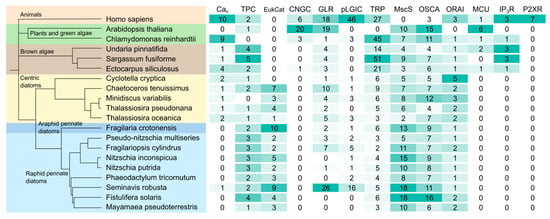
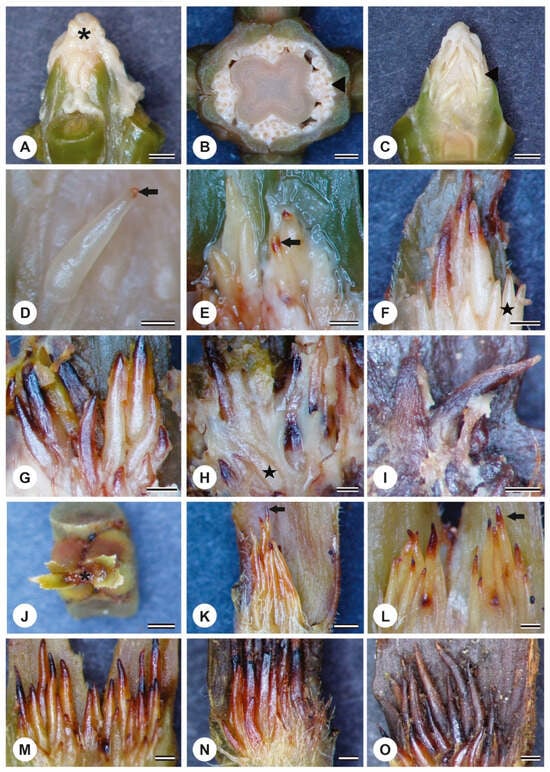
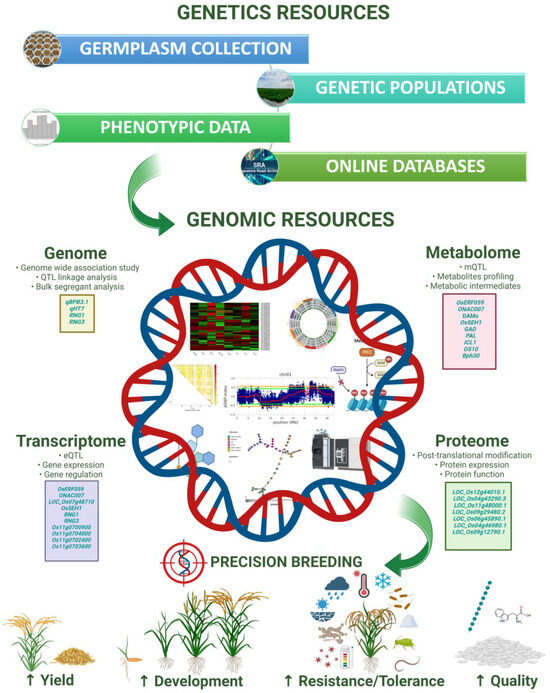
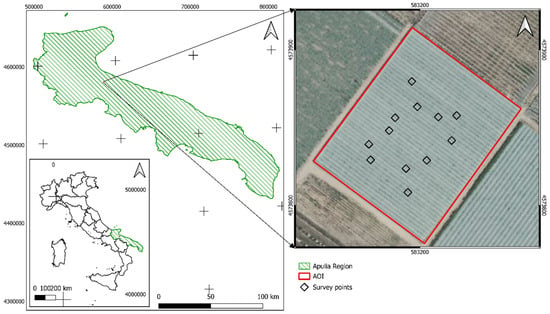
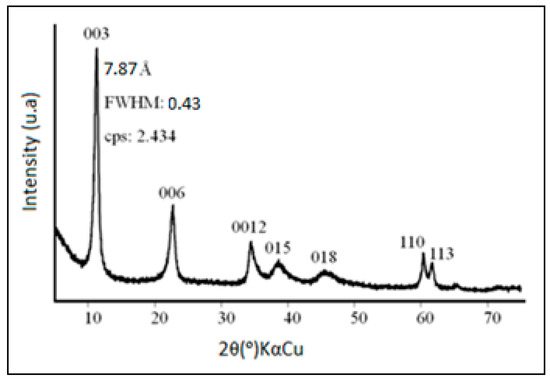
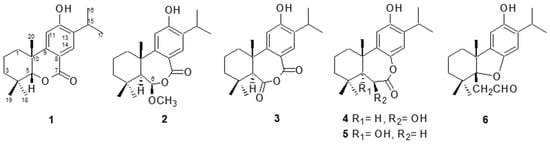
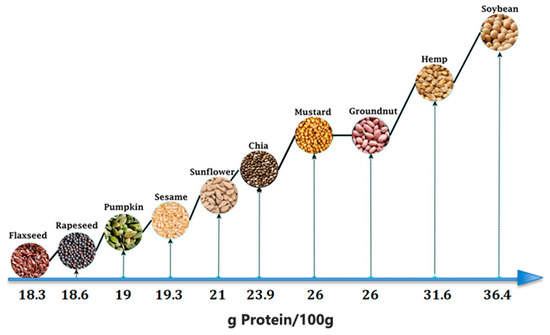
-
 Effects of Mars Global Simulant (MGS-1) on Growth and Physiology of Sweet Potato: A Space Model Plant
Effects of Mars Global Simulant (MGS-1) on Growth and Physiology of Sweet Potato: A Space Model Plant -
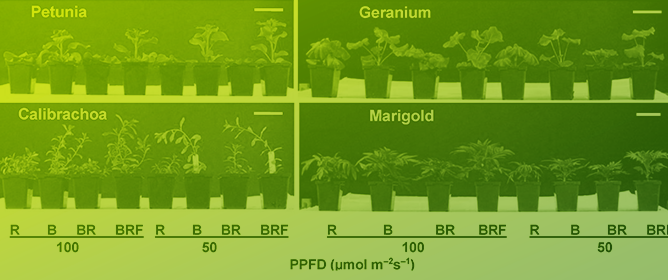 Magic Blue Light: A Versatile Mediator of Plant Elongation
Magic Blue Light: A Versatile Mediator of Plant Elongation -
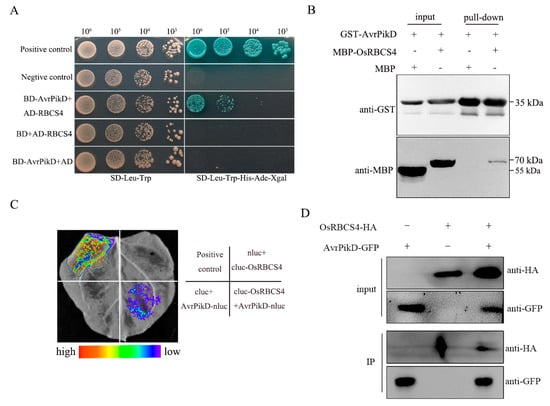
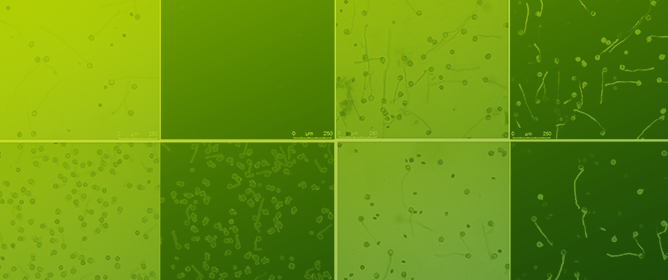 Calmodulin-Domain Protein Kinase PiCDPK1 Interacts with the 14-3-3-like Protein NtGF14 to Modulate Pollen Tube Growth
Calmodulin-Domain Protein Kinase PiCDPK1 Interacts with the 14-3-3-like Protein NtGF14 to Modulate Pollen Tube Growth -
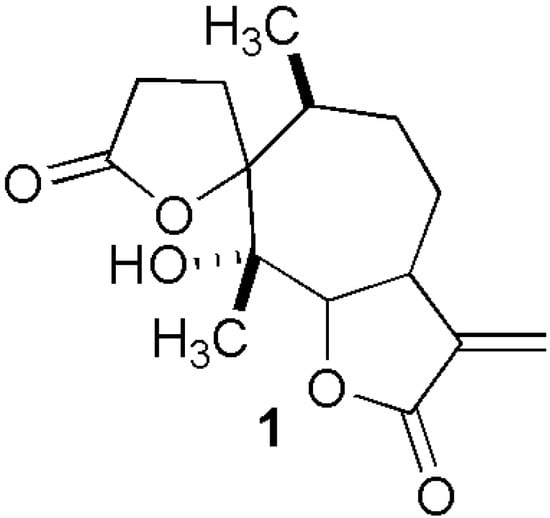
 Characterization of Almond Scion/Rootstock Communication in Cultivar and Rootstock Tissues through an RNA-Seq Approach
Characterization of Almond Scion/Rootstock Communication in Cultivar and Rootstock Tissues through an RNA-Seq Approach
Journal Description
Plants
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE (Web of Science), PubMed, PMC, PubAg, AGRIS, CAPlus / SciFinder, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q1 (Plant Sciences) / CiteScore - Q1 (Plant Science)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 15.3 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.8 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2023).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
Latest Articles
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Deadline: 30 April 2024
Deadline: 30 June 2024
Deadline: 31 July 2024
Deadline: 30 September 2024
Conferences
Special Issues
Deadline: 30 April 2024
Deadline: 25 May 2024
Deadline: 31 May 2024
Deadline: 20 June 2024