Feature Papers on Wind, Wave and Tidal Energy
Share This Topical Collection
Editors
 Prof. Dr. Len Gelman
Prof. Dr. Len Gelman
 Prof. Dr. Len Gelman
Prof. Dr. Len Gelman
E-Mail
Website
Guest Editor
School of Computing and Engineering, Department of Engineering and Technology, University of Huddersfield, Queensgate, Huddersfield HD1 3DH, UK
Interests: digital signal processing; structural health monitoring; condition monitoring; artificial intelligence; vibration analysis; motor current signature analysis; adaptation of diagnosis systems
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
The popularity of renewable and sustainable energy sources has increased considerably in the last decade. This is a result of the steady depletion of the fossil fuel reserve and the increased incentive to achieve zero-carbon pollution in the future. In many countries, sustainable wind, wave and tidal energies are identified as the most promising sources with the highest levels of technological readiness. We invite submissions for this Special Issue that address research and development in fields including, but not limited to, the following:
- Wind, wave and tidal energy converters;
- Experimental and computational investigations of wind, wave and tidal energy technologies
- Site and energy yield assessments;
- Health monitoring and lifetime assessment for wind, wave and tidal energy assets;
- Signal and image processing for wind, wave and tidal energy assets;
- Fault diagnosis, prognosis and root cause analysis for wind, wave and tidal energy assets for stationary and non-stationary operations;
- Modelling and finite element analysis for fault diagnosis, prognosis and root cause analysis for wind, wave and tidal energy assets;
- Economic aspects;
- Social acceptance;
- Grid and system integration;
- Usage of data driven approaches for wind, wave and tidal energy assessments.
Dr. Galih Bangga
Prof. Dr. Len Gelman
Guest Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Energies is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript.
The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2600 CHF (Swiss Francs).
Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's
English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- renewable energy
- power generation
- economic growth
- energy potential
- electrical and mechanical systems
- health monitoring and lifetime assessment
- signal and image processing
- fault diagnosis, prognosis and root cause analysis
- stationary and non-stationary operations of wind, wave and tidal energy assets
- modelling and finite element analysis
Published Papers (16 papers)
Open AccessArticle
Genetically Optimized Pitch Angle Controller of a Wind Turbine with Fuzzy Logic Design Approach
by
Ahmet Selim Pehlivan, Beste Bahceci and Kemalettin Erbatur
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 1409
Abstract
An important engineering challenge is the design of a wind turbine’s pitch angle controller. The dependability, safety, and power output maximization of a wind turbine are all impacted by this controller. In this study, a 2 MW doubly fed induction generator wind turbine’s
[...] Read more.
An important engineering challenge is the design of a wind turbine’s pitch angle controller. The dependability, safety, and power output maximization of a wind turbine are all impacted by this controller. In this study, a 2 MW doubly fed induction generator wind turbine’s blade angle controller design with a novel fuzzy logic controller is tested in a simulated environment. The evolutionary algorithm technique is used to optimize the fuzzy logic controller with three inputs. A genetic algorithm is used to optimize the specified pitch angle controller for a number of coefficients. After the optimization process, the controller’s performance is assessed in terms of power output, overshoot, and steady-state error characteristics.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Wind Power Potential in Highlands of the Bolivian Andes: A Numerical Approach
by
Rober Mamani and Patrick Hendrick
Viewed by 2237
Abstract
Wind resource assessment is a key factor for the development and implementation of wind farms with the purpose of generating green, eco-friendly and clean electricity. The Bolivian Andes, as a large dry region, represents an important source of renewable energy. However, the altitude
[...] Read more.
Wind resource assessment is a key factor for the development and implementation of wind farms with the purpose of generating green, eco-friendly and clean electricity. The Bolivian Andes, as a large dry region, represents an important source of renewable energy. However, the altitude and high wind energy resources of the Bolivian Andes require further knowledge and understanding of the wind energy resources. In this study, the GWA have been used to determine the total area available to install wind farms considering the protected areas, roads, cities and transmission lines. In addition, the Weather Research and Forecasting (WRF v3.8.1) model is employed to complement the results of the GWA based on the validation of WRF simulations with measurements from Qollpana wind farm. The main purpose is to estimate the wind power potential along the Bolivian Andes and its variability in time. The wind power simulations have been compared with the power generated by the Qollpana wind farm to verify the WRF’s performance. The wind power potential in the highlands of the Bolivian Andes could reach between 225 (WRF) and 277 (GWA) GW, distributed mainly over the Western and Eastern Cordillera of the Altiplano.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
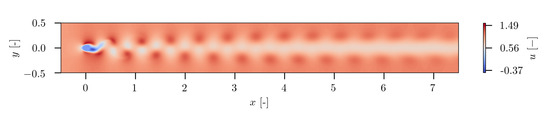
Data Reduction and Reconstruction of Wind Turbine Wake Employing Data Driven Approaches
by
Martin Geibel and Galih Bangga
Cited by 9 | Viewed by 2171
Abstract
Data driven approaches are utilized for optimal sensor placement as well as for velocity prediction of wind turbine wakes. In this work, several methods are investigated for suitability in the clustering analysis and for predicting the time history of the flow field. The
[...] Read more.
Data driven approaches are utilized for optimal sensor placement as well as for velocity prediction of wind turbine wakes. In this work, several methods are investigated for suitability in the clustering analysis and for predicting the time history of the flow field. The studies start by applying a proper orthogonal decomposition (POD) technique to extract the dynamics of the flow. This is followed by evaluations of different hyperparameters of the clustering and machine learning algorithms as well as their impacts on the prediction accuracy. Two test cases are considered: (1) the wake of a cylinder and (2) the wake of a rotating wind turbine rotor exposed to complex flow conditions. The training and test data for both cases are obtained from high fidelity CFD approaches. The studies reveal that the combination of a classification-based machine learning algorithm for optimal sensor placement and Bi-LSTM is sufficient for predicting periodic signals, but a more advanced technique is required for the highly complex data of the turbine near wake. This is done by exploiting the dynamics of the wake from the set of POD modes for flow field reconstruction. A satisfactory accuracy is achieved for an appropriately chosen prediction horizon of the Bi-LSTM networks. The obtained results show that data-driven approaches for wind turbine wake prediction can offer an alternative to conventional prediction approaches.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
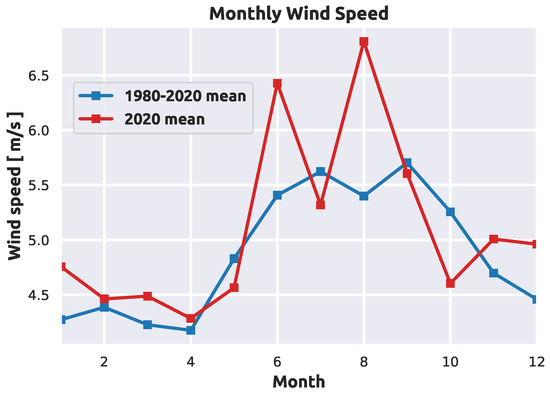
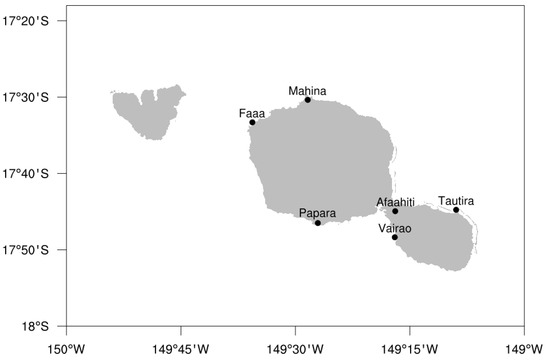
Investigating Wind Energy Potential in Tahiti, French Polynesia
by
Marania Hopuare, Tao Manni, Victoire Laurent and Keitapu Maamaatuaiahutapu
Cited by 4 | Viewed by 3079
Abstract
In order to achieve France’s goal of carbon neutrality by 2050, the French Polynesian administration has set the objective of producing 100% of the local electricity requirements from renewable energy resources. To this end, we present the wind characteristics at six selected locations
[...] Read more.
In order to achieve France’s goal of carbon neutrality by 2050, the French Polynesian administration has set the objective of producing 100% of the local electricity requirements from renewable energy resources. To this end, we present the wind characteristics at six selected locations in Tahiti. Surface wind observations from 2008 to 2020 obtained from the Meteorological Service of French Polynesia are analysed in terms of wind speed, dominant wind direction and power density to identify the most suitable locations for the deployment of wind farms. The Weibull distribution is used to fit the wind speed data recorded at 10 m above ground level, as it is widely used by turbine manufacturers. Then, wind speed is extrapolated vertically up to the hub height with the power law, which is also commonly used in wind energy studies. The theoretical annual energy output and capacity factor of four selected commercial wind turbines are assessed for each site in order to provide stakeholders with the relevant information regarding wind energy harvesting in Tahiti. Power law indices lower than 0.2 were chosen. Our results show that all year round, two sites, Faaa and Tautira, are suitable to host wind turbines, even with a power law index as low as 0.1.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
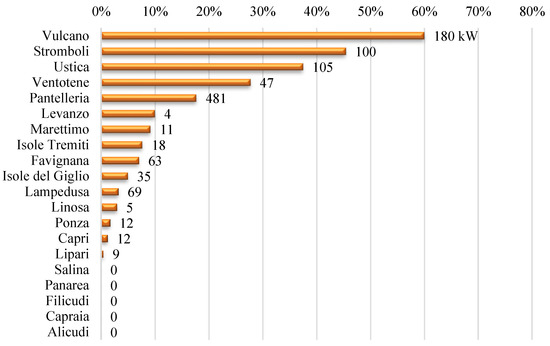
An Economic Approach to Size of a Renewable Energy Mix in Small Islands
by
Daniele Milone, Domenico Curto, Vincenzo Franzitta, Andrea Guercio, Maurizio Cirrincione and Ali Mohammadi
Cited by 16 | Viewed by 2060
Abstract
The importance of renewable energy exploitation reduces the energy dependence on fossil fuels. Despite technological progress, in several remote areas and small islands the energy production is nowadays dominated by the utilization of fossil fuels. With new, increasingly stringent laws on polluting emissions
[...] Read more.
The importance of renewable energy exploitation reduces the energy dependence on fossil fuels. Despite technological progress, in several remote areas and small islands the energy production is nowadays dominated by the utilization of fossil fuels. With new, increasingly stringent laws on polluting emissions and the need to lower production costs, it is necessary to exploit as many renewable sources as possible. In order to implement these considerations, it was decided to study renewable energy production. The study was carried out by estimating the energy production on a monthly and annual basis considering a mix of three plants, namely marine, solar, and wind. Simulations on wave production were carried out on a new device developed by the research team at the University of Palermo. In order to be able to perform these simulations, input climate data are required. These data are normally available in literature or obtainable by using specific GIS tools. As criterium, the Levelized Cost of Energy, normally applied to a single technology, is extended to the entire energy mix. Minimizing this parameter, the best solution is individuated, and capable of supplying 50% of the summer electrical load with renewable energy sources. The results carried out from a case study based in aeolian islands show that the solar production reaches 10.2%, the wind production reaches 45.47% and sea wave production reaches 3.04%. In this way, the diesel production decreases to 41.29%. This method can be easily applied for several small islands, estimating for several sites the ability to reduce the energy production from fossil fuels.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessCommunication
The Case for Policy in Developing Offshore Wind: Lessons from Norway
by
Iben Ringvej Dahl, Bård Wathne Tveiten and Emily Cowan
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 2812
Abstract
Offshore wind (OSW) has the potential to cut greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions and halt damaging climate change. However, policies to foster an OSW industry in Norway have long been small and scarce. Recent events suggest that this is changing, as the state-owned enterprise
[...] Read more.
Offshore wind (OSW) has the potential to cut greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions and halt damaging climate change. However, policies to foster an OSW industry in Norway have long been small and scarce. Recent events suggest that this is changing, as the state-owned enterprise Enova decided to grant a record NOK 2.3 bn to build the world’s largest floating offshore wind farm in 2019, the Hywind Tampen project. Based on previous work by the corresponding author, we summarize the political development of OSW in Norway to distil generalisable lessons. The corresponding author employed interviews, document analysis and process tracing, using a theory of policy change to characterise the observed political change. She found that the main obstacle for early OSW deployment has been that environmental and visibility concerns have exacerbated energy–political ones that are created by a longstanding lack of local energy demands. As the green energy demand on a global scale is soaring, the lack of OSW deployment for exports implies that climate–political objectives have been subordinated to energy–political ones, in the formulation of Norwegian OSW policies. This hierarchy of goals was not deemed to have changed, despite the recent political developments in the policy area of Norwegian OSW. Hence, the Norwegian case demonstrates the role of context and national sectoral policies in deciding the pace of sustainable energy transitions. It is suggested that future research considers how policy best practices for renewable energy deployment could be adjusted across varying national contexts to overcome political hurdles to the sustainable transition.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
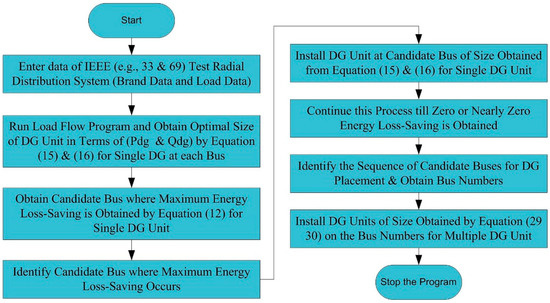
A Novel Analytical Approach for Optimal Integration of Renewable Energy Sources in Distribution Systems
by
Prem Prakash, Duli Chand Meena, Hasmat Malik, Majed A. Alotaibi and Irfan Ahmad Khan
Cited by 17 | Viewed by 1773
Abstract
The present research article focuses on an analytically based method for the optimal allocation and sizing of a renewable energy source (RES) capable of injecting both active and reactive powers in the distribution network. The placement of distributed generation (DG) in the distribution
[...] Read more.
The present research article focuses on an analytically based method for the optimal allocation and sizing of a renewable energy source (RES) capable of injecting both active and reactive powers in the distribution network. The placement of distributed generation (DG) in the distribution network reduces the magnitude of branch current in between the reference bus and the bus where DG is to be installed. Due to this, system power loss decreases significantly. The proposed method considers different levels of load in addition to peak load demand. The goal of the developed method is to minimize system losses by optimal DG allocations. In the proposed method, the optimum size of the DG is obtained on the basis of maximum loss saving criterion. For the execution of proposed method, only a base case load flow solution is required. The developed method has been tested on IEEE 69-bus and 33-bus radial distribution networks. On the basis of obtained results, it has been realized that the developed method is more capable of diminishing system energy losses.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
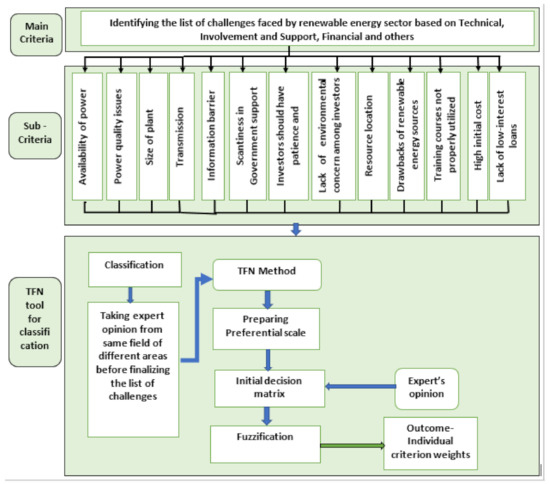
Fuzzy-Based Investigation of Challenges for the Deployment of Renewable Energy Power Generation
by
Shabbiruddin, Neeraj Kanwar, Vinay Kumar Jadoun, Majed A. Alotaibi, Hasmat Malik and Mohammed E. Nassar
Cited by 5 | Viewed by 2465
Abstract
Studying and analyzing the challenges that the renewable energy sector faces can help evaluate the risks and improve the planning. This research is done by considering the challenges in the implementation of sustainable generation of electricity through RESs in India, based on factors,
[...] Read more.
Studying and analyzing the challenges that the renewable energy sector faces can help evaluate the risks and improve the planning. This research is done by considering the challenges in the implementation of sustainable generation of electricity through RESs in India, based on factors, including technical, financial, involvement, support, and others. The triangular fuzzy number (TFN) method, based on fuzzy logic concept, is used to analyze the challenges in this study. In general, TFN comprises of three numbers, likewise Gaussian fuzzy numbers, trapezoidal fuzzy numbers also exist. The classified sets of numbers are denotations to decision-makers’ perspective or a choice towards the criterion preference. Although alternatives are many to design a fuzzy set depending on elements count, the TFNs are the ones considered as actual representations of a fuzzy number. On the other hand, cases the Gaussian or trapezoidal, are manifestations of fuzzy intervals. Another argument is that the membership function shape corresponding to the number of fuzzy set elements is largely dependent on the study. The challenges identified along with analysis in this paper will help the industry, governments, and policymakers focus and tackle essential issues to facilitate further the deployment of RESs in India towards a more sustainable country.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
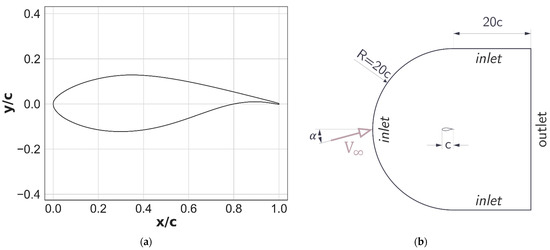
Accuracy of the Gamma Re-Theta Transition Model for Simulating the DU-91-W2-250 Airfoil at High Reynolds Numbers
by
Jan Michna, Krzysztof Rogowski, Galih Bangga and Martin O. L. Hansen
Cited by 13 | Viewed by 4413
Abstract
Accurate computation of the performance of a horizontal-axis wind turbine (HAWT) using Blade Element Momentum (BEM) based codes requires good quality aerodynamic characteristics of airfoils. This paper shows a numerical investigation of transitional flow over the DU 91-W2-250 airfoil with chord-based Reynolds number
[...] Read more.
Accurate computation of the performance of a horizontal-axis wind turbine (HAWT) using Blade Element Momentum (BEM) based codes requires good quality aerodynamic characteristics of airfoils. This paper shows a numerical investigation of transitional flow over the DU 91-W2-250 airfoil with chord-based Reynolds number ranging from 3 × 10
6 to 6 × 10
6. The primary goal of the present paper is to validate the unsteady Reynolds averaged Navier-Stokes (URANS) approach together with the four-equation transition SST turbulence model with experimental data from a wind tunnel. The main computational fluid dynamics (CFD) code used in this work was ANSYS Fluent. For comparison, two more CFD codes with the Transition SST model were used: FLOWer and STAR-CCM +. The obtained airfoil characteristics were also compared with the results of fully turbulent models published in other works. The XFOIL approach was also used in this work for comparison. The aerodynamic force coefficients obtained with the Transition SST model implemented in different CFD codes do not differ significantly from each other despite the different mesh distributions used. The drag coefficients obtained with fully turbulent models are too high. With the lowest Reynolds numbers analyzed in this work, the error in estimating the location of the transition was significant. This error decreases as the Reynolds number increases. The applicability of the uncalibrated transition SST approach for a two-dimensional thick airfoil is up to the critical angle of attack.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
Novel Instantaneous Wavelet Bicoherence for Vibration Fault Detection in Gear Systems
by
Len Gelman, Krzysztof Soliński and Andrew Ball
Cited by 9 | Viewed by 1645
Abstract
Higher order spectra exhibit a powerful detection capability of low-energy fault-related signal components, buried in background random noise. This paper investigates the powerful nonlinear non-stationary instantaneous wavelet bicoherence for local gear fault detection. The new methodology of selecting frequency bands that are relevant
[...] Read more.
Higher order spectra exhibit a powerful detection capability of low-energy fault-related signal components, buried in background random noise. This paper investigates the powerful nonlinear non-stationary instantaneous wavelet bicoherence for local gear fault detection. The new methodology of selecting frequency bands that are relevant for wavelet bicoherence fault detection is proposed and investigated. The capabilities of wavelet bicoherence are proven for early-stage fault detection in a gear pinion, in which natural pitting has developed in multiple pinion teeth in the course of endurance gearbox tests. The results of the WB-based fault detection are compared with a stereo optical fault evaluation. The reliability of WB-based fault detection is quantified based on the complete probability of correct identification. This paper is the first attempt to investigate instantaneous wavelet bicoherence technology for the detection of multiple natural early-stage local gear faults, based on comprehensive statistical evaluation of the industrially relevant detection effectiveness estimate—the complete probability of correct fault detection.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Design and Implementation of Frequency Controller for Wind Energy-Based Hybrid Power System Using Quasi-Oppositional Harmonic Search Algorithm
by
Tarkeshwar Mahto, Rakesh Kumar, Hasmat Malik, Irfan Ahmad Khan, Sattam Al Otaibi and Fahad R. Albogamy
Cited by 4 | Viewed by 1306
Abstract
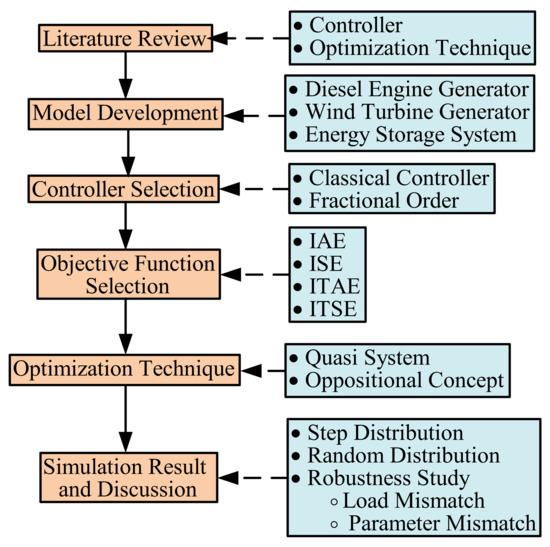
An innovative union of fuzzy controller and proportional-integral-derivative (PID) controller under the environment of fractional order (FO) calculus is described in the present study for an isolated hybrid power system (IHPS) in the context of load frequency control. The proposed controller is designated
[...] Read more.
An innovative union of fuzzy controller and proportional-integral-derivative (PID) controller under the environment of fractional order (FO) calculus is described in the present study for an isolated hybrid power system (IHPS) in the context of load frequency control. The proposed controller is designated as FO-fuzzy PID (FO-F-PID) controller. The undertaken model of IHPS presented here involves different independent power-producing units, a wind energy-based generator, a diesel engine-based generator and a device for energy storage (such as a superconducting magnetic energy storage system). The selection of the system and controller gains was achieved through a unique quasi-oppositional harmony search (QOHS) algorithm. The QOHS algorithm is based on the basic harmony search (HS) algorithm, in which the combined concept of quasi-opposition initialization and HS algorithm fastens the profile of convergence for the algorithm. The competency and potency of the intended FO-F-PID controller were verified by comparing its performance with three different controllers (integer-order (IO)-fuzzy-PID (IO-F-PID) controller, FO-PID and IO-PID controller) in terms of deviation in frequency and power under distinct perturbations in load demand conditions. The obtained simulation results validate the cutting-edge functioning of the projected FO-F-PID controller over the IO-F-PID, FO-PID and IO-PID controllers under non-linear and linear functioning conditions. In addition, the intended FO-F-PID controller, considered a hybrid model, proved to be more robust against the mismatches in loading and the non-linearity in the form of rate constraint under the deviation in frequency and power front.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Enhancement of the Flickermeter for Grid-Connected Wind Turbines
by
Chau-Shing Wang, Wen-Ren Yang and Yi-Cheng Hsu
Viewed by 1915
Abstract
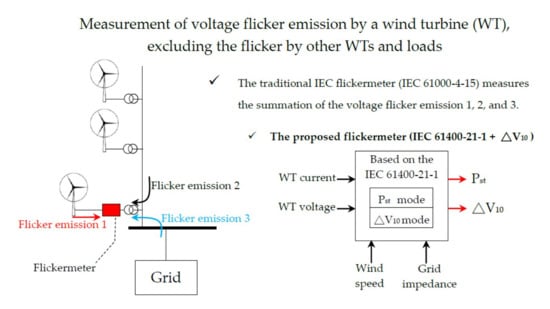
Distributed generators connected to the power system usually produce voltage fluctuations. For wind turbines connected to a grid, large changes in wind speed can cause voltage flicker at the point of common coupling. The measurement of voltage flicker caused only by wind turbines
[...] Read more.
Distributed generators connected to the power system usually produce voltage fluctuations. For wind turbines connected to a grid, large changes in wind speed can cause voltage flicker at the point of common coupling. The measurement of voltage flicker caused only by wind turbines is difficult. The wind turbine under test is usually connected to a medium voltage point, in which other fluctuating loads may produce significant voltage disturbances at the wind turbine terminal where the measurement is made. Although the IEC 61400-21-1 standard specifies a method to evaluate voltage flicker caused by wind turbines, because of the complex algorithm and process of the IEC standard, there is currently a lack of measurement equipment that meets the IEC standard. In addition, some countries that use other voltage flicker standards, such as ΔV
10, do not have suitable flicker measurements for wind turbines. Therefore, this study proposes an enhanced version of the IEC 61400-21-1 standard, which integrates the ΔV
10 method, so that the proposed measurement system complies with the IEC and ΔV
10 standards. In this study, the voltage flicker measurement system is successfully implemented, which can help engineers to predict the voltage flicker by wind turbines and assess whether a region or grid is suitable for installing wind turbines. Therefore, it can provide wind turbine companies with a quick assessment of voltage flicker to comply with the certification process.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Impacts of Renewable Sources of Energy on Bid Modeling Strategy in an Emerging Electricity Market Using Oppositional Gravitational Search Algorithm
by
Satyendra Singh, Manoj Fozdar, Hasmat Malik, Irfan Ahmad Khan, Sattam Al Otaibi and Fahad R. Albogamy
Cited by 10 | Viewed by 1621
Abstract
Power suppliers in a dynamic power market can achieve full benefit by introducing a bidding strategy mechanism. In the power sector, renewable resources have significant gradual usage and their effect on the production of detailed bidding approaches is becoming further complicated in the
[...] Read more.
Power suppliers in a dynamic power market can achieve full benefit by introducing a bidding strategy mechanism. In the power sector, renewable resources have significant gradual usage and their effect on the production of detailed bidding approaches is becoming further complicated in the industry. Due to the irregular nature of these renewable resources and because they are subject to several fluctuations, there is an inherent issue with generating electricity. Taking these considerations into account, attempts have been made to create a model of bidding strategy to optimize the benefit of the electricity producers using the oppositional gravitational search algorithm. The Weibull and Beta distribution functions are utilized to describe the stochastic characteristics of the wind-speed profile and solar-irradiation, respectively. For the IEEE-30 and IEEE-57 frameworks, the suggested method is being checked and explained. In comparison to other optimization approaches, the results of this approach were taken into account, and it was discovered that it outperformed other techniques in addressing bid difficulties. In addition, it is worth noting that the impact of renewable energy on the bidding strategy lowered market clearing and thermal power generating costs, and encouraged renewable influenced producers to put forward the excess electricity into the real-time market.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Exploring the Grid Value of Offshore Wind Energy in Oregon
by
Travis C. Douville and Dhruv Bhatnagar
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 3315
Abstract
The significant offshore wind energy potential of Oregon faces several challenges, including a power grid which was not developed for the purpose of transmitting energy from the ocean. The grid impacts of the energy resource are considered through the lenses of (i) resource
[...] Read more.
The significant offshore wind energy potential of Oregon faces several challenges, including a power grid which was not developed for the purpose of transmitting energy from the ocean. The grid impacts of the energy resource are considered through the lenses of (i) resource complementarity with Variable Renewable Energy resources; (ii) correlations with load profiles from the four balancing authorities with territory in Oregon; and (iii) spatial value to regional and coastal grids as represented through a production cost model of the Western Interconnection. The capacity implications of the interactions between offshore wind and the historical east-to-west power flows of the region are discussed. The existing system is shown to accommodate more than two gigawatts of offshore wind interconnections with minimal curtailment. Through three gigawatts of interconnection, transmission flows indicate a reduction of coastal and statewide energy imports as well as minimal statewide energy exports.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
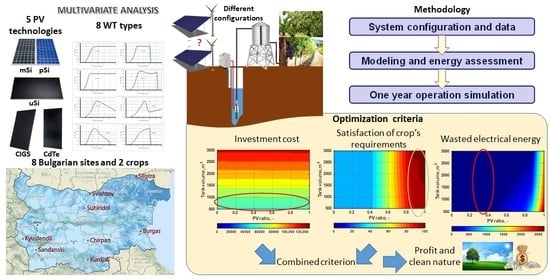
Multivariate Analysis of a Wind–PV-Based Water Pumping Hybrid System for Irrigation Purposes
by
Ludmil Stoyanov, Ivan Bachev, Zahari Zarkov, Vladimir Lazarov and Gilles Notton
Cited by 13 | Viewed by 2889
Abstract
The Green Deal and increased nutritional needs are driving factors in human activities nowadays. Agriculture is an essential economic sector that can profit from the application of renewable energy sources by the assimilation of off-grid, arid and barren terrains. Power supplied by hybrid
[...] Read more.
The Green Deal and increased nutritional needs are driving factors in human activities nowadays. Agriculture is an essential economic sector that can profit from the application of renewable energy sources by the assimilation of off-grid, arid and barren terrains. Power supplied by hybrid systems for water pumping is a solution for overcoming the stochastic character of the renewable energy sources. This paper presents a sizing methodology for a hybrid system with wind and PV generation and water tank storage, based on the consideration of the entire energy conversion chain with energy models and a one-year operation simulation. The PV generator is modeled using a reduced Durisch’s model, while for the wind generator a piecewise interpolation is used. The methodology is applied for sites in Bulgaria with specific agricultural crops and meteorological data. Combinations of PV (different technologies) and wind (different types) generators and water tank capacities are considered and discussed. The combinations are compared on the basis of three criteria: the investment cost, the satisfaction of crop requirements and system oversizing. The possibility for the introduction of battery storage is also examined. The results show some trends in the hybrid system sizing and the possibility to apply the proposed methodology for various sites, generators and crops.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
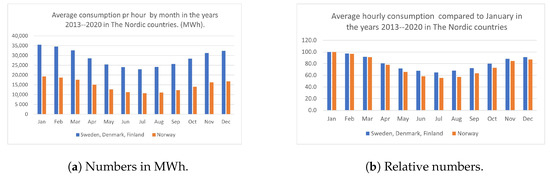
Open AccessArticle
Growth and Economic Performance of the Norwegian Wind Power Industry and Some Aspects of the Nordic Electricity Market
by
Johannes Idsø
Cited by 4 | Viewed by 2520
Abstract
Electricity has been produced in Norway in hydropower plants since 1877. The first wind power plant was put into operation in 1986. The growth in wind power production was weak in the first years after the turn of the millennium, but after Norway
[...] Read more.
Electricity has been produced in Norway in hydropower plants since 1877. The first wind power plant was put into operation in 1986. The growth in wind power production was weak in the first years after the turn of the millennium, but after Norway joined the Swedish subsidy scheme Tradable Green Certificates in 2012, there was significant growth in the wind power industry. While most of the hydropower production in Norway is owned by the public sector, the majority of wind power production is owned by foreign investors. Since wind power has been very much discussed in Norway, a levelized cost of energy (LCOE) model that can be well suited for this type of discussion is presented. The point here is that one must include all the costs, including the externalities. The Norwegian electricity market is dominated by a single player: Nord Pool. Ninety-six percent of all the electricity produced in Norway is sold through the power exchange Nord Pool, and the prices set by Nord Pool affect the finances of all the electricity producers in Norway, as well as producers in Scandinavia and the Baltic countries. This paper is a survey of the growth, development of production and economic performance of the Norwegian wind power industry and some aspects of the electricity market in the Nordic countries.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Planned Papers
The below list represents only planned manuscripts. Some of these
manuscripts have not been received by the Editorial Office yet. Papers
submitted to MDPI journals are subject to peer-review.
Title: The Role of Offshore Wind Farms in the Decarbonisation of Energy Systems to Tackle Climate Change
Authors: Subhamoy Bhattacharya; Vikram Pakrashi
Affiliation: 1. Columbia University, USA
2. U C Berkeley, USA