Journal Description
Rheumato
Rheumato
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on rheumatology research published quarterly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- Rapid Publication: first decisions in 16 days; acceptance to publication in 5.8 days (median values for MDPI journals in the second half of 2023).
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
- Rheumato is a companion journal of JCM.
Latest Articles
Subcutaneous Nodules as Manifestations of Systemic Disease
Rheumato 2024, 4(2), 75-87; https://doi.org/10.3390/rheumato4020007 (registering DOI) - 26 Apr 2024
Abstract
The spectrum of disorders/phenomena encompassed in the practice of rheumatology is quite broad. In addition, our expertise is typically sought whenever other physicians encounter phenomena outside their knowledge base. While skin alterations typically prompt referrals to dermatology practices, alterations underlying the skin (e.g.,
[...] Read more.
The spectrum of disorders/phenomena encompassed in the practice of rheumatology is quite broad. In addition, our expertise is typically sought whenever other physicians encounter phenomena outside their knowledge base. While skin alterations typically prompt referrals to dermatology practices, alterations underlying the skin (e.g., subcutaneous) may well represent localization in “no man’s land” or an orphaned localization, with rheumatology thus referred as to the specialty of last resort—one of the roles that rheumatology has fulfilled for more than half a century. The current review addresses the cacophony of disorders producing or associated with variouslysized subcutaneous nodules. Their classifications, while necessarily artificial, encompass the full spectrum of pathologic processes. They are delineated in the current style to facilitate the consideration required to distinguish among them and to facilitate recognize the underlying processes for which we as rheumatologists are renowned.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Primary Care Education in Musculoskeletal Disease)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
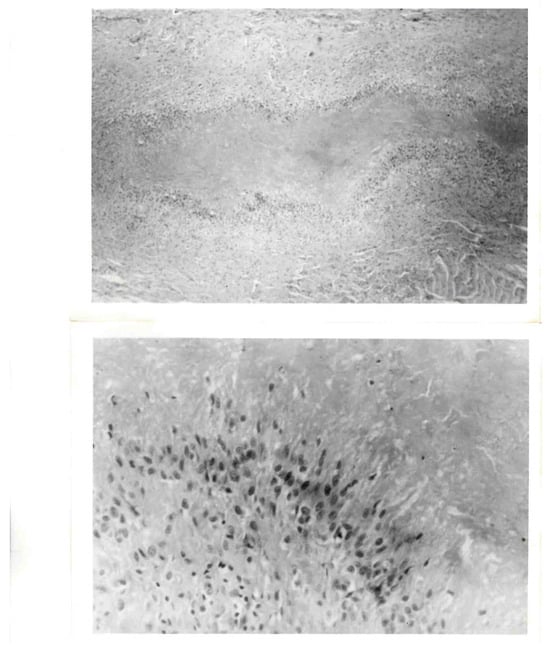
Anti-IL-6 Receptor Treatment in Giant Cell Arteritis Patients Reduces Levels of IL-1β-Receptor Antagonist but Not IL-1β
by
Joana J. da Costa, Lisa Christ, Peter M. Villiger, Monique Vogel and Martin F. Bachmann
Rheumato 2024, 4(2), 63-74; https://doi.org/10.3390/rheumato4020006 - 31 Mar 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This work aimed to investigate a potential link between serum IL-1β levels in patients with giant cell arteritis (GCA) and their responsiveness to combined anti-IL-6 receptor (IL-6R) and glucocorticoid (GC) treatments within the context of two separate clinical trials. IL-1β levels were analyzed
[...] Read more.
This work aimed to investigate a potential link between serum IL-1β levels in patients with giant cell arteritis (GCA) and their responsiveness to combined anti-IL-6 receptor (IL-6R) and glucocorticoid (GC) treatments within the context of two separate clinical trials. IL-1β levels were analyzed in serum samples of two prospective clinical trials investigating tocilizumab in GCA patients using quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR) based Proximity Ligation Assays (PLA). In the phase II randomized controlled trial, serum samples from five patients were quantified at two critical time points: the commencement of the trial (Week 2) and the conclusion of the trial (Week 52). In the GUSTO trial, serum samples from nine patients were similarly analyzed using PLA at Day 0 and Week 52. Furthermore, for the GUSTO trial, serum samples from 18 patients were assessed for IL-1β and IL-1RN at six time points: days 0, 3, and 10, weeks 4, 24, and 52 by a second assay (Proximity Extension Assay, PEA). PLA results from both studies indicated that IL-1β levels were below 1 pg/mL in most of the patients, resulting in notable signal deviations within the same samples. In the analysis of the GUSTO trial, both PLA and PEA exhibited similar trends in IL-1β variations among patients from day 0 to week 52. Notably, the PEA analysis did not show significant variation over time. Furthermore, we did not find a correlation of IL-1β levels with active disease as compared to remission, but interestingly, the measurement of IL-1β receptor antagonist (IL-1RN) revealed a substantial decrease over time. Our study shows that IL-1RN but not IL-1β concentration in serum samples could be directly related to anti-IL-6R treatment in patients diagnosed with GCA.
Full article
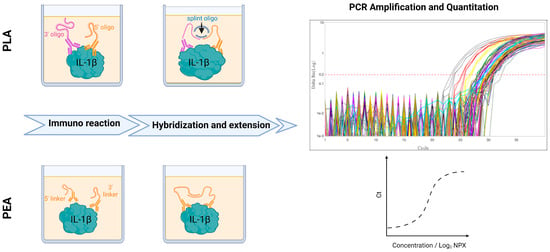
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Treatment of Gout in Patients with CrCl ≤30 mL/min and/or on Hemodialysis: A Review
by
Fares Saliba, Omar Mourad, Jonathan Mina, Fadi Haddadin, Laurence Aoun, Shaza Almardini, Saif Abu-baker, Koushik Sangaraju, Gaetano Di Pietro, Daniel Gaballa and Suzanne El-sayegh
Rheumato 2024, 4(1), 49-62; https://doi.org/10.3390/rheumato4010005 - 12 Mar 2024
Abstract
Gout is highly prevalent in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) and end-stage renal disease (ESRD), owing to impaired uric acid excretion. However, treating gout in this population is challenging due to concerns about medication safety and efficacy with reduced kidney function. This
[...] Read more.
Gout is highly prevalent in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) and end-stage renal disease (ESRD), owing to impaired uric acid excretion. However, treating gout in this population is challenging due to concerns about medication safety and efficacy with reduced kidney function. This review examines the evidence of various pharmacologic and non-pharmacologic approaches to managing gout in CKD/ESRD. For acute gout flares, there is insufficient evidence to guide optimal dosing of NSAIDs, colchicine, and corticosteroids in advanced CKD. The risks generally outweigh the benefits of NSAIDs and colchicine. Corticosteroids appear safer but require individual risk-benefit assessments. Interleukin-1 inhibitors show promise, but larger studies are needed. For long-term urate lowering, xanthine oxidase inhibitors like allopurinol and febuxostat are preferred over probenecid and other uricosurics. However, studies specifically evaluating urate-lowering therapies in CKD are scarce, resulting in conflicting expert guidelines. Starting with low allopurinol doses and gradual titration can mitigate the risks. Higher allopurinol doses may be needed to reach urate targets in some CKD patients. Febuxostat’s safety in advanced CKD remains debated. Optimal gout management in dialysis patients is also unclear, including when to continue urate-lowering therapy. Overall, gout is often suboptimally treated in CKD/ESRD, highlighting the need for more research to guide therapy in this population. Improving management can significantly reduce the burden of these comorbid diseases.
Full article
Open AccessReview
A Review of MDA-5 Dermatomyositis and Associated Interstitial Lung Disease
by
Sambhawana Bhandari, Lisa Zickuhr, Maun Ranjan Baral, Sanjeev Bhalla, Heather Jones, Robert Bucelli and Deepali Sen
Rheumato 2024, 4(1), 33-48; https://doi.org/10.3390/rheumato4010004 - 28 Feb 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Anti-melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 (MDA-5) dermatomyositis (DM) is noteworthy for its association with rapidly progressive interstitial lung disease (RP-ILD), vasculopathy, and distinctive cutaneous features. First identified in a Japanese cohort in 2005, MDA-5 DM carries a significant mortality risk, emphasizing the crucial need
[...] Read more.
Anti-melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 (MDA-5) dermatomyositis (DM) is noteworthy for its association with rapidly progressive interstitial lung disease (RP-ILD), vasculopathy, and distinctive cutaneous features. First identified in a Japanese cohort in 2005, MDA-5 DM carries a significant mortality risk, emphasizing the crucial need for early diagnosis. This review explores the pathogenesis, clinical presentation, diagnosis, management, and prognosis of MDA-5 DM and ILD and includes new research and recommendations regarding disease management.
Full article
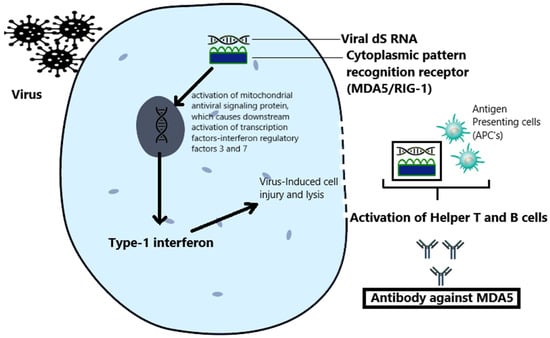
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Are TNF-α and IL-1β Independently Associated with Depression in Axial Spondyloarthritis Patients? A Case-Control Study
by
Md. Nazrul Islam, S M Ahamed Abed, Shirin Tarafder, Abul Khair Ahmedullah, Johannes J. Rasker and Md. Injamul Haq Methun
Rheumato 2024, 4(1), 19-32; https://doi.org/10.3390/rheumato4010003 - 30 Jan 2024
Abstract
Objectives: The aim of this study was to investigate whether serum TNF-α and IL-1β levels are independent risk factors for depression in axSpA patients. Methods: All axSpA patients with BASDAI ≥4 were invited consecutively between March 2021 and August 2021 to participate. Depression
[...] Read more.
Objectives: The aim of this study was to investigate whether serum TNF-α and IL-1β levels are independent risk factors for depression in axSpA patients. Methods: All axSpA patients with BASDAI ≥4 were invited consecutively between March 2021 and August 2021 to participate. Depression was evaluated with the WHO-5 Well-Being scale. Disease activity was assessed using BASDAI (0–10), ASDAS-CRP (0.61–7.22), ASDAS-ESR (0.29–7.61), and health status by ASAS-HI (0–17). Serum TNF-α and IL-1β levels were measured by ELISA. An association between depression and cytokine levels was investigated with Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient test. Results: A total of 252 axSpA patients (155 men) could be included; of these, 123 (48.81%) were depressed, and of these, 75 were male. Serum TNF-α and IL-1β were not significantly associated with depression (r −0.041 and 0.110, respectively). Serum TNF-α levels were higher in depressed female axSpA patients (20.05 vs. 17.87; p = 0.03). Differences between depressed and non-depressed patients were respectively: TNF-α (19.7 vs.18.0; p= 0.84), IL-1β (32.3 vs. 21.2; p= 0.04), BASDAI (5.47 vs. 4.77; p = 0.000), ASDAS-CRP (4.17 vs. 3.78; p = 0.000), ASDAS-ESR (3.86 vs. 3.39; p = 0.000), CRP (48.43 vs. 37.93 mg/L; p = 0.000), and ASAS-HI (13.37 vs. 10.24; p = 0.000). Factors associated with depression were: peripheral joint involvement (OR = 1.073, 95% CI 1.012–1.138), BASDAI (OR = 1.534, 95% CI 1.011–2.335), and ASAS-HI (OR = 1.39, 95% CI 1.239–1.557). Only in depressed patients with peripheral SPA were higher IL-1β levels found, though the differences were probably not clinically relevant. Conclusions: Serum TNF-α and IL-1β were not independently related to depression in axSpA patients. Disease activity, peripheral joint involvement, and reduced health status showed the highest association with depression.
Full article
Open AccessEditorial
Rheumato(Philes): A Publication Option for Rheumatology Devotees’ Creative Works
by
Bruce M. Rothschild
Rheumato 2024, 4(1), 13-18; https://doi.org/10.3390/rheumato4010002 - 26 Jan 2024
Abstract
This journal for Rheumato(philes) has provided a vehicle for the interdisciplinary sharing of the challenges and interventions of our specialty. The provision of state-of-the-art information is not at the expense of the basics from which it has grown. From its initial status as
[...] Read more.
This journal for Rheumato(philes) has provided a vehicle for the interdisciplinary sharing of the challenges and interventions of our specialty. The provision of state-of-the-art information is not at the expense of the basics from which it has grown. From its initial status as a source of discomfort, a review of back pain diagnostics and therapeutics provides a background for facilitating contemporary practice. We have met the enemy in the form of COVID-19, addressing its many rheumatologic complications, and have been introduced to the vagaries of IgG4 disease. Our clinical skills are tested in recognition of primary hypertrophic osteoarthropathy. The relationship of dental health to rheumatoid arthritis and nutritional issues is currently undergoing scientific review. A unique feature, one we seldom seem to discuss, is the evaluation of disease manifestations when the customary tools are not available. The latter brings us full circle in the evolution of our field. When our colleagues found diagnostic or treatment approaches elusive, they did not call for Ghostbusters; they called for us.
Full article
Open AccessReview
Renal and Urinary Tract Involvement in Fibrosclerosing or Fibroinflammatory Diseases: A Narrative Review
by
Giovanni Maria Rossi, Chiara Pala and Davide Gianfreda
Rheumato 2024, 4(1), 1-12; https://doi.org/10.3390/rheumato4010001 - 22 Dec 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Fibroinflammatory diseases are a group of rare pathologies in which the hallmark is the exuberant deposition of fibrotic tissue and inflammatory cellular infiltrates, characteristic of the specific disease. A sclerotic mass develops within soft tissues and/or organs, damaging and replacing them, with effects
[...] Read more.
Fibroinflammatory diseases are a group of rare pathologies in which the hallmark is the exuberant deposition of fibrotic tissue and inflammatory cellular infiltrates, characteristic of the specific disease. A sclerotic mass develops within soft tissues and/or organs, damaging and replacing them, with effects ranging from asymptomatic to life-threatening clinical manifestations. The kidneys and urinary tract can be involved in some of these diseases, which can lead to acute kidney injury, chronic kidney disease, and even end-stage kidney disease. IgG4-related disease, retroperitoneal fibrosis, and Erdheim–Chester disease are the three fibroinflammatory disorders that can involve the kidneys. Only a timely and accurate collection of clinical, radiological, metabolic, laboratory, and histological data allows prompt diagnosis and targeted treatment of these pathologies, allowing the stoppage of the evolution of renal and systemic manifestations, which can lead to complete remission. The epidemiology, clinical and histological features, and management of these conditions are herein described in a narrative fashion.
Full article
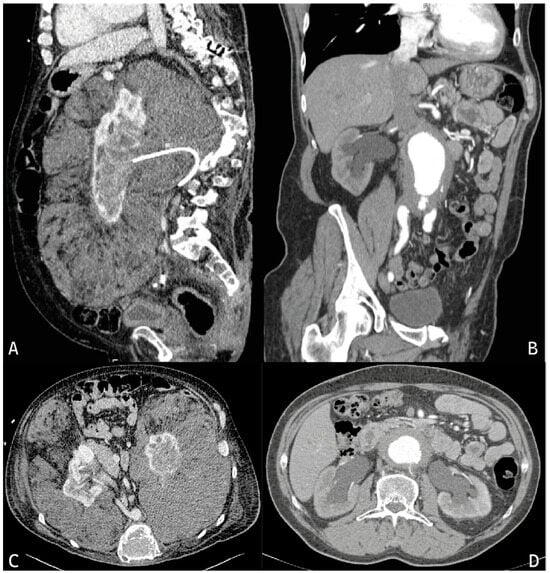
Figure 1
Open AccessCommunication
Recognising the Rheumatological Needs of Neurodivergent Females: Commentary
by
Ren Martin, Rachael Taylor and Clive Kelly
Rheumato 2023, 3(4), 221-227; https://doi.org/10.3390/rheumato3040017 - 28 Nov 2023
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
We experience life and interact with others in a multitude of ways. The term ‘neurodivergence’ refers to variations from what is considered typical or normal. Neurodivergence influences an individual’s behaviour in social situations and is associated with atypical emotional responses. This can precipitate
[...] Read more.
We experience life and interact with others in a multitude of ways. The term ‘neurodivergence’ refers to variations from what is considered typical or normal. Neurodivergence influences an individual’s behaviour in social situations and is associated with atypical emotional responses. This can precipitate inequity and rejection. Neurodivergent females are especially prone to many physical and psychological health issues, and musculoskeletal disorders account for a significant proportion of these. Research and education into neurodivergent conditions in females should inform the reassessment of clinicians’ present approach to those who present with multiple unexplained symptoms. Obtaining official confirmation of a neurodivergent condition improves access to support services and helps them and their family better understand themselves and the challenges they face. This commentary highlights the increased risk of developing rheumatological disease for females with neurodivergent conditions and suggests how clinicians might increase their awareness of this.
Full article
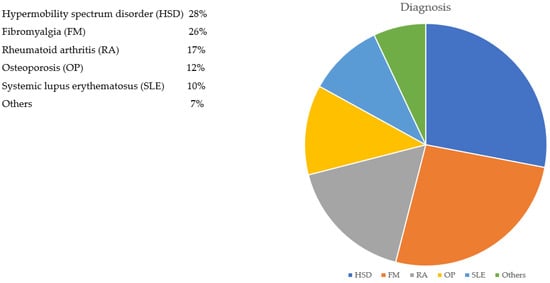
Figure 1
Open AccessPerspective
Diagnostic Considerations in Evaluation of Back Complaints
by
Bruce Rothschild
Rheumato 2023, 3(4), 210-220; https://doi.org/10.3390/rheumato3040016 - 31 Oct 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The axial skeleton, with the exception of spondyloarthropathy, is the most neglected aspect of rheumatology training and, as a result, perhaps the most complex. The clinical “problem” of back/neck pain could be considered the “orphan child” of medicine, and our perspective as rheumatologists
[...] Read more.
The axial skeleton, with the exception of spondyloarthropathy, is the most neglected aspect of rheumatology training and, as a result, perhaps the most complex. The clinical “problem” of back/neck pain could be considered the “orphan child” of medicine, and our perspective as rheumatologists is often sought for such entities. Sources of back/neck pain are myriad, and not all phenomena affecting the back are symptomatic. Perhaps the one that has most concerned rheumatologists is the cervical instability associated with rheumatoid arthritis. The current review examines intrinsic and extrinsic alterations in axial skeletal components, providing a guide to discriminating the causes (e.g., Scheuermann’s disease versus osteoporotic compression and the various forms of axial joint ankylosis) and the implications of vertebral endplate alterations. The specificity and sensitivity (limitations) of radiologic findings are reviewed, with a reminder that vertebral body osteophytes do not represent osteoarthritis and are therefore unlikely to explain back or neck complaints and that it is our clinical examination which will likely suggest symptom origin.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessCase Report
Kawasaki Disease Complicated with Macrophage Activation Syndrome: The Importance of Prompt Diagnosis and Treatment–Three Case Reports
by
Elena Corinaldesi, Marianna Fabi, Ilaria Scalabrini, Elena Rita Praticò, Laura Andreozzi, Francesco Torcetta and Marcello Lanari
Rheumato 2023, 3(4), 201-209; https://doi.org/10.3390/rheumato3040015 - 30 Sep 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Kawasaki disease (KD) is an acute vasculitis that mainly affects children under 5 years of age, leading to coronary artery alterations (CAAs) in 25% of untreated patients. Macrophage activation syndrome (MAS) is a secondary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) that can complicate the acute, subacute,
[...] Read more.
Kawasaki disease (KD) is an acute vasculitis that mainly affects children under 5 years of age, leading to coronary artery alterations (CAAs) in 25% of untreated patients. Macrophage activation syndrome (MAS) is a secondary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) that can complicate the acute, subacute, and chronic phases of KD. We retrospectively reviewed three cases of children affected by KD complicated with MAS hospitalized in two pediatric units in Emilia Romagna, a northern region of Italy. Case 1: a previously healthy 23-month-old female with full clinical criteria of KD and a hemorrhagic rash due to MAS during the acute phase of the illness. This patient responded promptly to a high dose of intravenous immune globulin (IVIG) and three pulses of high doses of methylprednisolone (MPD) with improvement in clinical signs and laboratory tests without the development of CAA at any phase of illness. Case 2: a previously healthy 10-month-old female with incomplete KD with persistent fever and maculopapular rash. This patient did not respond to IVIG and developed MAS during the subacute phase, characterized by persistent fever, hypertransaminasemia, hyperferritinemia, and hypofibrinogenemia after two high doses of IVIG and boluses of MPD. The patient responded to the addition of IL-1 blocker and anakinra and did not present CAA alterations during any phase of the illness. Case 3: a previously healthy 26-month-old male with incomplete KD with fever, maculopapular rash, cheilitis, and hyperemic conjunctivitis. This patient developed gallbladder hydrops and CAA in the acute phase and did not respond to two high doses of IVIG and a high dose of MPD. In the subacute phase, this patient was complicated with MAS and responded to intravenous anakinra. During the subacute phase, the patient developed transient aneurysms that regressed during the chronic phase. These cases reiterate that prompt diagnosis and aggressive immunomodulatory treatment can limit the most severe complications of MAS complicating KD. High doses of IVIG and MPD may result in a favorable outcome or more aggressive adjunctive treatment may be needed. Anakinra, cyclosporine, monoclonal antibodies, and plasmapheresis can be used as adjunctive treatment in the case of unresponsive MAS in KD. Notably, MAS, present during the subacute phase in cases 2 and 3, promptly responded to anakinra, an IL-1 blocker, without the use of cyclosporine. Our experience confirms that the IL-1 blocker can be considered an optimal choice after non-response to IVIG and MPD in KD complicating with MAS, avoiding over-treatment with cytotoxic drugs.
Full article
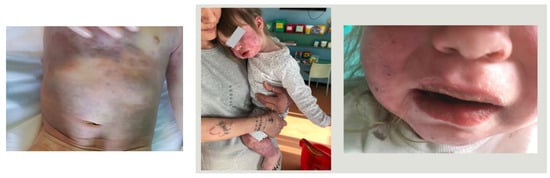
Figure 1
Open AccessCase Report
Lipoma Arborescens Might Be an Unusual Cause of Knee Pain in Adolescents: A Case Report
by
Lorenzo Moretti, Davide Bizzoca, Andrea Michele Abbaticchio, Alessandro Geronimo, Giuseppe Solarino and Biagio Moretti
Rheumato 2023, 3(3), 196-200; https://doi.org/10.3390/rheumato3030014 - 14 Aug 2023
Abstract
Lipoma arborescens (LA) is a rare benign soft tissue tumor characterised by a hyperproliferation of villi and fat cells in the joint synovium. It is most frequently localized in the knee as reported here. This is a case report of a 16-year-old adolescent,
[...] Read more.
Lipoma arborescens (LA) is a rare benign soft tissue tumor characterised by a hyperproliferation of villi and fat cells in the joint synovium. It is most frequently localized in the knee as reported here. This is a case report of a 16-year-old adolescent, affected by type I diabetes mellitus, who reported left knee pain and functional limitation to medical attention. She performed a physical examination, MRI and biopsy using an arthroscopic approach, leading to the LA diagnosis and classification. The LA has been thus treated with an arthroscopic synovectomy, which is the treatment of choice for LA, characterized by a low recurrence rate.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Primary Care Education in Musculoskeletal Disease)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessCommunication
Treatment of Chronic Pain in Patients with Osteoarthritis of the Hip and Knee with a Combination of Hydroxytyrosol, Omega 3 Fatty Acids and Curcumin: Results of a Pilot Study
by
Fernando Madero López, Lucinda Velázquez Alonso, Daniel Clemente Garulo and Juan Carlos López Robledillo
Rheumato 2023, 3(3), 189-195; https://doi.org/10.3390/rheumato3030013 - 31 Jul 2023
Abstract
Chronic pain is the most common symptom of osteoarthritis and is very often accompanied by limitations in the performance of activities of daily living and has a negative impact on patients’ quality of life. It is estimated that 14% of the elderly population
[...] Read more.
Chronic pain is the most common symptom of osteoarthritis and is very often accompanied by limitations in the performance of activities of daily living and has a negative impact on patients’ quality of life. It is estimated that 14% of the elderly population routinely use NSAIDs for pain management, not without serious adverse effects. Objective: We aimed to test the efficacy and possible side effects of OliminaDol (encapsulated combination of purified hydroxytyrosol, omega-3 fatty acids and curcumin) in the treatment of chronic osteoarthritis pain. Seventy-four patients with a diagnosis of osteoarthritis who had chronic pain were selected. The therapeutic intervention consisted of self-administering one capsule of the supplement every 12 h for 30 days. A visual analogue scale (VAS) was used for pain assessment. The efficacy was assessed by comparing the means of pain intensity at baseline and at the end of treatment. The data on the National Cancer Institute (NCI-CTCAE) version 4 criteria were also analyzed. Results: Thirty-six patients were evaluable for the primary objective. The mean value + standard deviation of pain intensity measured by the VAS scale at day +1 was 5.78 + 0.15 and the mean value of pain 30 days after initiation of treatment was 4.19 + 0.22. There was a decrease in pain intensity of 1.63 + 2.28 with p = 0.000. A total of 27 patients (75%) had pain reduction and in 19 of them (52.7%), the difference was greater than 2 points on the VAS scale. OliminaDOL administration was associated with very few and insignificant side effects, notably constipation in two patients (5.4%) and a fishy taste in three patients (8.1%). Conclusions: The administration of OliminaDOL produced a significant decrease in the mean value of pain intensity without side effects. These results, together with other published studies, demonstrate the possibility that some supplements, or a combination of them as in our case, can be an alternative for the treatment of chronic pain.
Full article
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
Chronic Plantar Fasciitis Treatment: A Randomized Trial Comparing Corticosteroid Injections Followed by Therapeutic Ultrasound with Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy
by
Nermeen Hassan A. Moneim, Mennatullah A. Hemed, Peter M. ten Klooster, Johannes J. Rasker and Nashwa K. El Shaarawy
Rheumato 2023, 3(3), 169-188; https://doi.org/10.3390/rheumato3030012 - 30 Jun 2023
Cited by 1
Abstract
This study aims to compare the effect of corticosteroid injection (CSI) followed by therapeutic ultrasound (TUS) with that of extracorporeal shock wave therapy (ESWT) in patients with chronic plantar fasciitis (PF) and to explore the impact of a sedentary lifestyle and obesity on
[...] Read more.
This study aims to compare the effect of corticosteroid injection (CSI) followed by therapeutic ultrasound (TUS) with that of extracorporeal shock wave therapy (ESWT) in patients with chronic plantar fasciitis (PF) and to explore the impact of a sedentary lifestyle and obesity on treatment outcomes. Female patients with PF were randomly allocated to receive ESWT (group A, n = 25) or CSI + TUS (group B, n = 25). Interventions: Group A received four once-weekly sessions of ESWT (2000 shocks, 2.5 bar pressure, 10.0 Hz frequency). Group B received a local injection of 40 mg triamcinolone acetonide with 2 mL 1% xylocaine, followed by three sessions of TUS per week for two weeks. Pain visual analog scale (VAS pain), plantar fasciitis pain and disability scale (PFPDS), and fascia thickness using musculoskeletal ultrasound were all measured at baseline, 4 weeks, and 12 weeks after the end of treatment. VAS pain and PFPDS improved significantly in both groups after 4 and 12 weeks. In the ESWT group, the pain improved significantly more at 12 weeks (p = 0.004). In obese patients (BMI > 29.9 kg/m2), ESWT gave more long-term pain relief at 12 weeks follow-up. In both the ESWT and CSI + TUS groups, after 12 weeks, the VAS pain improved more in patients with a sedentary daily life than in those with active life (p = 0.021 and p = 0.014, resp.), as well as the PFPDS (p = 0.014 and p = 0.019, resp.). Plantar fascia thickness decreased in both groups at 12 weeks. In both groups, improvements in function (PFPDS) correlated significantly with decreased plantar fascia thickness at 4 and 12 weeks. In the CSI + TUS group only, the decrease in plantar fascia thickness was correlated with pain improvement at both follow-up visits. Echogenicity changed from hypoechoic to iso- or hyperechoic and improved significantly in both groups at 12 weeks follow-up, but changes were not different between the groups (p = 0.208). Both CSI + TUS and ESWT are effective treatments for female patients with chronic plantar fasciitis resulting in pain relief and improved function and fascia thickness. ESWT gave more pain relief at 12 weeks follow-up. CSI + TUS is effective as a rapid and short-term modality for relieving PF pain. According to previous studies, the addition of TUS does not appear to make CSI much more effective.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Primary Care Education in Musculoskeletal Disease)
►▼
Show Figures
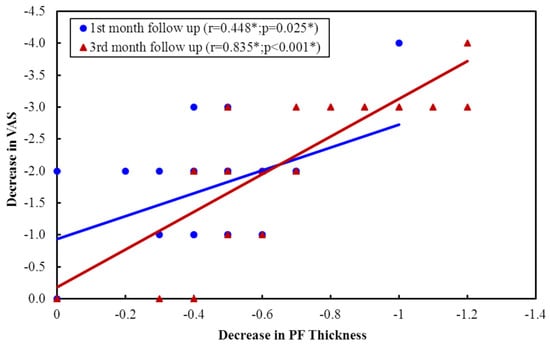
Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
Non-Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children—Postacute Sequelae of Paediatric COVID-19: Autoimmune or Autoinflammatory? A Systematic Review of the Reported Cases
by
Antoine Fakhry AbdelMassih, Maram Hamed Hanafy, Maryam ElAhmady, Sylvia Kozman, Nourine Diab, Reem Husseiny, Ashrakat Deyab, Aalaa Mady, Alia Yasser, Amira R. AbdelHalim, Aya Mohyeldin, Aya Sayed Serour, Ayat AbdelGadir, Eslam Abdelaziz, Farida ElGhamry, Hana Amr, Karim Milad, Lamya Fouda, Mawada Hesham, Mina Adly Riad, Mohamed Aoun, Rana AbdelTawab, Rana Sayed, Salma ElSenbawy, Sara ElAhmady Abdelkhalek, Nada Gamal and Yasmin Omaradd
Show full author list
remove
Hide full author list
Rheumato 2023, 3(2), 132-168; https://doi.org/10.3390/rheumato3020011 - 30 May 2023
Abstract
Three years after its emergence, coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) continues to be a leading cause of worldwide morbidity and mortality. This systematic review comprises relevant case reports that discuss non-multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (non-MIS-C) and postacute sequalae of COVID-19 (PASC) in the
[...] Read more.
Three years after its emergence, coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) continues to be a leading cause of worldwide morbidity and mortality. This systematic review comprises relevant case reports that discuss non-multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (non-MIS-C) and postacute sequalae of COVID-19 (PASC) in the paediatric population, also known as long COVID syndrome. The study aims to highlight the prevalent time interval between COVID-19 and the development of non-MIS-C post-infectious sequalae (PIS). Databases were searched for studies that met our inclusion and exclusion criteria. The final screening revealed an equal sex distribution where the commonest age intervals were school-age and adolescence, with 38% of the patients being older than six years. Interestingly, hospital admission during the course of COVID-19 was not a predictor of the subsequent PASC; forty-nine patients (44.9%) were hospitalized while sixty patients (55.1%) were not hospitalized. Moreover, the most predominant time interval between COVID-19 and the developing PASC was within 14 days from the start of COVID-19 infection (61%). These findings suggest a crucial link between COVID-19 and immune PIS in the paediatric population, especially those older than six years. Accordingly, follow-up and management are encouraged in case of unusual symptoms and signs following COVID-19 infection, regardless of the COVID-19 infection severity.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Post-COVID Rheumatic and Immune-Mediated Diseases)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Periodontal Health as Perceived by Rheumatologists and Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients
by
Natasha Proud, Grace Hughes, Cohen McCashney and Letícia Algarves Miranda
Rheumato 2023, 3(2), 118-131; https://doi.org/10.3390/rheumato3020010 - 21 Apr 2023
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The aim of the present study is to assess the knowledge and attitudes towards periodontal health among rheumatologists and rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients. Two questionnaires comprising questions on demographics, knowledge, and attitudes towards periodontal health were created via Qualtrics survey software. A link
[...] Read more.
The aim of the present study is to assess the knowledge and attitudes towards periodontal health among rheumatologists and rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients. Two questionnaires comprising questions on demographics, knowledge, and attitudes towards periodontal health were created via Qualtrics survey software. A link to the survey was sent via email to rheumatologists registered under the Australian Rheumatology Association (ARA) practising in Western Australia, and a separate survey was distributed to patients via Arthritis and Osteoporosis WA social media pages. Seven and 76 responses were received from rheumatologists and RA patients, respectively. Statistically significant results (p < 0.05) were found between the length of RA diagnosis and signs of periodontal disease, as well as the type of RA diagnosis and knowledge levels. Employed and retired participants attended the dentist more regularly, and a higher percentage believed that maintaining good oral hygiene is important for overall health. A significant correlation was found between patients who thought improving oral hygiene would impact their RA and whether they received periodontal treatment. No significant differences were found for rheumatologists; however, younger practitioners more frequently asked about their patients’ oral health and performed oral exams. There is a deficit in knowledge about the relationship between periodontal disease and RA among both rheumatoid patients and rheumatologists. The high prevalence of periodontitis and the two-way relationship between RA and periodontal disease would benefit from improved knowledge in relation to their association and could have significant benefits in their clinical and public health implications.
Full article
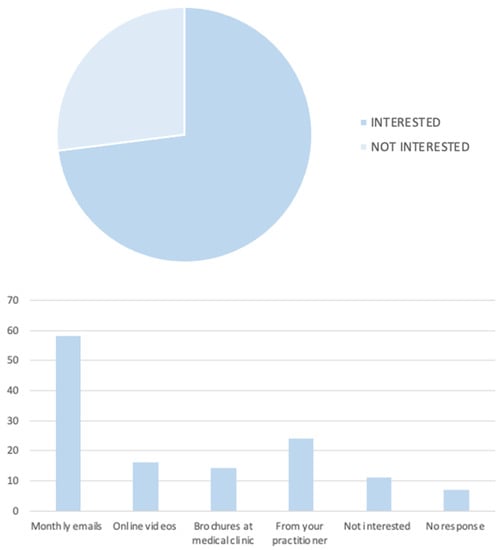
Figure 1
Open AccessProtocol
A Study Protocol on the Effectiveness of Radial Shockwave Therapy on Myofascial Pain Syndrome: A Mixed Methods Study That Combines a Randomised Control Trial and Semi-Structured Interviews
by
Collins Ogbeivor, Huda AlMubarak, Tola Akomolafe, Hamad Alkahtani, Hussain AlMugizel, Hala Aldosari and Nouf Aldhwayan
Rheumato 2023, 3(1), 106-117; https://doi.org/10.3390/rheumato3010009 - 16 Mar 2023
Abstract
Background: Myofascial pain syndrome (MPS) is a common, costly and often persistent musculoskeletal problem. Radial shockwave (RSW) is one of the most common treatments for MFS. However, there is very low-level evidence to support its short-term benefit, due to poor methodological qualities. Furthermore,
[...] Read more.
Background: Myofascial pain syndrome (MPS) is a common, costly and often persistent musculoskeletal problem. Radial shockwave (RSW) is one of the most common treatments for MFS. However, there is very low-level evidence to support its short-term benefit, due to poor methodological qualities. Furthermore, previous studies have not considered the experiences of patients regarding this intervention. This study will investigate the effectiveness of RSW compared to a sham (placebo) for patients with MPS and establish the experiences of patients receiving the treatment. Methods: A mixed methods study of a pragmatic randomised controlled trial and semi-structured-interviews that will involve 120 potential participants with MPS is used. The intervention group will receive six sessions of RSW: 1.5 bars, 2000 pulses, frequency 15 Hz. The control group will receive an identical treatment except that they will receive a no-energy shock of 0.3 bar. Results: The outcome measures are a numeric pain scale, neck disability index (NDI), pressure pain threshold (PPT) and SF-12 questionnaires at 4 and 8 weeks’ follow-up between the two groups. Conclusion: The expectation is that this study will add to the body of knowledge required to make effective treatment choices on RSW in the management MFS.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Primary Care Education in Musculoskeletal Disease)
►▼
Show Figures
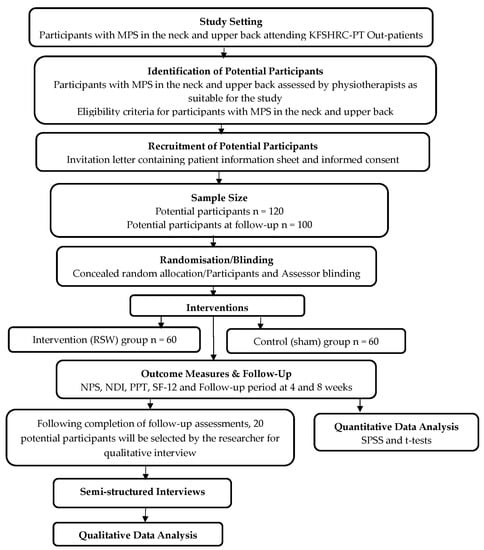
Figure 1
Open AccessCase Report
Pachydermoperiostosis Mimicking Inflammatory Arthritis: Case Description and Narrative Review
by
AKM Kamruzzaman, Maisha Farzana, Md Mainuddin Sohel, Emrul Kaiser, Nobendu Chowdhury, Md Hafizur Rahman, Syed Atiqul Haq and Johannes J. Rasker
Rheumato 2023, 3(1), 98-105; https://doi.org/10.3390/rheumato3010008 - 02 Mar 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Pachydermoperiostosis (PDP), also called primary hypertrophic osteoarthropathy (HOA), is a rare genetic disease with typical thickening of the skin (pachydermia) and rheumatic manifestations, with clubbing of the fingers and toes and periostosis of the long bones visible on X-rays, as well as arthritis
[...] Read more.
Pachydermoperiostosis (PDP), also called primary hypertrophic osteoarthropathy (HOA), is a rare genetic disease with typical thickening of the skin (pachydermia) and rheumatic manifestations, with clubbing of the fingers and toes and periostosis of the long bones visible on X-rays, as well as arthritis in large joints sometimes. Case: We describe a 23-year-old man with a complete form of PDP who presented with polyarthritis of the ankles and knees, with clubbing of the fingers and toes. He was treated with a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID), etoricoxib, and with bisphosphonates (initially pamidronic acid i.v. and later oral risedronate 35 mg weekly). His joint pains and swelling disappeared, so that he could resume his daily activities. After eight years, the periostosis on the X-rays had disappeared. Discussion: The case is discussed, the literature regarding PDP is summarized and the differential diagnosis and treatment options are reviewed. Conclusions: PDP may present as polyarthritis. Clinicians should be aware of this diagnosis, as treatment is available and may improve the outcome of the patient. It is important to rule out secondary HOA due to pulmonary or cardiac disease, gastrointestinal malignancies and liver cirrhosis, especially when the dermatological findings are not typical. Further, acromegaly, thyroid acropachy and rheumatologic diseases should be excluded.
Full article
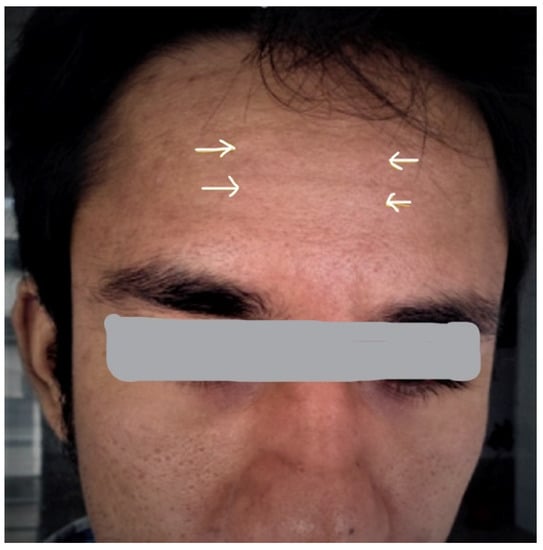
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A Preliminary Predictive Model for Proliferative Lupus Nephritis in Juvenile Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
by
Sern Chin Lim, Elaine Wan Ling Chan, Shikriti Suprakash Mandal and Swee Ping Tang
Rheumato 2023, 3(1), 86-97; https://doi.org/10.3390/rheumato3010007 - 22 Feb 2023
Abstract
Proliferative lupus nephritis, which is diagnosed by renal biopsy, has significant impact on the treatment choices and long-term prognosis of juvenile SLE (jSLE). Renal biopsies are however not always possible or available, thus leading to an ongoing search for alternative biomarkers. This study
[...] Read more.
Proliferative lupus nephritis, which is diagnosed by renal biopsy, has significant impact on the treatment choices and long-term prognosis of juvenile SLE (jSLE). Renal biopsies are however not always possible or available, thus leading to an ongoing search for alternative biomarkers. This study aimed to develop a clinical predictive machine learning model using routine standard parameters as an alternative tool to evaluate the probability of proliferative lupus nephritis (ISN/RPS Class III or IV). Data were collected retrospectively from jSLE patients seen at Selayang Hospital from 2004 to 2021. A total of 22 variables including demographic, clinical and laboratory features were analyzed. A recursive feature elimination technique was used to identify factors to predict pediatric proliferative lupus nephritis. Various models were then used to build predictive machine learning models and assessed for sensitivity, specificity and accuracy. There were 194 jSLE patients (165 females), of which 111 had lupus nephritis (54 proliferative pattern). A combination of 11 variables consisting of gender, ethnicity, fever, nephrotic state, hypertension, urine red blood cells (RBC), C3, C4, duration of illness, serum albumin, and proteinuria demonstrated the highest accuracy of 79.4% in predicting proliferative lupus nephritis. A decision-tree model performed the best with an AROC of 69.9%, accuracy of 73.85%, sensitivity of 78.72% and specificity of 61.11%. A potential clinically useful predictive model using a combination of 11 non-invasive variables to collectively predict pediatric proliferative lupus nephritis in daily practice was developed.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue The Kidneys in Autoimmune Disease: From Basic Mechanisms to Clinical Outcomes)
►▼
Show Figures
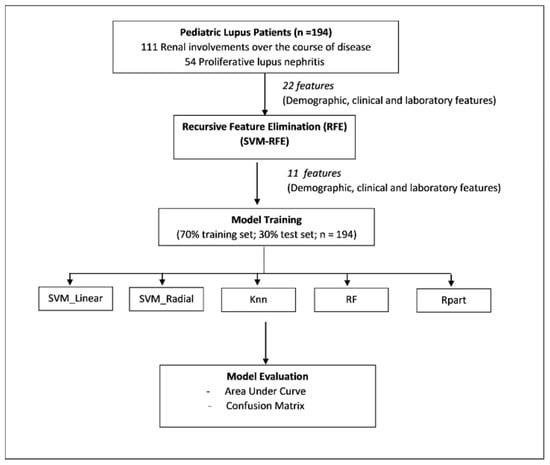
Figure 1
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
Urate-Lowering Therapy Use among US Adults with Gout and the Relationship between Patients’ Gout Treatment Status and Associated Comorbidities
by
Marcos Ortiz-Uriarte, Jeanlouis Betancourt-Gaztambide, Alexandra Perez and Youssef M. Roman
Rheumato 2023, 3(1), 74-85; https://doi.org/10.3390/rheumato3010006 - 03 Feb 2023
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Gout is one of the most common inflammatory conditions with a growing global prevalence. Individuals with gout are at higher risk of developing chronic conditions, such as diabetes, chronic kidney disease (CKD), and cardiovascular diseases. In this study, the association between urate-lowering therapy
[...] Read more.
Gout is one of the most common inflammatory conditions with a growing global prevalence. Individuals with gout are at higher risk of developing chronic conditions, such as diabetes, chronic kidney disease (CKD), and cardiovascular diseases. In this study, the association between urate-lowering therapy (ULT) use and the prevalence of these conditions was evaluated. This observational cross-sectional pharmacoepidemiologic study used the 2013–2018 biannual cycles of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. The inclusion criteria were adults that were 30 years of age or older that had a diagnosis of gout. The association between patients’ ULT treatment status and dyslipidemia, coronary heart disease, heart failure, hypertension, and chronic kidney disease was evaluated as well as its association with select clinical laboratory biomarkers. The prevalence of ULT use was 28.9% (95% CI 24.3–33.9%). Those receiving ULT had a higher prevalence of CKD diagnoses, of a college graduate or higher and of health insurance coverage, and they were older obese males. There was no significant association between ULT use and the prevalence of heart failure, coronary heart disease, hypertension, or dyslipidemia (p > 0.05). Those receiving ULT had lower high-sensitivity c-reactive protein levels compared to those who were not on treatment (4.74 versus 7.21 mg/L, p = 0.044). LDL and total cholesterol were significantly lower among those receiving ULT treatment (p < 0.05). ULT use continues to be low among US individuals diagnosed with gout. Socioeconomic factors may influence patients’ ULT treatment status. Also, gout risk factors, including obesity, male sex, and CKD, are associated with receiving ULT. While our findings may have reflected the guideline recommendations for ULT use in CKD patients, worsening kidney functions while receiving ULT is unlikely. Gout patients receiving ULT may garner added health benefits beyond lower urate levels. Further research is necessary to determine the long-term impact of ULTs on lipid fractions, kidney functions, and other cardiovascular biomarkers.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Dynamic Joint Stiffness of the Knee in Post-Menopausal Women with and without Rheumatoid Arthritis
by
Pedro Aleixo, Orlando Fernandes, José Vaz Patto and João Abrantes
Rheumato 2023, 3(1), 63-73; https://doi.org/10.3390/rheumato3010005 - 20 Jan 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This study compared rheumatoid arthritis (RA) post-menopausal women with pathological involvement of the lower limb joints and age-matched post-menopausal women without RA regarding the dynamic joint stiffness (DJS) of knee during the stance phase of gait. Eighteen RA women and eighteen age-matched women
[...] Read more.
This study compared rheumatoid arthritis (RA) post-menopausal women with pathological involvement of the lower limb joints and age-matched post-menopausal women without RA regarding the dynamic joint stiffness (DJS) of knee during the stance phase of gait. Eighteen RA women and eighteen age-matched women were selected. Gait assessed through a three-dimensional motion analysis system synchronized with a force plate. Subjects walked barefoot at self-selected speed, and 14 valid trials were collected (comprising 7 left and 7 right foot-steps on force plate). The “moment of force—angle” plot of knee in sagittal plane was determined. The stance phase was split into three sub-phases: first knee flexion sub-phase (1st KFS); knee extension sub-phase (KES); second knee flexion sub-phase (2nd KFS). A linear model represented each sub-phase and DJS calculated by the slope. Model fitting was assessed through the coefficient of determination (R2). R2 values for both groups were higher than 0.8 during 1st KFS and KES but not during 2nd KFS. RA women yielded a higher DJS value during 2nd KFS (p < 0.01). Concerning the other sub-phases, no differences were observed between groups. The findings suggested the splitting methodology used could be modelled by a linear “moment of force—angle” relationship, namely, during 1st KFS and KES. During 2nd KFS, RA women yielded a stiffer behavior.
Full article
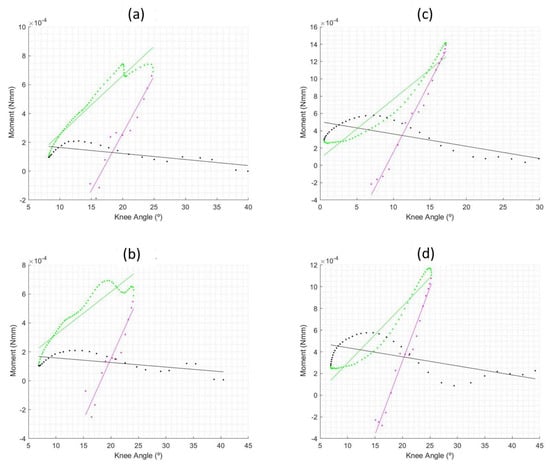
Figure 1
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Biomedicines, Clinics and Practice, Diagnostics, JCM, Rheumato
Rheumatic Disorder: From Basic Science to Clinical Practice
Topic Editors: Giulia Cassone, Caterina Vacchi, Andreina ManfrediDeadline: 20 December 2024

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Rheumato
Primary Care Education in Musculoskeletal Disease
Guest Editor: Bruce RothschildDeadline: 25 October 2024