Journal Description
Agronomy
Agronomy
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on agronomy and agroecology published monthly online by MDPI. The Spanish Society of Plant Physiology (SEFV) is affiliated with Agronomy and their members receive discounts on the article processing charges.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE (Web of Science), PubAg, AGRIS, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q1 (Agronomy) / CiteScore - Q1 (Agronomy and Crop Science)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 15.8 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.4 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2023).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
- Companion journals for Agronomy include: Seeds, Agrochemicals, Grasses and Crops.
Impact Factor:
3.7 (2022);
5-Year Impact Factor:
4.0 (2022)
Latest Articles
Optimizing Nitrogen Fertilizer Management Enhances Rice Yield, Dry Matter, and Nitrogen Use Efficiency
Agronomy 2024, 14(5), 919; https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14050919 (registering DOI) - 27 Apr 2024
Abstract
Optimizing nitrogen fertilizer management can effectively improve soil ecology, promote agricultural production, and increase the income of farmers and workers. Nitrogen fertilizer is an important factor in the growth and development of rice, and it is important to find out the optimal amount
[...] Read more.
Optimizing nitrogen fertilizer management can effectively improve soil ecology, promote agricultural production, and increase the income of farmers and workers. Nitrogen fertilizer is an important factor in the growth and development of rice, and it is important to find out the optimal amount and frequency of fertilizer application for the super-hybrid early rice ‘Zhu LiangYou 819’ in Hunan Province, to give full play to its high quality and high yield characteristics. Various N fertilizer application frequencies (P1, basal–tiller fertilizer = 5:5; P2, basal–tiller–spike fertilizer = 4:3:3; P3, basal–tiller–spike–grain fertilizer = 4:3:2:1) and N application amounts (N1, 90 kg ha−1; N2, 150 kg ha−1; N3, 210 kg ha−1) were applied to the hybrid rice ZLY819. The results show that, under the same frequency of N application, ZLY819 had the highest yield, agronomic efficiency, and physiological utilization rate of N fertilizer with the N2 treatment, averaging 7.53 t ha−1, 18.10 kg kg−1, and 34.34%, respectively, with the yield under N2 being 19.38% higher than that under N1. For the same amount of N application, the yield, agronomic efficiency, partial factor productivity of N (PFPN), N contribution to seed, and N use efficiency (NUE) increased with an increase in the frequency of N application, mainly in the order of P3 > P2 > P1, whereby the yield of P3 was 10.11% higher than that of P1. According to the regression equation, the yield is higher when the amount of nitrogen application is 202.15 kg ha−1 and the fertilization frequency is four times. Appropriate N fertilizer management (P3N2) improved the rice growth characteristics, dry matter accumulation, crop growth rate, dry matter transport rate, dry matter contribution rate, and NUE, thus promoting an increase in the rice yield and efficient use of nitrogen.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Fertigation Effects on Water and Nutrient Use Efficiency for Agro-Crop Plants)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Impact of Hood Steaming on Tuber Vitality of Yellow Nutsedge (Cyperus esculentus)
by
Jeroen Feys, Sander De Ryck, Clara Sciffer, Dirk Reheul, Joos Latré, Danny Callens and Benny De Cauwer
Agronomy 2024, 14(5), 918; https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14050918 (registering DOI) - 26 Apr 2024
Abstract
Cyperus esculentus is a hard-to-control, destructive perennial weed propagating and spreading through rhizomes and tubers. Currently, a combination of mechanical, cultural, and chemical measures sustained over time is required for satisfactory control of arable crops. Hood steaming is a promising thermal technique for
[...] Read more.
Cyperus esculentus is a hard-to-control, destructive perennial weed propagating and spreading through rhizomes and tubers. Currently, a combination of mechanical, cultural, and chemical measures sustained over time is required for satisfactory control of arable crops. Hood steaming is a promising thermal technique for rapid depletion of the soil tuber bank. The effect of hood steaming on C. esculentus tuber vitality was investigated using a dose–response experiment on two localities in Belgium. Steaming was performed for five durations (2, 4, 8, 16, and 32 min). Moreover, the effects of tuber burial depth (5, 15, and 25 cm), genetic C. esculentus clone (three different clones), and pedohydrological parameters (sandy and sandy, loamy soil) on hood steaming efficacy were determined. Additionally, the heat sensitivity of genetically diverse C. esculentus tubers was investigated in a laboratory incubator experiment in which incubation temperature and duration varied. To control tubers at depths of 5, 15, and 25 cm, treatment durations of 8, 16, and 32 min were required, respectively. In general, clones producing large tubers showed lower heat sensitivity. As pedohydrological parameters may affect heat transfer into the soil, they may affect steaming efficacy as well. To obtain complete control of C. esculentus tubers, soil temperature should be 50 °C or more for at least 42 min. Hood steaming is a highly suitable alternative technique for a rapid and strong depletion of the soil tuber bank in small well-delineated C. esculentus patches.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Weed Science and Weed Management)
Open AccessArticle
Calibration and Evaluation of the SIMPLE Crop Growth Model Applied to the Common Bean under Irrigation
by
Miguel Servín-Palestina, Irineo López-Cruz, Jorge A. Zegbe, Agustín Ruiz-García, Raquel Salazar-Moreno and José Ángel Cid-Ríos
Agronomy 2024, 14(5), 917; https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14050917 (registering DOI) - 26 Apr 2024
Abstract
Bean production is at risk due to climate change, declining water resources, and inadequate crop management. To address these challenges, dynamic models that predict crop growth and development can be used as fundamental tools to generate basic and applied knowledge such as production
[...] Read more.
Bean production is at risk due to climate change, declining water resources, and inadequate crop management. To address these challenges, dynamic models that predict crop growth and development can be used as fundamental tools to generate basic and applied knowledge such as production management and decision support. This study aimed to calibrate and evaluate the SIMPLE model under irrigation conditions for a semi-arid region in north-central Mexico and to simulate thermal time, biomass (Bio), and grain yield (GY) of common beans cv. ‘Pinto Saltillo’ using experimental data from four crop evapotranspiration treatments (ETct) (I50, I75, I100, and I125) applied during the 2020 and 2021 growing seasons. Both experiments were conducted in a randomized complete block design with three replicates. Model calibration was carried out by posing and solving an optimization problem with the differential-evolution algorithm with 2020 experimental data, while the evaluation was performed with 2021 experimental data. For Bio, calibration values had a root-mean-square error and Nash and Sutcliffe’s efficiency of < 0.58 t ha−1 and > 0.93, respectively, while the corresponding evaluation values were < 1.80 t ha−1 and > 0.89, respectively. The I50 and I100 ETct had better fit for calibration, while I50 and I75 had better fit in the evaluation. On average, the model fitted for the predicted GY values had estimation errors of 37% and 22% for the calibration and evaluation procedures, respectively. Therefore, an empirical model was proposed to estimate the harvest index (HI), which produced, on average, a relative error of 6.9% for the bean-GY estimation. The SIMPLE model was able to predict bean biomass under irrigated conditions for these semi-arid regions of Mexico. Also, the use of both crop Bio and transpiration simulated by the SIMPLE model to calculate the HI significantly improved GY prediction under ETct. However, the harvest index needs to be validated under other irrigation levels and field experiments in different locations to strengthen the proposed model and design different GY scenarios under water restrictions for irrigation due to climate change.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Predictions and Estimations in Agricultural Production under a Changing Climate—Volume II)
Open AccessArticle
Fertilising Maize with Bio-Based Mineral Fertilisers Gives Similar Growth to Conventional Fertilisers and Does Not Alter Soil Microbiome
by
Marcia Barquero, Cinta Cazador, Noemí Ortiz-Liébana, Maurizio Zotti, Javier Brañas and Fernando González-Andrés
Agronomy 2024, 14(5), 916; https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14050916 (registering DOI) - 26 Apr 2024
Abstract
The production of mineral fertilisers relies heavily on mineral deposits that are becoming depleted or is based on processes that are highly energy demanding. In this context, and in line with the circular economy and the European Green Deal, the recovery of nitrogen
[...] Read more.
The production of mineral fertilisers relies heavily on mineral deposits that are becoming depleted or is based on processes that are highly energy demanding. In this context, and in line with the circular economy and the European Green Deal, the recovery of nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K) from organic wastes using chemical technologies is an important strategy to produce secondary raw materials for incorporation into mineral fertilisers, partially replacing the traditional sources of N, P, and K. However, there are very few studies on the agronomic and environmental effects of such substitution. The aim of this work was to evaluate plant growth under microcosm conditions and the effect on the soil microbiome of mineral fertilisers in which part of the N, P, or K content comes from bio-based materials (BBMFs), namely ash, struvite, and a patented chemical process. The crop was maize, and a metataxonomic approach was used to assess the effect on the soil microbiome. The BBMF treatments were compared with a control treated with a conventional mineral fertiliser. The conventional fertiliser performed significantly better than the bio-based fertilisers in terms of maize biomass production at the first sampling point 60 days after sowing (DAS), but at the last sampling point, 90 DAS, the BBMFs showed comparable or even better biomass production than the conventional one. This suggests that BBMFs may have a slightly slower nutrient release rate. The use of fertiliser, whether conventional or BBMF, resulted in a significant increase in microbiome biodiversity (Shannon index), while it did not affect species richness. Interestingly, the use of fertilisers modulated the composition of the bacterial community, increasing the abundance of beneficial bacterial taxa considered to be plant-growth-promoting bacteria, without significant differences between the conventional mineral fertilisers and the BBMFs. The predominance of PGPRs in the rhizosphere of crops when BBMFs are used could be part of the reason why BBMFs perform similarly or even better than conventional fertilisers, even if the rate of nutrient release is slower. This hypothesis will be tested in future field trials. Thus, BBMFs are an interesting option to make the food chain more sustainable.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Soil and Plant Nutrition)
Open AccessArticle
Comparison of Morphological, Physiological, and Related Gene Expression Responses to Drought Stress in Five Camellia vietnamensis Cultivars
by
Shuaishuai Shen, Wuping Yan, Shuao Xie, Jing Yu, Guanglong Yao, Ya Liu, Dongmei Yang, Yougen Wu and Huageng Yang
Agronomy 2024, 14(5), 915; https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14050915 (registering DOI) - 26 Apr 2024
Abstract
The main production area of Camellia vietnamensis (C. vietnamensis) is in the low mountain and hilly areas of southern China. The low survival rate of seedlings caused by drought is one of the main obstacles restricting the development of the C.
[...] Read more.
The main production area of Camellia vietnamensis (C. vietnamensis) is in the low mountain and hilly areas of southern China. The low survival rate of seedlings caused by drought is one of the main obstacles restricting the development of the C. vietnamensis industry. An exploration of the key adaptation mechanism of C. vietnamensis to drought stress is important in order to improve its drought resistance. We conducted a study on the morphological, physiological, biochemical, and drought resistance-related genes of five C. vietnamensis cultivars grown in Hainan province under varying degrees of drought stress. The results indicate that drought stress can lead to a decrease in the relative water content and photosynthetic capacity of C. vietnamensis leaves. Compared with the control, the drought damage index, malondialdehyde, relative electrical conductivity, soluble protein, soluble sugar and proline contents of the five C. vietnamensis cultivars increased with drought-stress duration and degree. With increasing drought-stress intensity, the activity of antioxidant enzymes and the content of related metabolites (total polyphenols, total flavonoids, tea saponins) gradually increased, and the expression levels of phenylpropanoid pathway-related genes (Cv4CL1, CvCAD1, CvCAD2, CvPOX1, CvPOX2, CvPOX3) were upregulated. Based on the results of the drought tolerance coefficients, principal component analysis, and hierarchical cluster analysis, we classified five C. vietnamensis cultivars into drought-tolerant cultivars (‘Haida 1’); moderately drought-tolerant cultivars (‘Haida 4’ and ‘Wanhai 4’); and drought-sensitive cultivars (‘Wanhai 3’ and ‘Wanhai 1’). The results of this study provide a theoretical basis for the promotion and cultivation of C. vietnamensis and the selection of drought-resistant cultivars.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Crop Breeding and Genetics)
►▼
Show Figures
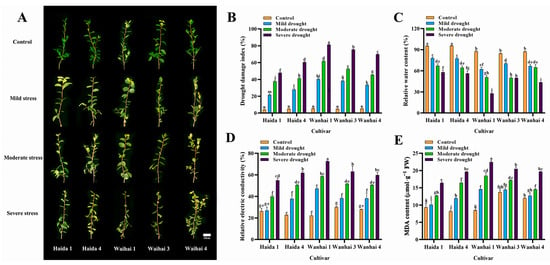
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Effects of Different N Fertilizer Doses on Phenology, Photosynthetic Fluorescence, and Yield of Quinoa
by
Yan Deng, Yan Zheng, Jingying Lu, Zeyun Guo, Xiaojing Sun, Li Zhao, Hongxia Guo, Liguang Zhang and Chuangyun Wang
Agronomy 2024, 14(5), 914; https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14050914 (registering DOI) - 26 Apr 2024
Abstract
Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) is gaining recognition as a pseudocereal due to its nutritional attributes and adaptability to challenging conditions and marginal soils. However, understanding the optimal fertilization for quinoa growth remains a challenge. This study investigates the effects of nitrogen fertilization
[...] Read more.
Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) is gaining recognition as a pseudocereal due to its nutritional attributes and adaptability to challenging conditions and marginal soils. However, understanding the optimal fertilization for quinoa growth remains a challenge. This study investigates the effects of nitrogen fertilization (0, 90, 120, and 150 kg using urea) on quinoa phenology, growth, and photosynthesis in the Loess Plateau region of China, a critical area facing soil erosion and ecological degradation. The results showed that nitrogen fertilization significantly influenced quinoa phenology, prompting early flowering and shorter growth at an optimum rate of 120 kg ha−1. Nitrogen application enhanced growth traits such as plant height, stem diameter, and chlorophyll content, particularly at the heading and flowering stages. Photosynthesis-related parameters, including net photosynthesis rate, transpiration rate, stomatal conductance, and intercellular CO2 concentration, were affected by nitrogen application, with higher values observed at 120 kg ha−1. Non-photochemical quenching was significantly increased by nitrogen application, indicating the efficient dissipation of excess energy. The study demonstrated a positive correlation between grain yield and growth traits, photosynthesis-related traits, and chlorophyll content. In conclusion, quinoa yield could be significantly improved at the Loess Plateau region under rainfed conditions by an optimal nitrogen fertilizer rate of 120 kg ha−1, which reduces the growth duration while increasing photosynthesis traits.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Agroecology Innovation: Achieving System Resilience)
Open AccessArticle
Complete Plastomes of Ten Rorippa Species (Brassicaceae): Comparative Analysis and Phylogenetic Relationships
by
Ting Ren, Lulu Xun, Yun Jia and Bin Li
Agronomy 2024, 14(5), 913; https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14050913 (registering DOI) - 26 Apr 2024
Abstract
The genus Rorippa belongs to the family Brassicaceae, and its members usually have high medicinal value. The genus consists of approximately 75 species and mainly grows in the Northern Hemisphere, occurring in every continent except Antarctica. The taxonomy and phylogenetic relationships of Rorippa
[...] Read more.
The genus Rorippa belongs to the family Brassicaceae, and its members usually have high medicinal value. The genus consists of approximately 75 species and mainly grows in the Northern Hemisphere, occurring in every continent except Antarctica. The taxonomy and phylogenetic relationships of Rorippa are still unsettled, largely due to complex morphological variations in Rorippa, which were caused by frequent hybridization events. Here, we sequenced four complete plastid genomes of Rorippa species by Illumina paired-end sequencing. The four new plastid genomes of Rorippa ranged in total size from 154,671 bp for R. palustris to 154,894 bp for R. sylvestris. There are 130 genes in the four plastomes, embodying 8 rRNA, 37 tRNA, and 85 protein-coding genes. Combining with six published plastid genomes, we carried on comparative and phylogenetic analyses. We found that the ten Rorippa plastid genomes were conservative in gene number and order, total size, genomic structure, codon usage, long repeat sequence, and SSR. Fourteen mutational hotspot regions could be selected as candidate DNA barcoding to distinguish Rorippa plants. The phylogenetic trees clearly identified that ten Rorippa species displayed monophyletic relationships within the tribe Cardamineae based on plastomes and nrDNA ITS sequences. However, there are significant cytonuclear discordances in the interspecific relationships within Rorippa, as well as the intergeneric relationships between Rorippa and its related genera. We inferred that the cytonuclear discordance is most likely a result of interspecific hybridization within Rorippa, as well as intergeneric hybridization with its related genera. These plastid genomes can offer precious information for studies of species authentication, evolutionary history, and the phylogeny of Rorippa.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Recognition and Utilization of Natural Genetic Resources for Advances in Plant Biology through Genomics and Biotechnology Volume II)
►▼
Show Figures
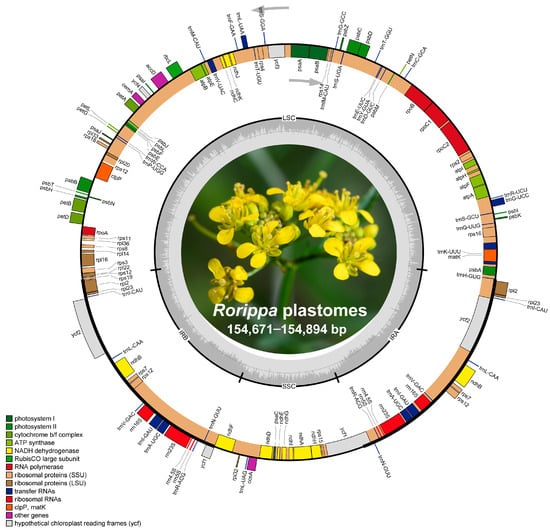
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Agronomic Biofortification of Fodder Maize (Zea mays L.) with Zn for Improving Herbage Productivity and Its Quality
by
Balwinder Kumar, Hari Ram and Jeff Schoenau
Agronomy 2024, 14(5), 912; https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14050912 (registering DOI) - 26 Apr 2024
Abstract
Zinc (Zn) deficiency in soils not only reduces the productivity of forage crops, but also results in inadequate dietary zinc intake for livestock. The objective of this study was to evaluate the impact of different rates and methods of applying ZnSO4 to
[...] Read more.
Zinc (Zn) deficiency in soils not only reduces the productivity of forage crops, but also results in inadequate dietary zinc intake for livestock. The objective of this study was to evaluate the impact of different rates and methods of applying ZnSO4 to both soil and foliage on the yield and quality of fodder maize grown in a sandy loam soil testing low in DTPA-extractable Zn. A 2-year field experiment was conducted with six treatments including control, foliar application of 0.3% ZnSO4 at 30 days after sowing (DAS) (F1), foliar application of 0.3% ZnSO4 at 30 and 40 DAS (F2), soil application of 16 kg ha−1 ZnSO4 (S16) and a combination of both soil and foliar ZnSO4 application (S16 + F1 and S16 + F2). Increase in green herbage yield by 25%, dry matter yield by 47% and Zn content by 79% was observed under S16 + F2 treatment over the control. Zinc application improved N, K, Cu and crude protein content of herbage significantly over the control. Thus, the study shows that significant improvement in growth parameters, herbage yield and quality of maize can be achieved with soil Zn application + two foliar sprays of ZnSO4 at 30 and 40 DAS, thereby ensuring availability of improved fodder Zn to the livestock.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Soil and Plant Nutrition)
►▼
Show Figures
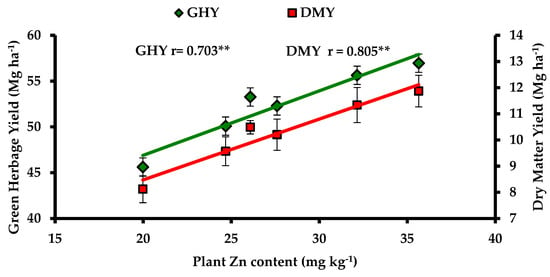
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Transcriptome Analysis and Validation of Anthracnose Resistance Genes in Walnut Varieties
by
Xiuzhen Li, Yuman Wang, Long Zhao, Wenxuan Ding, Sudan Chen, Xueqiang Li and Peijie Li
Agronomy 2024, 14(5), 911; https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14050911 (registering DOI) - 26 Apr 2024
Abstract
Anthracnose is extremely detrimental to walnut production, because it seriously affects its yield. Therefore, this study aimed to identify anthracnose resistance genes in walnuts, to lay the foundation for cultivating novel anthracnose-resistant walnut varieties. In this study, the fruits of walnut varieties “Qinyou
[...] Read more.
Anthracnose is extremely detrimental to walnut production, because it seriously affects its yield. Therefore, this study aimed to identify anthracnose resistance genes in walnuts, to lay the foundation for cultivating novel anthracnose-resistant walnut varieties. In this study, the fruits of walnut varieties “Qinyou 1” and “Qinyou 2”, exhibiting relatively weak resistance to anthracnose, were used for transcriptome sequencing and identifying differentially expressed genes (DEGs). Thereafter, we used a quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction to verify the reliability of the transcriptome data using the walnut varieties Qinyou 1, Qinyou 2, Qinyou 3, Liaohe 1, and Diamond 1. We identified 6326 DEGs post-infection in Qinyou 1, of which 3065 were upregulated and 3261 were downregulated. We also found 2055 DEGs (969 upregulated and 1086 downregulated genes) in the two varieties, after 6 days of anthracnose infection. Based on GO and KEGG enrichment analyses of the transcriptome data, we noted that the DEGs were primarily involved in metabolic processes, cell composition, cell structure, catalytic activity, and binding activity. Furthermore, KEGG functional enrichment analysis showed that the amino acid biosynthesis pathway and plant–pathogen interaction may be activated under anthracnose infection. We also noted that the expression levels of anthracnose resistance genes in different walnut varieties were significantly different. Thus, the findings of this study provide important genetic resources and molecular markers for the cultivation of novel anthracnose-resistant walnut varieties.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Crop Breeding and Genetics)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Detection of Gannan Navel Orange Ripeness in Natural Environment Based on YOLOv5-NMM
by
Binbin Zhou, Kaijun Wu and Ming Chen
Agronomy 2024, 14(5), 910; https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14050910 (registering DOI) - 26 Apr 2024
Abstract
In order to achieve fast and accurate detection of Gannan navel orange fruits with different ripeness levels in a natural environment under all-weather scenarios and then to realise automated harvesting of Gannan navel oranges, this paper proposes a YOLOv5-NMM (YOLOv5 with Navel orange
[...] Read more.
In order to achieve fast and accurate detection of Gannan navel orange fruits with different ripeness levels in a natural environment under all-weather scenarios and then to realise automated harvesting of Gannan navel oranges, this paper proposes a YOLOv5-NMM (YOLOv5 with Navel orange Measure Model) object detection model based on the improvement in the original YOLOv5 model. Based on the changes in the phenotypic characteristics of navel oranges and the Chinese national standard GB/T 21488-2008, the maturity of Gannan navel oranges is tested. And it addresses and improves the problems of occlusion, dense distribution, small target size, rainy days, and light changes in the detection of navel orange fruits. Firstly, a new detection head of 160 × 160 feature maps is constructed in the detection layer to improve the multi-scale target detection layer of YOLOv5 and to increase the detection accuracy of the different maturity levels of Gannan navel oranges of small sizes. Secondly, a convolutional block attention module is incorporated in its backbone layer to capture the correlations between features in different dimensions to improve the perceptual ability of the model. Then, the weighted bidirectional feature pyramid network structure is integrated into the Neck layer to improve the fusion efficiency of the network on the feature maps and reduce the amount of computation. Lastly, in order to reduce the loss of the target of the Gannan Navel Orange due to occlusion and overlapping, the detection frame is used to remove redundancy using the Soft-NMS algorithm to remove redundant candidate frames. The results show that the accuracy rate, recall rate, and average accuracy of the improved YOLOv5-NMM model are 93.2%, 89.6%, and 94.2%, respectively, and the number of parameters is only 7.2 M. Compared with the mainstream network models, such as Faster R-CNN, YOLOv3, the original model of YOLOv5, and YOLOv7-tiny, it is superior in terms of the accuracy rate, recall rate, and average accuracy mean, and also performs well in terms of the detection rate and memory occupation. This study shows that the YOLOv5-NMM model can effectively identify and detect the ripeness of Gannan navel oranges in natural environments, which provides an effective exploration of the automated harvesting of Gannan navel orange fruits.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Precision and Digital Agriculture)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessEditorial
Introduction to Special Issue on “The System of Rice Intensification (SRI)—Contributions to Agricultural Sustainability”
by
Norman Uphoff
Agronomy 2024, 14(5), 909; https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14050909 (registering DOI) - 26 Apr 2024
Abstract
The ideas and methods that constitute the System of Rice Intensification (SRI) were first synthesized in Madagascar by Henri de Laulanié in the early 1980s [...]
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue The System of Rice Intensification (SRI) Contributions to Agricultural Sustainability-II)
Open AccessArticle
Genome-Wide Identification and Analysis of Plasma Membrane H+-ATPases Associated with Waterlogging in Prunus persica (L.) Batsch
by
Yuyan Zhang, Qinsi Mao, Xin Guo, Ruijuan Ma, Mingliang Yu, Jianlan Xu and Shaolei Guo
Agronomy 2024, 14(5), 908; https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14050908 (registering DOI) - 26 Apr 2024
Abstract
Plant plasma membrane H+-ATPase is a transport protein that is generally located on the plasma membrane and generates energy by hydrolyzing adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to pump hydrogen ions (H+) in the cytoplasm out of the cell against a concentration
[...] Read more.
Plant plasma membrane H+-ATPase is a transport protein that is generally located on the plasma membrane and generates energy by hydrolyzing adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to pump hydrogen ions (H+) in the cytoplasm out of the cell against a concentration gradient. The plasma membrane H+-ATPases in plants are encoded by a multigene family and potentially play a fundamental role in regulating plant responses to various abiotic stresses, thus contributing to plant adaptation under adverse conditions. To understand the characteristics of the plasma membrane H+-ATPase family in peach (Prunus persica), this study analyzed the plasma membrane H+-ATPase family genes in peach. The results showed that there were 27 members of the plasma membrane H+-ATPase family in peach with amino acid sequences ranging from 943 to 1327. Subcellular localization showed that 23 of the 27 members were located on the cell membrane, and the phylogenetic tree analysis indicated that peach plasma membrane H+-ATPase members were divided into five groups. There were four genes with tandem repeat relationships, and six plasma membrane H+-ATPase genes were differentially expressed after 5 days of flooding and under non-flooding conditions based on the RNA-seq and RT-qPCR analyses. This study also investigated the characteristics and possible functions of the plasma membrane H+-ATPase family members in peach. The results provide theoretical support for further studies on their biological functions in peach.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Crop and Vegetable Physiology under Environmental Stresses)
►▼
Show Figures
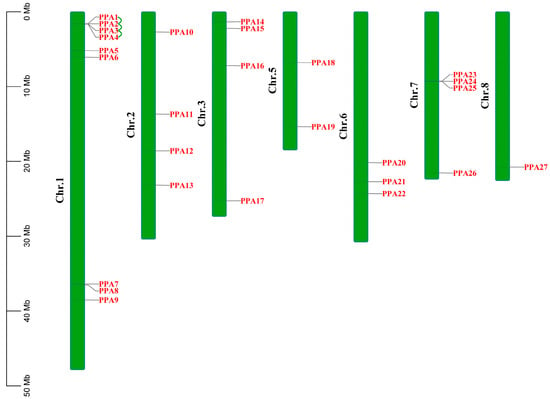
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Eastern Gamagrass Responds Inconsistently to Nitrogen Application in Long-Established Stands and within Diverse Ecotypes
by
James R. Kiniry, Amber S. Williams, Jacqueline Jacot, Sumin Kim and Merilynn C. Schantz
Agronomy 2024, 14(5), 907; https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14050907 (registering DOI) - 26 Apr 2024
Abstract
Eastern gamagrass (Tripsacum dactyloides) is a highly productive, highly palatable native grass tolerant to both drought and flooding. It has frequently shown great response to nitrogen (N) applications, but the responses of southern native ecotypes in upland and bottomland sites have
[...] Read more.
Eastern gamagrass (Tripsacum dactyloides) is a highly productive, highly palatable native grass tolerant to both drought and flooding. It has frequently shown great response to nitrogen (N) applications, but the responses of southern native ecotypes in upland and bottomland sites have yet to be reported. The objectives were to measure the responses of long-established eastern gamagrass with different N application rates in two bottomland hay pastures and two upland grazed sites, and to measure the N responses for six diverse ecotypes in a common garden. A randomized block design was used with ecotype as the main block and fertilizer rate as the subplot. In the long-established sites, 75 N peak yields were not statistically different to those of 0 N, while upland yields across the season were consistently higher for 150 N but varied for the bottomland. The common garden ecotypes had no significant difference in yield between treatments when averaged across years. Roaring Springs showed the most consistent and greatest benefit to additional N, more than doubling the dry weight of the control. All remaining ecotypes, however, had more modest responses. Eastern gamagrass responds inconsistently to applications of 75 N, whereas most applications of 150 N generally result in higher yield, though significant increases are not guaranteed.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue The Response of Grassland Ecosystem to Nutrient Additions)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Evaluation of the Best Management Practices for Reducing Phosphorus Load in a Watershed in Terms of Cost and Greenhouse Gas Emissions
by
Dae Seong Jeong, Joon Ha Kim, Jin Hwi Kim and Yongeun Park
Agronomy 2024, 14(5), 906; https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14050906 (registering DOI) - 26 Apr 2024
Abstract
Effective management of water quality in watersheds is crucial because it is directly linked to the sustainability of aquatic ecosystems. In conventional watershed management, best management practices (BMPs) have been instrumental in addressing deteriorating water quality issues caused by non-point source pollution. Greenhouse
[...] Read more.
Effective management of water quality in watersheds is crucial because it is directly linked to the sustainability of aquatic ecosystems. In conventional watershed management, best management practices (BMPs) have been instrumental in addressing deteriorating water quality issues caused by non-point source pollution. Greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions have emerged as a global concern, necessitating immediate and diverse environmental actions to mitigate their impacts. This study aims to explore BMPs that maximize total phosphorus (TP) load removal efficiencies, while minimizing costs and GHG emissions within watersheds, using the Soil and Water Assessment Tool (SWAT) and non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm III (NSGA-III). The Yeongsan River Watershed between 2012 and 2021 was selected as the study area. Hydrological and BMP data were analyzed. Applying identical BMPs to the watershed showed that the BMPs with high TP removal efficiency may not be effective in terms of cost and GHG emissions. Therefore, the optimal combination of BMPs for the Yeongsan River Watershed was determined using NSGA-III considering TP removal efficiency, cost, and GHG emissions. This study is the first to consider GHG emissions at the watershed level when applying BMPs and is expected to contribute to the development of BMP implementation incorporating GHG emissions.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Net-Zero Emissions for Sustainable Food Production and Land Management)
►▼
Show Figures
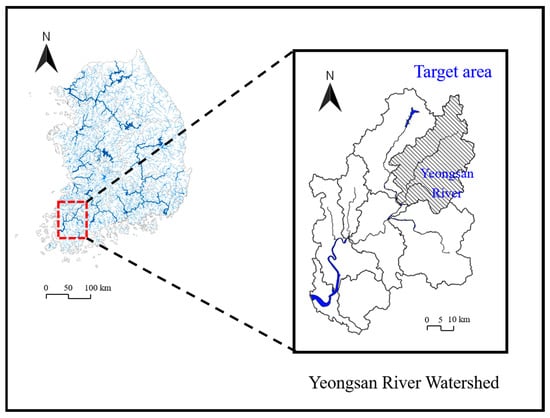
Figure 1
Open AccessCommunication
Comparative Analysis of Biodegradable Mulches on Soil Bacterial Community and Pepper Cultivation
by
Tuo Jin, Lin Li, Kewei Peng, Wei Li, Decai Jin, Wu Chen and Jianwei Peng
Agronomy 2024, 14(5), 905; https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14050905 (registering DOI) - 26 Apr 2024
Abstract
Biodegradable mulch films (BMFs) are becoming increasingly popular in agricultural practices. However, research on the ecological impact of biodegradable mulch films on pepper–soil systems is still scarce. To compare the differential effects of BMFs and polyethylene (PE) mulch on soil chemical properties, soil
[...] Read more.
Biodegradable mulch films (BMFs) are becoming increasingly popular in agricultural practices. However, research on the ecological impact of biodegradable mulch films on pepper–soil systems is still scarce. To compare the differential effects of BMFs and polyethylene (PE) mulch on soil chemical properties, soil bacterial community composition, and pepper cultivation, a study was conducted encompassing eight distinct treatments. These treatments included three varieties of polybutylene adipate terephthalate (PBAT) combined with polylactic acid (PLA) mulches: PP-JL, PP-SD, and PP-SH; a black polypropylene carbonate mulch (PPC-BK); a brown PPC mulch (PPC-BR); a polyethylene (PE) mulch; straw mulching (NCK); and an uncovered control (PCK). After applying mulches for 129 days, most PPC and PBAT + PLA films had reached the rupture phase, whereas the PE film was still in the induction phase. Pepper yield was obviously higher in all mulched treatments (4830 kg hm−1) than in the un-mulched control (3290 kg hm−1), especially the BMF PP-JL treatment, which showed the most notable improvements in yield. Although BMF treatments maintained a lower soil temperature than the PE film mulch, they were still higher than the un-mulched control. Furthermore, the soil bacterial community composition and ecological network were not markedly affected by different mulching conditions. However, the PP-SH treatment significantly increased the abundance of Pseudomonas, Nitrosomonas, and Streptomyces genera. Moreover, Lactobacillus and Gp16 were substantially more abundant in the PPC-black (BK) and PPC-brown (BR) treatments compared to the PE mulching treatment. This study could provide valuable insights into the ecological benefits of BMFs in pepper cultivation. However, as our experiments were conducted for only one season, it is imperative to undertake long-term experiments across consecutive seasons and years for a thorough understanding and comprehensive study.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue The Impact of Mulching on Crop Production and Farmland Environment)
►▼
Show Figures
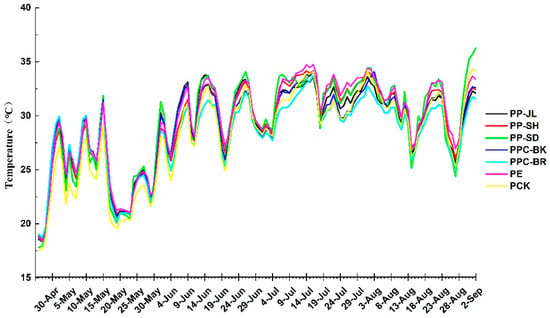
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Compatibility of Native Strains of Beauveria peruviensis and Metarhizium sp. as Strategy for Biological Control of Coffee Berry Borer (Hypothenemus hampei, Ferrari)
by
Manuel Oliva-Cruz, Jeisy M. Servan Bardales, Santos Triunfo Leiva-Espinoza, Carlos Oliva-Cruz, Lizette Daniana Mendez-Fasabi and Lily Juarez-Contreras
Agronomy 2024, 14(5), 904; https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14050904 (registering DOI) - 26 Apr 2024
Abstract
Coffee is a crop of global importance, and it is especially important in countries such as Peru. However, the presence of the pest Hypothenemus hampei represents a significant challenge with a notable economic impact. This study addresses this challenge using entomopathogenic fungi such
[...] Read more.
Coffee is a crop of global importance, and it is especially important in countries such as Peru. However, the presence of the pest Hypothenemus hampei represents a significant challenge with a notable economic impact. This study addresses this challenge using entomopathogenic fungi such as Beauveria peruviensis and Metarhizium sp. The compatibility of three strains of Beauveria peruviensis (F5, P19, and P4) and seven strains of Metarhizium sp. (MMR-M1, LLM-M2, MHR-M4, PMR-M12, MMR-M15, TOR-M16, and GOR-M18) was evaluated for approximately 2 months. A total of 14 treatments were designed, each consisting of one strain of B. peruviensis and one strain of Metarhizium sp. The Skott–Knott test (p ≤ 0.05) revealed that strain LLM-M2 (Metarhizium sp. strain) had the highest conidial production (3.75 × 107 conidia/mL). Except for T6 (MMR-M1/F5), which showed a mutual growth type interaction (type A), all other strain combinations showed a type B interaction (mutual inhibition by contact or separation between colony margins (<2 mm)). The combination with the highest germination rate was T10 (MHR-M4/F5) at 89%. In addition, the pathogenicity of the combined strains was evaluated, showing a direct correlation with mortality and mycosis development in the coffee berry borer in treatments T1 (PMR-M12/P19), T10 (MHR-M4/F5), and T11 (MMR-M15/P19), reaching 100% mortality at 72 h with grade 4 mycosis. Regarding mycelial growth, treatments T1 (PMR-M12/P19), T4 (MMR-M1/P19), and T12 (GOR-M18/P19) reached the highest percentages, between 85.8% and 83.10% at 240 h. This study demonstrates the feasibility of using native strains of B. peruviensis and Metarhizium sp. as a biocontrol strategy against the coffee berry borer in the Amazon department, presenting them as an alternative to traditional chemical methods.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Pest and Disease Management)
Open AccessArticle
Ultrasound-Assisted Alkaline Pretreatment of Biomass to Enhance the Extraction Yield of Valuable Chemicals
by
Adina I. Gavrila, Anamaria Vartolomei, Ioan Calinescu, Mircea Vinatoru, Oana C. Parvulescu, Grigore Psenovschi, Petre Chipurici and Adrian Trifan
Agronomy 2024, 14(5), 903; https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14050903 (registering DOI) - 26 Apr 2024
Abstract
As a renewable and sustainable resource, lignocellulosic biomass serves as a crucial raw material for the production of biofuels, biochemicals, and various value-added products. This paper aims to develop and optimize a mild alkaline treatment of sawdust assisted by ultrasound, along with enzymatic
[...] Read more.
As a renewable and sustainable resource, lignocellulosic biomass serves as a crucial raw material for the production of biofuels, biochemicals, and various value-added products. This paper aims to develop and optimize a mild alkaline treatment of sawdust assisted by ultrasound, along with enzymatic hydrolysis of the pretreated material. The alkaline sonochemical pretreatment emerged as the optimal approach to enhance the susceptibility of cellulose to subsequent enzymatic hydrolysis to improve the yield of reducing sugars. A comparative study was performed using various ultrasonic applicators (horn and bath) and conventional assisted alkaline pretreatment. The ultrasonic-assisted pretreatment revealed a higher delignification of 68% (horn) and 57% (bath) compared with conventional pretreatment. Processes were optimized using a statistical analysis based on a 23 factorial design. The ratios between sawdust and alkaline solution (RSL = 0.5–1.5 g/100 mL), US amplitude (A = 20–60%), and working temperature (t = 30–50 °C) were selected as process factors. The optimal operating conditions to maximize the reducing sugar yield (138.15 mg GE/gsubstrate) were found as follows: a solid/liquid ratio of RSL,opt = 1.25 g/100 mL, US amplitude of Aopt = 60%, and pretreatment temperature of topt = 50 °C. The overall outcomes clearly confirmed the intensification of delignification by ultrasound-assisted alkaline pretreatment.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Agricultural Biomass Waste Conversion into Value-Added Products)
►▼
Show Figures
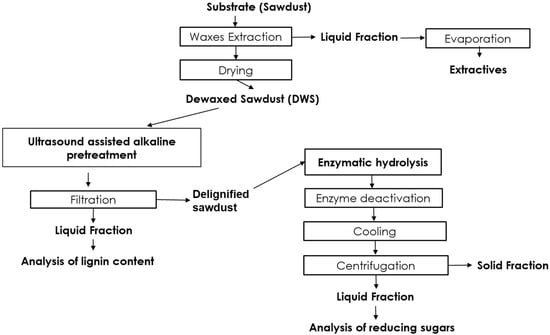
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Optimizing Crop Water Productivity in Greenhouse Pepper
by
Susana Zapata-García, Abdelmalek Temnani, Pablo Berríos, Pedro J. Espinosa, Claudia Monllor and Alejandro Pérez-Pastor
Agronomy 2024, 14(5), 902; https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14050902 (registering DOI) - 25 Apr 2024
Abstract
Although advanced production systems have been developed in the last 20 years, water scarcity is still a growing problem in agriculture. This study aims to evaluate the effect of different strategies that combine the application of seaweed and microbial biostimulants with regulated deficit
[...] Read more.
Although advanced production systems have been developed in the last 20 years, water scarcity is still a growing problem in agriculture. This study aims to evaluate the effect of different strategies that combine the application of seaweed and microbial biostimulants with regulated deficit irrigation (RDI) strategies on the irrigation water productivity (WPI), fruit quality parameters and soil enzymatic activity in pepper plants (Capsicum annum sp.) under two commercial greenhouse conditions. In each trial, two treatments were applied: (i) irrigation according to Farmer criteria without biostimulant applications and (ii) a combined treatment of RDI and the same biostimulation program, composed of Bacillus paralicheniformis and Ascophillum nodosum extracts. RDI was applied in different phenological stages in each greenhouse after the establishment until the 1st harvest in trial 1 or during the ripening and harvest period in trial 2. On average, the irrigation was reduced by 600 m3 ha−1 compared to the Farmer irrigation schedule. In both trials, biostimulation promoted an increase in fruit numbers, punctually in trial 1, leading to yield precocity, or generally in trial 2, obtaining a higher yield. Globally, WPI was increased when RDI was combined with biostimulation. This combined treatment also enhanced the root water absorption and improved the soil enzymatic activity in both greenhouses, suggesting that nutrients in the soil would become more available to plants. Thus, the combined action of biostimulation under different RDI strategies has been proved to be a useful strategy to improve agricultural sustainability.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Assessment and Mapping of Soil Water Balance)
Open AccessArticle
Assessment of Inter- and Intraspecific P Efficiency in Forage Legumes as Affected by Recycling Fertiliser
by
Yue Hu, Klaus J. Dehmer, Evelin Willner, Veysel Turan and Bettina Eichler-Löbermann
Agronomy 2024, 14(5), 901; https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14050901 (registering DOI) - 25 Apr 2024
Abstract
Legumes have a high demand for phosphorus (P) due to energetically costly biological nitrogen fixation, but they also have effective physiological and morphological strategies for P mobilization. To evaluate the inter- and intraspecific P efficiency of small-grain legumes supplied with different P recycling
[...] Read more.
Legumes have a high demand for phosphorus (P) due to energetically costly biological nitrogen fixation, but they also have effective physiological and morphological strategies for P mobilization. To evaluate the inter- and intraspecific P efficiency of small-grain legumes supplied with different P recycling fertilisers, eight accessions each of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) and red clover (Trifolium pratense L.) were cultivated in two pot experiments under greenhouse conditions until the flowering stage. To substantiate the results, some accessions were used in both experiments. Five treatments (no P, triple-superphosphate (TSP), sewage sludge ash (SSA), biowaste compost (compost), and struvite) were considered P sources. In addition to plant P uptake, the soil P pools were analysed in detail. Red clover showed higher yields and nutrient uptakes compared to alfalfa, but intraspecific effects were marginal. The addition of P resulted only partly in an increase in yield, despite the low P content in the soil. While struvite application clearly enhanced the P uptake of the plants in both experiments, SSA application had no effect compared to the control. The same treatment effect occurs with the bio-available soil P contents, which were on average 72.6 mg kg−1 after struvite and 44.3 mg kg−1 after SSA addition. Struvite as a P source was especially effective when applied to red clover. Our study aligns with previous field results and underscores the high potential of P mobilization of small-grain legumes without pronounced inter- or intraspecific differences. While struvite is suitable as a P fertiliser, the application of SSA to legumes is not recommended.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Application of Organic Amendments in Agricultural Production—Volume II)
Open AccessArticle
Simulation Model for Assessing High-Temperature Stress on Rice
by
Haoyang Zhou, Xianguan Chen, Minglu Li, Chunlin Shi and Min Jiang
Agronomy 2024, 14(5), 900; https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14050900 - 25 Apr 2024
Abstract
Rice is a staple grain crop extensively cultivated in Fujian Province, China. This study examined the impact of high-temperature stress on rice yield and its components, focusing on four representative rice varieties, including early and middle rice grown in Fujian Province. Results indicate
[...] Read more.
Rice is a staple grain crop extensively cultivated in Fujian Province, China. This study examined the impact of high-temperature stress on rice yield and its components, focusing on four representative rice varieties, including early and middle rice grown in Fujian Province. Results indicate significant yield losses, with the most severe reduction of 60.8% observed during the flowering stage of early rice and over 40% during the meiosis and flowering stages of middle rice. High-temperature stress primarily affects early rice yield more at the flowering stage than at the grain-filling stage, whereas in middle rice, it is more severe at the meiosis stage than at the flowering stage. Leveraging historical climatic data spanning the past 20 years, a simulation model for high-temperature stress on rice yield was developed to assess disaster-induced yield loss rates, aiming to enhance prevention and disaster damage assessment for rice under high-temperature stress. Application of the model to four rice planting sites in Fujian Province revealed contrasting temporal changes between loss rates and meteorological yield, with middle rice experiencing more severe damage than early rice. The model’s effectiveness is validated by the strong correspondence between yield loss rate and meteorological yield across different regions, highlighting its robust simulation capabilities.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Advances in Crop Simulation Modelling)

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Agronomy Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Society Collaborations
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Agronomy, Agriculture, Crops, Seeds
Advances in Industrial Crops Physioecology and Sustainable Cultivation
Topic Editors: Wei Hu, Zhiguo Zhou, Wenqing ZhaoDeadline: 30 April 2024
Topic in
Agronomy, Climate, Earth, Remote Sensing, Water
Advances in Crop Simulation Modelling
Topic Editors: Mavromatis Theodoros, Thomas Alexandridis, Vassilis AschonitisDeadline: 15 June 2024
Topic in
Agronomy, Beverages, Fermentation, Horticulturae, Plants
Grapevine Facing Climate Change: From Land, through Plants to Grapes and Wine
Topic Editors: Othmane Merah, Ana Fernandes De Oliveira, Daniela Satta, Mario Cunha, Jesus Yuste, Jalloul BouajilaDeadline: 30 June 2024
Topic in
Agronomy, Environments, Microorganisms, Pollutants, Sustainability, Water
Soil and Water Pollution Process and Remediation Technologies, 2nd Volume
Topic Editors: Hongbiao Cui, Ru Wang, Yu Shi, Haiying Lu, Lin ChenDeadline: 15 July 2024

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Agronomy
Fruits Crops Improvements in View of Marker Development, Genetic Diversity, Population Structure Traits Tagging and GWAS
Guest Editor: Manosh BiswasDeadline: 1 May 2024
Special Issue in
Agronomy
Mitigation of Ammonia and Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Livestock Systems
Guest Editors: David Fangueiro, José L. S. PereiraDeadline: 20 May 2024
Special Issue in
Agronomy
The Effects of Inoculation with Microorganisms on Plant Nutrition, Yield and Quality
Guest Editors: Marcelo Carvalho Minhoto Teixeira Filho, Mariangela HungriaDeadline: 30 May 2024
Special Issue in
Agronomy
Spatially-Based Services and Applications in Precision Farming: From Data to Field Information
Guest Editor: Enrico Corrado Borgogno MondinoDeadline: 20 June 2024
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Agronomy
Advances of Agricultural Robotics in Sustainable Agriculture 4.0
Collection Editors: Xiangjun Zou, Yunchao Tang, Junfeng Gao, Liang Gong, Simon van Mourik, Ya Xiong
Topical Collection in
Agronomy
Machine Learning in Digital Agriculture
Collection Editors: Ruhollah Taghizadeh-Mehrjardi, Thomas Scholten, Karsten Schmidt
Topical Collection in
Agronomy
A Series of Special Reviews and Topic Analyses That Explore Major Trends and Challenges in Agronomy
Collection Editors: Peter Langridge, Leslie A. Weston, Ilias Travlos
Topical Collection in
Agronomy
Agro-Ecology for Grassland-Based Farming Systems
Collection Editor: Gianni Bellocchi









