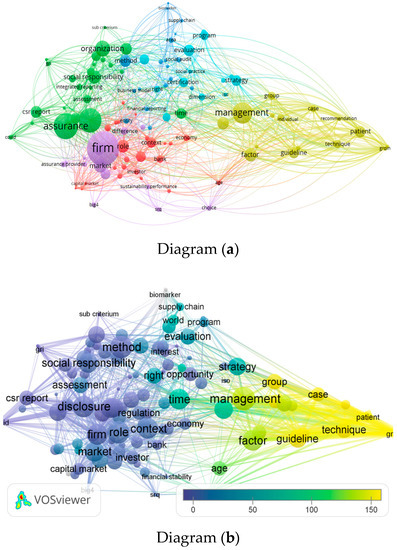
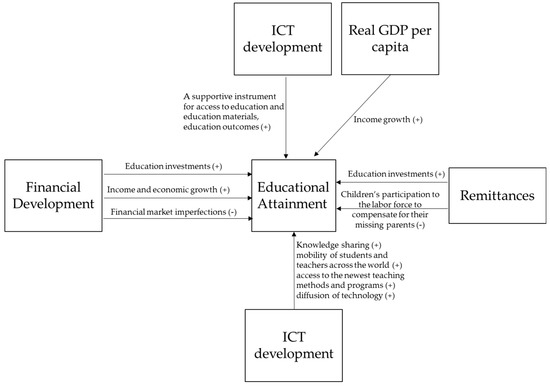
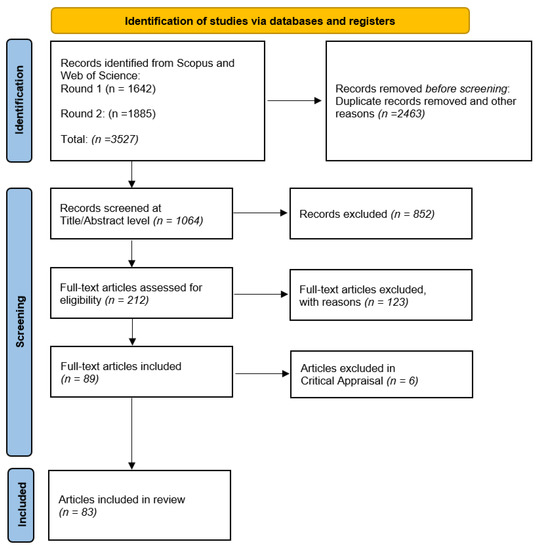
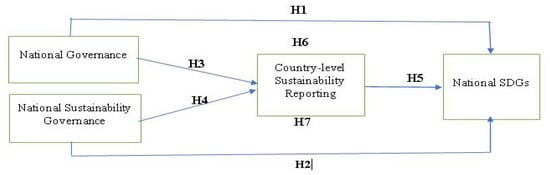
Measuring Progress towards the Achievement of Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
A topical collection in Sustainability (ISSN 2071-1050). This collection belongs to the section "Development Goals towards Sustainability".
Viewed by 13035
Editor
2. Department of Economics and Economic Policy, Economy I Doctoral School, Faculty of Theoretical and Applied Economics, The Bucharest University of Economic Studies, 010374 Bucharest, Romania
Interests: economics; management; finance; auditing; accounting; business counseling; financial analysis; control and evaluation; intellectual capital; corporate governance; sustainability; sustainable development; business environment; business process management; quality management; human resources management
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
This Special Issue focuses on the broad topic of “Measuring Progress Towards the Achievement of Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)” and includes novel research on the current status of the Global Goals adopted by the United Nations in 2015. The aim of the Special Issue is to expand the existing literature on this broad theme by offering new insights and future perspectives on sustainable economic development and growth in the light of today’s challenges, changes, opportunities and threats brought by the pandemic, while focusing on sustainability, the people’s health and well-being, the planet’s prosperity, clean energy, quality education and the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)—as presented and promoted by the United Nations (UN) Agenda. Theoretical and empirical articles on this topic are welcome.
In this Special Issue, original research articles and reviews are welcome. Research areas may include (but are not limited to) the following: the implications of sustainable development and sustainable businesses, international business environment, sustainable economic development and growth, cultural values and cultural practices, corporate sustainability performance, corporate sustainability policies and practices, health and well-being, happiness and happiness management, new methods and ways to achieve performance and excellence, entrepreneurship, small- and medium-sized enterprises, leadership, human resources management, successful business process management and quality management for businesses.
I look forward to receiving your contributions.
Prof. Dr. Cristina Raluca Gh. Popescu
Guest Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Sustainability is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2400 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- artificial intelligence
- auditing
- accounting
- business environment
- business excellence
- business performance
- business process management
- clean energy
- climate change
- circular economy
- corporate reporting
- corporate responsibility
- corporate sustainability performance
- corporate sustainability policies and practices
- control and evaluation
- corporate governance
- crisis management
- economics
- emerging markets
- happiness management
- human resources management
- inclusive businesses
- intangible assets
- intellectual capital
- intellectual property
- innovation
- finance
- global knowledge
- good health and well-being
- leadership
- quality education
- management
- multinational enterprises
- pandemic context
- prosperous, inclusive and sustainable society
- risk management
- small and medium-sized enterprises
- sustainability
- Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
- sustainable finance
- sustainability risks
- tangible assets
- technology and innovation management
- tourism sector
- United Nations (UN) Agenda