Advanced Power Electronics in Power Networks
Share This Topical Collection
Editor
 Prof. Dr. Paweł Szcześniak
Prof. Dr. Paweł Szcześniak
 Prof. Dr. Paweł Szcześniak
Prof. Dr. Paweł Szcześniak
E-Mail
Website
Collection Editor
Institute of Automatic Control, Electronics and Electrical Engineering, University of Zielona Góra, 65-516 Zielona Góra, Poland
Interests: power electronics; matrix converter; power systems; power quality; smart grid; energy storage devices
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
We would like to invite submissions to a new Topical Collection in the Applied Sciences Journal. The main topic of the Topical Collection will be, as titled, “Power Electronics in Power Networks”. Potential topics include, but are not limited to:
- Topologies of power electronic converters for power grid applications: integration of renewable generation and storage systems, microgrid interfaces, mixed AC/DC distribution systems, solid-state and hybrid transformers.
- Power electronics interfaces of distributed generators and distributed energy storage as devices providing ancillary services: voltage regulation, reactive power support, fault ride-through, harmonics compensation, reduction in the peak power, load following, customer energy management applications, local energy balancing, etc.
- Integration of charging stations for electric vehicles and vehicle-to-grid service.
- Power electronics for power quality compensators.
- Flexible AC transmission system (FACTS) and Custom Power Devices (CPD).
- Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) in power distribution networks with high penetration of power electronics.
- Advanced estimation or measurement techniques of the grid parameters (grid impedance, voltage, frequency, etc.) aiming to improve power quality or control of the power converters. Application of advanced control techniques of power electronic converters.
We invite authors to submit scientific and technical development papers as well as reviews of recent developments in the proposed research field.
Prof. Dr. Paweł Szcześniak
Collection Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. All papers will be peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for a preliminary check of suitability.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Applied Sciences is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2300 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- power electronics
- smart grid
- microgrid
- solid-state transformers
- power quality
- FACTS and CPD
- estimation or measurement of the grid parameters
- electromagnetic compatibility (EMC)
Published Papers (9 papers)
Open AccessArticle
A Methodology for Rating Electricity Transmission Lines to Assess the Most Important or Critical Lines
by
Artūras Trukšinas, Virginijus Radziukynas and Gediminas Kairaitis
Viewed by 735
Abstract
The proposed method, based on three combined criteria—Sn—design capacity of the power line, LF, (line flow)—power flow in an electric transmission line, MVA, and the ratio of LF/Sn—allows for ranking electric transmission lines when calculations are performed in normal/pre-emergency modes. A combined set
[...] Read more.
The proposed method, based on three combined criteria—Sn—design capacity of the power line, LF, (line flow)—power flow in an electric transmission line, MVA, and the ratio of LF/Sn—allows for ranking electric transmission lines when calculations are performed in normal/pre-emergency modes. A combined set of criteria used to study critical/post-emergency N-k modes is developed. The simulations were performed on the real Baltic 330 kV electricity transmission system. The results reveal that when the power system operates in different load modes, most of the critical power lines determined by our method fall into the actual set of important/“critical” power transmission lines. This allows us to significantly reduce the number of simulated combinations and shorten the calculation time required for it. During the study of the Baltic electricity system, it was found that the developed method was accurate and efficient and suitable for the assessment of the reliability of real electricity transmission networks when planning operational and perspective work modes. The simulations results revealed the high reliability of the Baltic electricity system. The 330 kV electricity transmission network of the Baltic countries fully meets the N-2 criterion (usually, electricity transmission networks are designed to meet the N-1 criterion).
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Operation of DR–HVdc-Connected Grid-Forming Wind Turbine Converters Using Robust Loop-Shaping Controllers
by
Jaime Martínez-Turégano, Antonio Sala, Ramon Blasco-Gimenez and Carlos Blanes
Viewed by 477
Abstract
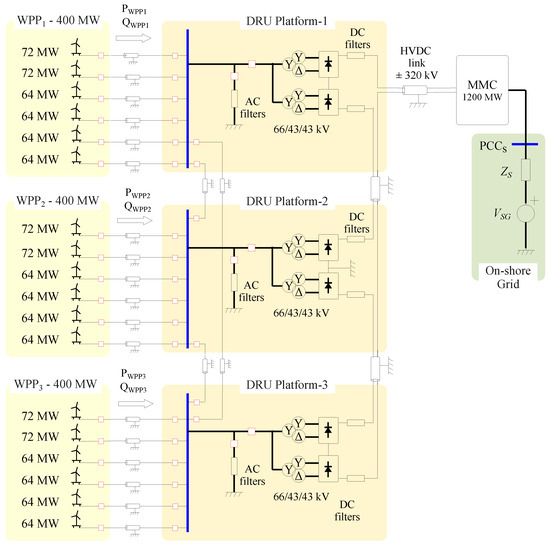
Off-shore wind power plants can be connected to the on-shore grid using diode rectifier HVdc links. As diode rectifiers are passive converters, off-shore WPPs require grid-forming capability. This paper shows how to improve the WTG dynamic response and the voltage and current harmonic
[...] Read more.
Off-shore wind power plants can be connected to the on-shore grid using diode rectifier HVdc links. As diode rectifiers are passive converters, off-shore WPPs require grid-forming capability. This paper shows how to improve the WTG dynamic response and the voltage and current harmonic rejection by using
-based controllers. The paper explains how to synthesise three different
voltage controllers: the first is a single-loop
controller, the second is a cascaded
controller and the third is a proportional–resonant controller that is optimised using
synthesis. The three
-based controllers improve the performance and the robustness obtained with a benchmark case PR controller tuned using the root locus technique. All the controllers are designed in continuous time and implemented in discrete time, applying bilinear discretisation with a sampling rate of 0.25 ms. Detailed PSCAD simulations validate the improvement of the performance and robustness, as well as an improvement in the harmonic rejection. The single
controller shows the best combined characteristics of all tried controllers, at the expense of losing the separation between voltage and current control loops.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
Multiport Energy Management System Design for a 150 kW Range-Extended Towing Vessel
by
Yachao Zhu, Hao Wang, Yuanyang Liu, Gang Lei and Jianguo Zhu
Viewed by 818
Abstract
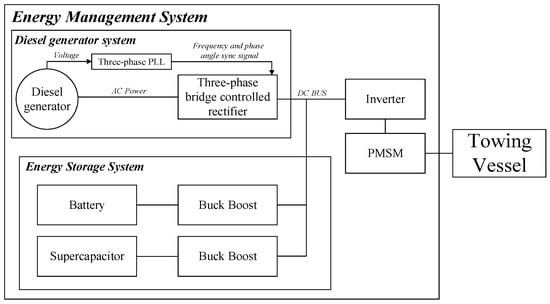
This paper proposes a multiport energy management system (EMS) and its rule-based expert control strategy for a 150 kW range-extended towing vessel (RETV). The system integrates a diesel generator system, a permanent magnet synchronous motor, a lithium battery, and supercapacitors. To verify its
[...] Read more.
This paper proposes a multiport energy management system (EMS) and its rule-based expert control strategy for a 150 kW range-extended towing vessel (RETV). The system integrates a diesel generator system, a permanent magnet synchronous motor, a lithium battery, and supercapacitors. To verify its feasibility and effectiveness, the proposed multiport EMS was modelled and tested through MATLAB/Simulink. Simulation results demonstrate that the designed multiport EMS works efficiently under the five typical operating conditions of the 150 kW RETV. In addition, two case studies were conducted and compared to investigate the impact of the battery’s initial state of charge (SoC) on the system’s energy efficiency. It was found that an overall 85% energy efficiency can be achieved for the RETV when the initial SoC is either 75% or 15%. The battery consistently operates within the optimal SoC range of 20% to 80%, and the supercapacitors effectively meet the instantaneous high-power demand.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
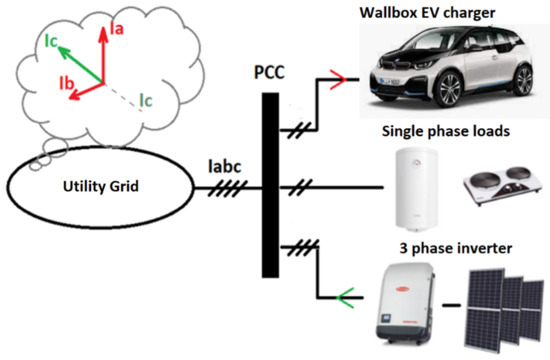
Voltage Control in LV Distribution Grid Using AC Voltage Compensator with Bipolar AC/AC Matrix Choppers
by
Elżbieta Sztajmec and Paweł Szcześniak
Viewed by 712
Abstract
The modern low-voltage distribution system is exposed to frequent changes in voltage amplitude due to the presence of high-power receivers with variable operating characteristics as well as distributed renewable energy sources whose generation levels depend on weather conditions. Maintaining the appropriate parameters related
[...] Read more.
The modern low-voltage distribution system is exposed to frequent changes in voltage amplitude due to the presence of high-power receivers with variable operating characteristics as well as distributed renewable energy sources whose generation levels depend on weather conditions. Maintaining the appropriate parameters related to power quality in the context of permissible voltage levels more and more often requires the use of additional voltage regulators. These are static systems in which the values of taps on transformers are changed, or dynamic compensators using power electronic converters. This article presents the continuation of research on one of the proposals of AC voltage compensators based on a bipolar AC/AC converter. The general properties of the presented system are reviewed and an analysis of the range of generated output voltages depending on the phase shift of the compensating voltage are presented. The next part of the article presents the formulas for calculating the duty cycle factors for the control functions of individual converters. The verification of the determined dependencies is presented on the basis of simulation tests of the proposed system. At the end of this article, the disadvantages of the proposed open-loop control system regulation and a proposal for further research are indicated.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Critical Current Degradation in HTS Tapes for Superconducting Fault Current Limiter under Repeated Overcurrent
by
Sylwia Hajdasz, Adam Kempski, Krzysztof Solak, Maciej Marc, Jacek Rusinski and Pawel Szczesniak
Viewed by 1279
Abstract
Superconducting fault current limiters (SFCL) can be an alternative to conventional devices limiting short-circuit currents in power systems. SFCL use high-temperature superconducting tapes of the second generation (HTS 2G) in SFCL, which, after reaching the characteristic critical current of the tape, go into
[...] Read more.
Superconducting fault current limiters (SFCL) can be an alternative to conventional devices limiting short-circuit currents in power systems. SFCL use high-temperature superconducting tapes of the second generation (HTS 2G) in SFCL, which, after reaching the characteristic critical current of the tape, go into the resistive state (quenching), limiting the short-circuit current. The critical current determines the moment of activation of the SFCL. Therefore, its value should not change during the operation of the device due to repeated limitation of short-circuit currents. The constancy of the critical current is a prerequisite for proper cooperation with the power system protection devices. Multiple quenching can cause microdamage in the superconducting layers responsible for lowering of the value of the critical current of the HTS tapes. The article presents the research results on the degradation processes of 2G HTS tapes intended for the construction of SFCL due to the action of prospective short-circuit currents with values exceeding the critical current of the tested tapes. The decrease in the value of the critical current of the HTS tape as a result of multiple transitions to the resistive state was investigated. The amount of energy emitted during the test current pulse of 0.2 s duration was determined. The limitation values of the voltage drop on the tape, which does not cause accelerated degradation processes, were defined. The microstructural tests of cross-sections of new HTS tapes subjected to prospective short-circuit currents were performed.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Sensorless Current Pulsation Compensation in a Hybrid Energy Storage
by
Karol Fatyga and Dariusz Zieliński
Cited by 1 | Viewed by 640
Abstract
This paper presents a dual active bridge DC/DC converter used as an AC current compensator in a hybrid energy storage application. The AC current in the DC link appears when a three-phase, four-wire inverter operates with unbalanced output currents—for example, when trying to
[...] Read more.
This paper presents a dual active bridge DC/DC converter used as an AC current compensator in a hybrid energy storage application. The AC current in the DC link appears when a three-phase, four-wire inverter operates with unbalanced output currents—for example, when trying to compensate for grid voltage unbalance. This AC current has adverse effects on the operation of the electrochemical energy storage, and it should be compensated. To achieve this, a compensator is introduced into the DC link circuit of the inverter—a DC/DC converter with a capacitor bank. The DC/DC converter is responsible for compensating the AC pulsation by creating its own pulsation with the opposite phase. In the paper, the genesis of this pulsation is explained, and a compensation circuit is proposed along with a sensorless compensation algorithm. The algorithm is based on symmetrical decomposition and is used to generate a reference signal for the compensator. The numerical analysis of the algorithm is presented, and the operation of the compensator is verified on the laboratory bench.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
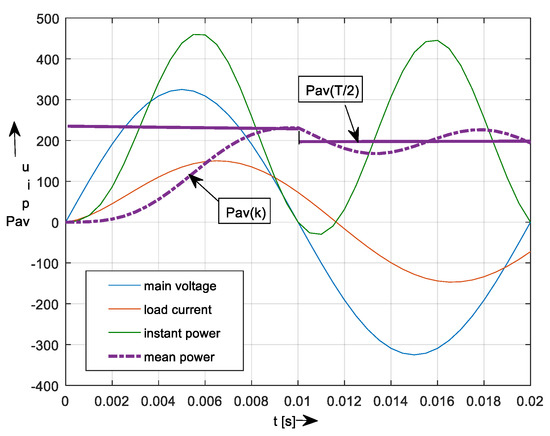
Single-Step Response and Determination of Power Components Mean Values of PES Using p-q Method during Transients
by
Branislav Dobrucký, Slavomír Kaščák, Jozef Šedo, Michal Praženica and Patrik Resutík
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 1027
Abstract
This paper deals with the quasi-instantaneous determination of an apparent-, active-, and reactive (i.e., blind and distortion) power mean values, including total power factor, total harmonic distortion, and phase shift of fundamentals of power electronic system (PES) using the
p-q method. The power
[...] Read more.
This paper deals with the quasi-instantaneous determination of an apparent-, active-, and reactive (i.e., blind and distortion) power mean values, including total power factor, total harmonic distortion, and phase shift of fundamentals of power electronic system (PES) using the
p-q method. The power components’ mean values are investigated both during transients and steady states. Using an integral calculus over one period and the moving average method (or digital filtering), the power components’ mean values can be determined within the next calculation step directly from phase current and voltage quantities. Consequently, with known values of a phase shift of fundamentals (using Fourier analysis), the power factor can be evaluated. The results of this study show how a distortion power component during transients is generated even under harmonic supplying and linear resistive-inductive load. The paper contains a theoretical base, modeling, and simulation for the 5-, 3-, and 2-phases of PES transients. A system compensated by switched capacitors as well as an active power filter shows a possibility to compensate for distortion and reactive power components in the next calculation step. Worked-out results can be used for the right determination and sizing of any PES. The presented approach brings the detailed time-waveform and improved quality of electrical quantities (time-waveforms), and through quasi-instantaneous (single step) response time of compensation, minimizes nascent overvoltage of the system.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
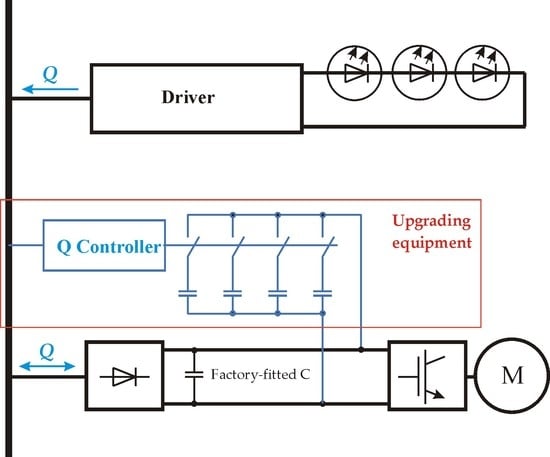
Application of Single-Phase Supply AC-DC-AC VFD for Power Factor Improvement in LED Lighting Devices Loaded Power Distribution Lines
by
Gytis Petrauskas and Gytis Svinkunas
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 1735
Abstract
More and more light-emitting diode lighting devices (LED) are being connected to modern power distribution lines. In addition to its many positive features, this poses problems in terms of reactive power compensation. The large number of LEDs interacting with traditional reactive power compensators
[...] Read more.
More and more light-emitting diode lighting devices (LED) are being connected to modern power distribution lines. In addition to its many positive features, this poses problems in terms of reactive power compensation. The large number of LEDs interacting with traditional reactive power compensators leads to a harmful phenomenon—overcompensation. This was experimentally determined in the investigated power distribution lines. Along with LEDs, a large number of devices with variable frequency drives (VFD) are connected to the same power distribution lines. This study presents an innovative approach to conventional diode rectifier supply side AC-DC-AC VFDs. It is proposed to use these VFDs as a reactive power compensation device while maintaining their main functions—motor powering and motor speed control. Minor improvements have been proposed to enable these VFDs to provide and draw out reactive power, thereby keeping power factors close to the unit in LED-loaded power distribution lines. The proposed improvements are based on the interaction between the power distribution lines inductivity and the DC circuit capacitance of the VFD. It has been shown that the power factor can be controlled by varying the capacity of the DC circuit. The ability of the AC-DC-AC VFD to compensate for the reactive power provided by the light-emitting diode lighting devices was confirmed by mathematical calculations and experimentally with a laboratory prototype.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
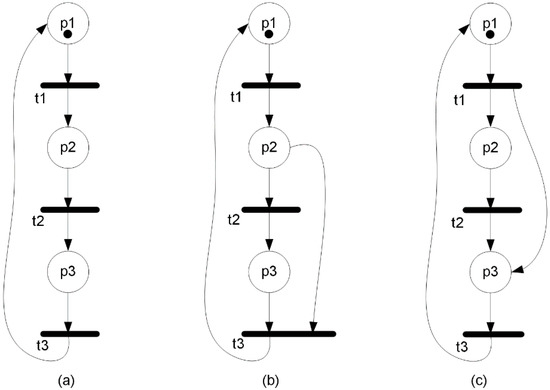
Interpreted Petri Nets Applied to Autonomous Components within Electric Power Systems
by
Iwona Grobelna and Paweł Szcześniak
Cited by 6 | Viewed by 1771
Abstract
In this article, interpreted Petri nets are applied to the area of power and energy systems. These kinds of nets, equipped with input and output signals for communication with the environment, have so far proved to be useful in the specification of control
[...] Read more.
In this article, interpreted Petri nets are applied to the area of power and energy systems. These kinds of nets, equipped with input and output signals for communication with the environment, have so far proved to be useful in the specification of control systems and cyber–physical systems (in particular, the control part), but they have not been used in power systems themselves. Here, interpreted Petri nets are applied to the specification of autonomous parts within power and energy systems. An electric energy storage (EES) system is presented as an application system for the provision of a system service for stabilizing the power of renewable energy sources (RES) or highly variable loads. The control algorithm for the EES is formally written as an interpreted Petri net, allowing it to benefit from existing analysis and verification methods. In particular, essential properties of such specifications can be checked, including, e.g., liveness, safety, reversibility, and determinism. This enables early detection of possible structural errors. The results indicate that interpreted Petri nets can be successfully used to model and analyze autonomous control components within power energy systems.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures