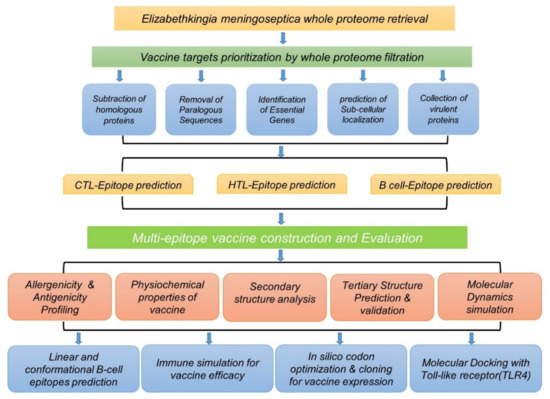
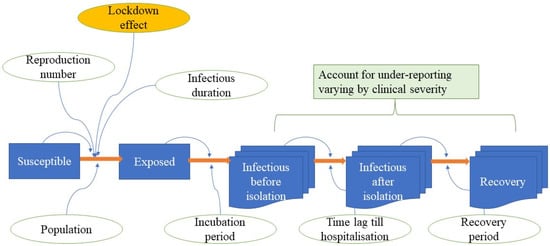
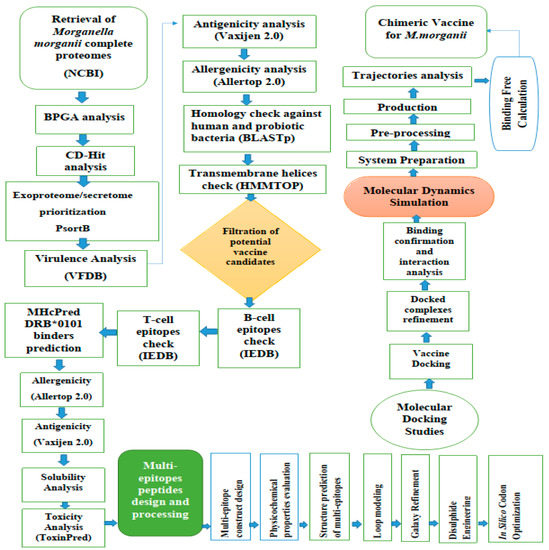
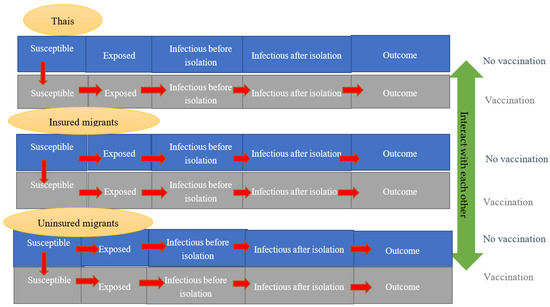
Vaccination Research for Public Health
A topical collection in International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health (ISSN 1660-4601). This collection belongs to the section "Global Health".
Viewed by 77164Editors
Interests: vaccines; preventable diseases; vaccine hesitancy; vaccines safety; vaccines logistics; history of vaccinology
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: vaccines; vaccine hesitancy; vaccine for specific populations; sexual health
Interests: vaccine-preventable diseases in adults and specific groups (immunocompromised, COPD, elderly, hard to reach populations); pneumococcal vaccines
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
Considered one of the most effective measures in the field of public health, vaccination has had a notable impact on the control and reduction of morbidity and mortality from communicable diseases. Immunization programs have contributed to the improvement of life expectancy and the well-being of the population, especially among children. There are still many gaps in the field, such as how to better approach specific, susceptible target populations, how to develop vaccines from disease with an important burden, or how to inform and discuss with antivaccine movements. The COVID-19 pandemic has also influenced the field of vaccinology in several aspects; on one hand, the strength of immunization programs is being tested, and some countries already fear that they may not reach the expected vaccination coverage, with the consequent risk of epidemic outbreaks; on the other hand, getting a vaccine against COVID-19 brings other issues to light: Who should be the initial recipients of the vaccine? What logistical problems will arise? Will they be well accepted by the population? Will the administration of this vaccine slow down the implementation of other vaccination programs?
In this Topical Collection of IJERPH, we invite you and your colleagues to submit original articles, reviews, comments, or new hypotheses aimed at answering the new challenges in the field of vaccinology.
Prof. Dr. José Tuells
Prof. Olivier Epaulard
Dr. Zitta Barrella Harboe
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health is an international peer-reviewed open access monthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2500 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- Vaccines
- Vaccine hesitancy
- Vaccine acceptance
- COVID-19 vaccines
- Vaccine coverage
- Public policies
- Logistic systems and supply chain
- Compulsory vaccination
- Vaccine-preventable diseases outbreaks
- Indirect effects of vaccines
- Vaccines for neglected diseases and diseases of poverty