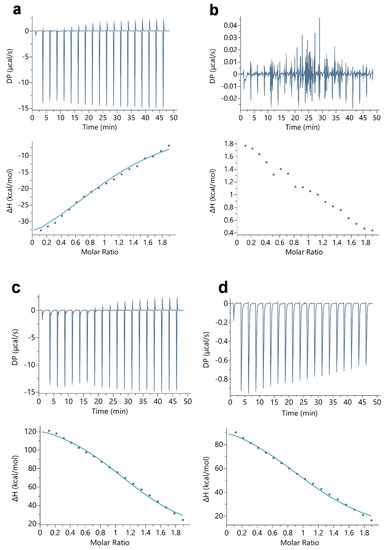
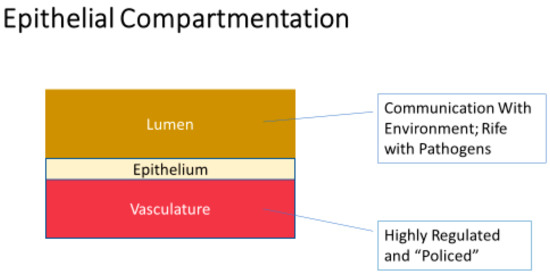
State-of-the-Art Bioactives and Nutraceuticals in USA (Closed)
A topical collection in International Journal of Molecular Sciences (ISSN 1422-0067). This collection belongs to the section "Bioactives and Nutraceuticals".
Viewed by 14175Editor
Interests: dermatology; testosterone; estrogens; steroids; endocrine disruption; reproductive endocrinology; molecular endocrinology; neuroendocrinology; stress physiology; reproductive biology
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
This Topical Collection aims to publish contributions that report on novel research findings regarding bioactive compounds and nutraceutical products in USA. We welcome submissions and studies on nutritional applications using biological, chemical, cellular, molecular, and immunological methods. Topics include but are not limited to:
- The discovery and/or use of novel bioactive natural products;
- The role of these products as active ingredients, supportive biochemical and molecular actions, functional foods, and hence potential physiological mediation for enhanced human nutrition and potential improvement of health;
- The use of in vitro and in vivo bioactivity research using cell lines and animal models as exemplars of human physiology;
- Clinical research examining novel bioactive natural products including nutrition, human disorders/disease covering aging, endocrine and metabolism and/or the microbiome axes (such as gut, skin, brain, lung, etc.), for advancing the understanding of biological interactions and/or the improvement of human health and wellbeing.
The only limitation is the main part of the study must be carried out in the USA or by researchers from the USA.
Importantly, the exact composition of active ingredient(s) of natural origin extracts, biosynthesis, or preparation must be reported in the submitted research manuscript, since papers describing the effects of mixed extraction from natural origin are not in the scope of the journal.
Prof. Dr. Edwin Lephart
Collection Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. International Journal of Molecular Sciences is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. There is an Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal. For details about the APC please see here. Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- bioactive
- nutraceutical
- nutrient
- health
- diet
- functional food
- obesity
- diabetes
- cancer
- cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases
- vitamins
- proteins
- peptides
- polysaccharides
- carotenoids
- polyphenols
- phytosterols and isoflavones
- saponins
- phytic acid
- probiotics
- prebiotics
- enzymes
- flavonoids
- caffeine
- carnitine
- choline
- creatine
- dithiolthiones
- phytoestrogens
- glucosinolates