-
 Development of a Seed Treatment with Pochonia chlamydosporia for Biocontrol Application
Development of a Seed Treatment with Pochonia chlamydosporia for Biocontrol Application -
 Characteristics and Migration Dynamics of Microplastics in Agricultural Soils
Characteristics and Migration Dynamics of Microplastics in Agricultural Soils -
 Optimizing Silage Strategies for Sustainable Livestock Feed: Preserving Retail Food Waste
Optimizing Silage Strategies for Sustainable Livestock Feed: Preserving Retail Food Waste -
 Genomic Prediction for Inbred and Hybrid Polysomic Tetraploid Potato Offspring
Genomic Prediction for Inbred and Hybrid Polysomic Tetraploid Potato Offspring -
 A Comprehensive Overview of Control Algorithms, Sensors, Actuators, and Communication Tools of Autonomous All-Terrain Vehicles in Agriculture
A Comprehensive Overview of Control Algorithms, Sensors, Actuators, and Communication Tools of Autonomous All-Terrain Vehicles in Agriculture
Journal Description
Agriculture
Agriculture
is an international, scientific peer-reviewed open access journal published monthly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE (Web of Science), PubAg, AGRIS, RePEc, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q1 (Agronomy) / CiteScore - Q2 (Plant Science)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 17.7 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.4 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2023).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
- Companion journals for Agriculture include: Poultry, Grasses and Crops.
Impact Factor:
3.6 (2022);
5-Year Impact Factor:
3.6 (2022)
Latest Articles
Research on the Evolution of the Spatial Association Network Structure and Driving Factors of China’s Agricultural Green Development
Agriculture 2024, 14(5), 683; https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14050683 (registering DOI) - 26 Apr 2024
Abstract
Against the backdrop of global environmental challenges and sustainable development goals, this paper pioneers the application of social network analysis to the study of spatial associations in China’s agricultural green development. It not only enhances the understanding of the spatial interconnectivity and network
[...] Read more.
Against the backdrop of global environmental challenges and sustainable development goals, this paper pioneers the application of social network analysis to the study of spatial associations in China’s agricultural green development. It not only enhances the understanding of the spatial interconnectivity and network structural characteristics of agricultural green developments, but also captures the complex dependencies and interactions among provinces through a network lens, offering a fresh perspective on regional agricultural cooperation and competition. The study reveals: (1) The spatial network of China’s agricultural green development displays strong overall connectivity and enhanced stability, with regional green development trends becoming increasingly interlinked and interdependent. (2) The network exhibits a clear hierarchical and core-periphery structure which, over time, shows signs of diminishing, indicating a narrowing of developmental disparities among regions. (3) Significant shifts in the roles and positions of provinces within the network occur due to the relocation of industrial focal points and adjustments in development strategies, highlighting the complexity of dynamic changes among regions. (4) The spatial association network can be divided into four main clusters: Net spillover block, Bidirectional spillover block, Net beneficial block, and Broker block, with significant gradient characteristics in the relationships between these clusters, suggesting directional and differential flows and exchanges of resources and information among regions. (5) Geographic proximity, economic development level, informatization, and agricultural technological advancement significantly influenced the development and structural evolution of the network.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Agricultural Economics, Policies and Rural Management)
Open AccessArticle
Parameter Optimization of a Conveying and Separating Device Based on a Five-Stage Screw and Vibrating Screen for Tiger Nut Harvesters
by
Jiangtao Qi, Jianping Gao, Shan Chen, Wenhui Chen, Luoyi Yang, Hewei Meng and Za Kan
Agriculture 2024, 14(5), 682; https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14050682 - 26 Apr 2024
Abstract
To tackle problems such as the difficult separation from sand and the high power consumption of tiger nut harvesting in the sandy areas of Xinjiang, a conveying and separating device for tiger nut harvesters was designed. The axial and radial migrations of materials
[...] Read more.
To tackle problems such as the difficult separation from sand and the high power consumption of tiger nut harvesting in the sandy areas of Xinjiang, a conveying and separating device for tiger nut harvesters was designed. The axial and radial migrations of materials under screw action and the separation process of materials under vibratory action were analyzed dynamically. A simulation analysis was carried out on the conveying and separating process based on EDEM software. The migration trajectories of tiger nuts and sand particles were extracted, the displacement variations of sand particles on the X-axis, Y-axis, and Z-axis were analyzed in the action area of the screen-cleaning spike teeth and the screw action area, respectively, and the conveying and separation law of the tiger nut harvest mixture was clarified. With key parameters such as the screw velocity ratio, amplitude, vibration frequency, and machine operation velocity as test factors, and with the sand removal rate, crushing rate, and power consumption as test evaluation indicators, a four-factor, five-level orthogonal central composite test design was implemented. The test results were analyzed via the regression variance analysis method, and relation models between variable factors and evaluation indicators were constructed. The test results show that under the combined conditions of a screw velocity ratio of 0.88, an amplitude of 4.7 mm, a vibration frequency of 7.5 Hz, and a machine operation velocity of 0.92 km/h, the sand removal rate is 90.40%, the crushing rate is 1.66%, and the power consumption is 2.24 kW in theory. The optimized results were verified by tests. The sand removal rate was 88.92%, the crushing rate was 1.71%, the total power consumption was 2.29 kW, and the errors from the predicted values were 1.6%, 3.0%, and 2.2%, respectively, meeting the requirements for tiger nut harvesting conveyance and separation. This research can provide support for the development of technology and equipment for mechanized harvesting of tiger nuts in the sandy areas of Xinjiang.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Agricultural Technology)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Two Mycological Sides of Ultraviolet-B Radiation: Harmless for Mushroom Mycelia, Harmful for Mycopathogenic Mould Spores
by
Raquel Hidalgo-Sanz, María-Ángeles Del-Castillo-Alonso, Susana Sanz, Carmen Olarte, Javier Martínez-Abaigar and Encarnación Núñez-Olivera
Agriculture 2024, 14(5), 681; https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14050681 - 26 Apr 2024
Abstract
Mycopathogenic moulds are responsible for the greatest crop losses of cultivated mushrooms, thus having a significant negative economic impact on industry. Pesticides are the most common treatment against mycopathogenic moulds, but ultraviolet-B (UV-B, 280–315 nm) radiation could be a more ecological alternative. Thus,
[...] Read more.
Mycopathogenic moulds are responsible for the greatest crop losses of cultivated mushrooms, thus having a significant negative economic impact on industry. Pesticides are the most common treatment against mycopathogenic moulds, but ultraviolet-B (UV-B, 280–315 nm) radiation could be a more ecological alternative. Thus, we studied the effect of UV-B (at doses from 8 to 192 kJ m−2) on four common mycopathogenic moulds (Cladobotryum mycophilum, Lecanicillium fungicola, Trichoderma aggressivum, and Mycogone perniciosa) under in vitro conditions, using four different culture media. UV-B was tremendously effective in inactivating mould spores even at the lowest dose, with the exception of those of T. aggresivum. Contrarily, UV-B did not present any effect on the development of the host mycelium (Agaricus bisporus), even at the highest dose, when cultivated on Compost Tea medium (CT). This is the most similar medium to the substrate used for commercial mushroom cultivation. UV-B reduced the mould mycelia development in a dose-response manner, but this reduction depended on the species, with the strongly pigmented T. aggressivum as the most tolerant species. Regarding the culture media, all of them (especially CT) absorbed UV-B intensely, contributing to the protection of the mycelia. Overall, UV-B radiation could constitute an ecologically friendly alternative to chemical treatments against mycopathogenic moulds, due to its capacity to inactivate their spores and (in some cases) their mycelia without affecting their hosts.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Crop Protection, Diseases, Pests and Weeds)
Open AccessArticle
How Does Information Acquisition Ability Affect Farmers’ Green Production Behaviors: Evidence from Chinese Apple Growers
by
Zheng Li, Disheng Zhang and Xiaohuan Yan
Agriculture 2024, 14(5), 680; https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14050680 - 26 Apr 2024
Abstract
Green production is crucial in promoting sustainable agricultural practices, ensuring food safety, and protecting the rural ecological environment. Farmers, as the main decision makers of agricultural production, and their green production behaviors (GPBs), directly determine the process of agricultural green development. Based on
[...] Read more.
Green production is crucial in promoting sustainable agricultural practices, ensuring food safety, and protecting the rural ecological environment. Farmers, as the main decision makers of agricultural production, and their green production behaviors (GPBs), directly determine the process of agricultural green development. Based on the survey data of 656 apple growers in Shaanxi and Gansu provinces in 2022, this paper uses a graded response model to measure the information acquisition ability (IAA) of farmers and constructs an ordered Logit model to empirically explore the influence mechanisms of IAA, green benefit cognition (GBC), and new technology learning attitude (NTLA) on farmers’ GPBs. The results show the following: (1) IAA has a significantly positive impact on the adoption of GPBs by farmers, and farmers with a high IAA are more conscious to adopt green production technologies; (2) in the process of IAA affecting farmers’ adoption of GPBs, GBC plays a positive mediating role; (3) NTLAs have a positive moderating effect on the process of GBC affecting farmers’ GPB adoption; (4) there are generational, educational and regional differences in the impact of IAA on farmers’ GPBs. Policy makers should improve rural information facilities, strengthen agricultural technology promotion and training, improve farmers’ IAA and benefit awareness level, and formulate relevant policies to mobilize farmers’ enthusiasm for learning new technologies.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Agricultural Economics, Policies and Rural Management)
►▼
Show Figures
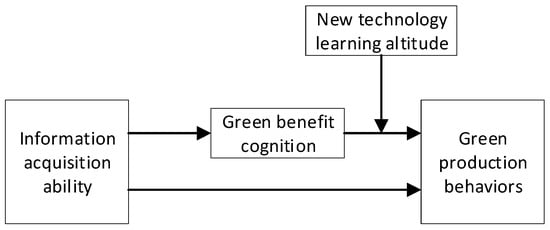
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Challenges of Including Wet Grasslands with Variable Groundwater Tables in Large-Area Crop Production Simulations
by
Valeh Khaledi, Bahareh Kamali, Gunnar Lischeid, Ottfried Dietrich, Mariel F. Davies and Claas Nendel
Agriculture 2024, 14(5), 679; https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14050679 - 26 Apr 2024
Abstract
Large-scale assessments of agricultural productivity necessitate integrated simulations of cropland and grassland ecosystems within their spatiotemporal context. However, simultaneous simulations face limitations due to assumptions of uniform species distribution. Grasslands, particularly those with shallow groundwater tables, are highly sensitive to water availability, undergoing
[...] Read more.
Large-scale assessments of agricultural productivity necessitate integrated simulations of cropland and grassland ecosystems within their spatiotemporal context. However, simultaneous simulations face limitations due to assumptions of uniform species distribution. Grasslands, particularly those with shallow groundwater tables, are highly sensitive to water availability, undergoing rapid species composition changes. We hypothesised that predicting above-ground biomass (AGB) remains challenging due to these dynamic responses. Ten years of data from four lysimeters at a German wet grassland site, with varying water table treatments, was utilised to test this hypothesis. Correlation analysis revealed a strong positive indirect effect of the water regime on AGB, with a one-year time lag (r = 0.97). The MONICA model initially exhibited fair agreement (d = 0.69) in simulating Leaf-Area-Index (LAI) but performed poorly in replicating AGB (d = 0.3). After removing the species composition change effect from the LAI and AGB datasets, the simulation notably improved, with the overall relative root mean square error (rRMSE) of AGB decreasing from 1.55 to 0.90 between the first and second simulations. This demonstrates MONICA’s ability to predict grass growth patterns amidst changing water supply levels for constant species composition. However, it needs a competition model to capture biomass growth changes with varying water supply.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Agricultural Water Management)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Delayed Sowing Can Improve Potassium Utilization Efficiency and Grain Potassium Concentration in Winter Wheat
by
Lijun Yin, Yaxin Liao and Xiao Mou
Agriculture 2024, 14(5), 678; https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14050678 - 26 Apr 2024
Abstract
Economic consumption and environmental impacts due to potassium (K) inputs in agriculture are gaining increasing attention. It is urgent to improve K use efficiency (KUE) for agricultural development. Delayed sowing has been shown to maintain grain yield in winter wheat. Still, there needs
[...] Read more.
Economic consumption and environmental impacts due to potassium (K) inputs in agriculture are gaining increasing attention. It is urgent to improve K use efficiency (KUE) for agricultural development. Delayed sowing has been shown to maintain grain yield in winter wheat. Still, there needs to be more information regarding the effect of sowing date on crop K status evaluated by the K nutrition index (KNI), KUE, K uptake efficiency (UPE), K utilization efficiency (UTE), and grain K concentration (GKC). Here, we assessed Shannong23 and Tainong18 winter wheat cultivars with three sowing date treatments composed of 26 September (early sowing), 8 October (normal sowing), and 22 October (late sowing) in the 2021–2022 and 2022–2023 growing seasons. The influences of sowing date on the KNI, tillering, grain yield formation, KUE, UPE, UTE, K transport, and GKC were examined. Our study indicated that late sowing in winter wheat was an almost optimal K nutritional situation, whereas early and normal sowing were under situations of excess K. As sowing was delayed, aboveground K uptake (AGK), UPE, and spike number per unit area decreased; UTE and grain number per spike increased; and grain yield and KUE were unchanged. A positive correlation between KNI and UPE and spike number per unit area and a negative correlation between KNI and UTE and grain number per spike were found, whereas no significant correlation between KNI and KUE was observed. Late sowing promoted K transport from pre-anthesis accumulation in vegetative organs to grain, resulting in a higher GKC, which could lead to high grain quality and K recovery. Therefore, late sowing winter wheat can use K more efficiently and increase GKC, implying that delayed sowing can reduce K input, favoring sustainable agriculture development.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Research on Technologies for Achieving High-Yield Wheat)
Open AccessArticle
Impacts of the National Nutrition Plan 2017–2030 on Listed Agrifood Enterprises: A Financial Statement Perspective
by
Jianxiong Chen, Chung-Cheng Yang and Yu Lin
Agriculture 2024, 14(5), 677; https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14050677 - 26 Apr 2024
Abstract
The Chinese government promulgated the National Nutrition Plan 2017–2030 to provide scientific guidance for agrifood consumption and enhance nutrition intake. We categorized the sample into pre-2018 and post-2018 periods. By evaluating the effects of the National Nutrition Plan 2017–2030 through economic theory and
[...] Read more.
The Chinese government promulgated the National Nutrition Plan 2017–2030 to provide scientific guidance for agrifood consumption and enhance nutrition intake. We categorized the sample into pre-2018 and post-2018 periods. By evaluating the effects of the National Nutrition Plan 2017–2030 through economic theory and a translog revenue function model based on financial statement data from 2015 to 2022, our findings indicate that the National Nutrition Plan 2017–2030 has increased the overall agrifood sales of listed agrifood enterprises, but the increase in agrifood sales produced by large listed agrifood enterprises has been slight. Finally, we offer policy recommendations for regulatory authorities and develop strategies for agrifood firms to encourage local food procurement. This study also contributes to our understanding of China’s agrifood industry dynamics and underscores the significance of the National Nutrition Plan 2017–2030 in enhancing nutritional intake and fostering sustainable growth in China’s agriculture industry.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Agricultural Markets and Agrifood Supply Chains)
►▼
Show Figures
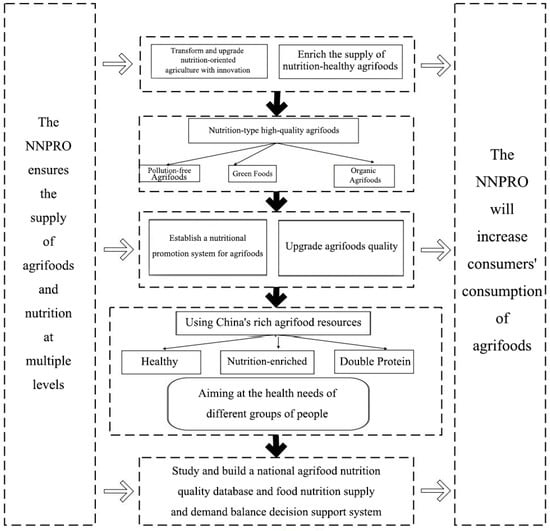
Figure 1
Open AccessEditorial
Research Progress of the Functional Properties of Fruit and Vegetables and Their Preserves
by
Anna Sadowska, Katarzyna Najman and Franciszek Świderski
Agriculture 2024, 14(5), 676; https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14050676 - 26 Apr 2024
Abstract
Fruits, vegetables, and their products are prized for their sensory values and play a very important role in our diet [...]
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Research Progress of the Functional Properties of Fruit and Vegetables and Their Preserves)
Open AccessArticle
Does Free Compulsory Education Matter for the Green Transformation of Agriculture? Evidence from Rural China
by
Junxu Zhou, Yajun Chang, Rong Peng, Zijun Liu, Hang Luo and Min Ji
Agriculture 2024, 14(5), 675; https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14050675 - 26 Apr 2024
Abstract
Education plays a crucial role in promoting green development by shaping environmentally friendly production behaviors and fostering low-carbon lifestyles. This research examines the impact of China’s free compulsory education (FCE) policy on agricultural green total factor productivity (AGTFP) using provincial panel data from
[...] Read more.
Education plays a crucial role in promoting green development by shaping environmentally friendly production behaviors and fostering low-carbon lifestyles. This research examines the impact of China’s free compulsory education (FCE) policy on agricultural green total factor productivity (AGTFP) using provincial panel data from 2002 to 2015. Additionally, it explores the impact mechanisms and regional heterogeneity. The results indicate that first, the FCE policy has a significantly positive effect on AGTFP, as confirmed through a series of robustness tests. Second, the FCE policy primarily influences AGTFP by increasing farmers’ awareness of green production and promoting the development of green technologies in agriculture. Third, the impact of the FCE policy varies across regions. It promotes green technologies in agriculture in developed provinces and fosters ecological awareness among farmers in less developed provinces. These findings offer valuable empirical evidence and policy implications for implementing education popularization projects and reducing agricultural carbon emissions in developing countries.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Agricultural Economics, Policies and Rural Management)
►▼
Show Figures
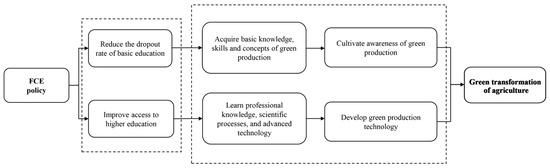
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Analysis of the Impact of Different Improvement Methods Based on YOLOV8 for Weed Detection
by
Cuncai He, Fangxin Wan, Guojun Ma, Xiaobin Mou, Kaikai Zhang, Xiangfeng Wu and Xiaopeng Huang
Agriculture 2024, 14(5), 674; https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14050674 - 26 Apr 2024
Abstract
In response to the issues of missed detection, false positives, and low recognition rates for specific weed species during weed detection, a YOLOv8-based improved weed detection algorithm named EDS-YOLOv8 is proposed. Improvements were made in three main aspects. First, the YOLOv8 backbone network
[...] Read more.
In response to the issues of missed detection, false positives, and low recognition rates for specific weed species during weed detection, a YOLOv8-based improved weed detection algorithm named EDS-YOLOv8 is proposed. Improvements were made in three main aspects. First, the YOLOv8 backbone network was enhanced with EfficientViT and RepViT architectures to improve the detection capability of dense-type weeds. Second, different attention mechanisms were added, such as SimAM and EMA, to learn 3D weights and achieve full fusion of features. BiFormer was introduced for dynamic sparse attention and resource allocation. Third, significant module improvement involved introducing dynamic snake convolution into the C2f module to further enhance detection capabilities for deformable objects, especially needle-shaped weeds. The improved model is validated on the established weed dataset. The results show that combining the original backbone network with dynamic snake convolutions yields the highest performance improvement. Precision, recall, mAP (0.5), and mAP (0.5:0.95) are improved by 5.6%, 5.8%, 6.4%, and 1%, respectively, and ablation experiments on the effects of the three improvement methods on model performance show that using EfficientViT as the backbone network while simultaneously improving the crucial module and adding the SimAM attention mechanism effectively enhances the model’s performance. Precision, recall, mAP (0.5), and mAP (0.5:0.95) are improved by 6%, 5.9%, 6.4%, and 0.7%, respectively.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Big Data Analytics and Machine Learning for Smart Agriculture—2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
How Social Networks Affect Farmers’ Willingness to Withdraw from Homesteads: Evidence from Jiangsu Province, China
by
Youlin Guo and Rongtian Zhang
Agriculture 2024, 14(5), 673; https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14050673 - 26 Apr 2024
Abstract
The orderly withdrawal from rural homesteads is an important path for the smooth promotion of rural revitalization and new urbanization. This study aims to explore the influence and mechanism of social networks on the willingness of farm households to withdraw from homesteads. The
[...] Read more.
The orderly withdrawal from rural homesteads is an important path for the smooth promotion of rural revitalization and new urbanization. This study aims to explore the influence and mechanism of social networks on the willingness of farm households to withdraw from homesteads. The study is based on a sample of 1971 farmer households in Jiangsu Province and analyzes the data using the logit model and mediation effect model. The results show that the social network has a significant positive effect on farmers’ willingness to withdraw from homesteads. As the social network expands, the probability for forming the willingness to withdraw from the homestead is higher for farmers with weaker social networks. In addition, the effect of social networks is different according to the level of regional economic development. The mechanism analysis suggests that social networks can indirectly increase the willingness to withdraw from homesteads by improving farmers’ risk resilience. Based on these findings, this study puts forward targeted policy recommendations: focusing on the cultivation and enhancement of farmers’ social networks, strengthening farmers’ risk resilience, and designing differentiated homestead exit policies.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Agricultural Economics, Policies and Rural Management)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
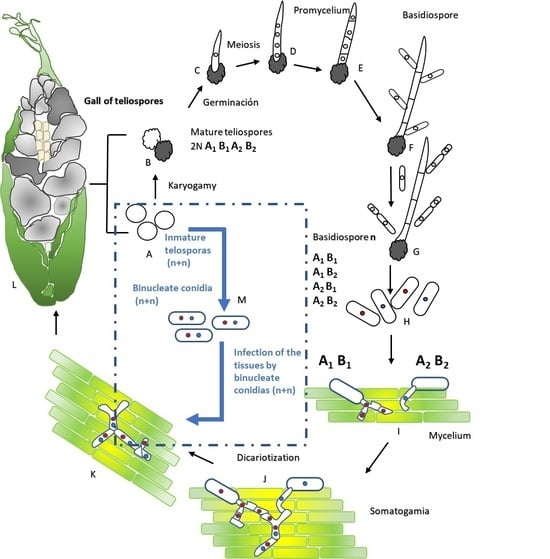
A New Method to Obtain Infective Ustilago maydis Binucleate Conidia for Corn Smut Production
by
Isaac Tello-Salgado, Dulce Teresa Hernández-Castañeda, Elizur Montiel-Arcos, Elizabeth Nava-García and Daniel Martínez-Carrera
Agriculture 2024, 14(5), 672; https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14050672 - 26 Apr 2024
Abstract
The fungus Ustilago maydis produces galls or tumors on corn ears called corn smut or huitlacoche. Used for human consumption in several countries for its nutritional and sensory traits, huitlacoche is considered a delicacy in Mexican cuisine and has a significant economic value.
[...] Read more.
The fungus Ustilago maydis produces galls or tumors on corn ears called corn smut or huitlacoche. Used for human consumption in several countries for its nutritional and sensory traits, huitlacoche is considered a delicacy in Mexican cuisine and has a significant economic value. Hybrid U. maydis strains are regularly used for the large-scale production of huitlacoche; however, depending on the genetic characteristics of the parent strains, the pathogenicity and infection rate of hybrid fungi are often suboptimal due to compatibility issues between different strains. Using double-loaded organisms is common in agriculture to improve product characteristics, performance, and shelf-life. A methodology to obtain unicellular U. maydis strains with a double genetic load (n + n) capable of producing galls on corn ears without mating (hybridization) is reported herein. This methodology resulted in 206 U. maydis isolates. Screening showed that 147 corn plants (>70%) underwent infection and gall production. Of the 147 gall-producing U. maydis strains, those with the highest field performance were selected. Three strains, Um-UAEMor-78 (yielding 21.65 ton/ha), Um-UAEMor-120 (22.31 ton/ha), and Um-UAEMor-187 (22.99 ton/ha), showed higher yields than the control strain, CP-436(a1b1) × CP-437(a2b2) (17.80 ton/ha). A specific methodology to obtain unicellular U. maydis strains with a double genetic load capable of infecting baby corn ears and forming galls is described for the first time, providing a novel alternative for producing huitlacoche and helping to improve the yields and morphological traits of galls.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Crop Protection, Diseases, Pests and Weeds)
►▼
Show Figures
Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Design and Test of a Grain Cleaning Loss Monitoring Device for Wheat Combine Harvester
by
Zhe Qu, Qi Lu, Haihao Shao, Jintao Le, Xilong Wang, Huihui Zhao and Wanzhang Wang
Agriculture 2024, 14(5), 671; https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14050671 - 25 Apr 2024
Abstract
As the world’s first large grain crop, wheat in its mechanized harvesting process faces a serious problem, namely, when the combine harvester operating parameters are not set reasonably, it leads to increased losses of wheat kernels to an extent exceeding the prescribed standard,
[...] Read more.
As the world’s first large grain crop, wheat in its mechanized harvesting process faces a serious problem, namely, when the combine harvester operating parameters are not set reasonably, it leads to increased losses of wheat kernels to an extent exceeding the prescribed standard, of which the loss of scavenging accounts for a large proportion. Excessive grain harvest loss will not only reduce the quality of the wheat harvest but also adversely affect its yield. Real-time monitoring of losses in the harvesting process is key to the dynamic adjustment of operating parameters to decrease machine harvesting losses. This article proposes a grain cleaning loss monitoring device for combine harvesters suitable for wheat crops. It aims to measure the loss of grain cleaning in the process of wheat harvesting in real time and adjust the operating parameters of the harvester timeously by feeding back the data to the driver in real time, so as to decrease the loss of wheat grains in the process of harvesting and achieve the purpose of reducing the loss of harvest. When the device was tested in the field, the wheat variety was Bainong 4199, the yield per mu was 625.83 kg (one mu is 1/15 of a hectare, or approximately 666.67 m2), the mass of grain was 43.21 g, and the water content was 14.2%. After the test, the monitoring error of the loss monitoring device was within 8%, and the average error rate was 6.69%. The test proves that the monitoring device achieves the expected design effect and meets design requirements. The results of this paper are of significance to the intelligent control system of wheat combine harvesters and provide a reference for research into grain cleaning loss monitoring devices for wheat combine harvesters.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Emerging Agricultural Engineering Sciences, Technologies, and Applications—2nd Edition)
Open AccessReview
Role of Genome Sequences of Major and Minor Millets in Strengthening Food and Nutritional Security for Future Generations
by
Theivanayagam Maharajan, Thumadath Palayullaparambil Ajeesh Krishna, Neenthamadathil Mohandas Krishnakumar, Mani Vetriventhan, Himabindu Kudapa and Stanislaus Antony Ceasar
Agriculture 2024, 14(5), 670; https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14050670 - 25 Apr 2024
Abstract
Millets are small-seeded cereals belonging to the family Poaceae. They are considered to be climate-resilient and future nutritional food cereals for humans. Millets are resistant to biotic and abiotic stressors compared to other major cereals and thrive in low-quality soils with little maintenance
[...] Read more.
Millets are small-seeded cereals belonging to the family Poaceae. They are considered to be climate-resilient and future nutritional food cereals for humans. Millets are resistant to biotic and abiotic stressors compared to other major cereals and thrive in low-quality soils with little maintenance and less rainfall. The importance of millets is still not well known to many people due to the lack of popularity and cultivation in semi-arid tropics of Asia and Africa. The United Nations has declared 2023 as the International Year of Millets (IYM 2023) to promote millet cultivation and popularize their health benefits globally. A few years ago, the application of molecular biology was in its infancy in millets due to the unavailability of genome sequences. Genome sequences are available for most of the millets on NCBI and Phytozome databases. In this review, we discuss the details of genome sequences for millets, candidate genes identified from the native genome of millets. The current status of quantitative trait loci and genome-wide association studies in millets are also discussed. The utilization of millet genome sequences in functional genomics research and translating the information for crop improvement will help millet and non-millet cereals survive harsh environments in the future. Such efforts will help strengthen food security and reduce malnutrition worldwide in 2050.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Feature Papers in Genotype Evaluation and Breeding)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Organic Certification, Online Market Access, and Agricultural Product Prices: Evidence from Chinese Apple Farmers
by
Li Zhang, Dong Liu, Qie Yin and Jundi Liu
Agriculture 2024, 14(5), 669; https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14050669 - 25 Apr 2024
Abstract
Motivated by the increasing interest in sustainable agriculture and the potential benefits associated with organic certification, this study employs a multidimensional fixed-effects model to analyze data derived from onsite surveys conducted among 681 apple farmers in the Loess Plateau region of China to
[...] Read more.
Motivated by the increasing interest in sustainable agriculture and the potential benefits associated with organic certification, this study employs a multidimensional fixed-effects model to analyze data derived from onsite surveys conducted among 681 apple farmers in the Loess Plateau region of China to explore the influence of organic certification on absolute and relative agricultural product prices given online market access. The findings indicated a significant increase in apple prices among farmers who held organic certifications and engaged in online market sales, with prices rising by CNY1.60 per half kilogram. Additionally, this study highlights that the amalgamation of organic certification with online market access significantly enhances agricultural product prices by facilitating better dissemination of market information among farmers. Furthermore, this research addresses a critical gap in the existing literature by clarifying the differential impact of organic certification across distinct farmer demographics and geographical regions. The more pronounced positive impact of organic certification on prices observed among cooperative members and farmers in the low-altitude areas is particularly noteworthy. These results underscore the crucial role of online market access in achieving premium effects and price stability for organically certified products.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Agricultural Economics, Policies and Rural Management)
►▼
Show Figures
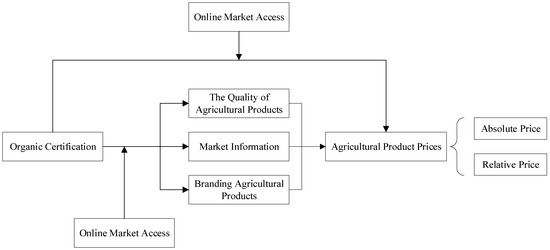
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Nectar Production and Three Main Sugars in Nectar of Salvia pratensis and Salvia glutinosa in Correlation with Abiotic Factors
by
Katja Malovrh, Blanka Ravnjak, Jože Bavcon and Mitja Križman
Agriculture 2024, 14(5), 668; https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14050668 - 25 Apr 2024
Abstract
Floral nectar is mainly a reward in the form of food for pollinators. Its composition plays an important role when pollinators choose their food. Several studies have shown that the popularity of flowers with nectar is influenced by the concentration and ratio of
[...] Read more.
Floral nectar is mainly a reward in the form of food for pollinators. Its composition plays an important role when pollinators choose their food. Several studies have shown that the popularity of flowers with nectar is influenced by the concentration and ratio of sugars. Here, we present the nectar chemical composition with regard to three main sugars and their concentrations in correlation with abiotic factors for the plant species Salvia pratensis L. and Salvia glutinosa L. through their 2023 flowering season. We sampled nectar using microcapillaries at three different times during the day on sites in nature. Our results show that nectar production in both species is the highest at around 12 a.m. The abiotic factor that affects nectar production in both species is the soil temperature, while UVB radiation does not influence nectar production. Air temperature and air humidity affect the nectar production of S. glutinosa, while soil humidity affects nectar production in S. pratensis. The most represented sugar in S. glutinosa nectar is sucrose, while S. pratensis nectar has more glucose and fructose. Our results show that UVB radiation has an effect on the sucrose level, although it does not have any direct effect on nectar productivity.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Agricultural Product Quality and Safety)
►▼
Show Figures
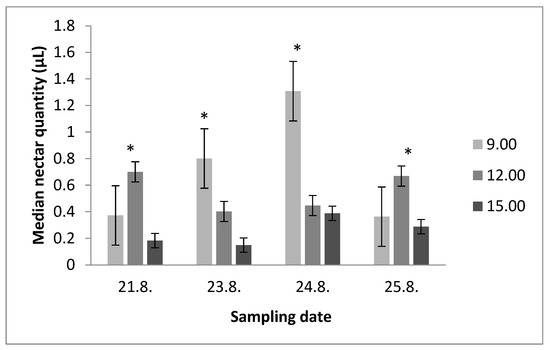
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Perceived Organizational Support, Inter-Temporal Choice, and Farmer Conservation Tillage Adoption
by
Tong Zhang, Liangming Lang, Nan Zhao, Qian Lu and Bailiang Sun
Agriculture 2024, 14(5), 667; https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14050667 - 25 Apr 2024
Abstract
To solve the problem of the insufficient driving force and low adoption rate of conservation tillage adoption and to enhance the effect of industrial organization in influencing technology diffusion, this paper explored the relationship and the mechanism of perceived organizational support and inter-temporal
[...] Read more.
To solve the problem of the insufficient driving force and low adoption rate of conservation tillage adoption and to enhance the effect of industrial organization in influencing technology diffusion, this paper explored the relationship and the mechanism of perceived organizational support and inter-temporal choice in the adoption of conservation tillage by using micro-research data from 725 melon farmers in the Shaanxi and Shanxi provinces in China and by applying the experimental economics method to obtain the inter-temporal choices of the farmers. This paper also analyzed farmers’ risk preferences’ moderating effect on the relationship between inter-temporal choice and conservation tillage. Additionally, it examined the impact of perceived organizational support on the differentiation of different conservation tillage technologies. The study found that perceived organizational support significantly contributes to adopting zero tillage and minimum tillage, and water-saving irrigation. Perceived organizational support was not conducive to farmers’ adoption of furrow and ridge tillage. The impact of perceived organizational support on technology adoption is heterogeneous, depending on the differences in the size of the family’s cultivated land. The inter-temporal choice of farmers significantly impedes the adoption of conservation tillage. The increase in risk preference helps alleviate the hindering effect of inter-temporal choice on farmers’ adoption of conservation tillage. Perceived organizational support can promote the adoption of conservation tillage by reducing farmers’ inter-temporal choices. Inter-temporal choice is an essential mechanism by which perceived organizational support affects the adoption of conservation tillage. Compared with the existing studies, this paper incorporates the technology-attribute-induced inter-temporal choice of farmers into the impact analysis framework and considers the relationship between perceived organizational support, inter-temporal choice, and the adoption of conservation tillage and the mechanism of its action. The findings of the study provide a theoretical basis for the enrichment of incentive mechanisms for the adoption of conservation tillage, which is of great significance for the improvement of the tool for the integration of small farmers in developing countries into the industrial activities of the new agricultural business central bodies and for promoting the diffusion of conservation tillage in agriculture.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Novel Studies in Agricultural Economics and Sustainable Farm Management)
►▼
Show Figures
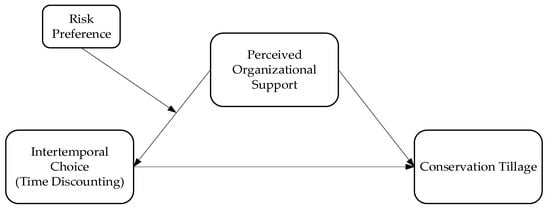
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Corn Leaf Spot Disease Recognition Based on Improved YOLOv8
by
Shixiong Yang, Jingfa Yao and Guifa Teng
Agriculture 2024, 14(5), 666; https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14050666 - 25 Apr 2024
Abstract
Leaf spot disease is an extremely common disease in the growth process of maize in Northern China and its degree of harm is quite significant. Therefore, the rapid and accurate identification of maize leaf spot disease is crucial for reducing economic losses in
[...] Read more.
Leaf spot disease is an extremely common disease in the growth process of maize in Northern China and its degree of harm is quite significant. Therefore, the rapid and accurate identification of maize leaf spot disease is crucial for reducing economic losses in maize. In complex field environments, traditional identification methods are susceptible to subjective interference and cannot quickly and accurately identify leaf spot disease through color or shape features. We present an advanced disease identification method utilizing YOLOv8. This method utilizes actual field images of diseased corn leaves to construct a dataset and accurately labels the diseased leaves in these images, thereby achieving rapid and accurate identification of target diseases in complex field environments. We have improved the model based on YOLOv8 by adding Slim-neck modules and GAM attention modules and introducing them to enhance the model’s ability to identify maize leaf spot disease. The enhanced YOLOv8 model achieved a precision (P) of 95.18%, a recall (R) of 89.11%, an average recognition accuracy (mAP50) of 94.65%, and an mAP50-95 of 71.62%, respectively. Compared to the original YOLOv8 model, the enhanced model showcased enhancements of 3.79%, 4.65%, 3.56%, and 7.3% in precision (P), recall (R), average recognition accuracy (mAP50), and mAP50-95, respectively. The model can effectively identify leaf spot disease and accurately calibrate its location. Under the same experimental conditions, we compared the improved model with the YOLOv3, YOLOv5, YOLOv6, Faster R-CNN, and SSD models. The results show that the improved model not only enhances performance, but also reduces parameter complexity and simplifies the network structure. The results indicated that the improved model enhanced performance, while reducing experimental time. Hence, the enhanced method proposed in this study, based on YOLOv8, exhibits the capability to identify maize leaf spot disease in intricate field environments, offering robust technical support for agricultural production.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Crop Protection, Diseases, Pests and Weeds)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
BerryNet-Lite: A Lightweight Convolutional Neural Network for Strawberry Disease Identification
by
Jianping Wang, Zhiyu Li, Guohong Gao, Yan Wang, Chenping Zhao, Haofan Bai, Yingying Lv, Xueyan Zhang and Qian Li
Agriculture 2024, 14(5), 665; https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14050665 - 25 Apr 2024
Abstract
With the rapid advancements in computer vision, using deep learning for strawberry disease recognition has emerged as a new trend. However, traditional identification methods heavily rely on manual discernment, consuming valuable time and imposing significant financial losses on growers. To address these challenges,
[...] Read more.
With the rapid advancements in computer vision, using deep learning for strawberry disease recognition has emerged as a new trend. However, traditional identification methods heavily rely on manual discernment, consuming valuable time and imposing significant financial losses on growers. To address these challenges, this paper presents BerryNet-Lite, a lightweight network designed for precise strawberry disease identification. First, a comprehensive dataset, encompassing various strawberry diseases at different maturity levels, is curated. Second, BerryNet-Lite is proposed, utilizing transfer learning to expedite convergence through pre-training on extensive datasets. Subsequently, we introduce expansion convolution into the receptive field expansion, promoting more robust feature extraction and ensuring accurate recognition. Furthermore, we adopt the efficient channel attention (ECA) as the attention mechanism module. Additionally, we incorporate a multilayer perceptron (MLP) module to enhance the generalization capability and better capture the abstract features. Finally, we present a novel classification head design approach which effectively combines the ECA and MLP modules. Experimental results demonstrate that BerryNet-Lite achieves an impressive accuracy of 99.45%. Compared to classic networks like ResNet34, VGG16, and AlexNet, BerryNet-Lite showcases superiority across metrics, including loss value, accuracy, precision, F1-score, and parameters. It holds significant promise for applications in strawberry disease identification.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Computer Vision and Artificial Intelligence in Agriculture)
►▼
Show Figures
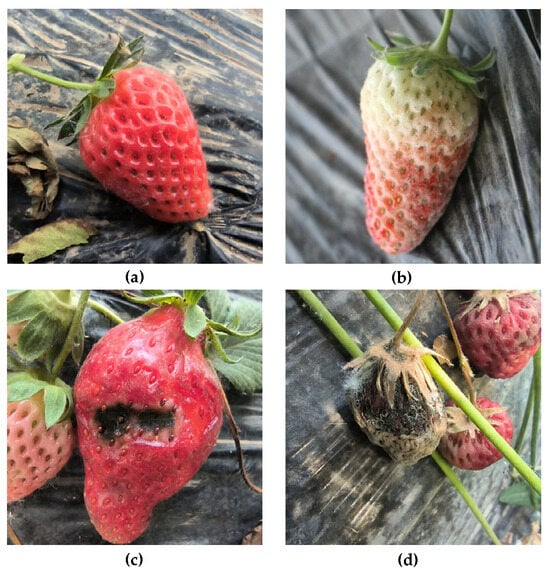

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Soil Bacterial Community of Medicinal Plant Rhizosphere in a Mediterranean System
by
Yosef Steinberger, Tirza Doniger, Chen Sherman, Mareeswaran Jeyaraman and Itaii Applebaum
Agriculture 2024, 14(5), 664; https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14050664 - 25 Apr 2024
Abstract
Several attempts have been made to evaluate the abundance and distribution of the bacterial community in the rhizosphere of medicinal plants. Many describe information based on an estimation of the community structure and the effects of plant cover in determining microbial community composition.
[...] Read more.
Several attempts have been made to evaluate the abundance and distribution of the bacterial community in the rhizosphere of medicinal plants. Many describe information based on an estimation of the community structure and the effects of plant cover in determining microbial community composition. The ability of plants to specifically shape their microbial community in general and medicinal plants in particular is largely unknown. With the arrival of molecular biology, understanding the microbial community’s composition, diversity, and function became possible. We hypothesized that microbial communities associated with medicinal shrubs would differ from each other. To test this hypothesis, we characterized the soil microbial composition under each of five Mediterranean medicinal plants, differentiated by their medicinal use and ecophysiological adaptation, namely, Salvia fruticosa, Pistacia lentiscus, Myrtus communis, Origanum syriacum, and Teucrium capitatum, and an open-space bare soil between the plants, inhabiting natural ecosystems characterized by similar climatic conditions typical of a Mediterranean environment. The results demonstrated the importance of plant ecophysiological adaptations, which play an important role in determining microbial community composition and functional diversity. The intensity of a plant’s response to its surroundings can have either positive or negative effects that will determine the microbial community composition and interactions among the belowground parts. A total of 11 phyla, 21 orders, and 409 genera were found in the soil rhizosphere in the vicinity of the four plants and open space samples. The distinguishing attributes of each shrub trigger and stimulate the microbial community’s rhizosphere. This results in distinct patterns of bacterial diversity and functionality between the different shrubs and the control. The rhizosphere bacterial community composition differed between the plants in a PERMANOVA test, but there was little difference in terms of phyla and order relative abundances. This study shows how five medicinal plants, coexisting in a common habitat, impact the bacterial community. The noticeable shift in bacterial composition further supports our discovery that root exudates effectively govern the makeup of soil bacterial communities.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Agricultural Soils)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Agronomy, Agriculture, Crops, Seeds
Advances in Industrial Crops Physioecology and Sustainable Cultivation
Topic Editors: Wei Hu, Zhiguo Zhou, Wenqing ZhaoDeadline: 30 April 2024
Topic in
Agriculture, Energies, Forests, Land, Sustainability
Low Carbon Economy and Sustainable Development
Topic Editors: Liang Liu, Xudong Chen, Guangxu Li, Baoguo Du, Xiaoying Lai, Yingwei AiDeadline: 31 May 2024
Topic in
Agriculture, Animals, Dairy, Ruminants, Veterinary Sciences
Practical Methods for Accommodating Behavioral Needs and Improving the Wellbeing of Both Farm Animals
Topic Editors: Temple Grandin, Kurt VogelDeadline: 20 June 2024
Topic in
Agriculture, Agronomy, Animals, Fishes, Poultry
Sustainable Development of Natural Bioactive Compounds/Products in Animal Resource and Agriculture Science: Volume II
Topic Editors: In Ho Kim, Balamuralikrishnan Balasubramanian, Shanmugam SureshkumarDeadline: 30 June 2024

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Agriculture
Biocontrol of Plant Pests and Pathogens
Guest Editors: Eirini Karanastasi, Danai GkiziDeadline: 10 May 2024
Special Issue in
Agriculture
Modern Reproductive Biotechnology Assists Farm Animal Conservation and Genetic Rescue
Guest Editors: Monika Trzcińska, Marcin SamiecDeadline: 15 May 2024
Special Issue in
Agriculture
Breeding of Horticultural Crops for Trait Improvement and Stress Resilience
Guest Editors: Evangelia Stavridou, Panagiotis Madesis, Irini Nianiou-ObeidatDeadline: 5 June 2024
Special Issue in
Agriculture
Integrated Management of Soil-Borne Diseases
Guest Editors: Aocheng Cao, Dongdong Yan, Wensheng FangDeadline: 10 June 2024





