Nutritional Interventions in Multiple Sclerosis
A special issue of Nutrients (ISSN 2072-6643). This special issue belongs to the section "Nutritional Epidemiology".
Deadline for manuscript submissions: closed (26 May 2023) | Viewed by 2822
Special Issue Editors
Interests: body composition; physical activity; bone health, nutrition
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: epidemiology and public health; lifestyle; nutrition; sleep disorders and sleep medicine; physical activity; sedentary behavior; mental health
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Special Issue Information
Dear Colleagues,
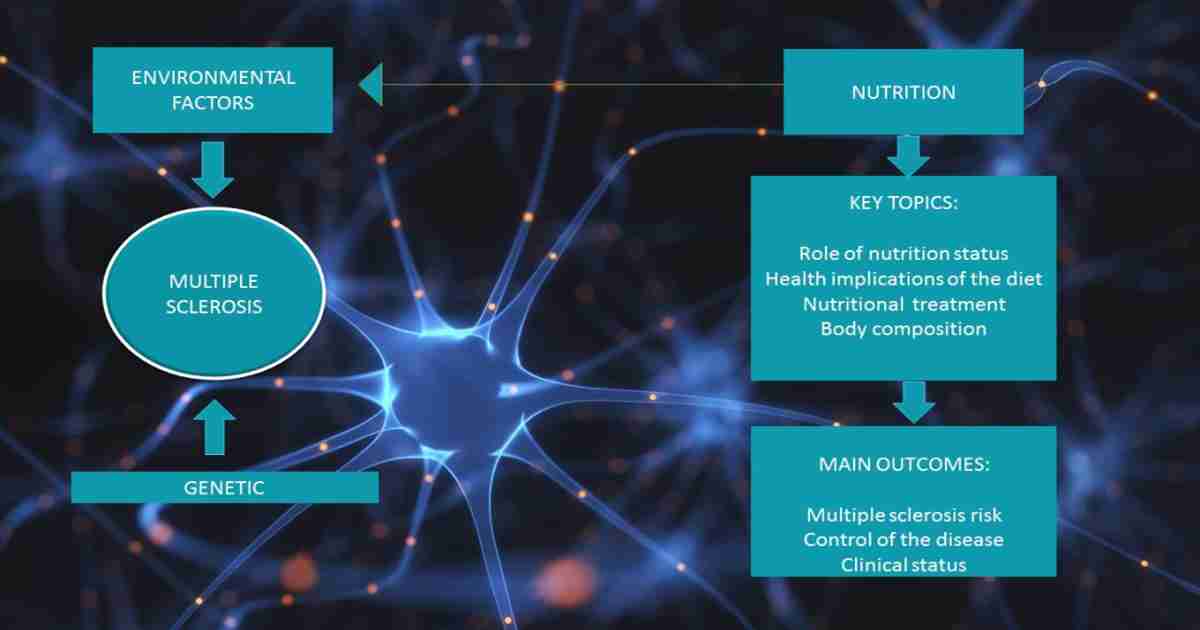
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic multifactorial, inflammatory and neurodegenerative disease of the central nervous system where genetic susceptibility interacts with environmental factors. Nutrition is one of the environmental factors that may be involved, and plays an essential role in the pathogenesis and evolution of the disease. However, most people with MS do not meet nutritional guidelines for a healthy diet, and usually self-experiment with diet without control of symptoms, medication interaction or adverse effects.
Particular diets or nutrients in the diet can influence the degree of the inflammatory response, suggesting that an appropriate nutritive intervention may improve the risk or prognosis of MS. However, at the present time, there is no strong evidence regarding the efficacy of dietary interventions as a complementary treatment of the disease.
The aim of this Special Issue is elucidate the role of nutrition status, health implications of the diet, nutritional treatment, and/or body composition in relation to MS risk, control, as well as clinical status.
Dr. Ana Torres-Costoso
Dr. Arthur Eumann Mesas
Guest Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the special issue website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Nutrients is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2900 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- multiple sclerosis
- nutrition
- nutrients
- diet
- malnutrition
- inflammation
- body composition






