Journal Description
Applied Biosciences
Applied Biosciences
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on all aspects of applied biosciences published quarterly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 37.7 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 7.5 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2023).
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
- Applied Biosciences is a companion journal of Applied Sciences.
Latest Articles
Impact of Salinity Fluctuations on Dunaliella salina Biomass Production
Appl. Biosci. 2024, 3(2), 213-219; https://doi.org/10.3390/applbiosci3020014 - 8 May 2024
Abstract
►
Show Figures
The utilization of microalgae as a green carbon source for chemical production has attracted attention for its potential use in sustainable and climate-friendly solutions. This study investigates the growth of Dunaliella salina, a unicellular green microalga, in response to salinity variations and
[...] Read more.
The utilization of microalgae as a green carbon source for chemical production has attracted attention for its potential use in sustainable and climate-friendly solutions. This study investigates the growth of Dunaliella salina, a unicellular green microalga, in response to salinity variations and water and seawater addition to compensate for evaporation in open cultures. The impact of continuous and non-continuous water addition, as well as seawater addition, on the growth of D. salina was analyzed though tank tests. The results showed that different water-addition methods did not significantly influence cell concentrations, indicating the organism’s resilience to salinity changes. Continuous water addition maintained stable salinity levels at 12%, but required continuous monitoring, while non-continuous addition reduced the intervention frequency. The overall results showed that a salinity range between 12 and 15% did not affect microalgae growth, suggesting flexibility in evaporation-loss compensation methods based on cultivation-system specifics and resource availability. Maintaining consistent biomass regardless of the water-addition method used suggests sustainable production within the tested salinity range, with seawater addition making microalgae cultivation more adaptable to regions with varying water availability. Further research, including outdoor pilot tests, is recommended to validate and extend these findings to natural environments.
Full article
Open AccessReview
Moringa oleifera Seed Cake: A Review on the Current Status of Green Nanoparticle Synthesis
by
Nuno Coelho, Alice S. Pereira and Pedro Tavares
Appl. Biosci. 2024, 3(2), 197-212; https://doi.org/10.3390/applbiosci3020013 - 29 Apr 2024
Abstract
Growing demands for sustainable and ecological nanoparticle synthesis methods have incentivized the scientific community to develop new approaches to counteract these challenges. Green synthesis resorts to biocomponents obtained from plants, bacteria, fungi, and other organisms to synthesize nanostructures, with beneficial gains in the
[...] Read more.
Growing demands for sustainable and ecological nanoparticle synthesis methods have incentivized the scientific community to develop new approaches to counteract these challenges. Green synthesis resorts to biocomponents obtained from plants, bacteria, fungi, and other organisms to synthesize nanostructures, with beneficial gains in the economic and ecological cost associated with the process, simplicity of the process, and resource efficiency. Moringa oleifera, a native plant originally from India with immense nutritive value, has long been used by researchers in the biosynthesis of nanoparticles. Leaves, flowers, bark, and seeds are among the “miracle tree” parts that can be used in nanoparticle green synthesis. Moringa oleifera seed cake, a by-product obtained from defatted seeds, is often overlooked due to its apparent low commercial value. The main objective of this review is to highlight the recent findings reported in the literature on nanoparticles/nanocomposites synthesized with seed cake biocompounds acting as reducing/capping agents. Furthermore, we analyzed the methods currently employed for the extraction of bioactive compounds. Moringa oleifera seed for industrial applications was also addressed.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Feature Papers in Applied Biosciences 2024)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessCommunication
The Antibacterial Activity of Novel Bacteriophages and the Emergence of Bacterial Resistance to Phage Infections: An In Vitro Study
by
Letícia de Souza Moda-Silva, Viviane de Cássia Oliveira, Tatiana Areas da Cruz, Amanda Carolina Souza Delfino da Rocha and Evandro Watanabe
Appl. Biosci. 2024, 3(2), 186-196; https://doi.org/10.3390/applbiosci3020012 - 12 Apr 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The emergence of bacteria resistant to bacteriophage (phage) infection may compromise the success and effectiveness of phage therapy. The aim of this study was to evaluate the in vitro antibacterial activity of five novel phages, as well as the emergence of bacterial resistance
[...] Read more.
The emergence of bacteria resistant to bacteriophage (phage) infection may compromise the success and effectiveness of phage therapy. The aim of this study was to evaluate the in vitro antibacterial activity of five novel phages, as well as the emergence of bacterial resistance to phage infections. The antibacterial activity of lytic phages was evaluated against standard strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa (ATCC 27853), Escherichia coli (ATCC 25927), Enterococcus faecalis (ATCC 29212) and Staphylococcus aureus (ATCC 6538). Phages were initially grown in the presence of host bacteria in an exponential growth phase, then purified and titrated. In a second exposure, 20 μL of each phage was inoculated with 106 CFU/mL of P. aeruginosa/E. coli/E. faecalis/S. aureus, separately. In a third exposure, resistant colonies were isolated, cultivated and exposed again to the phages. Bacterial colonies resistant to phage infection after the third exposure were evaluated for their susceptibility profile to different antibiotics via the diffusion disk technique. The diameters of the inhibition halos were evaluated with Image J software (version 1.54g) and the definition of the susceptibility profile to antibiotics was determined according to the European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST) criteria. In addition, fourteen cocktails with different phages were formulated to evaluate the emergence of a bacterial resistance to phage infections. The phages exhibited specificity for P. aeruginosa and did not infect E. coli, E. faecalis and S. aureus. The presence of bacterial colonies resistant to phage infection in the three successive exposures was identified, and the bacterial resistance to phage infection was confirmed in all phages titrated at 108 PFU/mL, in four phages titrated at 1010 PFU/mL and in one phage titrated at 1013 PFU/mL. The development of a resistance to infection by phages (~108 PFU/mL) did not change the susceptibility profile of P. aeruginosa to antibiotics and, when evaluating the emergence of a resistance to infection by phage cocktails (~108 PFU/mL, ~1010 PFU/mL, ~1013 PFU/mL), bacterial resistance to phage infection was confirmed in all cocktails with phages titrated at 108 PFU/mL, in ten cocktails with phages titrated at 1010 PFU/mL and in seven cocktails with phages titrated at 1013 PFU/mL. In conclusion, the presence of resistant P. aeruginosa colonies to phage infection after successive exposures was evidenced, although some phages at title ~1010 PFU/mL and ~1013 PFU/mL were effective in inhibiting the growth of resistant colonies. The development of resistance did not change the susceptibility profile of P. aeruginosa to antibiotics. Variants of P. aeruginosa that were resistant to phage infection were isolated and their resistance to infection via the phage cocktail was demonstrated regardless of the viral titer, although some cocktails at title ~1010 PFU/mL and ~1013 PFU/mL were effective in inhibiting the growth of resistant colonies. Despite the emergence of bacterial variants resistant to phage infection, new studies involving the applicability of phages in the control of infections must be conducted.
Full article
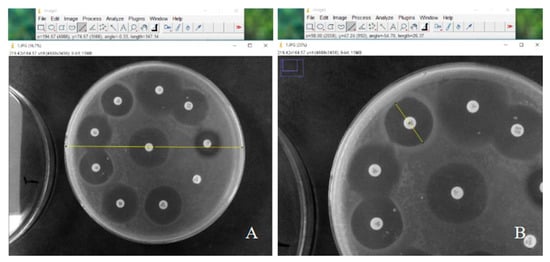
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Effects of Bone Marrow Sparing and TGF-β3 Treatment in Total Body Irradiation of C57BL/6J Mice
by
Ingunn Hanson, Jenny T. Vatne and Nina F. J. Edin
Appl. Biosci. 2024, 3(2), 165-185; https://doi.org/10.3390/applbiosci3020011 - 4 Apr 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Introduction: Mortality from acute radiation syndrome is frequently caused by hematopoietic or gastrointestinal radiotoxicity, the latter of which currently has no effective treatment. Transforming growth factor-beta 3 (TGF-β3) may decrease the severity of radiation-induced gastrointestinal damage in mice. In addition, treatment with TGF-β3
[...] Read more.
Introduction: Mortality from acute radiation syndrome is frequently caused by hematopoietic or gastrointestinal radiotoxicity, the latter of which currently has no effective treatment. Transforming growth factor-beta 3 (TGF-β3) may decrease the severity of radiation-induced gastrointestinal damage in mice. In addition, treatment with TGF-β3 may alleviate radiation-induced fibrosis. Objectives: The current study aimed to investigate the effect of TGF-β3 treatment on acute and late radiotoxicity in whole body irradiated mice. Methods: C57BL/6J mice were total body irradiated with 8.5 Gy X-rays with or without shielding of one hind leg to alleviate hematopoietic radiotoxicity. The effects of intravenous TGF-β3 treatment were investigated. Body weight and pain expression were monitored. Intestine, lung, and liver tissues were preserved and analyzed. Alpha smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) expression in MRC-5 cells after 3.5 Gy X-irradiation combined with TGF-β3 treatment was analyzed using flow cytometry. Results: All total body irradiated animals died within ten days after irradiation. Ninety-three percent of femur-shielded mice survived until sampling or termination. No effect of TGF-β3 treatment was observed in either group. No increase in collagen content was detected in the lungs or liver from irradiated mice regardless of TGF-β3 treatment. In vitro, α-SMA expression increased synergistically after irradiation and TGF-β3 treatment. Conclusions: Shielding of the femur during total body irradiation decreased acute gastrointestinal radiation toxicity and increased survival. TGF-β3 treatment did not impact symptoms or survival. TGF-β3 treatment and irradiation increased α-SMA expression in MRC-5 cells synergistically.
Full article
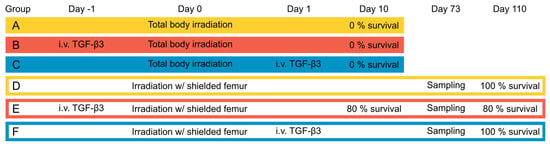
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Biostimulant Effect of Commercial Rhizobacteria Formulation on the Growth of Vitis vinifera L.: Case of Optimal and Water Deficit Conditions
by
Vasileios Papantzikos, Areti Papanikou, Vasileios Stournaras, Paraskevi Mpeza, Spiridon Mantzoukas and Georgios Patakioutas
Appl. Biosci. 2024, 3(1), 151-164; https://doi.org/10.3390/applbiosci3010010 - 8 Mar 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
As climate change is an imminent threat to the environment and agriculture, there is an increasing need to find immediate solutions capable of compensating for water deficits even in semi-arid conditions. This study is focused on the evaluation of the vegetative growth of
[...] Read more.
As climate change is an imminent threat to the environment and agriculture, there is an increasing need to find immediate solutions capable of compensating for water deficits even in semi-arid conditions. This study is focused on the evaluation of the vegetative growth of grapevine plants Vitis vinifera L., of the Greek variety “Debina” in a water deficit environment, with the application of two bacterial-based formulations: one with Bacillus amyloliquefaciens (strain QST 713) and one with Sinorhizobium meliloti (strain cepa B2352). The two formulations were tested under rational irrigation (100% of Available Water) and deficit irrigation (57% of AW). After 140 days, plant growth parameters, such as total plant growth length, leaf area, roots, shoots, and leaves dry biomass showed better performance on treatments with plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) formulations under either rational or deficit irrigation conditions. In addition, the metabolic response of the grapevine plants to the deficit irrigation stress, such as the total chlorophyll, leaf relative water, total phenolic, and proline content, proved to be enriched on the treatments with PGPR formulations during this experiment. The two formulations, in conditions of abiotic stress, achieved to almost compensate for the irrigation deficit, boosting the plant metabolism. This study reveals the need for further research on PGPR biostimulants, as this first trial of these formulations on grapevine could be significant in the case of water scarcity and climate change.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Exploring the Cellular Interactions of Flavonoids with Similar Structures in Cells Overexpressing the 70 kDa Human Heat Shock Protein
by
Garyfallia Papa, Yannis V. Simos, Antrea-Maria Athinodorou, Konstantinos I. Tsamis, Dimitrios Peschos, Charalampos Angelidis, Periklis Pappas and Patra Vezyraki
Appl. Biosci. 2024, 3(1), 137-150; https://doi.org/10.3390/applbiosci3010009 - 6 Mar 2024
Abstract
Flavonoids share a common structural framework that serves as a hallmark indicative of their biological activity. In this study, we investigated the effects of two structurally similar flavonoids, fisetin and morin, through independent and combined in vitro assessments on embryonic mouse cells overexpressing
[...] Read more.
Flavonoids share a common structural framework that serves as a hallmark indicative of their biological activity. In this study, we investigated the effects of two structurally similar flavonoids, fisetin and morin, through independent and combined in vitro assessments on embryonic mouse cells overexpressing the human 70 kDa heat shock protein (Hsp70) (Tg/Tg) and normal mouse fibroblast cell line (NIH/3T3). The primary objectives were to evaluate the biocompatibility and potential cytotoxicity of these flavonoids, along with assessing the cytoprotective role of Hsp70 in these cellular environments. To address these objectives, we conducted dose- and time-dependent cell survival tests. Additionally, we utilized flow cytometry to detect intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) production and to analyze apoptosis and the cell cycle. Throughout the experimental procedures, a notable observation was made: NIH/3T3 normal cells exhibited greater susceptibility compared to Tg/Tg cells when exposed to fisetin and morin. This difference in susceptibility is likely attributed to the robust cytoprotective effect of Hsp70 in Tg/Tg cells. Importantly, both cell lines demonstrated increased sensitivity to fisetin toxicity in comparison to morin, leading to significantly lower cell survival rates. These findings shed light on the differential responses of cell lines to flavonoid exposure, emphasizing the influence of Hsp70 and the distinct impact of fisetin and morin on cell viability.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Plant Natural Compounds: From Discovery to Application)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Fructooligosaccharides Supplementation: A Good Choice for the Prevention and Treatment of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease?
by
Priscila Nogueira Bezan, Héric Holland, Bárbara Ferreira Vercesi, Paula Payão Ovídio, Livia Maria Cordeiro Simões and Alceu Afonso Jordão
Appl. Biosci. 2024, 3(1), 123-136; https://doi.org/10.3390/applbiosci3010008 - 1 Mar 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background and objectives: Carbohydrates such as fructooligosaccharides (FOSs) are associated with improved gastrointestinal health and the prevention of excess body fat. We evaluated the long-term effects of high amounts of FOS on metabolic parameters, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and short-chain fatty acids
[...] Read more.
Background and objectives: Carbohydrates such as fructooligosaccharides (FOSs) are associated with improved gastrointestinal health and the prevention of excess body fat. We evaluated the long-term effects of high amounts of FOS on metabolic parameters, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs). Methods: Sixty C57BL/6 mice received the following diets for four months: control (C), normolipid rich in fiber (F), normolipid supplemented with FOS (FOS), high fat (HL), high fat with high fiber (HLF) and high fat with FOS (HLFOS). We analyzed the animal weight; body composition; food intake; fasting blood glucose; serum and liver lipid profiles; liver and intestinal histologies; malondialdehyde (MDA), hepatic retinol and α-tocopherol; and SCFAs in the feces. Results: Supplementation with FOS in a high-fat diet promoted less body weight gain and reduced liver and retroperitoneal adipose tissue weights compared to HL and HF. FOS prevented NASH and decreased alanine aminotransferase and serum cholesterol levels in experimental animal models of obesity and metabolic syndrome (MS). There were statistical differences found in the dosages of the three main SCFAs in feces (acetic, isobutyric and isovaleric acids). Conclusions: Long-term supplementation with high doses of FOS was effective in reducing weight, adiposity, NAFLD and serum cholesterol in C57BL mice with obesity and MS induced by a high-fat diet.
Full article
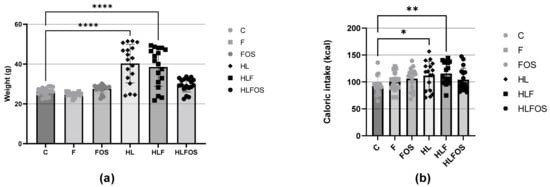
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Methods for Testing Meniscal Repair Using a 3D-Printed Meniscus
by
Andrew Nelson, Steven Voinier, Jeremy Tran, Kristin H. Gilchrist, Melvin Helgeson, Vincent B. Ho and George J. Klarmann
Appl. Biosci. 2024, 3(1), 102-122; https://doi.org/10.3390/applbiosci3010007 - 6 Feb 2024
Cited by 1
Abstract
Torn and damaged menisci resulting from trauma are very common knee injuries, which can cause pain and mobility limitations and lead to osteoarthritis. Meniscal injuries can require surgery to repair the tissue damage and restore mobility. Here we describe the biomechanical testing of
[...] Read more.
Torn and damaged menisci resulting from trauma are very common knee injuries, which can cause pain and mobility limitations and lead to osteoarthritis. Meniscal injuries can require surgery to repair the tissue damage and restore mobility. Here we describe the biomechanical testing of a 3D-printed meniscus to illustrate methods to determine if it has the strength and durability to effectively repair meniscal tears and restore knee biomechanics. This work was designed to demonstrate the steps needed to test novel meniscus repair devices prior to moving toward animal testing. The first testing step determined the ability of the 3D-printed meniscus to withstand surgical fixation by measuring the suture pull-out force. We show that vertical 2/0 silk or Fiberwire sutures need an average of 1.4 or 1.8 N, respectively, to pull through the meniscus, while horizontal sutures need only 0.7 and 1.2 N, respectively. The next step measured the compressive strength of normal, damaged, and repaired porcine meniscus tissue. Here, we show that meniscectomy decreased the stiffness of meniscus tissue from 26.7 ± 0.85 N to 7.43 ± 0.81 N at 25% strain. Menisci repaired with the 3D-printed tissue restored 66% of the measured force at 25% strain. The final step measured the contact pressures and areas in an ex vivo porcine knee before and after meniscal repair was made with the 3D-printed meniscus tissue. The example 3D-printed meniscus was successfully sutured into the porcine knee joint but failed to restore normal knee contact pressures. This work demonstrates the need for an iterative biomechanical testing process of biomaterial development, 3D-printing optimization, and knee kinematics to develop a durable and functional meniscus repair device. In summary, the methods described here serve as a guide for the functional evaluation of novel meniscus repair devices.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Anatomy and Regenerative Medicine: From Methods to Applications)
►▼
Show Figures
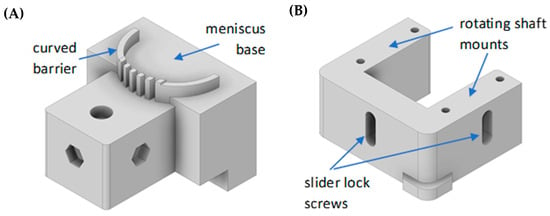
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
The Antioxidant and Antibacterial Potential of Thyme and Clove Essential Oils for Meat Preservation—An Overview
by
Sara Ricardo-Rodrigues, Maria Inês Rouxinol, Ana Cristina Agulheiro-Santos, Maria Eduarda Potes, Marta Laranjo and Miguel Elias
Appl. Biosci. 2024, 3(1), 87-101; https://doi.org/10.3390/applbiosci3010006 - 6 Feb 2024
Cited by 1
Abstract
Consumers are looking for safer and more natural food options that are produced through natural methods without using synthetic preservatives. They also desire extended shelf life for their food products. Several medicinal and aromatic plants species combine food, spice, aromatic, and medicinal recognized
[...] Read more.
Consumers are looking for safer and more natural food options that are produced through natural methods without using synthetic preservatives. They also desire extended shelf life for their food products. Several medicinal and aromatic plants species combine food, spice, aromatic, and medicinal recognized attributes. The essential oils from these plants contain a unique mixture of compounds specific to each plant, showing notable antioxidant and antimicrobial properties. Essential oils are used widely as they are environmentally friendly, non-toxic, and biodegradable substitutes for harsh chemical preservatives. Thyme and clove are aromatic plants commonly used in traditional gastronomy, particularly in meat-based recipes. The preservation effects of these essential oils on fresh meat have not been widely studied. Therefore, the aim of this study is to review the use of thyme and clove essential oils in meat preservation, with particular emphasis on their antioxidant properties to mitigate lipid and protein oxidation. Different strategies have been used to boost the effects of essential oils in foods, which include mixtures of essential oils, encapsulation and nanoemulsification techniques, with or without edible coatings. The final objective is to promote the wide use of essential oils for meat preservation, eventually in combination with other innovative approaches.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Plant Natural Compounds: From Discovery to Application)
►▼
Show Figures
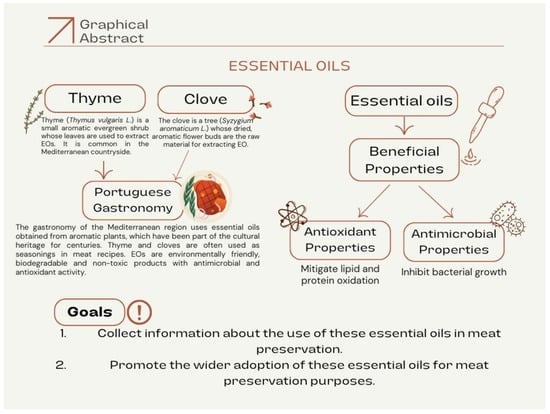
Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Refractance Window Drying as an Alternative Method for Brewer’s Spent Grain Preservation
by
Neiton C. Silva, Andressa O. Santos, Claudio R. Duarte and Marcos A. S. Barrozo
Appl. Biosci. 2024, 3(1), 71-86; https://doi.org/10.3390/applbiosci3010005 - 1 Feb 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Brewer’s spent grain (BSG) is a residue that holds significant potential for various applications. Given its inherently high moisture levels, it becomes imperative to explore methods for preserving it. This study investigates the use of refractance window (RW) for drying BSG. The final
[...] Read more.
Brewer’s spent grain (BSG) is a residue that holds significant potential for various applications. Given its inherently high moisture levels, it becomes imperative to explore methods for preserving it. This study investigates the use of refractance window (RW) for drying BSG. The final moisture content, water activity, and drying kinetics were assessed. Various kinetic models were analyzed, including Lewis, Page, Overhults, Brooker, and Midilli. Employing a central composite design, this study also investigated the effects of the variables temperature (55.9 to 84.1 °C) and drying time (1.6 to 4.4 h) on the quality of the dried product. The quality was assessed based on the content of bioactive compounds: phenolics, flavonoids, citric acid, and ascorbic acid. The results suggest that refractance window (RW) drying can yield a product with reduced moisture content and water activity levels (lower than 10.0% and 0.600, respectively). The phenolic, flavonoid, and citric acid higher contents were found at 70 °C and 3 to 4 h of drying. The best ascorbic acid results were found at 55 to 65 °C after 3 h of drying. The use of RW emerges as an interesting alternative for processing BSG, offering a sustainable approach to better utilize this residue.
Full article
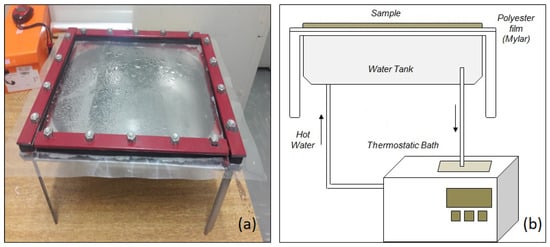
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Fostering Resilience and Wellness: The Synergy of Mindful Eating and the Mediterranean Lifestyle
by
Efstratios Christodoulou, Georgia-Eirini Deligiannidou, Christos Kontogiorgis, Constantinos Giaginis and Antonios E. Koutelidakis
Appl. Biosci. 2024, 3(1), 59-70; https://doi.org/10.3390/applbiosci3010004 - 17 Jan 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Increasing evidence indicates that the cultivation of mindful eating, adherence to the Mediterranean lifestyle, and the development of psychological resilience may contribute to the enhancement of overall health and well-being. The purpose of this study was to explore the association between mindful eating
[...] Read more.
Increasing evidence indicates that the cultivation of mindful eating, adherence to the Mediterranean lifestyle, and the development of psychological resilience may contribute to the enhancement of overall health and well-being. The purpose of this study was to explore the association between mindful eating and the Mediterranean lifestyle in relation to psychological resilience and the maintenance of a healthy weight. In the framework of a cross-sectional study, 288 individuals voluntarily took part in an online research survey conducted in Greece. Results showed that both mindful eating and the Mediterranean diet were significantly correlated (p < 0.001) with psychological resilience. Multiple regression models identified mindful eating and the Mediterranean diet as predictive factors of psychological resilience (p < 0.001). There was a statistically significant (p < 0.05) intercorrelation between mindful eating, the Mediterranean diet, and psychological resilience. Following the application of multiple regression models, mindful eating and Mediterranean diet were identified as predictive factors of psychological resilience (p < 0.0001). Individuals with a normal Body Mass Index (BMI) displayed stronger adherence to mindful eating and the Mediterranean lifestyle, in contrast to those classified in the overweight and obesity BMI groups. People with higher mindful eating scores had 14% better odds of maintaining their weight loss after a weight-reducing diet than those with a lower mindful eating score (OR: 1.142, 95% CI: 1.084, 1.204, p < 0.0001). In summary, the integration of mindful eating and the Mediterranean lifestyle may represent a feasible approach to bolstering psychological resilience, overall health, and well-being.
Full article
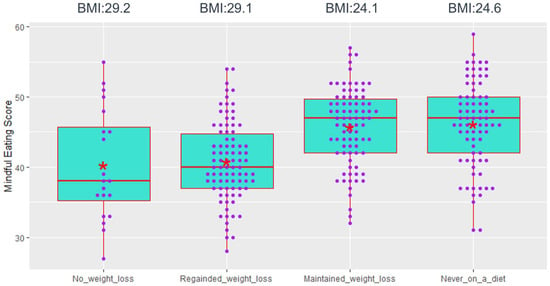
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Heat Shock Proteins Mediate Intercellular Communications within the Tumor Microenvironment through Extracellular Vesicles
by
Renata F. Saito, Camila Maria Longo Machado, Ana Luiza Oliveira Lomba, Andréia Hanada Otake and Maria Cristina Rangel
Appl. Biosci. 2024, 3(1), 45-58; https://doi.org/10.3390/applbiosci3010003 - 1 Jan 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
From an evolutive perspective, tumor cells endure successive turnover upon stress conditions and pressure to adapt to new environments. These cells use exceptional communication skills to share biological information to “survive upon every metabolic cost”. The tumor microenvironment (TME) is a miscellaneous collection
[...] Read more.
From an evolutive perspective, tumor cells endure successive turnover upon stress conditions and pressure to adapt to new environments. These cells use exceptional communication skills to share biological information to “survive upon every metabolic cost”. The tumor microenvironment (TME) is a miscellaneous collection of cells, factors, and extracellular vesicles (EVs). EVs are small lipid bilayer-delimited particles derived from cells with sizes ranging from 100 to 1000 nm. Exosomes (<160 nm) are the minor subtype of EVs, originating from the endosomal pathways. The TME also contains “giant” vesicles, microvesicles (100–1000 nm, MV), originated from membrane blebbing. EVs can act as intercellular communication mediators, contributing to many biological processes, by carrying different biomolecules, such as proteins, lipids, nucleic acids, and metabolites. EV secretion can promote either tumor cell survival or manage their stress to death. Tumor-derived EVs transfer adaptative stress signaling to recipient cells, reprograming these cells. Heat shock proteins (HSP) are prominent stress response regulators, specifically carried by exosomes. HSP-loaded EVs reprogram tumor and TME cells to acquire mechanisms contributing to tumor progression and therapy resistance. The intercellular communication mediated by HSP-loaded EVs favors the escape of tumor cells from the endoplasmic reticulum stress, hypoxia, apoptosis, and anticancer therapies. Extracellular HSPs activate and deactivate the immune response, induce cell differentiation, change vascular homeostasis, and help to augment the pre-metastatic niche formation. Here we explore EVs’ mechanisms of HSP transmission among TME cells and the relevance of these intercellular communications in resistance to therapy.
Full article
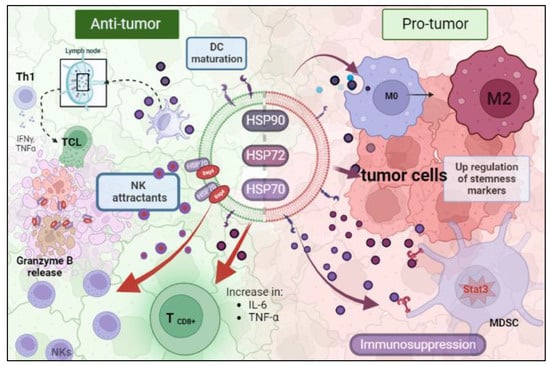
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
The Integration of Artificial Intelligence into Clinical Practice
by
Vangelis D. Karalis
Appl. Biosci. 2024, 3(1), 14-44; https://doi.org/10.3390/applbiosci3010002 - 1 Jan 2024
Cited by 5
Abstract
The purpose of this literature review is to provide a fundamental synopsis of current research pertaining to artificial intelligence (AI) within the domain of clinical practice. Artificial intelligence has revolutionized the field of medicine and healthcare by providing innovative solutions to complex problems.
[...] Read more.
The purpose of this literature review is to provide a fundamental synopsis of current research pertaining to artificial intelligence (AI) within the domain of clinical practice. Artificial intelligence has revolutionized the field of medicine and healthcare by providing innovative solutions to complex problems. One of the most important benefits of AI in clinical practice is its ability to investigate extensive volumes of data with efficiency and precision. This has led to the development of various applications that have improved patient outcomes and reduced the workload of healthcare professionals. AI can support doctors in making more accurate diagnoses and developing personalized treatment plans. Successful examples of AI applications are outlined for a series of medical specialties like cardiology, surgery, gastroenterology, pneumology, nephrology, urology, dermatology, orthopedics, neurology, gynecology, ophthalmology, pediatrics, hematology, and critically ill patients, as well as diagnostic methods. Special reference is made to legal and ethical considerations like accuracy, informed consent, privacy issues, data security, regulatory framework, product liability, explainability, and transparency. Finally, this review closes by critically appraising AI use in clinical practice and its future perspectives. However, it is also important to approach its development and implementation cautiously to ensure ethical considerations are met.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Feature Papers in Applied Biosciences 2023)
►▼
Show Figures
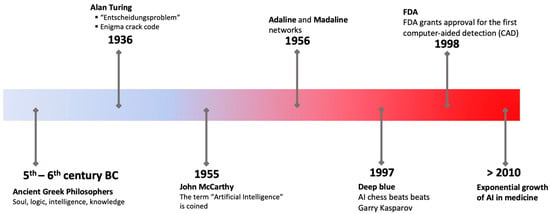
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A Single Dose of Microencapsulated Cocoa Supplementation Does Not Speed up Muscle Force Recovery after Eccentric Exercise-Induced Muscle Damage: A Placebo-Controlled, Double-Blind, Crossover Study
by
Olavo João Frederico Ramos Junior, Karen Souza dos Santos, Isabela Ribeiro Grangeira Tavares, Gustavo Vieira de Oliveira and Thiago Silveira Alvares
Appl. Biosci. 2024, 3(1), 1-13; https://doi.org/10.3390/applbiosci3010001 - 22 Dec 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Exercise-induced muscle damage is associated with symptoms such as inflammation, delayed-onset muscle soreness, and impaired muscle performance. The intake of cocoa polyphenols has been suggested to improve muscle recovery due to their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory capacity. However, their bioavailability presents a challenge. Therefore,
[...] Read more.
Exercise-induced muscle damage is associated with symptoms such as inflammation, delayed-onset muscle soreness, and impaired muscle performance. The intake of cocoa polyphenols has been suggested to improve muscle recovery due to their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory capacity. However, their bioavailability presents a challenge. Therefore, food microencapsulation may be an alternative to protect polyphenols, ensuring their biological effects. This study aimed to investigate the effect of a single dose of microencapsulated cocoa on the changes in muscle damage markers after eccentric exercise. In this randomized, double-blind, crossover study, fourteen healthy volunteers with previous resistance training experience performed 6 × 10 maximal isokinetic eccentric contractions of their elbow flexors using an isokinetic dynamometer after ingesting 25 g of microencapsulated cocoa or placebo. Peak isometric torque was measured using maximal voluntary isometric contractions, and pain was measured using a visual analogic scale both before and 24 h, 48 h, and 72 h after the damage protocol. Plasma glutathione and malondialdehyde levels were measured using high-performance liquid chromatography, and concentrations of myoglobin and C-reactive protein were determined using a fluorescence immunoassay analyzer. Significant decreases were seen in the peak isometric torque and pain measures from pre- to 72 h post-eccentric exercise. A significant main effect for time was found only for plasma myoglobin at 2 h, 48 h, and 72 h, and for C-reactive protein at 2 h, compared to the pre-eccentric exercise values. No significant time-treatment effects were observed (all p > 0.05). This study demonstrated that microencapsulated cocoa cannot improve muscle recovery after eccentric exercise, at least when a single dose is consumed.
Full article
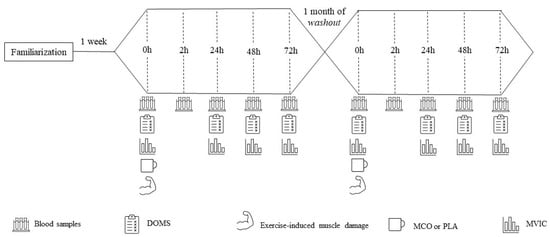
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Statistical Analysis of Ceiling and Floor Effects in Medical Trials
by
Janan Arslan and Kurt Benke
Appl. Biosci. 2023, 2(4), 668-681; https://doi.org/10.3390/applbiosci2040042 - 4 Dec 2023
Cited by 2
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Exploratory data analysis and statistical moments were used to investigate the potential impact of ceiling and floor effects in medical trials. A total of 150 treatment-naive eyes were assessed in a retrospective case study of patients who were treated with anti-VEGF injections for
[...] Read more.
Exploratory data analysis and statistical moments were used to investigate the potential impact of ceiling and floor effects in medical trials. A total of 150 treatment-naive eyes were assessed in a retrospective case study of patients who were treated with anti-VEGF injections for wet age-related macular degeneration. The experimental results revealed that ceiling and floor effects are problematic in data analysis and may result in serious errors when using standard parametric tests. The case study provided insights relating to methodology in medical trials, experimental data analysis, and statistical inference, as applied to the interpretation of treatment response limits. Suggestions are provided for statistical data pre-processing and post-processing when significantly skewed distributions are present in response groups.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
AG1®, a Novel Synbiotic, Demonstrates Superior Mineral Bioaccessibility and Bioavailability Compared to a Tablet Multivitamin and Mineral Supplement Using an In Vitro Model of the Upper Gastrointestinal Tract
by
Philip A. Sapp, Jeremy R. Townsend, Trevor O. Kirby, Marlies Govaert, Cindy Duysburgh, Massimo Marzorati, Tess M. Marshall and Ralph Esposito
Appl. Biosci. 2023, 2(4), 656-667; https://doi.org/10.3390/applbiosci2040041 - 1 Dec 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
While traditional multivitamin and mineral (MVM) supplements generally come in tablet form, new powder forms of MVM supplements are available with theoretically higher bioavailability relative to tablet MVM supplements. The purpose of this study was to assess the bioaccessibility and bioavailability of minerals
[...] Read more.
While traditional multivitamin and mineral (MVM) supplements generally come in tablet form, new powder forms of MVM supplements are available with theoretically higher bioavailability relative to tablet MVM supplements. The purpose of this study was to assess the bioaccessibility and bioavailability of minerals (magnesium (Mg), zinc (Zn), calcium (Ca), and potassium (K)) in a tablet MVM supplement compared to a novel powder Foundational Nutrition supplement (AG1®), containing minerals, vitamins, phytochemicals, and pre-/probiotics, in the upper gastrointestinal tract. The tablet MVM supplement was specifically formulated for this study, with matched mineral contents and identical chemical structures. The adapted Simulator of the Human Intestinal Microbial Ecosystem (SHIME®) model was used to assess the bioaccessibility and bioavailability of soluble minerals using a simulated upper gastrointestinal tract and dialysis membrane to mimic human digestion and absorption. The bioaccessibility was assessed at the end of the stomach and duodenum. The bioaccessibility and bioavailability were assessed at 1, 2, and 3 h following dialysis. The preliminary soluble mineral analysis of the tablet (crushed to a powder) and AG1 powder demonstrated significantly higher (p < 0.05) soluble fractions of Zn and Ca, but lower Mg in the AG1 powder vs. the tablet. The total soluble mineral percentages at the stomach and duodenum end were all significantly higher for the AG1 powder vs. the tablet (p < 0.05). Mg, Ca, and Zn were more (p < 0.05) bioaccessible and bioavailable in the powder compared to the tablet during the small intestine simulation. The bioaccessible fraction of K was higher (p < 0.05) only at 3 h for the tablet vs. the powder. These preclinical data demonstrate that the AG1 powder has superior dissolution and disintegration characteristics compared to the tablet, leading to increased bioaccessibility and bioavailability in vitro.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessReview
Unlocking Insights into Folding, Structure, and Function of Proteins through Circular Dichroism Spectroscopy—A Short Review
by
Leonardo A. Linhares and Carlos H. I. Ramos
Appl. Biosci. 2023, 2(4), 639-655; https://doi.org/10.3390/applbiosci2040040 - 24 Nov 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Circular dichroism (CD) spectroscopy has emerged as a powerful tool in the study of protein folding, structure, and function. This review explores the versatile applications of CD spectroscopy in unraveling the intricate relationship between protein conformation and biological activity. A key advantage of
[...] Read more.
Circular dichroism (CD) spectroscopy has emerged as a powerful tool in the study of protein folding, structure, and function. This review explores the versatile applications of CD spectroscopy in unraveling the intricate relationship between protein conformation and biological activity. A key advantage of CD spectroscopy is its ability to analyze protein samples with minimal quantity requirements, making it an attractive technique for studying proteins that are scarce or difficult to produce. Moreover, CD spectroscopy enables the monitoring of physical and chemical environmental effects on protein structures, providing valuable insights into the dynamic behavior of proteins in different conditions. In recent years, the use of synchrotron radiation as a light source for CD measurements has gained traction, offering enhanced sensitivity and resolution. By combining the advantages of CD spectroscopy, such as minimal sample requirements and the ability to probe environmental effects, with the emerging capabilities of synchrotron radiation (SRCD), researchers have an unprecedented opportunity to explore the diverse aspects of protein behavior. This review highlights the significance of CD spectroscopy in protein research and the growing role of synchrotron radiation in advancing our understanding of protein behavior, aiming to provide novel insights and applications in various fields, including drug discovery, protein engineering, and biotechnology. A brief overview of Solid-State Circular Dichroism (SSCD) is also included.
Full article
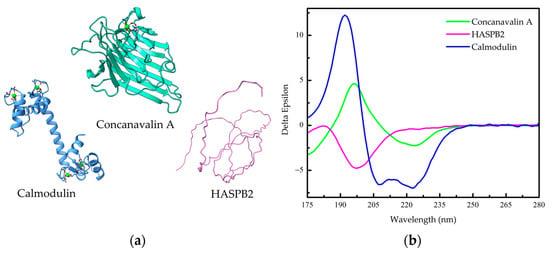
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Nanobiotechnology in Bone Tissue Engineering Applications: Recent Advances and Future Perspectives
by
Neelam Iqbal, Tejal Pant, Nanda Rohra, Abhishek Goyal, Merin Lawrence, Anomitra Dey and Payal Ganguly
Appl. Biosci. 2023, 2(4), 617-638; https://doi.org/10.3390/applbiosci2040039 - 15 Nov 2023
Cited by 1
Abstract
Bone regeneration and repair are complex processes with the potential of added complications, like delayed repair, fracture non-union, and post-surgical infections. These conditions remain a challenge globally, pressurizing the economy and patients suffering from these conditions. Applications of nanotechnology (NBT) in the field
[...] Read more.
Bone regeneration and repair are complex processes with the potential of added complications, like delayed repair, fracture non-union, and post-surgical infections. These conditions remain a challenge globally, pressurizing the economy and patients suffering from these conditions. Applications of nanotechnology (NBT) in the field of medicine have provided a medium for several approaches to support these global challenges. Tissue engineering is one such field that has been on the rise in the last three decades through the utilization of NBT for addressing the challenges related to bone regeneration. First, NBT enables the formation of scaffolds at the nanoscale needed for bone tissue engineering (BTE) using natural and synthetic polymers, as well as with minerals and metals. Then, it aids the development of the nano-formulation strategized to deliver antimicrobial drugs and/or growth factors through various ways to enhance bone repair through the scaffold. Third, NBT facilitates the use of specialized nanoparticles to image and track cellular events in vitro as well as in vivo. This review is an effort to bring together the current knowledge in the field of BTE and present the scope of ever-evolving NBT, a contribution towards precision medicine.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Anatomy and Regenerative Medicine: From Methods to Applications)
►▼
Show Figures
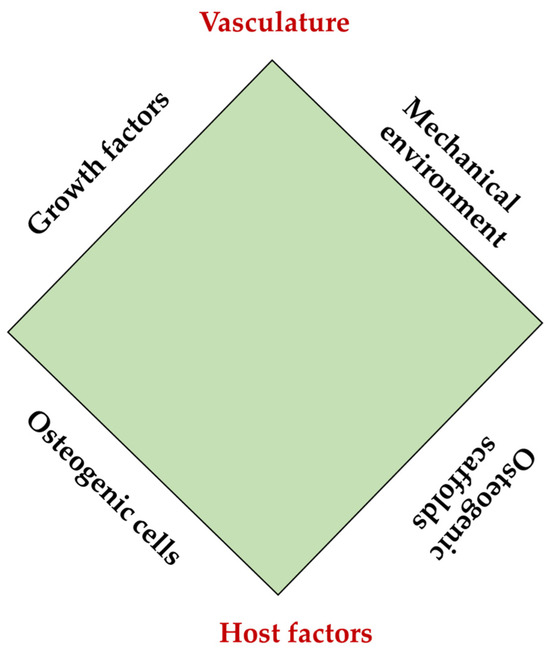
Figure 1
Open AccessPerspective
The Chaperone Hsp90, a Key Player in Salivary Gland Tumorigenesis
by
Charbel A. Basset, Inaya Hajj Hussein, Abdo R. Jurjus, Francesco Cappello, Everly Conway de Macario, Alberto J. L. Macario and Angelo Leone
Appl. Biosci. 2023, 2(4), 607-616; https://doi.org/10.3390/applbiosci2040038 - 7 Nov 2023
Abstract
The chaperone system (CS) is emerging as a key multistage participant in carcinogenesis. The CS chief components are the molecular chaperones (some of which are named heat shock proteins or Hsp), which are typically cytoprotective but if abnormal in structure, location, or quantity,
[...] Read more.
The chaperone system (CS) is emerging as a key multistage participant in carcinogenesis. The CS chief components are the molecular chaperones (some of which are named heat shock proteins or Hsp), which are typically cytoprotective but if abnormal in structure, location, or quantity, can become etiopathogenic and cause diseases, known as chaperonopathies, including some cancers. For example, abnormal Hsp90 expression is associated with tumorigenesis and poor prognosis. Hsp90 is positioned at the center of several key oncogenic pathways by stabilizing and activating oncogenic kinases responsible for driving cell proliferation and survival. Consequently, inhibition of Hsp90 is being investigated as a possible anti-cancer strategy and some results are encouraging. However, the 5-year survival rate for patients suffering from salivary gland carcinomas is still unsatisfactory. Because of the rarity of these malignancies, they may have been overlooked and understudied and, thus, novel therapies (e.g., inhibition of CS components like Hsp90 and others) are urgently needed. In this review, we also summarize the histopathological quantitative patterns and the intra- and extra-cellular location characteristics of Hsp90 in tumors of salivary glands, pointing to their potential for differential diagnosis, prognostication, and patient monitoring.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Feature Papers in Applied Biosciences 2023)
►▼
Show Figures
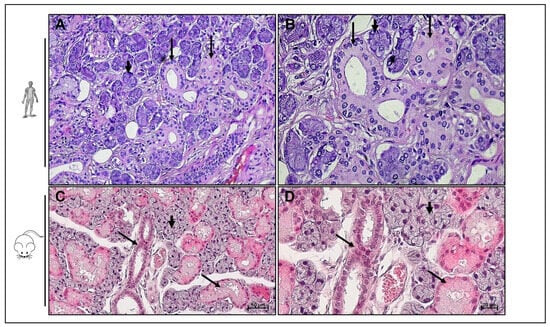
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Determination of Target Crop Loads for Maximising Fruit Quality and Return Bloom in Several Apple Cultivars
by
Sally A. Bound
Appl. Biosci. 2023, 2(4), 586-606; https://doi.org/10.3390/applbiosci2040037 - 1 Nov 2023
Cited by 1
Abstract
In apple (Malus domestica), the level and timing of crop load have a major impact on the final fruit size and can also play a role in optimising internal fruit quality. Ideal crop loads vary with cultivar, but very few cultivars
[...] Read more.
In apple (Malus domestica), the level and timing of crop load have a major impact on the final fruit size and can also play a role in optimising internal fruit quality. Ideal crop loads vary with cultivar, but very few cultivars have recommended crop load targets that consider the effect of crop load on both return bloom and fruit quality. To address this issue, studies examining a range of crop loads and thinning times were undertaken on several apple cultivars. Return bloom and multiple fruit quality parameters were examined. The results of these studies demonstrate positive effects for early thinning, not only on fruit size but also on firmness and soluble solids content. Early-thinned fruit showed higher sugar levels than late-thinned fruit. Previously undemonstrated positive relationships between fruit sugar content and weight and between fruit firmness and weight in both ‘Fuji’ and ‘Delicious’, as well as between fruit sugar content and fruit firmness in ‘Delicious’, indicate that early thinning is a valuable tool in improving fruit quality. The current target crop load recommendations of 4–6 fruit cm−2 trunk cross-sectional area (TCSA) for ‘Fuji’ and 2–4 fruit cm−2 TCSA for ‘Delicious’ are confirmed by this study. New recommendations are proposed for the other cultivars in this study taking into account the impact of crop load on both fruit quality and return bloom. Both ‘Pink Lady’ and ‘Gala’ can support crop loads of up to eight fruit cm−2 TCSA without impacting return bloom, but fruit quality is compromised; hence, lower targets in the range of 4–6 fruit cm−2 TCSA are recommended. Large fruit size and good return bloom can be maintained in ‘Jonagold’ at crop loads of eight fruit cm−2 TCSA, while crop loads of four fruit cm−2 TCSA are suggested for ‘Braeburn’ to sustain regular bearing and good fruit size.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Feature Papers in Applied Biosciences 2023)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Applied Biosciences, JMSE, Marine Drugs, Toxins, Molecules
Marine Biotoxins and Bioactive Marine Natural Products
Topic Editors: Naomasa Oshiro, Ana Gago-Martínez, Takeshi Tsumuraya, Tsuyoshi IkeharaDeadline: 31 August 2024
Topic in
Applied Biosciences, Applied Sciences, Biomolecules, Materials, Polymers
Proteins and Protein-Based Biomaterials from Organisms in Extreme Environments
Topic Editors: Hak Jun Kim, Hackwon DoDeadline: 31 January 2025

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Applied Biosciences
Plant Natural Compounds: From Discovery to Application
Guest Editors: Adriana Basile, Viviana Maresca, Piergiorgio CianciulloDeadline: 31 July 2024
Special Issue in
Applied Biosciences
Experimental Biology: From Methods to Applications. Under the Auspices of the Italian Society of Experimental Biology, SIBS-1925
Guest Editors: Francesco Cappello, Maria Grazia PalmeriniDeadline: 31 August 2024
Special Issue in
Applied Biosciences
Anatomy and Regenerative Medicine: From Methods to Applications
Guest Editors: Alessandro Pitruzzella, Alberto Fucarino, Fabio BucchieriDeadline: 30 September 2024
Special Issue in
Applied Biosciences
Neural Networks and Deep Learning for Biosciences
Guest Editor: Nikolaos KourkoumelisDeadline: 31 October 2024






