-
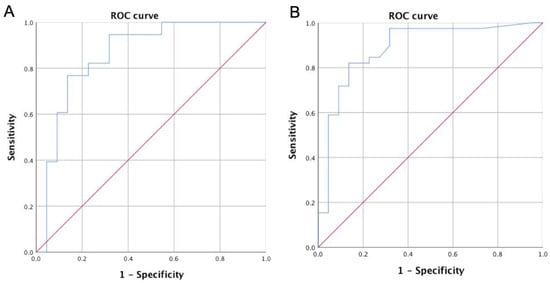
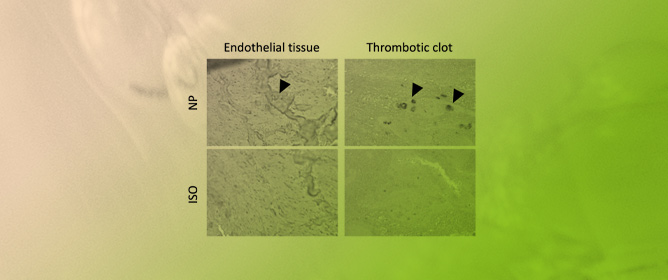 In Situ Endothelial SARS-CoV-2 Presence and PROS1 Plasma Levels Alteration in SARS-CoV-2-Associated Coagulopathies
In Situ Endothelial SARS-CoV-2 Presence and PROS1 Plasma Levels Alteration in SARS-CoV-2-Associated Coagulopathies -
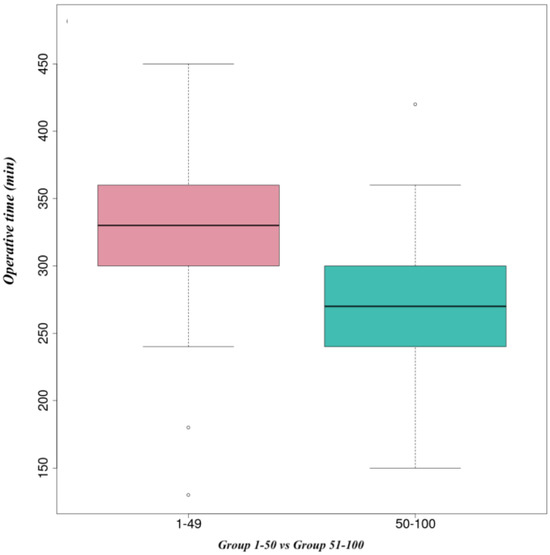
![Induction of Arterial Inflammation by Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy in Lung Cancer Patients as Measured by 2-[<sup>18</sup>F]FDG Positron Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography Depends on Pre-Existing Vascular Inflammation](https://pub.mdpi-res.com/title_story/title_story_17105057485939.jpg?1714056809) Induction of Arterial Inflammation by Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy in Lung Cancer Patients as Measured by 2-[18F]FDG Positron Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography Depends on Pre-Existing Vascular Inflammation
Induction of Arterial Inflammation by Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy in Lung Cancer Patients as Measured by 2-[18F]FDG Positron Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography Depends on Pre-Existing Vascular Inflammation -
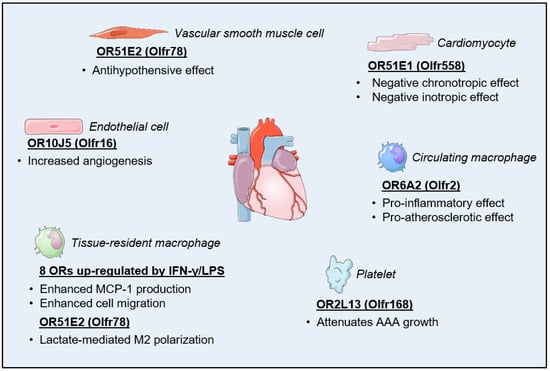
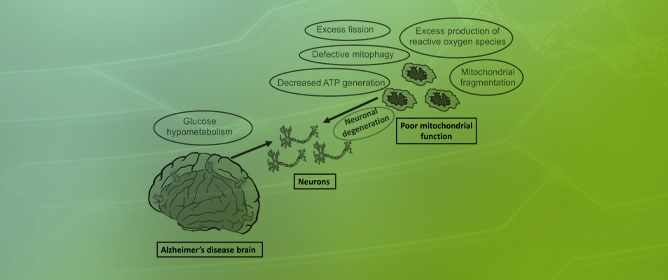 Mitochondria in Alzheimer’s Disease Pathogenesis
Mitochondria in Alzheimer’s Disease Pathogenesis -
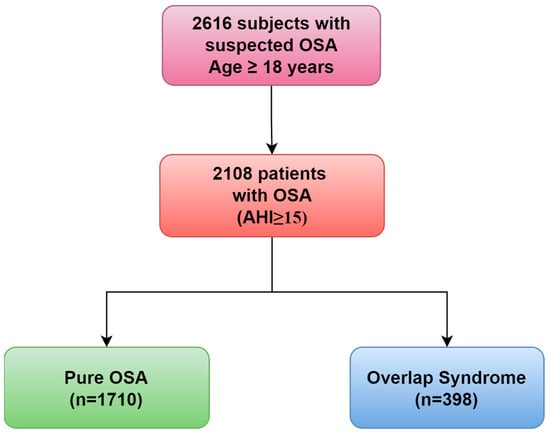
 Quantifying Carotid Stenosis: History, Current Applications, Limitations, and Potential: How Imaging Is Changing the Scenario
Quantifying Carotid Stenosis: History, Current Applications, Limitations, and Potential: How Imaging Is Changing the Scenario
Journal Description
Life
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE (Web of Science), PubMed, PMC, CAPlus / SciFinder, AGRIS, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q2 (Biology) / CiteScore - Q2 (Paleontology)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 17.5 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.5 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2023).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
- Testimonials: See what our editors and authors say about Life.
- Companion journals for Life include: Gastroenterology Insights, Physiologia, Hydrobiology, and Anatomia.
Latest Articles
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Deadline: 31 May 2024
Deadline: 30 June 2024
Deadline: 31 August 2024
Deadline: 30 September 2024
Conferences
Special Issues
Deadline: 30 April 2024
Deadline: 20 May 2024
Deadline: 31 May 2024
Deadline: 14 June 2024