New Electrochemical Performance of Solid-State Batteries: Development and Challenges
A special issue of Batteries (ISSN 2313-0105). This special issue belongs to the section "Battery Performance, Ageing, Reliability and Safety".
Deadline for manuscript submissions: 5 November 2024 | Viewed by 2179
Special Issue Editors
Interests: lithium-ion battery; solid state lithium battery
Special Issue Information
Dear Colleagues,
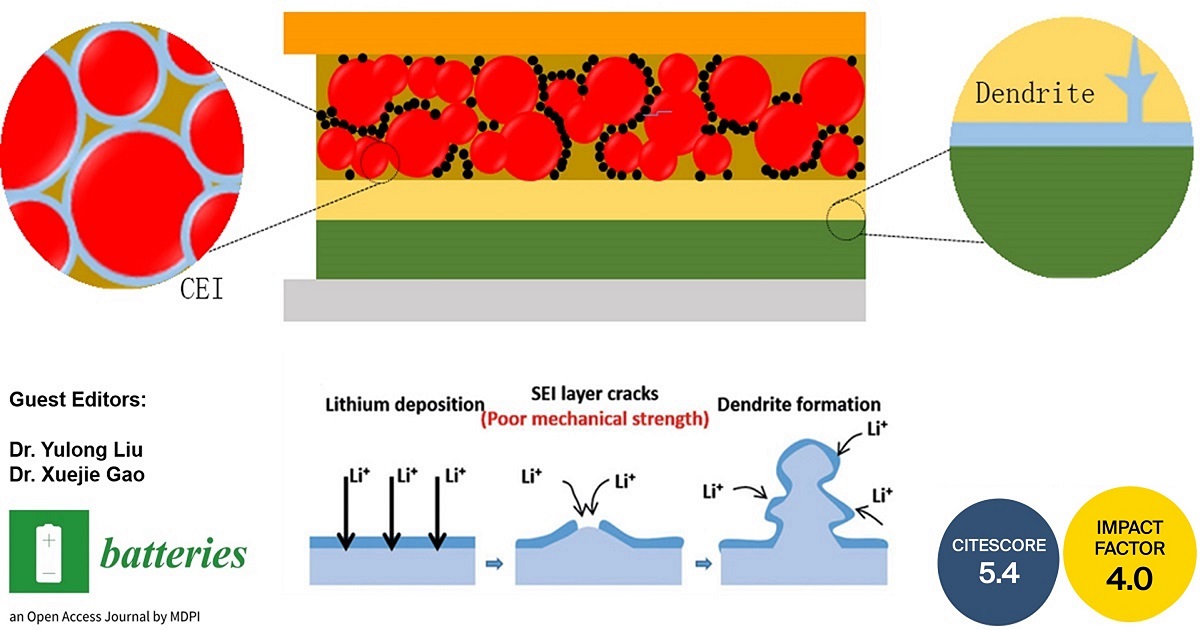
This Special Issue on All-Solid-State Batteries is focused on new electrolytes, interfaces and manufacturing technologies. Solid-state batteries have high safety and high-energy density, making them suitable for next-generation energy storage devices. However, their energy density reaches a limitation due to the narrow electrochemical window of solid electrolytes. Few electrode materials are compatible with solid electrolytes, preventing their wide application. At the electrolyte/electrode interface, there are side reactions at the anode and cathode. New strategies are needed to reduce the side reactions, thereby improving the electrochemical performance of solid-state batteries. To understand the change in interface, advanced characterizations are necessary, which can offer scientific evidence to increase the interface stability in the future.
In this Special Issue, we are looking for contributions helping to:
- Understand lithium dendrite formation mechanisms in a battery;
- Understanding the capacity decay phenomenon in a solid-state battery;
- Characterization of interface with an in-depth understanding;
- Develop new in situ approaches to solidify electrolytes;
- Develop new self-healing materials with ionic conductivity;
- Determine the impact of the interface on the cycling of the SSB.
Dr. Yulong Liu
Dr. Xuejie Gao
Guest Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the special issue website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Batteries is an international peer-reviewed open access monthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2700 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- solid state electrolyte
- polymer solid electrolyte
- novel electrolyte
- Li metal
- solid state battery
- interface
- quasi-solid-state battery






