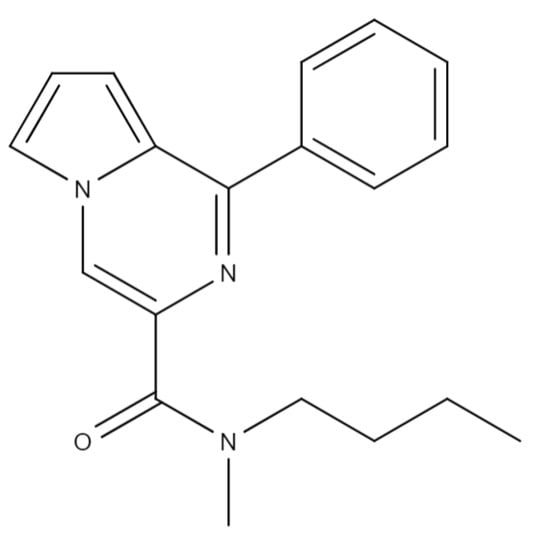
State-of-the-Art Macromolecules in Russia
A topical collection in International Journal of Molecular Sciences (ISSN 1422-0067). This collection belongs to the section "Macromolecules".
Viewed by 47380Editors
Interests: single-site catalysis in polymerization and transformations of α-olefins and dienes; coordination catalysis and organocatalysis for ring-opening polymerization; synthesis of advanced petrochemical products; biodegradable polymers; materials for biomedical applications
2. Institute of Theoretical and Experimental Biophysics, Russian Academy of Sciences, 142290 Pushchino, Russia
Interests: protein folding; bioinformatics and proteomics; aggregation; Alzheimer’s disease; intrinsically disordered proteins; antibacterial peptides
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
We are pleased to announce a call for submissions for a Topical Collection of the International Journal of Molecular Sciences comprising original research articles and comprehensive review papers on all fundamental aspects of macromolecular science in Russia.
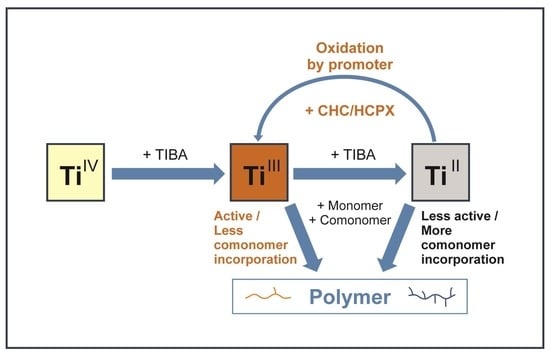
At present, polymer chemistry is progressing rapidly to address the challenges of the twenty-first century. New catalytic solutions for petrochemical industry, advanced biodegradable materials for household and biomedical applications, recycling and up-cycling of polymer wastes, polymers from renewable raw materials, macromolecular photonics, power source membranes and electrolytes—this is not a complete list of current areas of research.
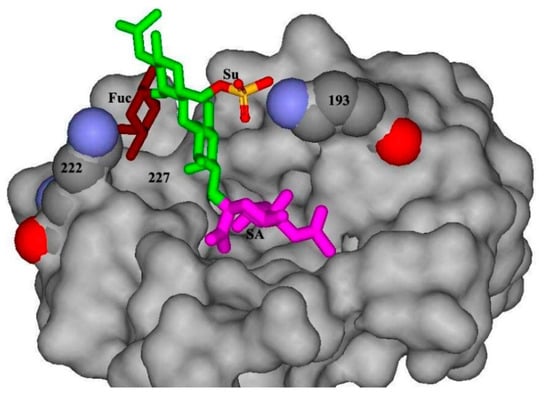
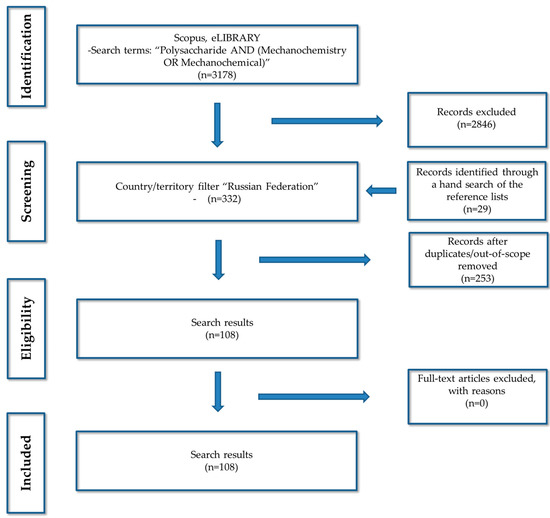
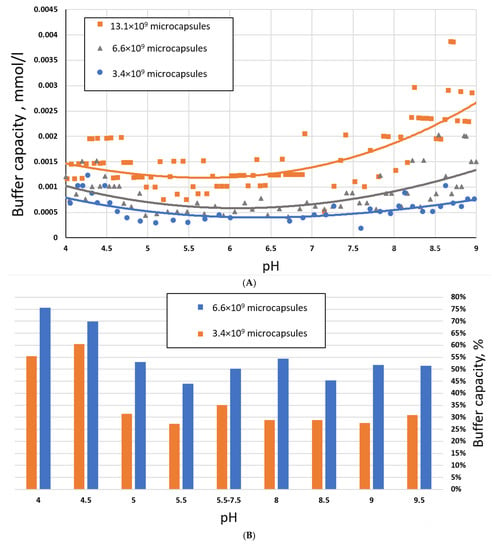
This Topical Collection focuses on creating a multidisciplinary forum of discussion on recent advances in polymer chemistry in the Russian Federation. All topics related to the design, synthesis, characterization, post-modification of macromolecules, new macromolecular structures, mechanisms explaining the formation of macromolecular architectures, polymerization kinetics and thermodynamics, and application of synthetic and biological macromolecules are covered, including biomacromolecules (proteins, nucleic acids, polysaccharides, lipids, etc.), sustainable macromolecules, degradable polymers, and conjugated polymers. Computational studies offering new insights into an understanding of experimental results will also be appreciated.
We welcome all Russian colleagues to submit their high-quality manuscripts.
Prof. Dr. Ilya Nifant'ev
Prof. Dr. Oxana V. Galzitskaya
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. International Journal of Molecular Sciences is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. There is an Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal. For details about the APC please see here. Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- coordination polymerization
- free radical polymerization
- cationic polymerization
- anionic polymerization
- ring-opening polymerization
- polycondensation
- macromolecules modification
- single-site catalysts
- biomacromolecules
- biodegradable polymers
- drug delivery
- stimulus-responsive macromolecules
- sustainable polymers
- renewable polymers
- polyamides
- polyamines
- polydienes
- polyesters
- polyethers
- polyolefins
- polyphosphoesters
- polysaccharides
- macromolecular composition
- macromolecular topology
- polymer microstructure
- structure–properties relationships
- functional macromolecules
- supramolecular conjugates
- spectroscopy
- molecular modeling