Journal Description
Engineering Proceedings
Engineering Proceedings
is an open access journal dedicated to publishing findings resulting from conferences, workshops, and similar events, in all areas of engineering. The conference organizers and proceedings editors are responsible for managing the peer-review process and selecting papers for conference proceedings.
Latest Articles
The Influence of Air Pressure on Surface Roughness Values in the Sandblasting Process of ST-37 Steel Plates
Eng. Proc. 2024, 63(1), 28; https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2024063028 - 24 Apr 2024
Abstract
This research explores the influence of air pressure on the surface roughness of ST-37 steel plates in the sandblasting process. Sandblasting is a common method in industry to enhance material surfaces. This study focuses on the effects of varying air pressure on surface
[...] Read more.
This research explores the influence of air pressure on the surface roughness of ST-37 steel plates in the sandblasting process. Sandblasting is a common method in industry to enhance material surfaces. This study focuses on the effects of varying air pressure on surface roughness, crucial for achieving the desired quality. ST-37 steel plates, known for their strength and versatility, are used in various applications. The research involves a sandblasting process with different air pressures, analyzing surface roughness and contact area. The results indicate a direct correlation between increased air pressure, surface roughness, and contact area.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Proceedings of The 7th Mechanical Engineering, Science and Technology International Conference)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessProceeding Paper
Facial Expression Recognition Using Pre-trained Architectures
by
Resmi K. Reghunathan, Vineetha K. Ramankutty, Amrutha Kallingal and Vishnu Vinod
Eng. Proc. 2024, 62(1), 22; https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2024062022 - 22 Apr 2024
Abstract
In the area of computer vision, one of the most difficult and challenging tasks is facial emotion recognition. Facial expression recognition (FER) stands out as a pivotal focus within computer vision research, with applications in various domains such as emotion analysis, mental health
[...] Read more.
In the area of computer vision, one of the most difficult and challenging tasks is facial emotion recognition. Facial expression recognition (FER) stands out as a pivotal focus within computer vision research, with applications in various domains such as emotion analysis, mental health assessment, and human–computer interaction. In this study, we explore the effectiveness of ensemble methods that combine pre-trained deep learning architectures, specifically AlexNet, ResNet50, and Inception V3, to enhance FER performance on the FER2013 dataset. The results from this study offer insights into the potential advantages of ensemble-based approaches for FER, demonstrating that combining pre-trained architectures can yield superior recognition outcomes.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Proceedings of The 2nd Computing Congress 2023)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessEditorial
Preface: Proceedings of the 10th International Electronic Conference on Sensors and Applications
by
Stefano Mariani, Francisco Falcone, Stefan Bosse and Jean-Marc Laheurte
Eng. Proc. 2023, 58(1), 134; https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsa058134 - 15 Apr 2024
Abstract
This Issue of Engineering Proceedings assembles the papers presented at the 10th International Electronic Conference on Sensors and Applications (ECSA-10), held online on 15–30 November 2023 through the sciforum [...]
Full article
(This article belongs to the Proceedings of The 10th International Electronic Conference on Sensors and Applications)
Open AccessEditorial
Statement of Peer Review
by
Stefano Mariani, Francisco Falcone, Stefan Bosse and Jean-Marc Laheurte
Eng. Proc. 2023, 58(1), 133; https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsa058133 - 15 Apr 2024
Abstract
In submitting conference proceedings to Engineering Proceedings, the volume editors of the proceedings certify to the publisher that all papers published in this volume have been subjected to peer review administered by the volume editors [...]
Full article
(This article belongs to the Proceedings of The 10th International Electronic Conference on Sensors and Applications)
Open AccessProceeding Paper
Evaluation of Combined Effect of Zero Flux and Convective Boundary Conditions on Magnetohydrodynamic Boundary-Layer Flow of Nanofluid over Moving Surface Using Buongiorno’s Model
by
Purnima Rai and Upendra Mishra
Eng. Proc. 2023, 59(1), 245; https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2023059245 - 10 Apr 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This study explores the synergistic impact of zero flux and convective boundary conditions on the magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) boundary-layer slip flow of nanofluid over a moving surface, utilizing Buongiorno’s model. In a landscape of expanding nanofluid applications, understanding boundary condition interactions is crucial. Employing
[...] Read more.
This study explores the synergistic impact of zero flux and convective boundary conditions on the magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) boundary-layer slip flow of nanofluid over a moving surface, utilizing Buongiorno’s model. In a landscape of expanding nanofluid applications, understanding boundary condition interactions is crucial. Employing a systematic approach, we varied key parameters, including surface velocity, thermophoresis, Brownian motion, Eckert number, Prandtl number, and Lewis number, systematically investigating their effects on flow and heat transfer. Numerical simulations focused on critical metrics such as skin friction coefficients; Nusselt and Sherwood numbers; and temperature, concentration, and velocity profiles. Noteworthy findings include the amplifying effect of a magnetic field and viscous dissipation on temperature profiles and the dual impact of heightened velocity slip on temperature and velocity profiles, which result in a thicker concentration boundary layer. Beyond academia, we envision our research having practical applications in optimizing high-temperature processes, bio-sensors, paints, pharmaceuticals, coatings, cosmetics, and space technology.
Full article
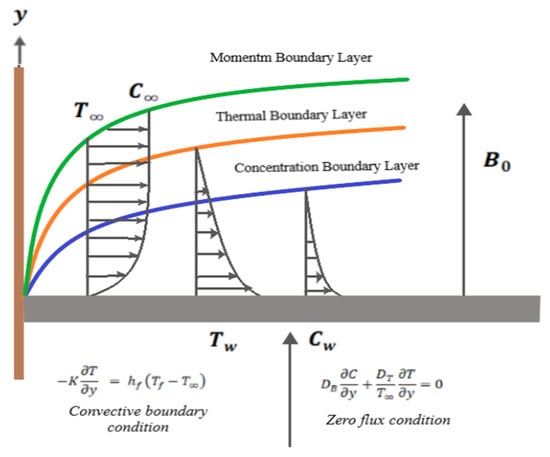
Figure 1
Open AccessProceeding Paper
Stitching as a Feasible Connection Method for Washable Textile-Encapsulated Flexible Solar Cells
by
Zhuo Li, Elina Ilén and Monica Ardanuy
Eng. Proc. 2023, 52(1), 32; https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2023052032 - 07 Apr 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Commercial solar cells can be embedded between textile layers by laminating to harvest energy in e-textile applications. However, techniques for connecting conductive textile wires to flexible and solid solar cells have not been studied in depth. Based on the literature and experimental validation,
[...] Read more.
Commercial solar cells can be embedded between textile layers by laminating to harvest energy in e-textile applications. However, techniques for connecting conductive textile wires to flexible and solid solar cells have not been studied in depth. Based on the literature and experimental validation, this study proposes a stitching connection technique for solar textiles. The feasibility of stitching was experimentally validated. First, the textile wires were joined to flexible solar cells by stitching with a sewing machine, and then embedded between fabric layers with TPU-lamination to simulate a real set-up in e-textile application. The machine washing durability of textile solar cell components with stitch-connected conductive textile wires was successfully verified.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessProceeding Paper
Comparing New Wireless Sensor Network Protocols through Simulation and Data Analysis
by
Himanshu Agarwal, Atul Pratap Singh, Ajeet Singh, Amit Kumar, Pratik K. Agrawal and S. Saranya
Eng. Proc. 2024, 62(1), 21; https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2024062021 - 07 Apr 2024
Abstract
The resource-constrained nature of wireless sensor networks (WSNs) creates a number of difficulties in their operation and design that lower their performance. However, distinct applications with unique constraints in their nature make it more difficult for such resource-constrained networks to meet application objectives.
[...] Read more.
The resource-constrained nature of wireless sensor networks (WSNs) creates a number of difficulties in their operation and design that lower their performance. However, distinct applications with unique constraints in their nature make it more difficult for such resource-constrained networks to meet application objectives. These issues can be observed at various WSN layers, from the physical layer up to the application layer. Routing protocols are primarily focused on WSN functioning at the routing layer. These obstacles make routing protocols perform worse, which lowers the performance of WSNs as a whole. This study’s objective is to pinpoint WSN performance issues and examine how they affect routing protocol performance. To this end, a detailed literature review was conducted to determine the problems influencing the performance of the routing protocols. Then, an actual investigation was carried out by simulating various routing protocols, taking into consideration these issues, in order to validate the impact of the discovered challenges from the literature. The findings are shown. On the basis of the findings from the empirical study and the literature review, suggestions are offered for a better protocol choice in light of the application nature and the problems that need to be addressed.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Proceedings of The 2nd Computing Congress 2023)
►▼
Show Figures
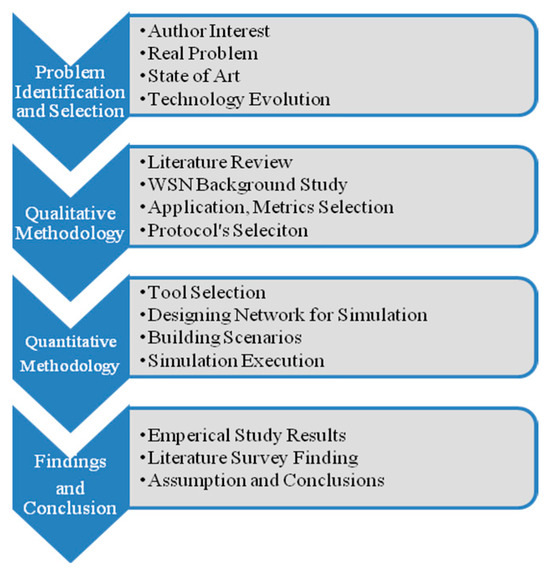
Figure 1
Open AccessProceeding Paper
Spectrophotometric Determination of Amaranth Dye Using a Two-Step Green Cloud Point and Magnetic Solid-Phase Extraction Approach
by
Remah A. Hassan and Zianab Tariq
Eng. Proc. 2023, 59(1), 244; https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2023059244 - 04 Apr 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The present study introduces a two-step extraction methodology that integrates cloud point extraction (CPE) with magnetic solid-phase extraction (MSPE) for the extraction and quantification of amaranth dye. Initially, the dye is extracted using CPE in the micellar phase of the non-ionic surfactant Triton
[...] Read more.
The present study introduces a two-step extraction methodology that integrates cloud point extraction (CPE) with magnetic solid-phase extraction (MSPE) for the extraction and quantification of amaranth dye. Initially, the dye is extracted using CPE in the micellar phase of the non-ionic surfactant Triton X-114. Subsequently, hydrophobic tetraethyl orthosilicate (TEOS)-modified Fe
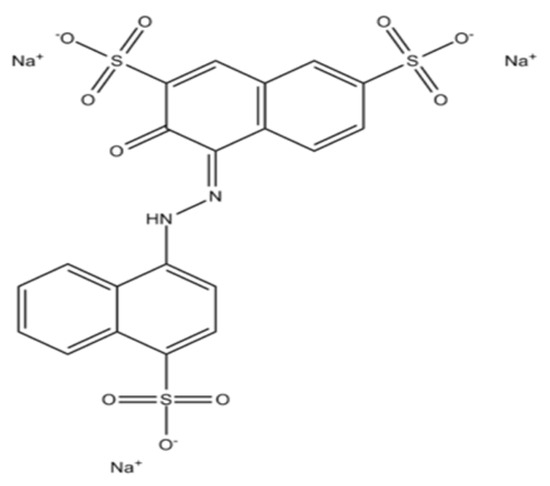
Figure 1
Open AccessProceeding Paper
The Benefits of Using an Advanced Material for Production of Spherical Impact Pad for Tundish
by
Branislav Buľko, Peter Demeter, Ivan Priesol, Slavomír Hubatka, Lukáš Fogaraš, Jaroslav Demeter, Martina Hrubovčáková, Andrii Pylypenko, Dominik Dubec, Dagmara Varcholová and Oleksii Lapenko
Eng. Proc. 2024, 64(1), 17; https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2024064017 - 04 Apr 2024
Abstract
This study presents the development of a novel material for a spherical impact pad for tundishes during steel production, focusing on improving steel cleanliness and flow optimization. Traditional low-carbon and ultra-low carbon concrete (LCC/ULCC) materials are replaced with a new cement-free mixture, utilizing
[...] Read more.
This study presents the development of a novel material for a spherical impact pad for tundishes during steel production, focusing on improving steel cleanliness and flow optimization. Traditional low-carbon and ultra-low carbon concrete (LCC/ULCC) materials are replaced with a new cement-free mixture, utilizing a sol–gel method binder. This innovative approach leads to the creation of IPC TECAST BPV CST, a refractory concrete with enhanced resistance to corrosion and shape stability under extreme conditions. The material’s effectiveness is demonstrated through operational tests, showing remarkable durability and no erosion defects after extensive use in casting liquid metal. The sol–gel binder significantly reduces the carbon footprint and energy consumption during the drying process, compared to traditional concretes. This study concludes that the new material not only withstands the dynamic environment of liquid steel but also ensures consistent dynamic flow conditions throughout the steel casting process, marking a significant advancement in tundish impact pad technology.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Proceedings of International Scientific Conference Modern Metallurgy—Iron and Steelmaking 2023)
►▼
Show Figures
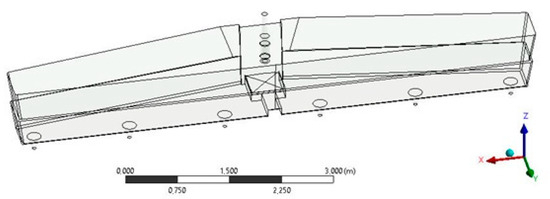
Figure 1
Open AccessProceeding Paper
Investigating the Benefits of Using Implicit Averaging in Construction Simulation Optimization Models
by
Mohammed Mawlana and Faridaddin Vahdatikhaki
Eng. Proc. 2023, 53(1), 58; https://doi.org/10.3390/IOCBD2023-16949 - 03 Apr 2024
Abstract
Stochastic simulation optimization has been proposed by several researchers to optimize construction operations. Traditionally, explicit averaging is used to estimate the objective functions of candidate solutions. This is carried out by calculating the average estimates of the objective functions obtained from a number
[...] Read more.
Stochastic simulation optimization has been proposed by several researchers to optimize construction operations. Traditionally, explicit averaging is used to estimate the objective functions of candidate solutions. This is carried out by calculating the average estimates of the objective functions obtained from a number of simulation replications. However, the computation effort increases as the number of replications and the size of the search space increase. The main objective of this paper is to study the benefits of using implicit averaging and common random numbers to improve the quality of the optimum solutions while reducing the computation time. The initial results of this study showed a 91% reduction in the computation time and 2.6% improvement in the quality of the optimum solutions.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Proceedings of The 1st International Online Conference on Buildings)
►▼
Show Figures
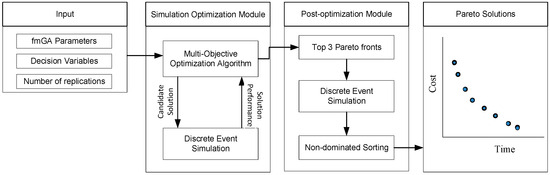
Figure 1
Open AccessRetraction
RETRACTED: Rista, A.; Kadriu, A. Designing an ASR Corpus for the Albanian Language. Eng. Proc. 2023, 56, 207
by
Engineering Proceedings Editorial Office
Eng. Proc. 2023, 56(1), 337; https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2023056337 - 02 Apr 2024
Abstract
The Editorial Office of Engineering Proceedings retracts the article, Designing an ASR Corpus for the Albanian Language [...]
Full article
(This article belongs to the Proceedings of The 4th International Electronic Conference on Applied Sciences)
Open AccessProceeding Paper
An Introduction to the Methodology of Quality Monitoring of Zinc Alloy Castings Produced by HPDC in Additively Manufactured Shaped Mould Parts
by
Kamil Koza, Karel Gryc, Ladislav Socha, Martin Pinta, Roman Kubeš, Václav Sochacký, Adnan Mohamed and Jaromír Trobl
Eng. Proc. 2024, 64(1), 16; https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2024064016 - 02 Apr 2024
Abstract
Using 3D scanning, coordinate measuring machine, and roughness measurements we evaluated and compared zinc alloy castings produced in conventionally and additively manufactured shaped mould parts. Tests were conducted on castings from new shaped parts and subsequently after approximately every 100,000 shots. Castings from
[...] Read more.
Using 3D scanning, coordinate measuring machine, and roughness measurements we evaluated and compared zinc alloy castings produced in conventionally and additively manufactured shaped mould parts. Tests were conducted on castings from new shaped parts and subsequently after approximately every 100,000 shots. Castings from conventional parts had higher dimensional stability, but both types showed decreasing dimensional deviations over time. Castings from new additively manufactured parts had higher roughness initially, but this improved with use. Overall, there were no significant issues, and the benefits of additive-shaped parts prevailed. However, more testing is needed for a final recommendation for use in real operating conditions, requiring hundreds of thousands more shots.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Proceedings of International Scientific Conference Modern Metallurgy—Iron and Steelmaking 2023)
►▼
Show Figures
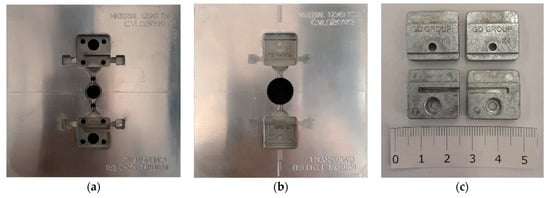
Figure 1
Open AccessProceeding Paper
Impact of Gd2O3 Incorporation in Structural, Optical, Thermal, Mechanical, and Radiation Blocking Nature in HMO Boro-Tellurite Glasses
by
Ashwitha Nancy D’Souza, M. I. Sayyed and Sudha D. Kamath
Eng. Proc. 2023, 55(1), 97; https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2023055097 - 26 Mar 2024
Abstract
The glass system of B2O3-SiO2-TeO2-Bi2O3-ZnO-BaO doped with Gd2O3 (x = 0, 1, 2, 3, and 4 mol%) (BiTeGd-x) was prepared by using the melt-quench technique. The density of
[...] Read more.
The glass system of B2O3-SiO2-TeO2-Bi2O3-ZnO-BaO doped with Gd2O3 (x = 0, 1, 2, 3, and 4 mol%) (BiTeGd-x) was prepared by using the melt-quench technique. The density of glasses increased from 5.323–5.579 g cm−3 for 0–4 mol% with an increase in Gd2O3 concentration. The simulation results obtained using Photon Shielding and Dosimetry (PSD) software (Phy-X version) produced the maximum mass attenuation coefficient (MAC) and minimum half-value layer (HVL) in the entire photon energy spectrum 0.015–15 MeV, suggesting the highest potential of BiTeGd-4 glass to act as a shield against low and high-energy radiation photons.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Proceedings of 2023 IEEE 5th Eurasia Conference on Biomedical Engineering, Healthcare and Sustainability)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessProceeding Paper
Additive Manufacturing Powder Particle Size Distributions: Comparison of Histogram Binning Methods
by
Courtney Gallagher, Emmett Kerr and Shaun McFadden
Eng. Proc. 2024, 65(1), 14; https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2024065014 - 25 Mar 2024
Abstract
Additive manufacturing powders require a well-defined particle size distribution (PSD) and spherical morphology to ensure good flowability. To simplify characterisation, powders can be prepared using standard metallurgical techniques followed by optical imaging of the cross-sectioned particles. Measured PSDs of particle sections are typically
[...] Read more.
Additive manufacturing powders require a well-defined particle size distribution (PSD) and spherical morphology to ensure good flowability. To simplify characterisation, powders can be prepared using standard metallurgical techniques followed by optical imaging of the cross-sectioned particles. Measured PSDs of particle sections are typically underestimates of the true PSD; hence, stereological corrections are required. Variations arise in the histogram binning methods (central binning versus upper limit binning) of commonly used stereological corrections. Although the results show some sensitivity to the binning method used, the GCO method seemed reasonably robust to changes in the binning method. However, authors are encouraged to follow the method as it is intended within the literature, which was found to be especially true when using Saltykov’s method.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Proceedings of The 39th International Manufacturing Conference)
►▼
Show Figures
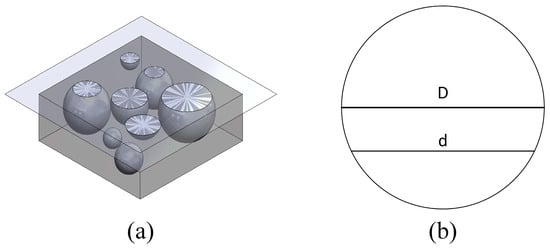
Figure 1
Open AccessProceeding Paper
Comparing Different Machine Learning Techniques in Predicting Diabetes on Early Stage
by
Shweta Yadu, Rashmi Chandra and Vivek Kumar Sinha
Eng. Proc. 2024, 62(1), 20; https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2024062020 - 22 Mar 2024
Abstract
One of the diseases that is constantly spreading and is estimated to cause a significant number of deaths worldwide is diabetes mellitus. It is determined by the quantity of a blood sugar molecule made from glucose. The possibility of this disease has been
[...] Read more.
One of the diseases that is constantly spreading and is estimated to cause a significant number of deaths worldwide is diabetes mellitus. It is determined by the quantity of a blood sugar molecule made from glucose. The possibility of this disease has been predicted using a variety of methods. To forecast diabetes at an early stage, adequate and clear data on diabetic individuals are needed. In this study, 520 records from a hospital in Bangladesh with 16 different characteristic numbers were used to make predictions. At UCI, this dataset is accessible to everyone. We used Random Forest, Ada Booster, KNN, and Bagging algorithms after feature selection. Through 10-fold cross-validation, it was discovered that the Random Forest method had the best test accuracy, scoring 97.03% correctly and 95.03% correctly.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Proceedings of The 2nd Computing Congress 2023)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1
Open AccessProceeding Paper
Traffic Signal Control System Using Contour Approximation Deep Q-Learning
by
R. S. Ramya, K. K. Bharath, K. Revanth Krishna, Kancham Jaswanth Reddy, Maddipudi Sri Bhuvan and K. R. Venugopal
Eng. Proc. 2024, 62(1), 19; https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2024062019 - 22 Mar 2024
Abstract
A reliable transit system is essential and offers a lot of advantages. However, traffic has always been an issue in major cities, and one of the main causes of congestion in these places is intersections. To reduce traffic, a reliable traffic control system
[...] Read more.
A reliable transit system is essential and offers a lot of advantages. However, traffic has always been an issue in major cities, and one of the main causes of congestion in these places is intersections. To reduce traffic, a reliable traffic control system must be put in place. This research sheds light on how to consider dynamic traffic at intersections and minimize traffic congestion using an end-to-end deep reinforcement learning approach. The goal of the model is to reduce waiting times at these crossings by controlling traffic in various scenarios after receiving the necessary training.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Proceedings of The 2nd Computing Congress 2023)
►▼
Show Figures
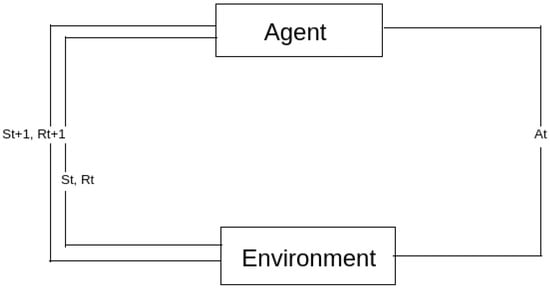
Figure 1
Open AccessProceeding Paper
A Textile Solid-State Zinc-Ion Capacitor
by
Sheng Yong, Wenli Wei and Stephen Beeby
Eng. Proc. 2023, 52(1), 31; https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2023052031 - 21 Mar 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This work reports an encapsulated and flexible solid-state AIC screen printed on top of a polyester–cotton textile. The proposed zinc-ion capacitor (ZIC) arrays were fabricated on top of a polymer-coated polyester–cotton textile with solution-based processes and inexpensive electrodes and electrolyte materials. This battery
[...] Read more.
This work reports an encapsulated and flexible solid-state AIC screen printed on top of a polyester–cotton textile. The proposed zinc-ion capacitor (ZIC) arrays were fabricated on top of a polymer-coated polyester–cotton textile with solution-based processes and inexpensive electrodes and electrolyte materials. This battery achieved an energy density of 0.47 μWh·cm−2 (per device area) or 0.51 mWh·cm−2 (per active material area) in a galvanostatic cycling test between 0.1 V and 1.8 V.
Full article
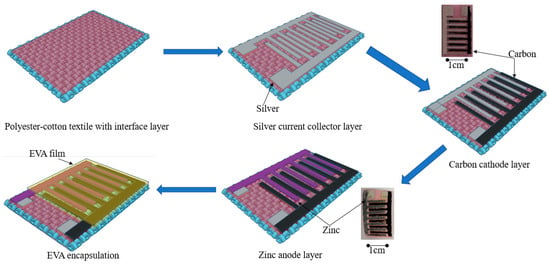
Figure 1
Open AccessProceeding Paper
Optimization of Turning Parameters and Cooling Techniques for Enhanced Machining Performance of EN8 Steel Using L9 Orthogonal Array
by
Barkur Shrinivasa Somayaji, Ritesh Bhat, Nithesh Naik and Beedu Rajendra
Eng. Proc. 2023, 59(1), 243; https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2023059243 - 20 Mar 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This study presents a detailed analysis of the effects of machining parameters, including the cutting speed (v), feed (f), depth of cut (d), and type of coolant flow (CF), on two primary performance characteristics in a machining process, namely, surface roughness (Ra) and
[...] Read more.
This study presents a detailed analysis of the effects of machining parameters, including the cutting speed (v), feed (f), depth of cut (d), and type of coolant flow (CF), on two primary performance characteristics in a machining process, namely, surface roughness (Ra) and material removal rate (MRR). A series of experiments were conducted, and the resulting data were analyzed using regression models, analysis of variance (ANOVA), Taguchi’s L9 orthogonal array analysis, and grey relational analysis. The initial findings from the raw experimental data revealed that, while Ra appeared to be influenced by a combination of parameters, an increasing trend in MRR was observed with higher values of feed rate and depth of cut. The regression models suggested the significant influence of the machining parameters on the Ra and MRR, with the type of coolant flow playing a critical baseline role. The ANOVA results statistically validated these models and ranked the significance of each parameter in affecting Ra and MRR. Furthermore, Taguchi’s analysis supported the findings and highlighted the potential for process optimization. The grey relational analysis revealed that the combination with a speed of 130 m/min, a feed of 0.1 mm/rev, a depth of cut of 0.15 mm, and a minimum quantity lubrication type of coolant flow provided the optimal result, with a GRG of 0.704, ranking first among all other parameter combinations, providing valuable insights for improving machining processes. The results, thus, indicated that the best results were generally obtained with higher speeds, lower feed rates, and moderate depths of cut under minimal quantity lubrication conditions. These findings could greatly benefit industry professionals in optimizing their processes for efficiency and quality, though it is noted that results may vary with different materials and machining conditions, presenting potential areas for future research.
Full article
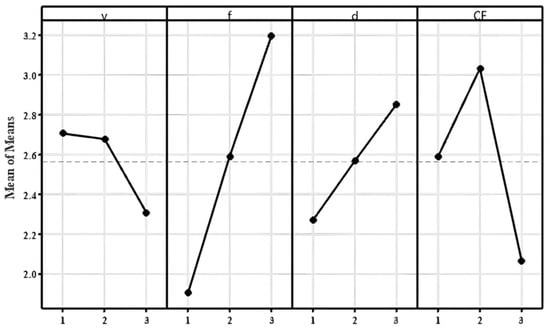
Figure 1
Open AccessProceeding Paper
Exploring Flexural Strength in High-Performance Concrete with Iron Slag and Copper Slag as Sand Substitutes
by
Ravindranatha, Ashwin Shenoy and Sidharth
Eng. Proc. 2023, 59(1), 242; https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2023059242 - 20 Mar 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The primary objective of this study is to explore the potential of iron slag and copper slag as alternatives to traditional sand in concrete, with an emphasis on assessing the impact on flexural strength. This investigation experimented with three distinct mixtures: a combination
[...] Read more.
The primary objective of this study is to explore the potential of iron slag and copper slag as alternatives to traditional sand in concrete, with an emphasis on assessing the impact on flexural strength. This investigation experimented with three distinct mixtures: a combination of cement with iron slag and copper slag, a blend of cement with sand and iron slag, and a mixture of cement with sand and copper slag. The study varied the proportions of the combinations and the duration of curing, which included intervals of 7, 28, 56, and 90 days, to serve as independent variables. The experimental results suggested that a mixture of iron slag and copper slag in a ratio of 40:60, in conjunction with cement, yielded the most promising results, with an enhancement in flexural strength of up to 92% observed over the 90-day curing period compared to the initial 7-day strength measurement. The findings from this research offer valuable insights into the utilization of waste materials in the construction industry, addressing crucial concerns related to environmental sustainability and solid waste management. The implications of this study extend beyond mere technical outcomes, emphasizing the need for innovative approaches in the construction sector that contribute to ecological conservation and waste reduction.
Full article
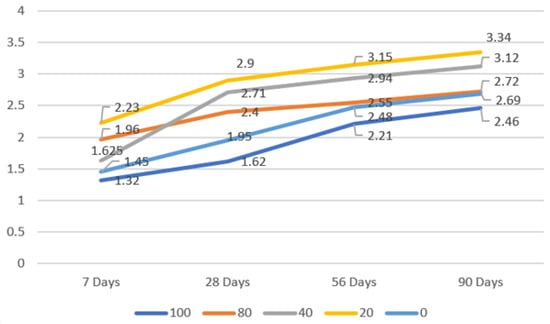
Figure 1
Open AccessProceeding Paper
The Development of Early Flood Monitoring and a WhatsApp-Based Alert System for Timely Disaster Preparedness and Response in Vulnerable Communities
by
P. Kavitha, Yatheesh.K.C., Akash Anand, Sruthi Sreenivasan, Hashim Mohammed S, Naiwrita Borah and Dhrubajyoti Saikia
Eng. Proc. 2024, 62(1), 18; https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2024062018 - 20 Mar 2024
Abstract
Although many innovations have been achieved and natural disasters are well known to be extremely detrimental to persons and property, there is still no 100% assurance that alerts and real-time monitoring will work. Vulnerable communities sometimes relied on crude warning systems, such as
[...] Read more.
Although many innovations have been achieved and natural disasters are well known to be extremely detrimental to persons and property, there is still no 100% assurance that alerts and real-time monitoring will work. Vulnerable communities sometimes relied on crude warning systems, such as flood gauges, observation towers, and local messengers, to deal with the unpredictable nature of floods. However, the effectiveness and reach of these strategies were constrained, leaving many people vulnerable to the disastrous effects of flooding. Therefore, the integration of cutting-edge technology and a system that is integrated and innovative overcomes the limits of conventional flood monitoring systems. The incorporation of WhatsApp, a widely used messaging service, into the flood monitoring and alerting process is a unique aspect of our system. We increase the reach and efficiency of our early flood warning system by combining standard SMS with WhatsApp messages. Additionally, our system includes sophisticated flood monitoring features that continuously monitor crucial parameters, including water levels. Administrators and authorized operators can respond quickly when the system sends alerts in reaction to aberrations from established thresholds. This invention bridges the gap between cutting-edge hardware and modern communication methods, representing a substantial advance in flood management technology. In conclusion, this research emphasizes how technology has the potential to improve catastrophe preparedness and response. It offers evidence of how innovation may be used to solve pressing problems and protect vulnerable areas from natural catastrophes, ultimately boosting resilience to flood events.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Proceedings of The 2nd Computing Congress 2023)
►▼
Show Figures
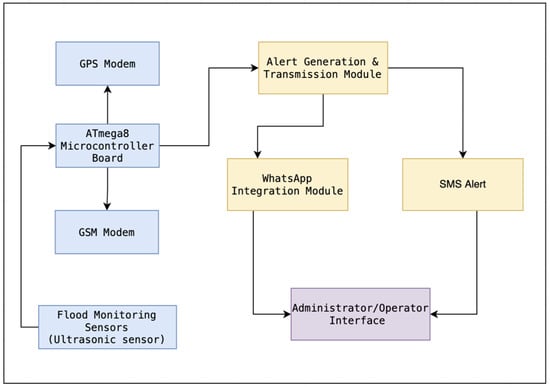
Figure 1
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics















