Remote Sensing)
Open AccessArticle
Combatting Climate Change within the EU Green Deal in Contemporary Forestry Administrative Systems: A Case Study of the Umbria Region
by
Francesco Barbarese, Zacharoula S. Andreopoulou, Walter Mattioli, Loredana Oreti and Francesco Carbone
Forests 2024, 15(5), 745; https://doi.org/10.3390/f15050745 - 24 Apr 2024
Abstract
The integration of digital technologies into forest management is crucial for the European Union’s Green Deal, the Forestry Strategy 2030, and Italy’s national forestry strategy, aiming to enhance governance and efficiency. However, sustainable forest management’s administrative aspects are often overlooked, despite the potential
[...] Read more.
The integration of digital technologies into forest management is crucial for the European Union’s Green Deal, the Forestry Strategy 2030, and Italy’s national forestry strategy, aiming to enhance governance and efficiency. However, sustainable forest management’s administrative aspects are often overlooked, despite the potential for digital tools to significantly improve environmental performance. Through a Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) for a case study in the Umbria region, the research quantifies CO2 emissions associated with over-threshold forestry administrative procedures under both current and future digitalisation scenarios. Data were collected from legislative documents, interviews with forestry professionals, and emissions calculated according to ISO standards. The findings reveal a considerable reduction in CO2 emissions through digitalisation, from 75.07 kgCO2 to 38.14 kgCO2, with the implementation of the LIFE FOLIAGE project’s digital platform. This underscores digitalisation’s role in climate change mitigation, highlighting the significant, albeit modest per procedure, of the cumulative national impact. The main findings support further digitalisation in forest management as a method of increasing resource efficiency and reducing greenhouse gas emissions, thus contributing to the Green Deal’s and Italy’s forest sustainability goals.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Forest Economics, Policy, and Social Science)
Open AccessArticle
Mixed-Species Stands Improve the Coordination between Leaf and Fine Root Traits in a Common Garden Experiment
by
Yuxin Li, Cancan Zhang, Yiqing Cheng, Shiqi Zeng, Shiyun Yang, Xiaofan Lin, Jianmin Shi and Wensheng Bu
Forests 2024, 15(5), 744; https://doi.org/10.3390/f15050744 - 24 Apr 2024
Abstract
The coordination between leaf and root traits is conducive to an integrated understanding of whole-plant ecological strategies and reveals how community composition and diversity contribute to defining the functions and services of ecosystems. However, there is limited understanding regarding the impact of species
[...] Read more.
The coordination between leaf and root traits is conducive to an integrated understanding of whole-plant ecological strategies and reveals how community composition and diversity contribute to defining the functions and services of ecosystems. However, there is limited understanding regarding the impact of species richness and trait categories on the coordination between leaf and root traits. Based on a 9-year common garden experiment, we investigated the leaf and fine root traits of 56 plots (25.8 m × 25.8 m) encompassing various trait categories (trait categories were defined according to the root depth, leaf habit, and mycorrhizal type) and different levels of species richness (1, 2, 4, 8) in the context of a forest biodiversity and ecosystem functioning experiment conducted in subtropical China (BEF-China). We found the following: (1) Our findings indicate that there was generally a significant difference in leaf traits, occasionally in absorptive root traits, and no difference in transport root traits between different trait categories. (2) Conversely, species richness significantly influenced all transport root traits except root nitrogen and most leaf and absorptive root traits. (3) The results demonstrated that trait categories played a crucial role in the coordination between leaf and fine root traits. Additionally, the coordination between leaf and fine root traits increased with higher species richness, particularly in deep-rooted, evergreen, and ectomycorrhizal fungi species. Furthermore, the coordination between leaf and fine root traits was significantly lower in monocultures compared to four- and eight-species mixtures. These results suggest that a significant mixture effect exists in the coordination between leaf and fine root traits due to the comprehensive and divergent capture of above- and belowground resources and reduced intraspecific competition. Therefore, compared to monocultures, mixed-species stands can enhance the coordination of leaf and fine root traits, and it is advisable to establish forests with mixtures of more than four species, dominated by deep-rooted, evergreen, and ectomycorrhizal fungi species, to maintain ecosystem stability and functional integrity.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Forest Biodiversity)
►▼
Show Figures
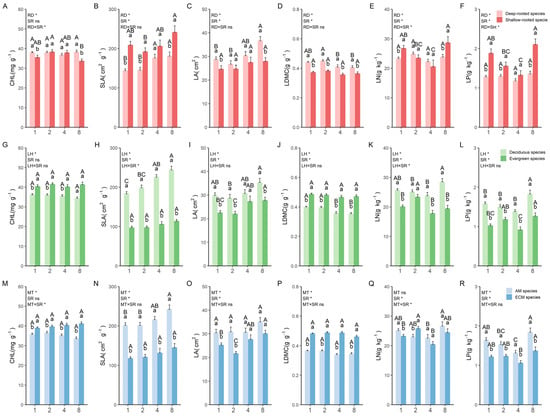
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Response of Soil Fungal-Community Structure to Crop-Tree Thinning in Pinus massoniana Plantation
by
Qian Lyu, Huiqin Yang, Biran Yin, Yongqi Xiang, Kuangji Zhao, Guirong Hou, Gang Chen, Chuan Fan and Xianwei Li
Forests 2024, 15(5), 743; https://doi.org/10.3390/f15050743 - 24 Apr 2024
Abstract
To address the ecological challenges arising from pure forest plantations and the wood supply–demand imbalance, implementing sustainable forest management is paramount. Accordingly, we studied crop trees at three densities (100, 150, and 200 N/ha) in a subtropical Pinus massoniana plantation. Our study revealed
[...] Read more.
To address the ecological challenges arising from pure forest plantations and the wood supply–demand imbalance, implementing sustainable forest management is paramount. Accordingly, we studied crop trees at three densities (100, 150, and 200 N/ha) in a subtropical Pinus massoniana plantation. Our study revealed that the dominant phyla and genera within the fungal community remained largely consistent, with Basidiomycota and Ascomycota occupying prominent positions. Notably, the β diversity of the fungal community exhibited significant changes. Ectomycorrhizal and saprophytic fungi emerged as crucial functional guilds, and crop-tree thinning contributed to increased complexity within the fungal network, with a prevalence of positive rather than negative correlations among genera. The significant roles played by Camphor plants and ferns were evident in the fungal networks. Additionally, under crop-tree thinning, plant diversity experienced a significant boost, fostering interactions with the fungal community. Herb diversity played a vital role in the fungal community, affecting it either directly or indirectly, by altering the content of total phosphorus or organic matter in the soil. This study underscores the relationship between undergrowth plants and soil fungal communities, offering a scientific basis for evaluating the sustainability of restoring inefficient forest-plantation ecosystems.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Aboveground and Belowground Interaction and Forest Carbon Cycling—Volume II)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Unveiling the Influence of Climate and Technology on Forest Efficiency: Evidence from Chinese Provinces
by
Rizwana Yasmeen and Wasi Ul Hassan Shah
Forests 2024, 15(5), 742; https://doi.org/10.3390/f15050742 - 24 Apr 2024
Abstract
The objective of this study is to examine the impact of climate and technology on forest efficiency (FE) in China’s provinces from 2002 to 2020. First, the study used SBM-data envelopment analysis (SBM-DEA) to estimate Chinese provinces’ FE using multidimensional forest inputs and
[...] Read more.
The objective of this study is to examine the impact of climate and technology on forest efficiency (FE) in China’s provinces from 2002 to 2020. First, the study used SBM-data envelopment analysis (SBM-DEA) to estimate Chinese provinces’ FE using multidimensional forest inputs and outputs. The climate influence is assessed using temperature, precipitation, sunlight hours, and carbon dioxide levels in the second phase. A climate index was created using principal component analysis (PCA) for a complete estimation. In addition to prior research, we analyze the technology impact through two technological indicators: (i) research and development, and (ii) investment in forests. Furthermore, we explore the non-linear influence of economic development on both FE and climate quality. The regression study by CupFM and CupBC found that temperature and precipitation increase FE, whereas sunlight hours and carbon emissions decrease it. The positive association observed between Climate Index1, and the negative relationship noted for Climate Index2, suggests that forests positively influence climate conditions, signifying that an improvement in FE leads to an improvement in climate quality. Technology boosts forest productivity and climatic quality. The environmental Kuznets curve shows an inverted U-shape relationship between economic development and FE. Similarly, climate and economic development have an inverted U-shaped EKC relationship. Urbanization reduces FE due to human growth and activity. Our findings are important for forest management, climate change, and sustainable development policymakers and scholars.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Forest Inventory, Modeling and Remote Sensing)
►▼
Show Figures
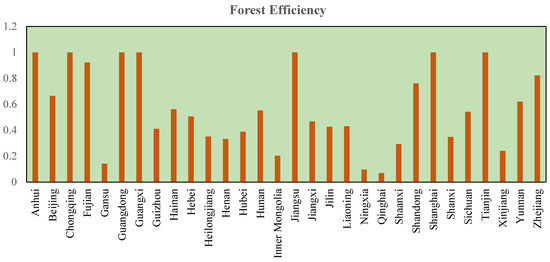
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Drought Impact on Eco-Physiological Responses and Growth Performance of Healthy and Declining Pinus sylvestris L. Trees Growing in a Dry Area of Southern Poland
by
Barbara Benisiewicz, Sławomira Pawełczyk, Francesco Niccoli, Jerzy Piotr Kabala and Giovanna Battipaglia
Forests 2024, 15(5), 741; https://doi.org/10.3390/f15050741 - 24 Apr 2024
Abstract
In recent years, several drought events hit Poland, affecting its forests. In Opole, Poland, tons of Pinus sylvestris L. deadwood is removed every year due to drought. Understanding the physiological mechanisms underlying tree vulnerability to drought, and tree responses, is important to develop
[...] Read more.
In recent years, several drought events hit Poland, affecting its forests. In Opole, Poland, tons of Pinus sylvestris L. deadwood is removed every year due to drought. Understanding the physiological mechanisms underlying tree vulnerability to drought, and tree responses, is important to develop forest management strategies to face the ongoing climate change. This research provides comprehensive local-scale analyses of the sensitivity of healthy and declining trees to drought. We used dendrochronology and stable isotope analysis to compare five healthy and five declining trees. The analysis focused particularly on comparisons of basal area increment (BAI), δ13C, and intrinsic water-use efficiency (iWUE), as well as tree resistance, resilience, and recovery in response to drought events and sensitivity to selected meteorological parameters. We observed a significant reduction in BAI values in declining trees after 2000. Fifteen years later, the reduction was also visible in the iWUE values of these trees. Despite similar δ13C chronology patterns, declining trees showed higher δ13C correlations with meteorological parameters. We have shown that dendrochronology enables early detection of poor forest health conditions. Differences in iWUE chronologies occurring in recent years suggest that trees of both groups have chosen different adaptive strategies to cope with drought stress.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Forest Ecophysiology and Biology)
►▼
Show Figures
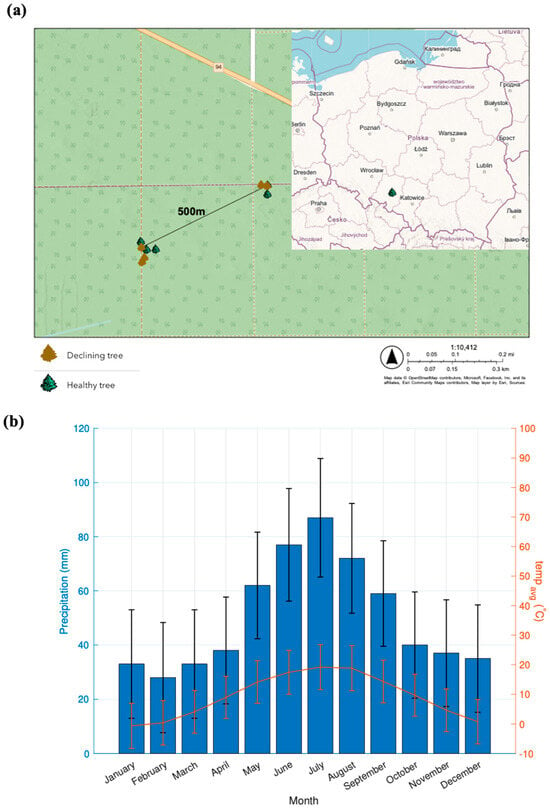
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Characteristics of Bacterial Communities under Different Tree Species and Their Response to Soil Physicochemical Properties
by
Zhe Chen, Suyan Li, Xiangyang Sun, Libing He, Wenzhi Zhou, Guanyu Zhao, Jiantao Yu, Xueting Bai and Jinshuo Zhang
Forests 2024, 15(5), 740; https://doi.org/10.3390/f15050740 - 24 Apr 2024
Abstract
This study investigates the structure of soil bacterial communities in the brown mountain soils beneath the deciduous broadleaf forests of Dongling Mountain and their response to soil physicochemical properties. Aiming to provide a scientific basis for soil conservation and sustainable forest development under
[...] Read more.
This study investigates the structure of soil bacterial communities in the brown mountain soils beneath the deciduous broadleaf forests of Dongling Mountain and their response to soil physicochemical properties. Aiming to provide a scientific basis for soil conservation and sustainable forest development under deciduous broadleaf forests, this research utilized high-throughput sequencing technology to examine the diversity and community structure of bacteria in soil under different tree species, alongside assessing soil physicochemical properties. The results revealed significant differences in nutrient content between the 0–20 cm and 20–40 cm soil layers. Additionally, the N:P in the brown mountain soils of Dongling Mountain was found to be below the national average, indicating potential nitrogen limitation. Dominant bacterial phylum included Actinobacteria, Proteobacteria, and Acidobacteria. The study also found that soil bacterial community structure was similar under different tree species at the same depth but varied significantly with soil depth. Furthermore, redundancy analysis (RDA) showed that the available potassium (AK), total nitrogen (TN), and ammonium nitrogen (NH4+-N) significantly influenced the structural changes in the soil bacterial community. This research highlights the characteristics of soil bacterial community structure beneath deciduous broadleaf forests and its relationship with soil physicochemical properties, offering valuable insights for regional soil ecosystem conservation and forest management.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Forest Soil)
►▼
Show Figures
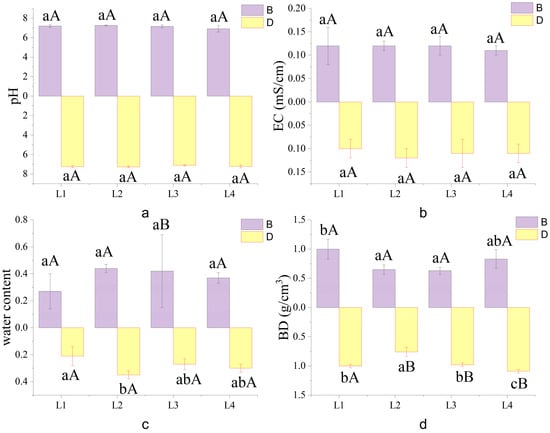
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Morpho-Anatomical Characteristics and Volatile Profiles of Pinus nigra J.F.Arnold from the Balkan Peninsula and Southern Carpathians
by
Zorica S. Mitić, Biljana M. Nikolić, Jelena P. Stojković, Snežana Č. Jevtović, Gordana S. Stojanović, Bojan K. Zlatković and Petar D. Marin
Forests 2024, 15(5), 739; https://doi.org/10.3390/f15050739 - 24 Apr 2024
Abstract
This is the first report on morpho-anatomical and phytochemical differentiation of 19 native populations representing different Pinus nigra J.F.Arnold subspecies (banatica (Borbás) Novák, dalmatica (Vis.) Franco, nigra, and pallasiana (Lamb.) Holmboe) in the Balkans and Southern Carpathians. The 9 morpho-anatomical characteristics
[...] Read more.
This is the first report on morpho-anatomical and phytochemical differentiation of 19 native populations representing different Pinus nigra J.F.Arnold subspecies (banatica (Borbás) Novák, dalmatica (Vis.) Franco, nigra, and pallasiana (Lamb.) Holmboe) in the Balkans and Southern Carpathians. The 9 morpho-anatomical characteristics and 10 headspace volatiles of needles were analyzed with multivariate statistical analyses. The combination of results from all multivariate analyses with both types of markers revealed that P. nigra is differentiated into three groups within the studied area (the Dalmatian coast, Greece, and the rest of the Balkans with the Southern Carpathians). The first group included the population from an island in Dalmatia that corresponds to P. nigra subsp. dalmatica. The third group consisted of populations from continental Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Serbia, Romania, and Bulgaria, which corresponds to P. nigra subsp. nigra. In light of the recent molecular data that indicated that the Greek populations (the second group) represent a distinct genetic lineage of P. nigra placed between the populations from the principal area (P. nigra subsp. nigra) and Turkey (P. nigra subsp. pallasiana), one can speculate that there is one more subspecies of P. nigra in this region that corresponds to populations from Greece. Extending our analyses to Asia Minor and Crimea could bring additional results that would be valuable for clarifying the intriguing issue of the diversification of P. nigra in the eastern part of its range.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Forest Ecophysiology and Biology)
►▼
Show Figures
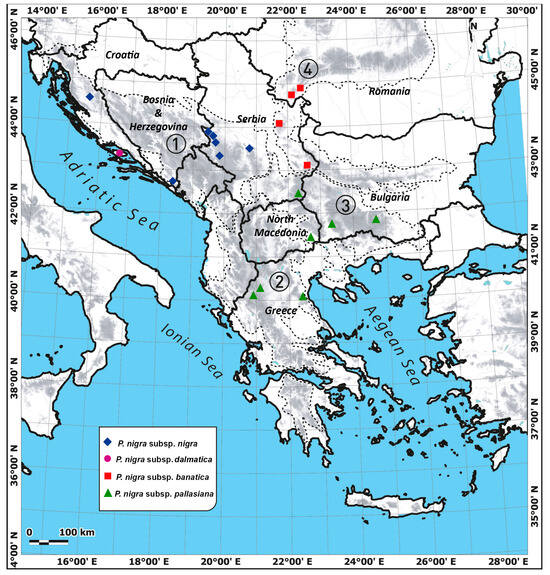
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Effects of Different Thinning Intensities on Carbon Storage in Pinus koraiensis Middle-Aged Plantations in Northeast China
by
Nazmus Sakib, Tika Ram Poudel, Yuanqin Hao, Nathan James Roberts, Abdul-Qadir Iddrisu, Saraswoti Adhikari and Peng Zhang
Forests 2024, 15(5), 738; https://doi.org/10.3390/f15050738 - 24 Apr 2024
Abstract
Forest ecosystems are essential to the global carbon cycle because they are the biggest terrestrial carbon reserves. In the management of forests, thinning is a commonly employed strategy, impacting the respiration and biomass loss of trees, thereby modifying forest carbon dynamics. However, there
[...] Read more.
Forest ecosystems are essential to the global carbon cycle because they are the biggest terrestrial carbon reserves. In the management of forests, thinning is a commonly employed strategy, impacting the respiration and biomass loss of trees, thereby modifying forest carbon dynamics. However, there is a lack of scientific research to confirm the impacts of thinning intensities on carbon storage in trees, soil layers, shrubs, and ground vegetation layers as well as its impact on wood production and growth rate. The goal of this study was to find the optimal thinning levels for increasing carbon sequestration during the growth stage of the Korean pine (Pinus koraiensis) middle-aged plantations in Northeast China. In this study, thinning intensity (0, 10, 11, 16, 18, and 22%) affected the carbon storage of trees, tree growth, volume, and, we suspected, soil layer, shrubs, and vegetation (herbs, litter, and grass) also. Specifically, after four years of thinning, the 18% treatment significantly increased total carbon storage, individual organ storage, growth, and tree volume (p < 0.05). These results give us abundant information about how thinning affects the dynamics of carbon storage, wood production, and the interactions between soil and plants in P. koraiensis plantations, contributing to multi-objective management strategies for optimizing carbon sequestration, wood production, and ecosystem health.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Silviculture and Management Strategy in Coniferous Forests)
►▼
Show Figures
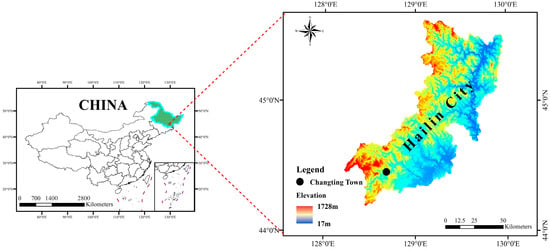
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Pine-YOLO: A Method for Detecting Pine Wilt Disease in Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Remote Sensing Images
by
Junsheng Yao, Bin Song, Xuanyu Chen, Mengqi Zhang, Xiaotong Dong, Huiwen Liu, Fangchao Liu, Li Zhang, Ying-Bo Lu, Chang Xu and Ran Kang
Forests 2024, 15(5), 737; https://doi.org/10.3390/f15050737 - 23 Apr 2024
Abstract
Pine wilt disease is a highly contagious forest quarantine ailment that spreads rapidly. In this study, we designed a new Pine-YOLO model for pine wilt disease detection by incorporating Dynamic Snake Convolution (DSConv), the Multidimensional Collaborative Attention Mechanism (MCA), and Wise-IoU v3 (WIoUv3)
[...] Read more.
Pine wilt disease is a highly contagious forest quarantine ailment that spreads rapidly. In this study, we designed a new Pine-YOLO model for pine wilt disease detection by incorporating Dynamic Snake Convolution (DSConv), the Multidimensional Collaborative Attention Mechanism (MCA), and Wise-IoU v3 (WIoUv3) into a YOLOv8 network. Firstly, we collected UAV images from Beihai Forest and Linhai Park in Weihai City to construct a dataset via a sliding window method. Then, we used this dataset to train and test Pine-YOLO. We found that DSConv adaptively focuses on fragile and curved local features and then enhances the perception of delicate tubular structures in discolored pine branches. MCA strengthens the attention to the specific features of pine trees, helps to enhance the representational capability, and improves the generalization to diseased pine tree recognition in variable natural environments. The bounding box loss function has been optimized to WIoUv3, thereby improving the overall recognition accuracy and robustness of the model. The experimental results reveal that our Pine-YOLO model achieved the following values across various evaluation metrics: MAP@0.5 at 90.69%, mAP@0.5:0.95 at 49.72%, precision at 91.31%, recall at 85.72%, and F1-score at 88.43%. These outcomes underscore the high effectiveness of our model. Therefore, our newly designed Pine-YOLO perfectly addresses the disadvantages of the original YOLO network, which helps to maintain the health and stability of the ecological environment.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Individual Tree Detection (ITD) and Its Applications)

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Forests Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Buildings, Forests, Land, Remote Sensing, Smart Cities, Sustainability
Biophilic Cities and Communities: Towards Natural Resources, Environmental and Social Sustainability
Topic Editors: Xin-Chen Hong, Baojie He, Jiang Liu, Jinda Qi, Guangyu Wang, Shi ChengDeadline: 30 April 2024
Topic in
Agriculture, Energies, Forests, Land, Sustainability
Low Carbon Economy and Sustainable Development
Topic Editors: Liang Liu, Xudong Chen, Guangxu Li, Baoguo Du, Xiaoying Lai, Yingwei AiDeadline: 31 May 2024
Topic in
Forests, Geomatics, Remote Sensing, Sensors
Information Fusion for Vegetation Characterization
Topic Editors: Baoxin Hu, Linhai JingDeadline: 30 June 2024
Topic in
Agronomy, Diversity, Forests, IJPB, Plants
Plant Invasion
Topic Editors: Bruce Osborne, Panayiotis G. DimitrakopoulosDeadline: 31 July 2024

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Forests
Somatic Embryogenesis and Other Vegetative Propagation Technologies
Guest Editors: Rodica Catana, Larisa I. Florescu, Mirela Moldoveanu, Anush KosakyanDeadline: 26 April 2024
Special Issue in
Forests
Reviews on Structure and Physical and Mechanical Properties of Wood
Guest Editors: Luis García Esteban, Paloma de Palacios, Francisco Garcia FernándezDeadline: 10 May 2024
Special Issue in
Forests
Abiotic Stress in Tree Species
Guest Editors: Hou-Ling Wang, Liu-Qiang WangDeadline: 15 May 2024
Special Issue in
Forests
Structure and Species Composition of Forests – Prospects and Challenges for Adaptative Forest Management
Guest Editors: Ion Catalin Petritan, Jarosław PaluchDeadline: 31 May 2024
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Forests
Forests Carbon Fluxes and Sequestration
Collection Editor: Mark Harmon
Topical Collection in
Forests
Sustainable Forest Management: Past, Present, Future
Collection Editor: Heli Peltola
Topical Collection in
Forests
Reviews and Meta-Analyses in Forest Meteorology and Climate Change
Collection Editors: Giacomo Alessandro Gerosa, Riccardo Marzuoli
Topical Collection in
Forests
Forest Sustainable Management in Europe
Collection Editor: Ignacio Diaz-Maroto







