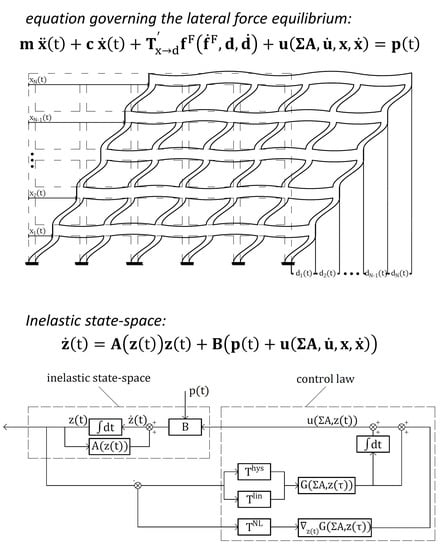
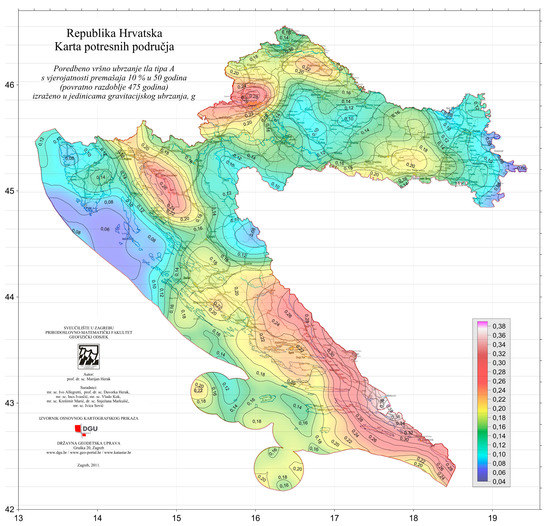
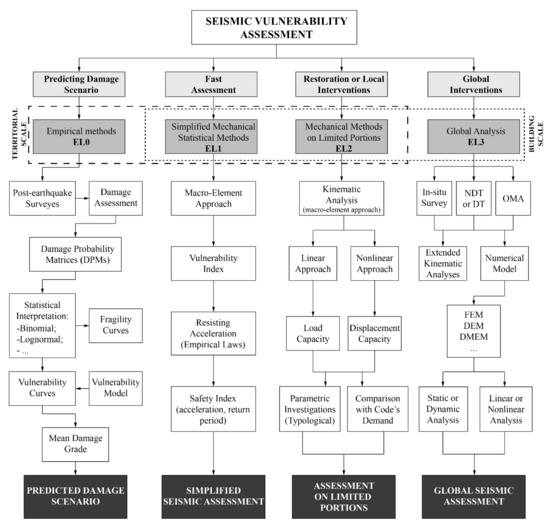
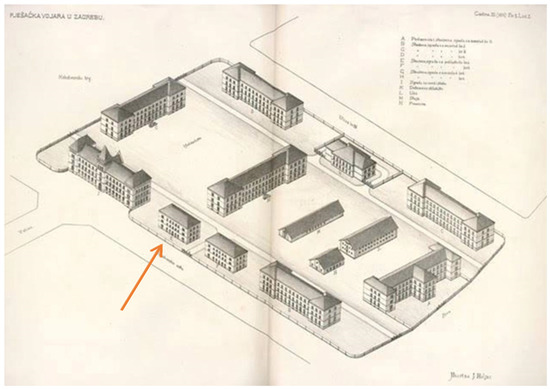
Assessment, Reconstruction and Decision Procedures for the Preservation of Existing Structures after Earthquakes
A topical collection in Buildings (ISSN 2075-5309). This collection belongs to the section "Building Structures".
Viewed by 27536Editors
Interests: structural assessment; historic structures; timber structures; masonry structures; scan to fem; seismic risk; drones
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: structural engineering; materials; design; numerical analysis; experimental testing
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: seismic assessment of historic masonry structures; dynamic of structures; scan to fem; composite structures; fracture mechanics
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: civil engineering; composites; construction; structural analysis; earthquake engineering; construction materials; construction engineering; finite element analysis; mechanical properties
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
In 2020, there were destructive earthquakes all around the world, causing loss of lives, building collapses, and severe structural and non-structural damage and economic losses (e.g., M7.4 Oaxaca (Mexico), M7.0 Aegean Sea (Turkey–Greece), M 6.7 Elazig (East Turkey), M5.3 and M6.4 Croatia, M5.8 Khoy (Iran–Turkey) earthquakes). All these events have made it evident once again that society’s preparedness is crucial for better responding to natural disasters. Identification of vulnerability characteristics and earthquake performance assessment of existing structures are essential steps in reducing earthquake losses and eventually making the societies and cities resilient.
In the past, most of the initial work on structural assessment was based only on the visual inspection of buildings, NDT methods, and engineering judgement. The last decade, however, has seen a growth in the technological development of various tools which can greatly support the prediction of structural safety and behavior of existing structures. The mentioned topics and issues are greatly expressed in pre- and post- earthquake assessments, reconstructions, and renovations of buildings and cities. Case studies of real examples of assessment and reconstruction of existing buildings represent a bridge between practice and research. They provide a method for research in which the complexity of the process and outcome of results contribute to a valuable database for all techniques in preserving existing building stock. The preservation is of particular interest for buildings of cultural value and/or under heritage protection.
This Topical Collection aims at collecting original and high-quality papers and good practices discussing case studies on the assessment, monitoring, reconstruction, maintenance, and preservation of existing structures. Descriptive papers addressing the existing masonry, concrete and timber structures are welcome. Case studies can refer to any processes preserving the built environment, from architectural digitalization to modern techniques of reconstruction of individual buildings and society as a whole.
The main idea of this Topical Collection is to gather a database of case studies regarding the:
- Assessment of existing masonry, timber, and concrete structures;
- Heritage preservation;
- The role of material, component, and assembly aspects in the behavior of existing structures;
- Seismic risk and vulnerability;
- Immediate response after an earthquake;
- Maintenance of structures;
- Use of emerging technologies in the prediction of structural behavior;
- Advances in numerical modeling of existing structures;
- Decision-making process and reconstruction of existing structures;
- Retrofit and mitigation strategies for existing structures;
- Energy renovation of existing structures;
- Teaching initiatives preservation of the built environment.
Dr. Mislav Stepinac
Dr. Chiara Bedon
Dr. Marco Francesco Funari
Prof. Dr. Tomislav Kišiček
Dr. Ufuk Hancilar
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Buildings is an international peer-reviewed open access monthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2600 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- case studies
- existing structures
- seismic design
- assessment
- NDT
- structural updating
- seismic risk
- immediate response
- numerical modeling
- reconstruction