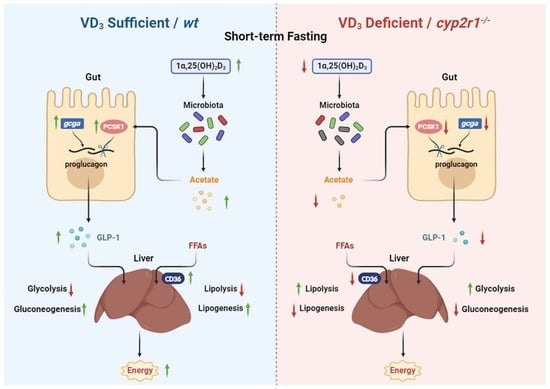
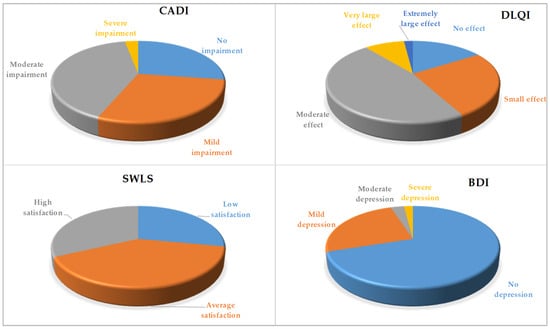
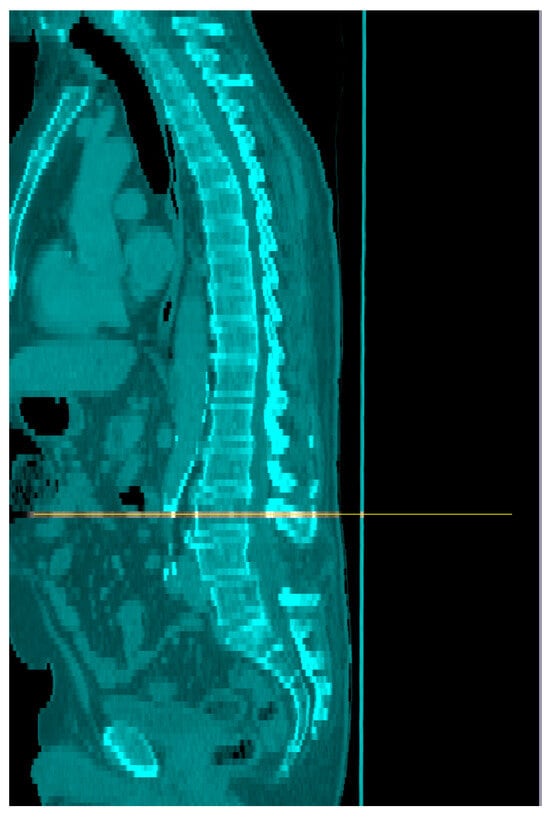
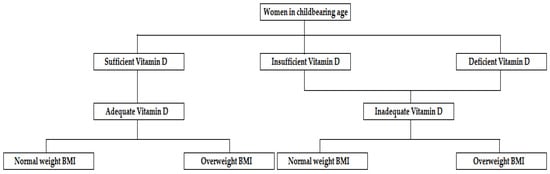
-
 Twelve Weeks of Daily Lentil Consumption Improves Fasting Cholesterol and Postprandial Glucose and Inflammatory Responses—A Randomized Clinical Trial
Twelve Weeks of Daily Lentil Consumption Improves Fasting Cholesterol and Postprandial Glucose and Inflammatory Responses—A Randomized Clinical Trial -
 Effect of 100% Orange Juice and a Volume-Matched Sugar-Sweetened Drink on Subjective Appetite, Food Intake, and Glycemic Response in Adults
Effect of 100% Orange Juice and a Volume-Matched Sugar-Sweetened Drink on Subjective Appetite, Food Intake, and Glycemic Response in Adults -
 Cow’s Milk: A Benefit for Human Health? Omics Tools and Precision Nutrition for Lactose Intolerance Management
Cow’s Milk: A Benefit for Human Health? Omics Tools and Precision Nutrition for Lactose Intolerance Management -
 Intermittent Fasting: Does It Affect Sports Performance? A Systematic Review
Intermittent Fasting: Does It Affect Sports Performance? A Systematic Review -
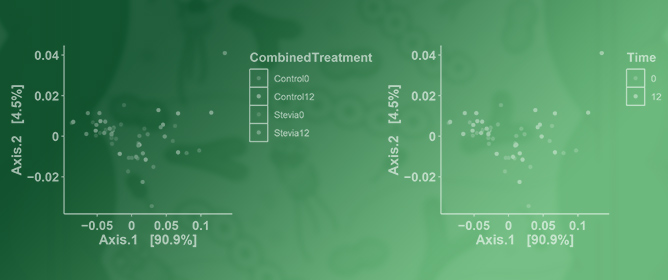 Consumption of the Non-Nutritive Sweetener Stevia for 12 Weeks Does Not Alter the Composition of the Human Gut Microbiota
Consumption of the Non-Nutritive Sweetener Stevia for 12 Weeks Does Not Alter the Composition of the Human Gut Microbiota
Journal Description
Nutrients
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE (Web of Science), PubMed, MEDLINE, PMC, Embase, PubAg, AGRIS, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q1 (Nutrition & Dietetics) / CiteScore - Q1 (Nutrition and Dietetics)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 14.5 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.4 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2023).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
- Companion journal: Dietetics
Latest Articles
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Deadline: 30 April 2024
Deadline: 30 June 2024
Deadline: 31 July 2024
Deadline: 12 August 2024
Conferences

Special Issues
Deadline: 25 April 2024
Deadline: 5 May 2024
Deadline: 25 May 2024
Deadline: 5 June 2024