Journal Description
Environments
Environments
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on environmental sciences published monthly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, ESCI (Web of Science), PubAg, AGRIS, GeoRef, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: CiteScore - Q1 (Ecology, Evolution, Behavior and Systematics)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 23.7 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 3.7 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2023).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
- Testimonials: See what our editors and authors say about the Environments.
Impact Factor:
3.7 (2022);
5-Year Impact Factor:
3.6 (2022)
Latest Articles
Plant-Wide Models for Optimizing the Operation and Maintenance of BTEX-Contaminated Wastewater Treatment and Reuse
Environments 2024, 11(5), 88; https://doi.org/10.3390/environments11050088 (registering DOI) - 25 Apr 2024
Abstract
Benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene and xylenes, collectively known as BTEX compounds, are significant emerging contaminants in municipal wastewater. Stricter effluent quality regulations necessitate their removal, especially with concerns about organic micropollutant concentrations. Water scarcity further underscores the need for wastewater treatment to ensure safe
[...] Read more.
Benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene and xylenes, collectively known as BTEX compounds, are significant emerging contaminants in municipal wastewater. Stricter effluent quality regulations necessitate their removal, especially with concerns about organic micropollutant concentrations. Water scarcity further underscores the need for wastewater treatment to ensure safe agricultural or drinking water supplies. Although biological treatment partially reduces BTEX levels through processes like biodegradation and sorption, additional purification using physico-chemical methods is crucial for substantial reduction. This paper aims to outline plant-wide simulation methods for treating BTEX-contaminated sewage and facilitating reuse, adhering to IWA Good Modelling Practice Guidelines. The model, built upon the MiniSumo process model, incorporates equations detailing BTEX metabolism and removal kinetics, informed by an extensive literature review. Using a variant of the Benchmark Simulation Model with granular activated carbon for water reuse, the study examines strategies for improving effluent quality and minimizing operational costs. These strategies include adjusting the sludge retention time and airflow to enhance BTEX degradation and stripping, respectively, and comparing maintenance approaches for the GAC tower.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advanced Technologies of Water and Wastewater Treatment)
Open AccessArticle
Analysing the Evidence of the Effects of Climate Change, Air Pollutants, and Occupational Factors in the Appearance of Cataracts
by
Lucía Echevarría-Lucas, José Mª Senciales-González and Jesús Rodrigo-Comino
Environments 2024, 11(5), 87; https://doi.org/10.3390/environments11050087 - 24 Apr 2024
Abstract
Cataracts are ocular conditions characterized by the opacification of the natural lens within the eye, which develops gradually over time and can affect one or both eyes. This condition commonly results from age-related changes in the lens, but can also arise from various
[...] Read more.
Cataracts are ocular conditions characterized by the opacification of the natural lens within the eye, which develops gradually over time and can affect one or both eyes. This condition commonly results from age-related changes in the lens, but can also arise from various factors. Cataract surgeries are expensive, particularly in states such as Spain, where they receive full support from the Spanish social welfare system. Despite a significant body of research on cataracts, few studies address the social and environmental factors triggering their development or consider the spatiotemporal evolution of their impacts. We analysed the incidence of cataracts in a southern region of Spain, differentiating between senile cataracts (those over 60 years old) and early cataracts (those between 15 and 59 years old). Twenty-one socio-economic, climate, and air pollution variables were statistically analysed using bivariate correlation, cluster analysis, and Geographic Information Systems. Eleven years of observation show a decadal increase in annually averaged maximum temperature and a decrease in annual precipitation, partially explaining the rising incidence of operable cataracts in the following year (r = 0.77 and −0.84, respectively; p < 0.05). Furthermore, early cataracts responded spatially to % agricultural employment (r = 0.85; p < 0.05) and moderately to maximum temperatures, insolation, and various constituents.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Air Quality, Health and Climate)
►▼
Show Figures
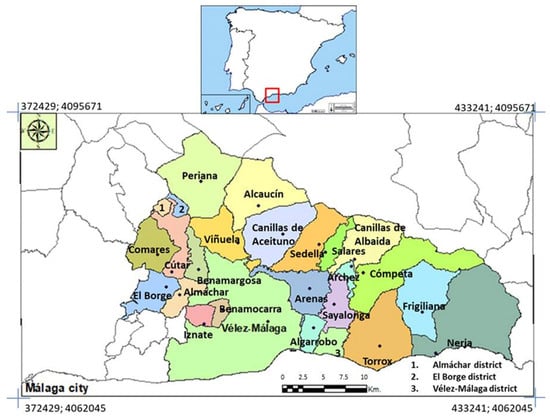
Figure 1
Open AccessOpinion
Challenges in Restoring Mediterranean Seagrass Ecosystems in the Anthropocene
by
Monica Montefalcone
Environments 2024, 11(5), 86; https://doi.org/10.3390/environments11050086 - 23 Apr 2024
Abstract
The intense human pressures in the Anthropocene epoch are causing an alarming decline in marine coastal ecosystems and an unprecedented loss of biodiversity. This situation underscores the urgency of making ecological restoration a global priority to recover degraded ecosystems. Meadows of the endemic
[...] Read more.
The intense human pressures in the Anthropocene epoch are causing an alarming decline in marine coastal ecosystems and an unprecedented loss of biodiversity. This situation underscores the urgency of making ecological restoration a global priority to recover degraded ecosystems. Meadows of the endemic Mediterranean seagrass Posidonia oceanica have lost more than half of their original extent in the last century, necessitating immediate conservation and management measures, supported by active restoration interventions. This paper explores new opportunities and provides specific recommendations to enhance restoration as a fundamental strategy for reversing the decline of P. oceanica ecosystems in the Mediterranean Sea. When a return to a historical pristine reference condition may not be feasible in the short term or desirable given current environmental conditions and uncertainty, transplanting the tolerant and fast-growing seagrass species Cymodocea nodosa could facilitate natural recolonization. This would occur through secondary ecological succession, benefiting the sensitive and slow-growing species P. oceanica. Future global and local efforts should primarily focus on proactive management to prevent further alterations by planning appropriate conservation measures in a timely manner to mitigate and reverse global changes. As a secondary step, restoration programs can be implemented with a focus on ‘target-oriented’ rather than ‘reference-oriented’ conditions, aiming to establish ecosystems capable of sustaining the future rather than replicating the historical environment.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Ecological Restoration in Marine Environments)
Open AccessArticle
Detection of Emerging Stress in Trees Using Hyperspectral Indices as Classification Features
by
Laura M. Moley, Douglas G. Goodin and William P. Winslow III
Environments 2024, 11(4), 85; https://doi.org/10.3390/environments11040085 - 22 Apr 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This research presents a classification methodology for the detection of new or emerging stress in trees using indices derived from hyperspectral data and tests whether existing hyperspectral indices are effective when used as the classification features for this problem. We tested six existing
[...] Read more.
This research presents a classification methodology for the detection of new or emerging stress in trees using indices derived from hyperspectral data and tests whether existing hyperspectral indices are effective when used as the classification features for this problem. We tested six existing indices—Water Band Index (WBI), Gitelson–Merzlyak B Index (GMb), Normalized Phaeophytization Index (NPQI), Combined Carotenoid/Chlorophyll Ratio Index (CCRI), Photochemical Reflectance Index (PRI), and Red-Edge Chlorophyll Index (CIre)—along with a seventh Test Index—generated as a composite of PRI and Cire—as classification features. Analysis was conducted using data collected from trees with and without emerald ash borer (EAB) infestation to develop a methodology that could be adapted to measure emerging stress from other pathogens or invasive pests in other tree species. Previous work has focused specifically on the identification of damage or stress symptoms caused by a specific pathogen. In this study, we adapted that work to develop a system of classification that can be applied to the identification of stress symptoms from a range of sources, measurable in trees based on spectral response and, in some cases, detectable prior to the onset of visible symptoms that can be measured through human observation. Our data indicate that existing indices derived from hyperspectral data are effective as classification features when measuring spectral responses indicative of emerging stress in trees.
Full article
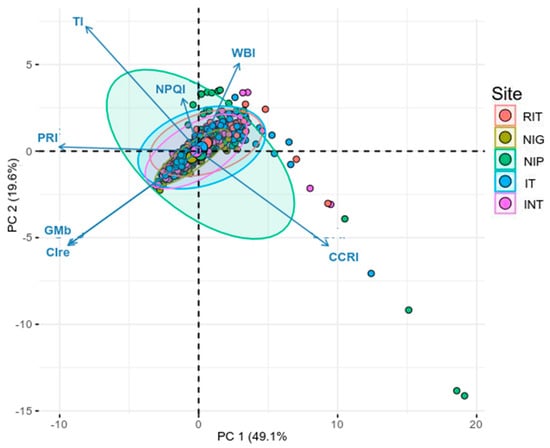
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Cold Ironing and the Study of RES Utilization for Maritime Electrification on Lesvos Island Port
by
Alexandros Kelmalis, Andreas Dimou, Demetris Francis Lekkas and Stergios Vakalis
Environments 2024, 11(4), 84; https://doi.org/10.3390/environments11040084 - 19 Apr 2024
Abstract
The maritime industry is addressing environmental issues, and “cold ironing” offers a promising solution. This method involves supplying ships at port with energy, reducing fossil fuel dependence and emissions, and aiding in global climate change efforts. It is especially important for islands like
[...] Read more.
The maritime industry is addressing environmental issues, and “cold ironing” offers a promising solution. This method involves supplying ships at port with energy, reducing fossil fuel dependence and emissions, and aiding in global climate change efforts. It is especially important for islands like Lesvos, which suffer from high energy costs and environmental issues due to imported fossil fuel reliance. However, research gaps exist in using renewable energy sources (RES) for cold ironing, mainly due to insufficient data on power needs and lack of monitoring for precise calculations and the very limited applications for the case of non-interconnected islands. This study uses real data from the port of Lesvos to evaluate power requirements for cold ironing and assesses the viability of a wind power park for an electrified port with the novelty and uniqueness of developing the application on a non-interconnected island. It also examines potential CO2 emission reductions. Data from Marine Traffic S.A. were used, considering factors like ship arrivals, hoteling duration, and engine types. This study also includes a simulation using RETScreen software for a 20 MW wind park intended for port operations. The findings show that the monthly energy demand at Mytilene port is around 6118 MWh, with an average power demand of 8.2 MW. The simulated wind park could supply about 72,080 MWh yearly, with a significant surplus (14,956 MWh annually) exportable to the grid. However, demand fluctuations mean the port might need an extra 924 MWh from the main grid. This underscores the need for additional strategies like energy storage and demand–response practices to fully transition to 100% RES-powered operations.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Environmental Science and Technologies for the Management of Natural Ecosystems and the Sustainable Development of Urban Areas II)
►▼
Show Figures
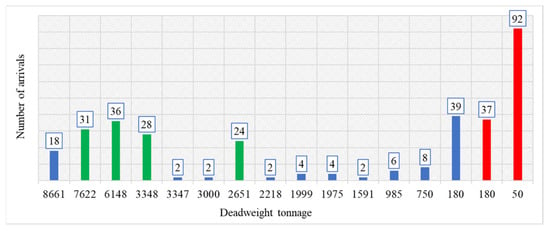
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Anthropogenic Microparticles Abundance in Sandy Beach Sediments along the Tetouan Coast (Morocco Mediterranean)
by
Assia Bouzekry, Bilal Mghili, Monique Mancuso, Oumayma Bouadil, Teresa Bottari and Mustapha Aksissou
Environments 2024, 11(4), 83; https://doi.org/10.3390/environments11040083 - 19 Apr 2024
Abstract
Despite the widespread presence of anthropogenic microparticles (AMs) in beach sediments, research on their occurrence on Moroccan Mediterranean beaches is still limited. This study is the first report on AM pollution in four sandy beaches along the Tetouan coast (Morocco Mediterranean). The findings
[...] Read more.
Despite the widespread presence of anthropogenic microparticles (AMs) in beach sediments, research on their occurrence on Moroccan Mediterranean beaches is still limited. This study is the first report on AM pollution in four sandy beaches along the Tetouan coast (Morocco Mediterranean). The findings reveal an average AM concentration of 483.12 ± 157.04 AMs/kg of beach sediment. The most common AM types were fibers (75.54%) and fragments (24.06%). AMs were predominantly black, red, and blue, measuring between 0.1 and 1 mm. The evaluation of the anthropogenic microparticles pollution index (AMPI) and the coefficient of anthropogenic microparticles impact (CAMI) for the study area indicated a “very high abundance” of AMs and an “extreme” level of impact. The polymers identified in these areas included PS, PE, PP, and PET. Tourism, fishing, domestic activities, and poor solid waste management practices are the primary sources of AM pollution in this region. To protect Moroccan beaches, the implementation of a consistent plastic waste management strategy is recommended.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Transport, Distribution and Composition of Floating Macro and Micro-Litter in the Marine Environment)
►▼
Show Figures
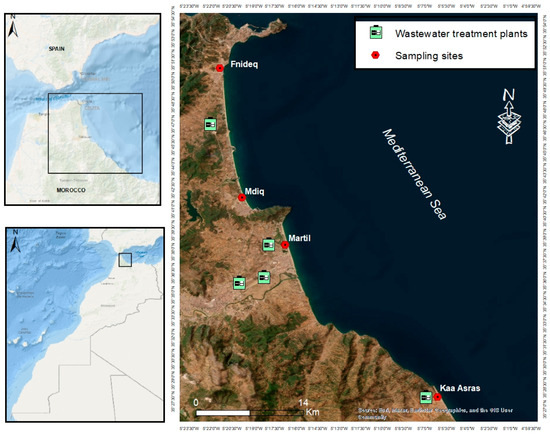
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
ClimateDT: A Global Scale-Free Dynamic Downscaling Portal for Historic and Future Climate Data
by
Maurizio Marchi, Gabriele Bucci, Paolo Iovieno and Duncan Ray
Environments 2024, 11(4), 82; https://doi.org/10.3390/environments11040082 - 17 Apr 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Statistical downscaling of climate data has been widely described in the literature, with the aim of improving the reliability of local climatic parameters from coarse-resolution (often >20 km) global datasets. In this article, we present ClimateDT, a dynamic downscaling web tool for monthly
[...] Read more.
Statistical downscaling of climate data has been widely described in the literature, with the aim of improving the reliability of local climatic parameters from coarse-resolution (often >20 km) global datasets. In this article, we present ClimateDT, a dynamic downscaling web tool for monthly historical and future time series at a global scale. The core of ClimateDT is the 1 km 1981–2010 climatology from CHELSA Climate (version 2.1), where the CRU-TS layers for the period 1901-current are overlayed to generate a historic time series. ClimateDT also provides future scenarios from CMIP5 using UKCP18 projections (rcp2.6 and rcp8.5) and CMIP6 using 5 GCMs, also available on the CHELSA website. The system can downscale the grids using a dynamic approach (scale-free) by computing a local environmental lapse rate for each location as an adjustment for spatial interpolation. Local predictions of temperature and precipitation obtained by ClimateDT were compared with climate time series assembled from 12,000 meteorological stations, and the Mean Absolute Error (MAE) and the explained variance (R2) were used as indicators of performance. The average MAEs for monthly values on the whole temporal scale (1901–2022) were around 1.26 °C for the maximum monthly temperature, 0.80 °C for the average monthly temperature, and 1.32 °C for the minimum monthly temperature. Regarding monthly total precipitation, the average MAE was 19 mm. As for the proportion of variance explained, average R2 values were always greater than 0.95 for temperatures and around 0.70 for precipitation due to the different degrees of temporal autocorrelation of precipitation data across time and space, which makes the estimation more complex. The elevation adjustment resulted in very accurate estimates in mountainous regions and areas with complex topography and substantially improved the local climatic parameter estimations in the downscaling process. Since its first release in November 2022, more than 1300 submissions have been processed. It takes less than 2 min to calculate 45 locations and around 8 min for the full dataset (512 records).
Full article
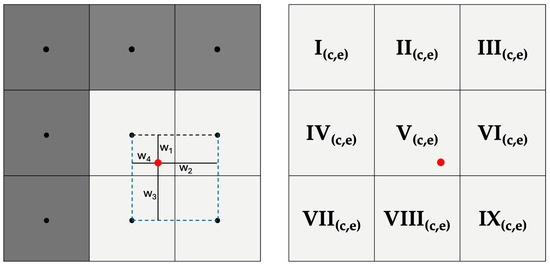
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Water Reuse: A Comprehensive Review
by
Fivos Florides, Maria Giannakoudi, Giorgos Ioannou, Despoina Lazaridou, Elissavet Lamprinidou, Nikolaos Loukoutos, Maria Spyridou, Eleftherios Tosounidis, Maria Xanthopoulou and Ioannis A. Katsoyiannis
Environments 2024, 11(4), 81; https://doi.org/10.3390/environments11040081 - 13 Apr 2024
Abstract
Water scarcity has emerged as a pressing global concern, driven by population growth, urbanization, and climate change. As freshwater resources dwindle, the imperative for water reuse becomes increasingly apparent. Reusing water presents a sustainable solution to mitigate scarcity, offering a way to maximize
[...] Read more.
Water scarcity has emerged as a pressing global concern, driven by population growth, urbanization, and climate change. As freshwater resources dwindle, the imperative for water reuse becomes increasingly apparent. Reusing water presents a sustainable solution to mitigate scarcity, offering a way to maximize the efficiency of available resources. This review delves into the multifaceted landscape of water consumption and reuse, aiming to provide a comprehensive analysis and understanding of this critical issue. It explores the diverse implications of unregulated water consumption, spanning from its impacts on household routines to its profound influence on economic activities. Additionally, it scrutinizes the legislative framework surrounding water usage, shedding light on the policies and regulations in place. Furthermore, the review investigates the current status of water reuse practices in Europe, delving into various methods of water recovery. Finally, it examines public perceptions and attitudes toward recycled water, offering insights into the societal outlook on this increasingly vital aspect of water management.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advanced Technologies of Water and Wastewater Treatment)
►▼
Show Figures
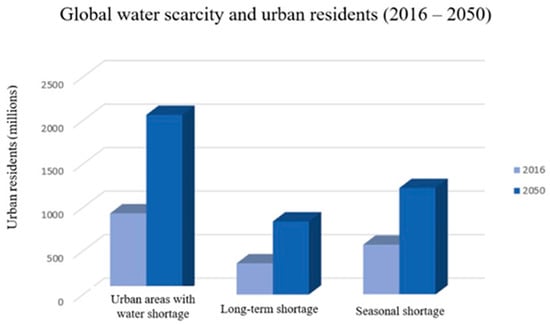
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Evaluating Wastewater Quality Parameters as an Alternative or Complement to Molecular Indicators for Normalization during SARS-CoV-2 Wastewater-Based Epidemiology
by
Judith Straathof and Natalie M. Hull
Environments 2024, 11(4), 80; https://doi.org/10.3390/environments11040080 - 12 Apr 2024
Abstract
Measuring fecal nucleic acid indicators for data normalization can increase costs during wastewater-based epidemiology (WBE). The efficacy of routinely assayed water quality parameters was assessed as an alternative or complement to fecal nucleic acid viral indicator data for their utility in adjusting measured
[...] Read more.
Measuring fecal nucleic acid indicators for data normalization can increase costs during wastewater-based epidemiology (WBE). The efficacy of routinely assayed water quality parameters was assessed as an alternative or complement to fecal nucleic acid viral indicator data for their utility in adjusting measured SARS-CoV-2 gene concentrations to improve the relationship between wastewater molecular data and clinical COVID-19 case data. This research covers two study designs: grab samples collected from sewers serving The Ohio State University campus and composite influent samples collected at five wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) across the state of Ohio. Weekly mandatory clinical testing was used to monitor infections in the student population, and statewide cases were reported through voluntary clinical testing. Statewide WWTP results showed significant strong correlation between SARS-CoV-2 concentrations in the wastewater and confirmed COVID-19 cases, and correlation increased when normalized by flow and additionally increased when normalized by pH, total suspended solids, and temperature, but correlation decreased when normalized by a nucleic acid fecal viral indicator (PMMoV). On campus, correlations were generally not significant unless normalized by PMMoV and/or UV absorbance parameters. Because water quality parameters are routinely assayed at wastewater treatment plants and some may be collected by autosamplers, incorporating wastewater quality data may improve WBE models and could minimize molecular and cellular testing for fecal indicators to decrease costs.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Wastewater-Based Epidemiology Assessment)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Health Benefits of Airborne Terpenoids and Aeroanions: Insights from Thematic Review of Chinese-Language Research on Forest Sensory Experiences
by
Ralf Buckley, Linsheng Zhong, Hu Yu, Dongfang Zhu and Mary-Ann Cooper
Environments 2024, 11(4), 79; https://doi.org/10.3390/environments11040079 - 11 Apr 2024
Abstract
Most research on air chemistry and human health has focused on negative consequences of air pollution from cities, rural dust, mining, or industrial sites. Research on nature tourism and nature therapy, in contrast, focuses on positive benefits of air quality for physical and
[...] Read more.
Most research on air chemistry and human health has focused on negative consequences of air pollution from cities, rural dust, mining, or industrial sites. Research on nature tourism and nature therapy, in contrast, focuses on positive benefits of air quality for physical and mental health, e.g., via “clean air clean water” holidays. Aeroanions and terpenoids in forests have received particular attention, especially in China, Japan, and Korea. We review and analyse several hundred articles published in English and Chinese. With a few recent exceptions, English-language research has tested indoor negative ion generators, and concluded that they have no measurable health benefit. It has tested terpenoids in indoor aroma marketing. Chinese-language research, in contrast, has analysed fine-scale components of outdoor environments that affect concentrations of aeroanions and terpenoids: ecosystem, latitude, altitude, temperature, proximity to water, and individual plant species. Historically, health outcomes have been taken for granted, with little rigorous testing. Air quality research has shown that aeroanions can become attached to fine water droplets, e.g., after rain in forests, or in mists produced locally by waterfalls. We hypothesise that the health benefits of aeroanions in natural environments may arise through the scavenging of airborne particulates by negatively charged mists, creating especially clean, dust-free air. We propose that this particularly clean-tasting air, contrasting strongly with polluted urban air, creates positive effects on human mental health and perhaps, also on pulmonary physical health. Mechanisms and outcomes remain to be tested. We also propose testing psychological health effects of airborne terpenoid scents from forest trees.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Air Quality, Health and Climate)
►▼
Show Figures
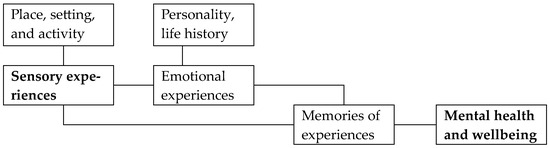
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
The Origin of Phthalates in Algae: Biosynthesis and Environmental Bioaccumulation
by
Andrea Pace, Alessandro Vaglica, Antonella Maccotta and Dario Savoca
Environments 2024, 11(4), 78; https://doi.org/10.3390/environments11040078 - 11 Apr 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Phthalic acid esters (PAEs) are a class of ubiquitous and dangerous lipophilic chemicals widely used as additives in various products to improve their physical and chemical properties. Although they have been banned in many countries, their persistence in all environmental compartments is of
[...] Read more.
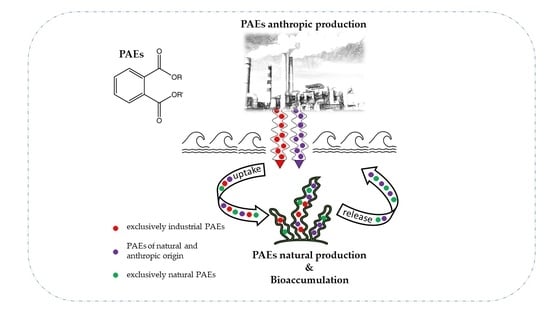
Phthalic acid esters (PAEs) are a class of ubiquitous and dangerous lipophilic chemicals widely used as additives in various products to improve their physical and chemical properties. Although they have been banned in many countries, their persistence in all environmental compartments is of particular concern. The aquatic environment is especially affected by these compounds because it is strongly influenced both by contamination of anthropic origin and natural contaminants including those produced biosynthetically by some organisms such as algae. In this context, algal organisms can be a source and remedy for phthalate pollution. Both the increase and decrease in uptake and production depend on the physicochemical characteristics of the environment. The dynamics of the natural processes are aimed at achieving an optimal environmental state for their competitiveness and balance of the cellular homeostasis. This review summarizes the studies dealing with biosynthesis and bioaccumulation of phthalates in algae and investigates the source of their origin by suggesting strategies to identify the process leading to their presence.
Full article
Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Heavy Metal Accumulation in Three Varieties of Mustard Grown under Five Soil Management Practices
by
Anjan Nepal, George F. Antonious, Frederick N. Bebe, Thomas C. Webster, Buddhi R. Gyawali and Basanta Neupane
Environments 2024, 11(4), 77; https://doi.org/10.3390/environments11040077 - 11 Apr 2024
Abstract
Heavy metal pollution represents a global health issue. Different methods and technologies are adopted to mitigate the problem of heavy metal pollution. Phytoremediation has been gaining attention as an environmentally friendly method to remediate this problem. The purpose of this research is to
[...] Read more.
Heavy metal pollution represents a global health issue. Different methods and technologies are adopted to mitigate the problem of heavy metal pollution. Phytoremediation has been gaining attention as an environmentally friendly method to remediate this problem. The purpose of this research is to explore the effectiveness of phytoremediation in agricultural settings to assess the effect of five soil management practices (chicken manure, sewage sludge, leaf compost, cow manure, and vermicompost) on Cd, Cu, Mo, Ni, Pb, and Zn accumulation in the mustard (leaves and pods) of three mustard Brassica juncea varieties (black mustard, yellow mustard, and mighty mustard). The accumulation in mustard was quantified using the Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectrometer (ICP-OES). The results showed that the bioaccumulation factor (BAF) of the three mustard varieties exceeded one (BAF > 1) for Cd and Mo. It indicates that mustard is a good accumulator of Cd and Mo, whereas BAF values for Cu, Pb, Ni, and Zn were less than one (BAF < 1). The accumulated Cu, Mo, Ni, and Zn levels were below the allowable limit, whereas the Cd and Pb levels were beyond the limit. This result indicates that the investigated mustard varieties can be grown on heavy metal polluted sites for Cd and Mo phytoremediation purposes, but care is needed with regard to Cd and Mo toxicity.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Soil and Water Pollution Process and Remediation Technologies, 2nd Volume)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Assessing Ecological Gains: A Review of How Arthropods, Bats and Birds Benefit from Green Roofs and Walls
by
Patrícia Tiago, Ana I. Leal and Cristina Matos Silva
Environments 2024, 11(4), 76; https://doi.org/10.3390/environments11040076 - 10 Apr 2024
Abstract
Because of the immense amount of infrastructure in cities, the introduction of vegetation into these constructions is expected to play a critical role in reducing the heat island effect, in mitigating the effects of climate change, and in supporting habitat connectivity and associated
[...] Read more.
Because of the immense amount of infrastructure in cities, the introduction of vegetation into these constructions is expected to play a critical role in reducing the heat island effect, in mitigating the effects of climate change, and in supporting habitat connectivity and associated biodiversity. Although there is the perception that these solutions can improve the biodiversity of cities, their real value is still unclear. This paper focuses on two aspects of urban greening: green roofs and green walls. It provides a systematic review on biodiversity present in green roofs and walls, through an exhaustive worldwide literature analysis. Arthropods, bats, and birds were the three taxonomic groups analyzed in the papers included in our review. We observed a strong increase in the number of recent publications, thus demonstrating a growing interest in this topic. In summary, we found that green roofs/walls offered additional opportunities for plants and animals to thrive in urban environments because of habitat creation and greater spatial connectivity. In addition, the enhancement of other ecosystem services such as stormwater management and heat island mitigation was noted. By incorporating green features into urban design and planning, cities can support biodiversity while also improving the overall sustainability and livability of urban spaces.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Collection Trends and Innovations in Environmental Impact Assessment)
►▼
Show Figures
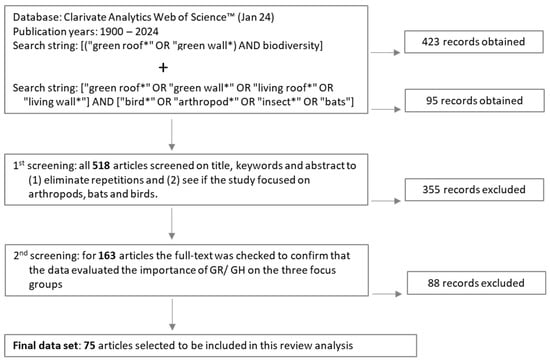
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Dynamics of the Concentration and Speciation of Arsenic in Private Drinking Water Wells in Eastern Wisconsin, USA
by
Evvan Plank, Yin Wang and Shangping Xu
Environments 2024, 11(4), 75; https://doi.org/10.3390/environments11040075 - 09 Apr 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
About 2.5 billion people rely on groundwater as their main drinking water source, and arsenic pollution within the groundwater system can cause serious short- and long-term health issues. Within the natural environment, arsenic generally exists as oxyanions which have two oxidation states, As(III)
[...] Read more.
About 2.5 billion people rely on groundwater as their main drinking water source, and arsenic pollution within the groundwater system can cause serious short- and long-term health issues. Within the natural environment, arsenic generally exists as oxyanions which have two oxidation states, As(III) and As(V). Under ambient pH conditions, As(V) is primarily present as an anion (i.e., H2AsO4−) while As(III) tends to be uncharged (i.e., H3AsO3), making it much more difficult to remove As(III) through existing treatment techniques such as adsorption and reverse osmosis (RO). In Eastern Wisconsin, the dolomite and dolomite/sandstone aquifers represent a major drinking water source and high arsenic concentrations have been observed. Previous studies showed that arsenic can be released into private drinking water wells due to the oxidation of sulfide-bearing minerals with arsenic impurities that are usually dispersed within the dolomite and sandstone bedrock. However, there is a lack of information on the concentrations of each arsenic species as well as arsenic dynamics during water pumping/usage. The primary goals of this research were (1) to quantify the baseline concentrations of each arsenic species within selected Eastern Wisconsin private drinking water wells, and (2) to determine how the arsenic concentrations and species could be affected by continuous water usage. Our results showed that As(III) was the dominant species of arsenic, and during continuous water usage, there could be an upward trend in arsenic concentration (there was minimal change in arsenic speciation). Upon the completion of water pumping, arsenic concentrations decreased over time and returned to pre-pumping levels. Our findings highlighted the importance of quantifying the speciation and dynamics of arsenic during water use to the assessment of public health risks and the design of appropriate water treatment techniques.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Effects of Sampling Time and Depth on Phytoplankton Metrics in Agricultural Irrigation Ponds
by
Jaclyn E. Smith, Jennifer L. Wolny, Matthew D. Stocker and Yakov Pachepsky
Environments 2024, 11(4), 74; https://doi.org/10.3390/environments11040074 - 04 Apr 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Spatiotemporal variations of phytoplankton populations in agricultural irrigation ponds need to be accounted for in order to properly assess water quality. Phytoplankton cell and photosynthetic pigment concentrations are two common metrics used to characterize phytoplankton communities. This work evaluated depth and time of
[...] Read more.
Spatiotemporal variations of phytoplankton populations in agricultural irrigation ponds need to be accounted for in order to properly assess water quality. Phytoplankton cell and photosynthetic pigment concentrations are two common metrics used to characterize phytoplankton communities. This work evaluated depth and time of the day as factors affecting discrete sampling of phytoplankton. The abundance of chlorophytes, diatoms, cyanobacteria, flagellates, and dinoflagellates, as well as chlorophyll-a and phycocyanin pigments, were determined in samples taken at the surface and depth, in 0.5 m increments, in three to five spatial replications at 9 a.m., 12 p.m., and 3 p.m. in two ponds in Maryland, USA. Depth was a significant factor for photosynthetic pigment concentration variations in both ponds on most sampling dates and time of day was a significant factor for photosynthetic pigment concentrations in half of the sampling dates. Depth was not a significant factor in cell concentration variations for any of the phytoplankton groups observed, but time of day was a significant factor in 40% of the sampling dates. Two distinct patterns in pigment concentration daily variation were observed. The first featured a continuous increase with depth throughout the day. The second showed maximum concentrations at the surface in the morning changing to maximum concentrations at 0.5 m depth at 12 p.m. and 3 p.m.; these patterns corresponded to different morning solar irradiance levels. This indicates that sampling depth and time can be a significant factor when evaluating photosynthetic pigments and should be accounted for in monitoring programs that rely on pigments for decision-making.
Full article
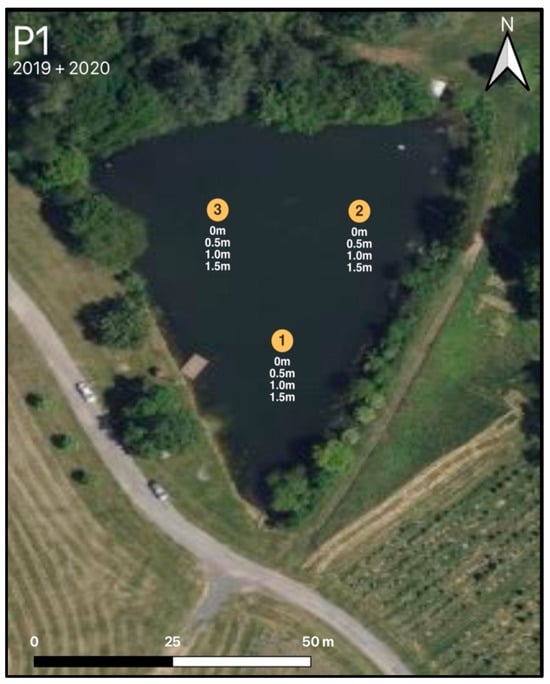
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Organic Carbon Stock in Mineral Soils in Cropland and Grassland in Latvia
by
Guna Petaja, Ieva Ivbule, Zaiga Anna Zvaigzne, Dana Purviņa, Emīls Mārtiņš Upenieks, Ieva Līcīte and Andis Lazdiņš
Environments 2024, 11(4), 73; https://doi.org/10.3390/environments11040073 - 03 Apr 2024
Abstract
This study aimed to assess soil organic carbon (SOC) concentration and stock in mineral soils in cropland and grassland in Latvia, considering soil groups and texture classes. It covered 197 sites across Latvia (152 in cropland, 45 in grassland). Soil profile description and
[...] Read more.
This study aimed to assess soil organic carbon (SOC) concentration and stock in mineral soils in cropland and grassland in Latvia, considering soil groups and texture classes. It covered 197 sites across Latvia (152 in cropland, 45 in grassland). Soil profile description and sampling (at depths of 0–10 cm, 10–20 cm, and 20–40 cm) were conducted between 2021 and 2023. Laboratory analyses included soil bulk density (SBD), total carbon (TC), total nitrogen (TN), carbonate content, pH, and extractable phosphorus (P), potassium (K), calcium (Ca), and magnesium (Mg). SOC stock was calculated, and correlations with other soil parameters were determined. In cropland sites, Arenosols and Stagnosols had the lowest SOC concentration and stock, while Gleysols and Phaeozems had the highest. In grassland sites, Retisols exhibited the lowest SOC concentration in the 0–20 cm layer, while Planosols had the highest SOC concentration in this layer. Conversely, in the 20–40 cm layer, Retisols showed the highest SOC concentration, while Gleysols had the lowest concentration. Regarding SOC stock in grassland sites, Planosols exhibited the highest values, while the lowest values were observed for Retisols and Umbrisols. Contrary to our hypothesis that grassland exhibits higher SOC stock than cropland, our results show the reverse for Phaeozems, the dominant WRB soil group in this study: a higher average SOC concentration and stock in cropland compared to grassland. However, very low occurrence of some soil groups and lack of some soil groups for grassland sites hinders the correct interpretation of these results, and further investigations are required in future studies.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Soil Organic Carbon Assessment, 2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures
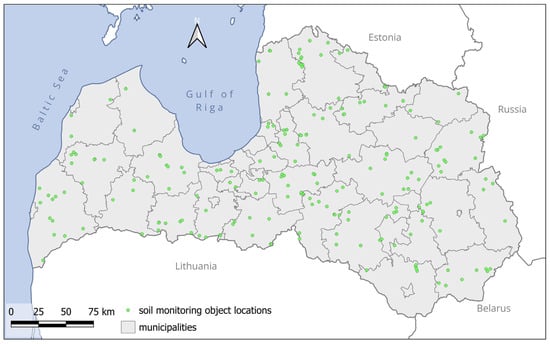
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Impacts of Freshwater Sources on Salinity Structure in a Large, Shallow Estuary
by
Mohamed Z. Moustafa, Zhen-Gang Ji and John Hamrick
Environments 2024, 11(4), 72; https://doi.org/10.3390/environments11040072 - 03 Apr 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Florida Bay, a large and shallow estuary, serves as a vital habitat for a diverse range of marine species and holds significant environmental, commercial, and recreational value. The salinity structure of the bay plays a key role in the bay’s ecosystem. Florida Bay
[...] Read more.
Florida Bay, a large and shallow estuary, serves as a vital habitat for a diverse range of marine species and holds significant environmental, commercial, and recreational value. The salinity structure of the bay plays a key role in the bay’s ecosystem. Florida Bay receives 45% of its freshwater directly from rainfall, the largest source of freshwater, while the Taylor River is the second largest source. A hydrodynamic model was applied to determine if doubling the Taylor River flow, as currently planned, is adequate to meet salinity performance measures and protect the bay’s ecosystem health. Model-predicted salinity indicated that rainfall caused the largest reduction (10–15 ppt) followed by Taylor River discharges, and none of the predicted salinity scenario means exceeded 38 ppt. The salinity restoration target was achieved more than 70% of the time, by doubling the Taylor River freshwater discharges, only for the existing bay conditions. To protect Florida Bay’s ecosystem health and counterbalance saltwater intrusion in the Everglades wetlands, caused by future sea-level rise, additional freshwater sources needs to be identified. Yet, the question becomes, do we have enough available freshwater sources to achieve the restoration target and protect the bay’s ecosystem health now and for future sea-level rise?
Full article
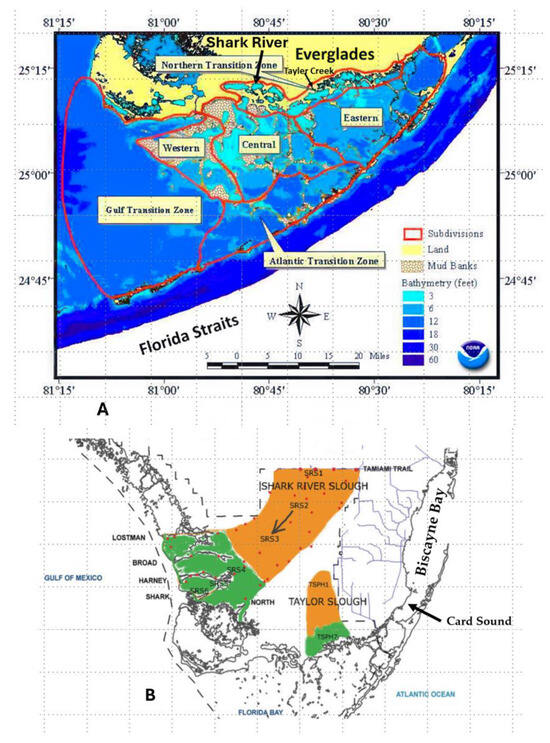
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Flexible Green Ammonia Production Plants: Small-Scale Simulations Based on Energy Aspects
by
Guillermo de la Hera, Gema Ruiz-Gutiérrez, Javier R. Viguri and Berta Galán
Environments 2024, 11(4), 71; https://doi.org/10.3390/environments11040071 - 02 Apr 2024
Abstract
The conventional Haber–Bosch process (HBP) for NH3 production results in CO2 emissions of almost 400 Mt/y and is responsible for 1–2% of global energy consumption; furthermore, HBP requires large-scale industrial equipment. Green or e-ammonia produced with hydrogen from alkaline water electrolysis
[...] Read more.
The conventional Haber–Bosch process (HBP) for NH3 production results in CO2 emissions of almost 400 Mt/y and is responsible for 1–2% of global energy consumption; furthermore, HBP requires large-scale industrial equipment. Green or e-ammonia produced with hydrogen from alkaline water electrolysis using renewable energy and nitrogen from the air is considered an alternative to fossil-fuel-based ammonia production. Small-scale plants with the distributed on-site production of e-ammonia will begin to supplant centralized manufacturing in a carbon-neutral framework due to its flexibility and agility. In this study, a flexible small-scale NH3 plant is analyzed with respect to three steps—H2 generation, air separation, and NH3 synthesis—to understand if milder operating conditions can benefit the process. This study investigates the aspects of flexible small-scale NH3 plants powered by alkaline electrolyzer units with three specific capacities: 1 MW, 5 MW, and 10 MW. The analysis is carried out through Aspen Plus V14 simulations, and the primary criteria for selecting the pressure, temperature, and number of reactors are based on the maximum ammonia conversion and minimum energy consumption. The results show that: (i) the plant can be operated across a wide range of process variables while maintaining low energy consumption and (ii) alkaline electrolysis is responsible for the majority of energy consumption, followed by the ammonia synthesis loop and the obtention of N2, which is negligible.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Environments: 10 Years of Science Together)
►▼
Show Figures
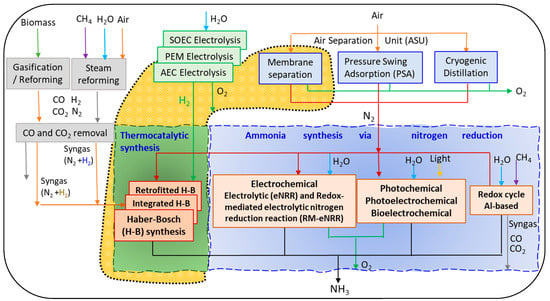
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Dryland Soil Carbon and Nitrogen Stocks in Response to Cropping Systems and Nitrogen Fertilization
by
Upendra M. Sainju
Environments 2024, 11(4), 70; https://doi.org/10.3390/environments11040070 - 02 Apr 2024
Abstract
Innovative management practices are needed to mitigate greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from the agricultural sector by enhancing soil carbon (C) and nitrogen (N) stocks, which serve as major reservoirs of C and N in the terrestrial ecosystem. The effect of cropping systems and
[...] Read more.
Innovative management practices are needed to mitigate greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from the agricultural sector by enhancing soil carbon (C) and nitrogen (N) stocks, which serve as major reservoirs of C and N in the terrestrial ecosystem. The effect of cropping systems and N fertilization rates were examined on soil organic C (SOC) and soil total N (STN) stocks at the 0–120 cm depth from 2011 to 2018 in a dryland farm in the US northern Great Plains. Cropping systems were no-till continuous spring wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) (NTCW), no-till spring wheat–pea (Pisum sativum L.) (NTWP), no-till spring wheat–fallow (NTWF), and conventional till spring wheat–fallow (CTWF) and N fertilization rates were 0, 50, 100, and 150 kg N ha−1 applied to spring wheat. The SOC and STN were greater for NTWP than other cropping systems at most N fertilization rates and depth layers. Increasing N fertilization rate increased SOC at 0–30 cm for NTWP and NTCW, but had a variable effect on STN for various cropping systems and soil depths. The NTWP with 50–100 kg N ha−1 can enhance SOC and STN at 0–30 cm compared to other cropping systems and N fertilization rates in the US northern Great Plains.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Soil Organic Carbon Assessment, 2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Acoustic Characterization of Potential Quiet Areas in Dortmund, Germany
by
Bryce T. Lawrence, Andreas Frücht, Damian Heying, Kai Schröer and Dietwald Gruehn
Environments 2024, 11(4), 69; https://doi.org/10.3390/environments11040069 - 31 Mar 2024
Abstract
German noise action plans aim to reduce negative health outcomes from noise exposure and identify quiet areas free of noise pollution. Quiet area identification in German noise action plans is based primarily on noise mapping and spatial analysis and not empirical or qualitative
[...] Read more.
German noise action plans aim to reduce negative health outcomes from noise exposure and identify quiet areas free of noise pollution. Quiet area identification in German noise action plans is based primarily on noise mapping and spatial analysis and not empirical or qualitative data about acoustic environments, thus leaving a gap in the understanding of the quality of formally recognized quiet areas in noise action plans. This work presents a comparative empirical case study in Dortmund, Germany, with the aim to describe the diurnal dB(A) and biophonic properties of quiet areas versus noise ‘hot spots’. Sound observations (n = 282,764) were collected in five different natural or recreational land use patch types larger than four acres within 33 proposed quiet areas in Dortmund (n = 70) and 23 noise hot spots between 27 April 2022 and 2 March 2023. We found that quiet areas are on average more than 20 dB(A) quieter than noise hot spots almost every hour of the day. Forests, managed tree stands, cemeteries, and agriculture diel patterns are dominated by dawn dusk chorus in spring and summer, whereas sports and recreation as well as noise hot spots are dominated by traffic and human noise. A novel composite biophony mapping procedure is presented that finds distinct temporal distribution of biophony in forested and agriculture peri-urban locations positively associated with patch size, distance away from LDEN > 55, proximity to water, and the number of vegetation layers in the plant community. Anthrophony distribution dominates urban land uses in all hours of the day but expands during the day and evening and contracts at night and in dusk hours. The procedures presented here illustrate how qualitative information regarding quiet areas can be integrated into German noise action planning.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue New Solutions Mitigating Environmental Noise Pollution II)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Environments Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Topical Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Water, Toxics, Land, Environments
Fate and Transport of Artificial Radionuclides in Soil-Water Environment
Topic Editors: Alexei Konoplev, Mikhail KomissarovDeadline: 30 April 2024
Topic in
Energies, Environments, Fractal Fract, Materials, Remote Sensing
Geomechanics for Energy and the Environment
Topic Editors: Gan Feng, Ang Liu, Reza Taherdangkoo, Qiao LyuDeadline: 31 May 2024
Topic in
Clean Technol., Energies, Environments, Processes, Sustainability
Sustainable Energy: Efficient Technological Solutions Combining Environmental, Economic, Political and Social Aspects
Topic Editors: Fabio Orecchini, Adriano Santiangeli, Fabrizio ZuccariDeadline: 15 June 2024
Topic in
Environments, Forests, Land, Remote Sensing, Soil Systems
New Advances in Vegetation Dynamics and Soil Systems Related to Biogeochemical Cycles
Topic Editors: Hirohiko Nagano, Hiroki Ikawa, Morimaru Kida, Masataka NakayamaDeadline: 30 June 2024

Conferences
28 September 2021–30 September 2031
2021 International conference on Future Environment Pollution and Prevention (ICFEPP 2021)

Special Issues
Special Issue in
Environments
Recent Advances in Waste Management and Recycling
Guest Editor: Paulo FerrãoDeadline: 30 April 2024
Special Issue in
Environments
Environmental Science and Technologies for the Management of Natural Ecosystems and the Sustainable Development of Urban Areas II
Guest Editors: Yiannis Matsinos, Aggelos Tsaligopoulos, Demetris Francis LekkasDeadline: 25 May 2024
Special Issue in
Environments
Advanced Technologies of Water and Wastewater Treatment
Guest Editors: Athanasia Tolkou, George Z. KyzasDeadline: 31 May 2024
Special Issue in
Environments
Plastics Pollution in Aquatic Environments
Guest Editors: Juliana Aristéia De Lima, Karin MattssonDeadline: 20 June 2024
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Environments
Trends and Innovations in Environmental Impact Assessment
Collection Editor: Manuel Duarte Pinheiro






