Journal Description
Forensic Sciences
Forensic Sciences
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on all aspects of forensic science published quarterly online by MDPI. The Portuguese Association of Forensic Sciences (APCF) is affiliated with Forensic Sciences and their members receive a discount on the article processing charges.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, EBSCO, and other databases.
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 15.9 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 5.9 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2023).
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
Latest Articles
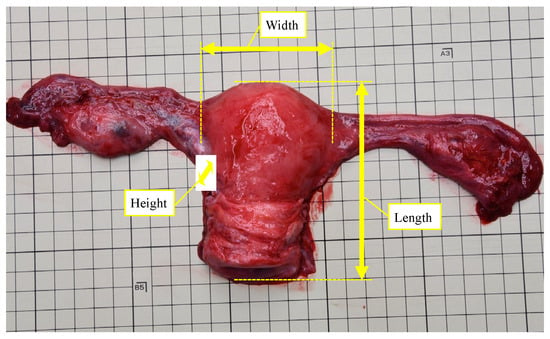
Ovarian Weight and Uterine Volume Index Are Useful for Age Estimation in Adult Women
Forensic Sci. 2024, 4(2), 211-220; https://doi.org/10.3390/forensicsci4020014 - 20 Apr 2024
Abstract
►
Show Figures
Practically, when only parts of an unidentified human body are found, age estimation with limited materials is required. The purpose of this study was to investigate methods for estimating age using the uterus and ovaries. Among forensic autopsies performed between January 2011 and
[...] Read more.
Practically, when only parts of an unidentified human body are found, age estimation with limited materials is required. The purpose of this study was to investigate methods for estimating age using the uterus and ovaries. Among forensic autopsies performed between January 2011 and March 2022, 211 uteruses and 521 ovaries of 322 women were used for this study. Measured values for ovarian weight and uterine volume index were corrected by body surface area to consider the effect of body size. The corrected uterine volume index increased in teenage years and achieved its maximum in the 40–49 group, then gradually decreased with increasing age. The corrected ovarian weight increased until the twenties, after which it decreased with age. For women aged 20 years or more, receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis suggested that a uterine volume index of 41.2 cm3/m2 was the cutoff value for classifying the age as ≥60 years or <60 years, with an area under the ROC curve (AUC) value of 0.751. Ovarian weights of 2.27 g/m2 and 1.92 g/m2 were the cutoff values for classifying the age as ≥40 years or <40 years, or ≥50 years or <50 years, with AUC values of 0.935 and 0.930, respectively. These methods can help determine an unknown individual’s age group simply and quickly, even for incomplete cadavers.
Full article
Open AccessCase Report
Application of X-STRs for Forensic Identification in Mixed DNA Profile: A Case Report
by
Nunzia Ilaria Vacca, Giacoma Mongelli, Stefania Ceccardi, Elisabetta Moroni and Vincenzo Agostini
Forensic Sci. 2024, 4(2), 202-210; https://doi.org/10.3390/forensicsci4020013 - 12 Apr 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Autosomal polymorphisms (STRs) or Y-Chromosome polymorphisms (Y-STRs) are usually used for the study and deconvolution of mixed DNA profiles in forensic genetics, accompanying data interpretation with biostatistical evaluations (e.g., RMP, RMNE, LR). Sometimes, however, some mixed DNA profiles are so complex that autosomal
[...] Read more.
Autosomal polymorphisms (STRs) or Y-Chromosome polymorphisms (Y-STRs) are usually used for the study and deconvolution of mixed DNA profiles in forensic genetics, accompanying data interpretation with biostatistical evaluations (e.g., RMP, RMNE, LR). Sometimes, however, some mixed DNA profiles are so complex that autosomal and Y markers are not sufficient for correct discrimination and identification. In this work is reported a robbery case in which the analysis of the polymorphic markers of the X Chromosome (X-STRs) was applied to the mixed profiles obtained from the traces. This falls outside the classic use of the X-STRs. Indeed, the aim of the authors is to encourage the usage of X-STRs not only in parental relationships, but also in pure forensic cases for interpreting complex mixed DNA profiles, since their application in case resolution could be more decisive than autosomal STRs and Y-STRs.
Full article
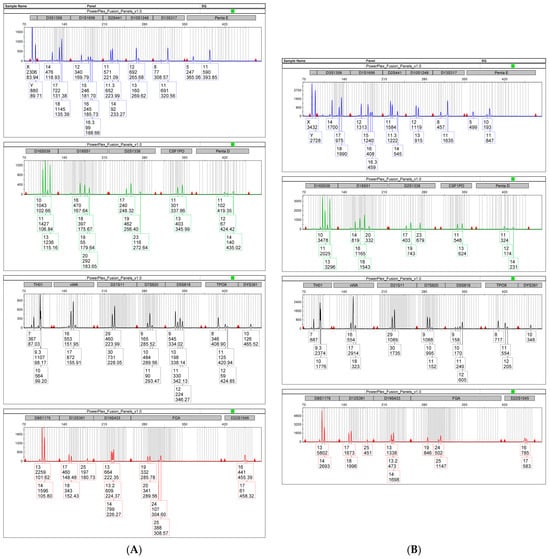
Figure 1
Open AccessCorrection
Correction: Chovalopoulou et al. Skeletal Sex Estimation Methods Based on the Athens Collection. Forensic Sci. 2022, 2, 715–724
by
Maria-Eleni Chovalopoulou, Efstratios Valakos and Efthymia Nikita
Forensic Sci. 2024, 4(2), 201; https://doi.org/10.3390/forensicsci4020012 - 26 Mar 2024
Abstract
The authors wish to make the following corrections to this paper [...]
Full article
(This article belongs to the Collection The Rise of Forensic Anthropology and Documented Human Osteological Collections)
Open AccessArticle
Intelligence and the Value of Forensic Science
by
Paul J. Speaker
Forensic Sci. 2024, 4(1), 184-200; https://doi.org/10.3390/forensicsci4010011 - 18 Mar 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Recent research has seen a rapid expansion in the reference to front-end forensics as an indication of the untapped value of forensic science. While some of these contributions have centered on development of forensic intelligence from a single area of investigation, others call
[...] Read more.
Recent research has seen a rapid expansion in the reference to front-end forensics as an indication of the untapped value of forensic science. While some of these contributions have centered on development of forensic intelligence from a single area of investigation, others call for a more fundamental change in the relationship between crime laboratories and policing, particularly relating early laboratory analysis with big datasets to provide leads to investigators. We highlight several recently implemented tactical strategies of crime laboratories that contribute to the body of forensic intelligence. Beyond the scientific gains from these tactical applications, the corresponding details on associated efficiencies, costs, time savings, and quality improvements offer insights towards patterns of success for the community of crime laboratories. Further details expand an interpretation of what constitutes success with an eye on the contributions of the crime laboratory towards public health, safety, and protection of the innocent in addition to societal gains from conviction of the guilty. The economic interpretation of the value provided by the forensic laboratory assists in the cost–benefit review of strategic and tactical decisions and supports the justification for laboratory public funding with measures of the return on investment from public support of the forensic laboratory. Examples of the cost savings from crimes avoided include the returns from testing the backlog of unsubmitted sexual assault kits with USD 81 of costs avoided for each USD 1 spent to high-efficiency laboratories achieving gains of USD 646 for each UD 1 spent on de novo case submissions.
Full article
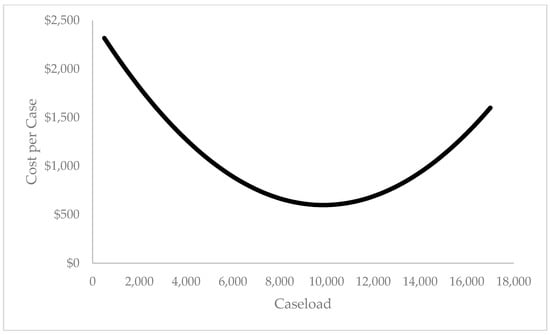
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Simple Methods for Improving the Forensic Classification between Computer-Graphics Images and Natural Images
by
Yacine Bouhamidi and Kai Wang
Forensic Sci. 2024, 4(1), 164-183; https://doi.org/10.3390/forensicsci4010010 - 14 Mar 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
From the information forensics point of view, it is important to correctly classify between natural images (outputs of digital cameras) and computer-graphics images (outputs of advanced graphics rendering engines), so as to know the source of the images and the authenticity of the
[...] Read more.
From the information forensics point of view, it is important to correctly classify between natural images (outputs of digital cameras) and computer-graphics images (outputs of advanced graphics rendering engines), so as to know the source of the images and the authenticity of the scenes described in the images. It is challenging to achieve good classification performance when the forensic classifier is tested on computer-graphics images generated by unknown rendering engines and when we have a limited number of training samples. In this paper, we propose two simple yet effective methods to improve the classification performance under such challenging situations, respectively based on data augmentation and the combination of local and global prediction results. Compared with existing methods, our methods are conceptually simple and computationally efficient, while achieving satisfying classification accuracy. Experimental results on datasets comprising computer-graphics images generated by four popular and advanced graphics rendering engines demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed methods.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessTechnical Note
Use of the Investigator ESSplex SE QS Kit (QIAGEN) at Half PCR Reaction Volumes for the Analysis of Forensic Samples
by
Anna Barbaro, Giacomo Falcone, Angelo La Marca and Aldo Barbaro
Forensic Sci. 2024, 4(1), 152-163; https://doi.org/10.3390/forensicsci4010009 - 14 Mar 2024
Abstract
The Investigator ESSplex SE QS Kit (Qiagen) is a next-generation polymerase chain reaction (PCR) kit that, in 60 min, amplifies 17 Short Tandem Repeat (STR) markers, including the five European Standard Set (ESS) loci (D10S1248, D12S391, D1S1656, D22S1045, D2S441), the SE33 marker, and
[...] Read more.
The Investigator ESSplex SE QS Kit (Qiagen) is a next-generation polymerase chain reaction (PCR) kit that, in 60 min, amplifies 17 Short Tandem Repeat (STR) markers, including the five European Standard Set (ESS) loci (D10S1248, D12S391, D1S1656, D22S1045, D2S441), the SE33 marker, and the locus Amelogenin for sex determination. Two quality sensors (QS1 and QS2) are also co-amplified to check PCR performance. Since forensic laboratories carry out hundreds of DNA typings annually, we verified the kit’s performance using half reaction volumes with the aim of improving the number of samples that may be amplified with a single kit and consequently reducing laboratory costs. In the present study, intended as a technical note rather than internal validation, some control samples (oral swabs) with known DNA profiles and 40 real casework samples were analyzed. We observed that reducing the total reaction volume, while keeping all component ratios unaltered, yields DNA profiles comparable to those obtained using standard reaction volumes and with allele peaks higher than those with regular volumes. Using half volumes for PCR amplification enables the analysis of a larger number of samples compared to the standard protocol, thereby reducing laboratory costs without compromising the quality of the analysis.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Feature Papers in Forensic Sciences in 2023)
►▼
Show Figures
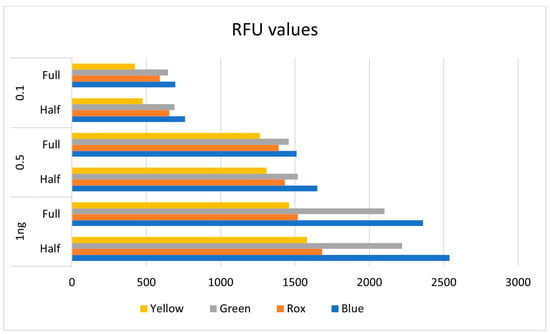
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
An Interdisciplinary Approach to Enhancing Cyber Threat Prediction Utilizing Forensic Cyberpsychology and Digital Forensics
by
Marshall S. Rich and Mary P. Aiken
Forensic Sci. 2024, 4(1), 110-151; https://doi.org/10.3390/forensicsci4010008 - 04 Mar 2024
Abstract
The Cyber Forensics Behavioral Analysis (CFBA) model merges Cyber Behavioral Sciences and Digital Forensics to improve the prediction and effectiveness of cyber threats from Autonomous System Numbers (ASNs). Traditional cybersecurity strategies, focused mainly on technical aspects, must be revised for the complex cyber
[...] Read more.
The Cyber Forensics Behavioral Analysis (CFBA) model merges Cyber Behavioral Sciences and Digital Forensics to improve the prediction and effectiveness of cyber threats from Autonomous System Numbers (ASNs). Traditional cybersecurity strategies, focused mainly on technical aspects, must be revised for the complex cyber threat landscape. This research proposes an approach combining technical expertise with cybercriminal behavior insights. The study utilizes a mixed-methods approach and integrates various disciplines, including digital forensics, cybersecurity, computer science, and forensic psychology. Central to the model are four key concepts: forensic cyberpsychology, digital forensics, predictive modeling, and the Cyber Behavioral Analysis Metric (CBAM) and Score (CBS) for evaluating ASNs. The CFBA model addresses initial challenges in traditional cyber defense methods and emphasizes the need for an interdisciplinary, comprehensive approach. This research offers practical tools and frameworks for accurately predicting cyber threats, advocating for ongoing collaboration in the ever-evolving field of cybersecurity.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Human and Technical Drivers of Cybercrime)
►▼
Show Figures
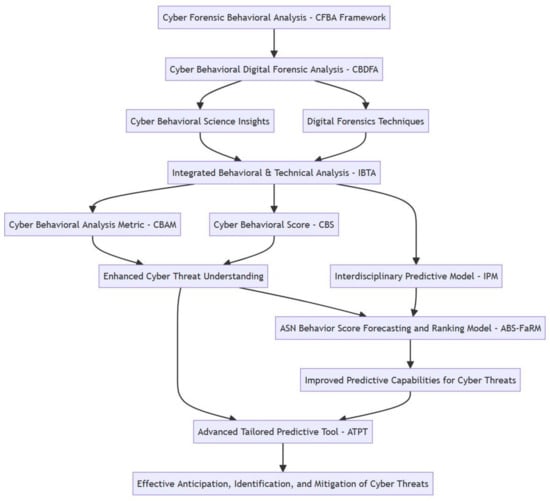
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Discrimination Efficiency of Thermogravimetry and Differential Scanning Calorimetry in Soil Forensics
by
Rodrigo Studart Corrêa, Renata Esteves Ribeiro, Marina Pereira Borges, Ettore Ferrari Júnior and Juliano de Andrade Gomes
Forensic Sci. 2024, 4(1), 96-109; https://doi.org/10.3390/forensicsci4010007 - 02 Mar 2024
Abstract
Forensic soil analysis is crucial in criminal investigations, necessitating robust analytical methodologies for an accurate discrimination of soil types and origins. This study explored the discrimination efficiency of thermogravimetric and differential scanning calorimetric analyses of Inceptisol, reddish Oxisol, and yellowish Oxisol soils from
[...] Read more.
Forensic soil analysis is crucial in criminal investigations, necessitating robust analytical methodologies for an accurate discrimination of soil types and origins. This study explored the discrimination efficiency of thermogravimetric and differential scanning calorimetric analyses of Inceptisol, reddish Oxisol, and yellowish Oxisol soils from Brazil’s Cerrado region. Ninety air-dried soil samples collected at various locations underwent thermal analysis, focusing on mass loss of gibbsite, goethite, and kaolinite at specific temperatures. The log-transformed data were submitted to principal component analysis, nonmetric multidimensional scaling, and cluster analysis. The thermogravimetry emerged as a highly discriminatory tool, effectively delineating between soil types, and even detecting spatial variations. In contrast, the differential scanning calorimetry exhibited limited discriminatory power. The findings underscore the thermogravimetric potential as a valuable technique in soil forensics, providing critical insights into composition and spatial variations essential for criminal investigations. This study highlights the need for further research to explore synergies with complementary techniques, aiming to enhance forensic discrimination across diverse soil types and geographic contexts. The objective representation of results in this abstract emphasizes the significance of thermogravimetry in advancing forensic analysis of soil vestiges.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Feature Papers in Forensic Sciences in 2023)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
What Are the Limitations and Challenges of Swab-Based DNA Sampling?
by
Brigitte Bruijns
Forensic Sci. 2024, 4(1), 76-95; https://doi.org/10.3390/forensicsci4010006 - 26 Feb 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Selecting the optimal sampling method is an essential component of the DNA analysis process. Errors or omissions in targeting and gathering relevant samples can significantly reduce the likelihood of obtaining a valuable DNA profile, affecting the profile’s quality and evidential value and ultimately
[...] Read more.
Selecting the optimal sampling method is an essential component of the DNA analysis process. Errors or omissions in targeting and gathering relevant samples can significantly reduce the likelihood of obtaining a valuable DNA profile, affecting the profile’s quality and evidential value and ultimately hindering its ability to support the justice system. While DNA typing techniques have become significantly more sensitive in recent years, there is an ongoing need for further advancements in the recovery of DNA from crime scenes. It is essential to improve the accuracy and reliability of forensic investigations, particularly in cases where only tiny amounts of DNA are present, such as touch DNA samples or degraded forensic evidence. Parameters, including swab material, type of substrate, and swabbing protocol, that influence the efficiency of a swab are discussed in this review. This is followed by a literature review of studies that have compared swab types and/or other sampling conditions. While swabs are the most-used collection tools at a crime scene, alternatives are available. These alternatives are reviewed, including their advantages and disadvantages. A critical discussion and conclusions make clear that, unfortunately, neither swabs nor their alternatives are highly effective in recovering DNA from a substrate.
Full article
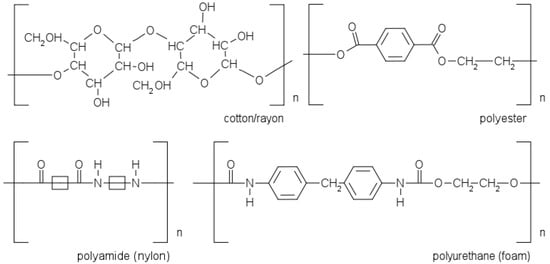
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
New More Generic and Inclusive Regression Formulae for the Estimation of Stature from Long Bone Lengths in Children
by
Nicola J. Murray, Laure Spake, Marianna Cervantes, John Albanese and Hugo F. V. Cardoso
Forensic Sci. 2024, 4(1), 62-75; https://doi.org/10.3390/forensicsci4010005 - 21 Feb 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Existing child stature estimation methods have a number of disadvantages. This paper addresses some of these limitations by developing regression-based stature estimation formulae that are more generic and inclusive. A sample of 142 individuals under 12 years of age from the Hamann—Todd Human
[...] Read more.
Existing child stature estimation methods have a number of disadvantages. This paper addresses some of these limitations by developing regression-based stature estimation formulae that are more generic and inclusive. A sample of 142 individuals under 12 years of age from the Hamann—Todd Human Osteological Collection and the New Mexico Decedent Images Database were used to generate five least squares linear regression formulae to estimate stature from the diaphyseal length of long bones. All models showed excellent fits to the data (R2 close to or at 0.98), and internal validation confirmed the stability and accuracy of model parameters. External validation was performed using a sample of 14 individuals from the Lisbon Collection and the Victoria Institute of Forensic Medicine. Overall, the humerus provides the most accurate estimate of stature, but the femur and tibia showed the greatest coverage. These formulae can be used in a variety of contexts and are not dependent on group affiliation, including sex.
Full article
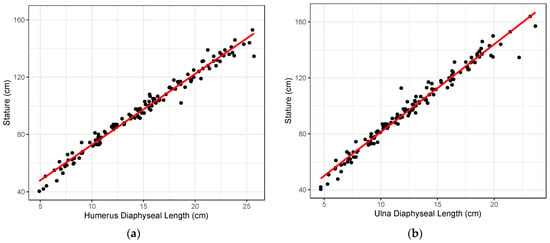
Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
Biobanks: Archives or Resources? Their Secondary Use for Forensic Purposes—A Systematic Review
by
Giulia Sguazzi, Giulia Fasani, Filippo Renò and Sarah Gino
Forensic Sci. 2024, 4(1), 42-61; https://doi.org/10.3390/forensicsci4010004 - 01 Feb 2024
Abstract
Since the biobanks’ inception in 1980, millions of human biological samples have been stored worldwide for medical research or treatment purposes. Today the secondary use of biobanks plays an increasingly important role in research projects because it allows large-scale research starting from professional
[...] Read more.
Since the biobanks’ inception in 1980, millions of human biological samples have been stored worldwide for medical research or treatment purposes. Today the secondary use of biobanks plays an increasingly important role in research projects because it allows large-scale research starting from professional collections of biospecimens and related clinical data. It would be limiting, in the “-omics” era, to not consider the enormous potential value to law enforcement of these biospecimens, where the availability of high-performance techniques makes it possible to obtain a large amount of data, even within a single session. Therefore, the quality of the sample, in addition to the associated clinical information, becomes of crucial importance to derive scientifically valid information, including for forensic research purposes. Proposing the introduction of the concept of “solidarity”, traditionally applied only to medical and research biobanks, led to public commitment to forensic medicine. Granting the forensic researcher this possibility certainly raises some questions regarding regulatory and ethical aspects of consent, privacy, confidentiality, transparency, and participant/donor trust. Since the debate has not stopped since the origin of biobanks, this review aims to explore the state of the art relating to the use of human biological material in medical biobanks for biomedical and forensic research.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Feature Papers in Forensic Sciences in 2023)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Intention to Hack? Applying the Theory of Planned Behaviour to Youth Criminal Hacking
by
Mary P. Aiken, Julia C. Davidson, Michel Walrave, Koen S. Ponnet, Kirsty Phillips and Ruby R. Farr
Forensic Sci. 2024, 4(1), 24-41; https://doi.org/10.3390/forensicsci4010003 - 30 Jan 2024
Cited by 1
Abstract
Adolescents are currently the most digitally connected generation in history. There is an ever-growing need to understand how typical adolescent risk-taking intersects with the vastly criminogenic potential of digital technology. Criminal hacking in older adolescents (16–19-year-olds) was assessed using an adapted Theory of
[...] Read more.
Adolescents are currently the most digitally connected generation in history. There is an ever-growing need to understand how typical adolescent risk-taking intersects with the vastly criminogenic potential of digital technology. Criminal hacking in older adolescents (16–19-year-olds) was assessed using an adapted Theory of Planned Behaviour (TPB) model, a cohesive theoretical framework that incorporates cognitive processes and human drivers (informed by psychology, cyberpsychology, and criminology theory). In 2021, a large-scale anonymous online survey was conducted across nine European countries. Criminal hacking was assessed using data from 3985 participants (M = 1895, 47.55%; F = 1968, 49.39%). This study formulated a powerful predictive model of youth hacking intention (accounting for 38.8% of the variance) and behaviour (accounting for 33.6% of the variance). A significant minority, approximately one in six (16.34%), were found to have engaged in hacking, and approximately 2% reported engaging in hacking often or very often. Increased age, being male, and offline deviant behaviour were significant predictors of hacking behaviour. In line with the TPB, intention was the strongest individual predictor of hacking behaviour, which in turn was significantly predicted by cognitive processes accounted for by TPB constructs: subjective norms of family and peers, attitudes towards hacking, and perceived behavioural control. These TPB constructs were found to be significantly associated with human factors of risk-taking, toxic online disinhibition, offline deviant behaviour, and demographic variables of age and gender. Implications for future research, interventions, policy, and practice are discussed.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Human and Technical Drivers of Cybercrime)
►▼
Show Figures
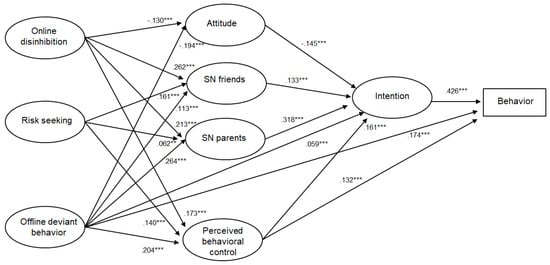
Figure 1
Open AccessTechnical Note
Instrumenting OpenCTI with a Capability for Attack Attribution Support
by
Sami Ruohonen, Alexey Kirichenko, Dmitriy Komashinskiy and Mariam Pogosova
Forensic Sci. 2024, 4(1), 12-23; https://doi.org/10.3390/forensicsci4010002 - 23 Jan 2024
Abstract
In addition to identifying and prosecuting cyber attackers, attack attribution activities can provide valuable information for guiding defenders’ security procedures and supporting incident response and remediation. However, the technical analysis involved in cyberattack attribution requires skills, experience, access to up-to-date Cyber Threat Intelligence,
[...] Read more.
In addition to identifying and prosecuting cyber attackers, attack attribution activities can provide valuable information for guiding defenders’ security procedures and supporting incident response and remediation. However, the technical analysis involved in cyberattack attribution requires skills, experience, access to up-to-date Cyber Threat Intelligence, and significant investigator effort. Attribution results are not always reliable, and skillful attackers often work hard to hide or remove the traces of their operations and to mislead or confuse investigators. In this article, we translate the technical attack attribution problem to the supervised machine learning domain and present a tool designed to support technical attack attribution, implemented as a machine learning model extending the OpenCTI platform. We also discuss the tool’s performance in the investigation of recent cyberattacks, which shows its potential in increasing the effectiveness and efficiency of attribution operations.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Human and Technical Drivers of Cybercrime)
►▼
Show Figures
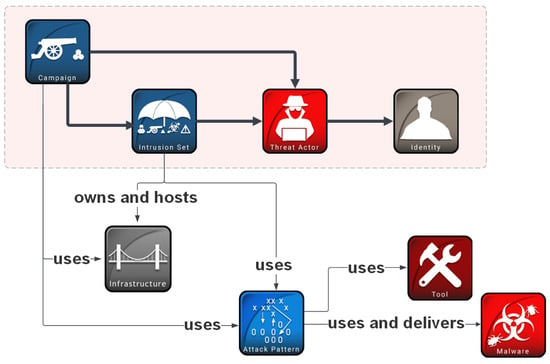
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Eigenfemora—Age-at-Death Estimation in the Proximal Femur through an Image Processing Approach
by
David Navega, Maria Teresa Ferreira and Francisco Curate
Forensic Sci. 2024, 4(1), 1-11; https://doi.org/10.3390/forensicsci4010001 - 31 Dec 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Estimating age at death is essential to establish biological profiles from human skeletal remains in both forensic and archeological settings. Imaging studies of skeletal age changes in adults have described the metamorphosis of trabecular bone structure and bone loss in the proximal femur
[...] Read more.
Estimating age at death is essential to establish biological profiles from human skeletal remains in both forensic and archeological settings. Imaging studies of skeletal age changes in adults have described the metamorphosis of trabecular bone structure and bone loss in the proximal femur as well as changes in morphology during different stages of life. This study aims to assess the utility of a digital representation of conventional X-ray films of the proximal femur for the estimation of age at death in a sample of 91 adult individuals (47 females and 44 males) of the Coimbra Identified Skeletal Collection. The proposed approach showed a root mean squared error (RMSE) of 17.32 years (and mean absolute error of 13.47 years) for females and an RMSE of 14.06 years (mean absolute error of 11.08 years) for males. The main advantage of this approach is consistency in feature detection and extraction, as X-ray images projected on the femora space will always produce the same set features to be analyzed for age estimation, while more traditional methods rely heavily on operator experience that can lead to inconsistent age estimates among experts.
Full article
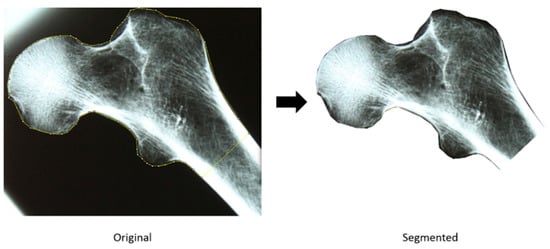
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Chemical Analysis of Sexual Lubricant Residue: A Comparison of Medical Examination Swabs Analyzed Using Spectroscopic Techniques
by
Safiya J. Best, Santana Thomas, Nancy Flynn and Candice Bridge
Forensic Sci. 2023, 3(4), 620-637; https://doi.org/10.3390/forensicsci3040045 - 08 Dec 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Sexual assault kits are the standard method for collecting and preserving sexual assault evidence. During the sexual assault examination, swabs are commonly used to collect bodily fluids as sexual assault evidence from the vagina, anus, mouth, and skin. The type of fiber swab
[...] Read more.
Sexual assault kits are the standard method for collecting and preserving sexual assault evidence. During the sexual assault examination, swabs are commonly used to collect bodily fluids as sexual assault evidence from the vagina, anus, mouth, and skin. The type of fiber swab used during collection can greatly influence the recovery of the substrate. In cases where lubricant residue may be present, it would be useful to identify the swab type that would be the most efficient in the collection of lubricant residues. In this study, four types of swabs with different fibers (i.e., cotton, polyester, rayon, and foam) with sexual lubricants present, were extracted in various solvents. The extracts were analyzed using attenuated total reflectance Fourier-transform infrared (ATR-FTIR) and Raman spectroscopy. The Pearson correlation coefficient (PCCs) test was applied to determine a pairwise comparison between swab lube extracts and the standard lubricant reference. Visual comparisons of the lubricant reference, blank fiber swab, and the fiber lubricant extract were used to determine peak overlap, significance, and matrix interference.
Full article
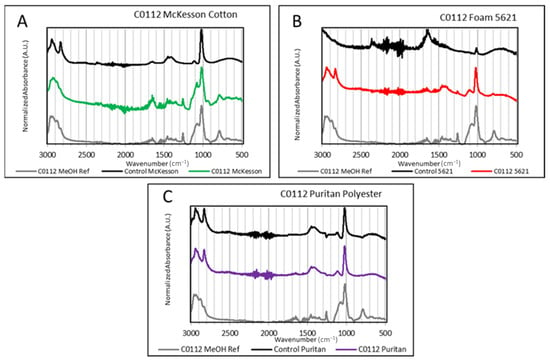
Figure 1
Open AccessBrief Report
An Assessment of Intra- and Interobserver Error in Luminol Chemiluminescence as a Presumptive Test for Postmortem Interval Estimation
by
Catarina Ermida, Joana Rosa, Eugénia Cunha and Maria Teresa Ferreira
Forensic Sci. 2023, 3(4), 611-619; https://doi.org/10.3390/forensicsci3040044 - 05 Dec 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Postmortem interval (PMI) estimation constitutes a challenge for forensic anthropologists. The application of the luminol technique as a preliminary test for PMI estimation is considered easy to use and inexpensive. The objective of our study is to validate luminol chemiluminescence testing through the
[...] Read more.
Postmortem interval (PMI) estimation constitutes a challenge for forensic anthropologists. The application of the luminol technique as a preliminary test for PMI estimation is considered easy to use and inexpensive. The objective of our study is to validate luminol chemiluminescence testing through the assessment of intra- and interobserver error. Our sample included 266 human clavicles, with known PMIs ranging between 2655 days and 450 years. After sample preparation, luminol was applied, and the results were observed by two different observers. The intensity of the reaction was measured using a binary scale and a 5-level scale, according to the increasing degree of chemiluminescence. The Kappa statistic was used for the assessment of the intra- and interobserver agreement. The obtained results showed total interobserver error agreement regarding the binary scale and a K = 0.98 (95% CI: 0.97–0.99) regarding the 5-level scale. Additionally, Observer 1 and Observer 2 obtained a 100% agreement concerning the binary scale and a K = 1 (95%CI 0.99–1) and K = 0.99 (95% CI 0.99–1), respectively, concerning the 5-level scale. According to our research, it is possible to conclude that luminol chemiluminescence testing is suitable as a rapid diagnostic test, revealing this method as practically independent of observation error.
Full article
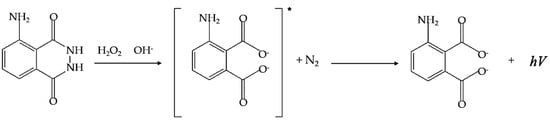
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Interlaboratory Comparison of SpermX™ and Conventional Differential Extractions Indicated High Male DNA Recovery by the SpermX Method
by
Joanne B. Sgueglia, Hailey Holt, Erin Hanson, Justina Nichols, Tim Kalafut, Mah-ro Khan, Thomas Walsh, Megan Foley, Hiromi Brown, Jack Ballantyne and Sudhir K. Sinha
Forensic Sci. 2023, 3(4), 592-610; https://doi.org/10.3390/forensicsci3040043 - 01 Dec 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The National Institute of Justice reported that current methods for processing sexual assault samples have a high failure rate, with 60 to 80 percent of tested kits unable to produce usable DNA profiles. Even when samples test positive for male DNA, 34 percent
[...] Read more.
The National Institute of Justice reported that current methods for processing sexual assault samples have a high failure rate, with 60 to 80 percent of tested kits unable to produce usable DNA profiles. Even when samples test positive for male DNA, 34 percent of sexual assault kits (SAKs) do not yield recovered male DNA after differential extraction. Less than 30% recovery of available sperm DNA contributes to this low success rate. The SpermX™ method (SX) has been shown to recover 80 percent or more of sperm DNA from sexual assault samples. An interlaboratory evaluation compared SX to standard differential extraction (DE) protocols. Mock samples with known ratios of female epithelial cells and sperm cells were processed using both methods. Results revealed that SX consistently provided CODIS up-loadable DNA profiles, even with as few as 25 sperm cells, whereas DE failed to produce usable results. On average, SX yielded a seven-fold increase in the recovery of unshared male alleles compared to DE. In conclusion, SX outperformed DE in recovering higher quantities of male DNA with minimal female carryover in sexual assault-type samples. This improved success rate in obtaining usable DNA profiles can significantly aid in solving sexual assault cases.
Full article
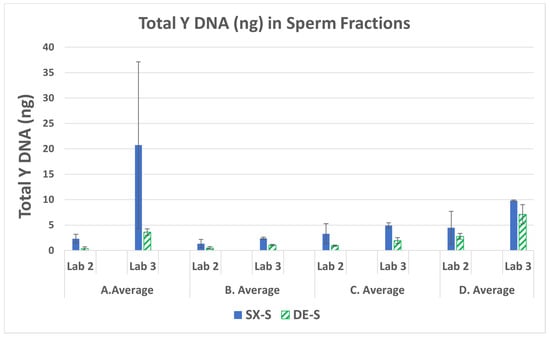
Figure 1
Open AccessCase Report
Establishing the Manner of Death: A 3D Reconstruction of a Case of Hanging
by
Marcello Benevento, Laura Ambrosi, Eloisa Maselli, Davide Ferorelli, Biagio Solarino and Aldo Di Fazio
Forensic Sci. 2023, 3(4), 582-591; https://doi.org/10.3390/forensicsci3040042 - 15 Nov 2023
Abstract
Establishing the manner of death is one of the most challenging tasks for forensic pathologists. We present the case of a 24-year-old woman found dead in the early morning on a flyover. The body was sitting on the ground with the back leaning
[...] Read more.
Establishing the manner of death is one of the most challenging tasks for forensic pathologists. We present the case of a 24-year-old woman found dead in the early morning on a flyover. The body was sitting on the ground with the back leaning against a wall. The neck was encircled by a white phone charger cable knotted to the staircase’s handrail. The victim had argued with her boyfriend and tried to jump out of his car while coming home from a wedding party the night before. After that, she left home alone with her phone charger in her hand. Due to self-harm behaviors, the first hypothesis was suicide by hanging. However, the ligature crossed immediately beneath the thyroid cartilage and encircled the neck twice horizontally; the two ends of the cable overlapped, forming a cross-over point in the front-right of the neck. Then, the ligature passed obliquely through the nape, gradually disappearing, forming a gap in the mark. The mark was sharply defined, stiff, yellow, and parchment-like. The investigators performed a three-dimensional scene reconstruction using the Trimble X7 Laser Scanner and the PC-Crash Multibody System. Even though the geometry of the ligature mark in the present case raised doubts about the manner of death, the three-dimensional reconstruction confirmed that the hanging was feasible without any external intervention.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue The Analysis and Interpretation of the Mechanisms and Signs of Asphyxiation in Cadavers: A Challenge for the Forensic Pathologist)
►▼
Show Figures
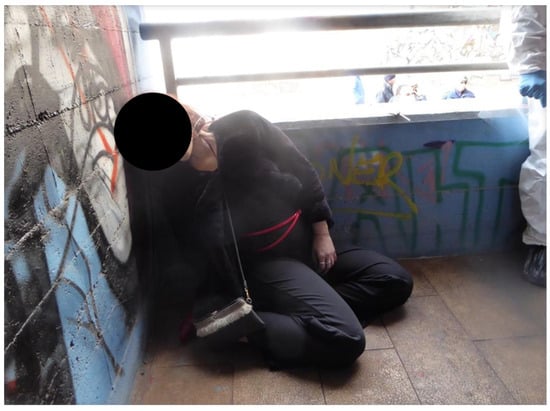

Figure 1
Open AccessCommunication
Sternal Rib Ends as a Method of Age Estimation at the CIL: A Brief Note
by
Alexander F. Christensen
Forensic Sci. 2023, 3(4), 576-581; https://doi.org/10.3390/forensicsci3040041 - 09 Nov 2023
Abstract
This communication reports the relationship between skeletal age estimates based on the sternal rib ends (using the phase method of İşcan and colleagues, later revised by Hartnett) and the chronological age at the death of 221 U.S. military casualties processed by the Scientific
[...] Read more.
This communication reports the relationship between skeletal age estimates based on the sternal rib ends (using the phase method of İşcan and colleagues, later revised by Hartnett) and the chronological age at the death of 221 U.S. military casualties processed by the Scientific Analysis section of the Defense POW/MIA Accounting Agency and its predecessor laboratories from 2000 to the present. Previously published age ranges for each phase do not provide accurate estimates for a sufficient proportion of the cases for forensic use; as an example, the age ranges that accompany reference cast sets proved accurate for 55% of CIL cases. Combining the published age ranges of İşcan and Hartnett, on the other hand, proved accurate in 99% of the cases.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Estimating Age in Forensic Anthropology)
Open AccessOpinion
Marijuana: Forensics of Abuse, Medical Uses, Controversy, and AI
by
Olen R. Brown
Forensic Sci. 2023, 3(4), 571-575; https://doi.org/10.3390/forensicsci3040040 - 07 Nov 2023
Abstract
Motor vehicle accidents are a significant consequence of marijuana abuse. Limitations of its roadside detection and the forensic problems with establishing impairment require innovations that are scientifically achievable. Marijuana abuse currently is at an all-time high in the United States and its physiological
[...] Read more.
Motor vehicle accidents are a significant consequence of marijuana abuse. Limitations of its roadside detection and the forensic problems with establishing impairment require innovations that are scientifically achievable. Marijuana abuse currently is at an all-time high in the United States and its physiological effects make it a popular recreational drug that is reported to be a leading cause of preventable morbidity and mortality among the youth in the 18 most affluent nations. The medical benefits of drugs derived from marijuana complicate its forensic regulation. In an extensive 2017 report by The American Academy of Sciences, the evidence for the medical benefits of delta-9 tetrahydrocannabinol (derived from marijuana) were stated to be conclusive or substantial for the treatment of chronic pain in adults, as an antiemetic for treatment of chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting, and for improving patient-reported multiple sclerosis spasticity symptoms. The benefits from treatment for many other medical conditions were inconclusive or absent. The evidence is clear that safely driving a motor vehicle is significantly impaired while under the influence of marijuana. However, there is no roadside forensic test that reliably detects impairment, and there is an urgent need for such to protect the public while insuring the legal rights of users. There is strong societal pressure to relax marijuana’s forensic regulation, including removing it from Schedule I of the Controlled Substances Act. Artificial intelligence (AI) should be implemented with appropriate human control to resolve controversies.
Full article
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Forensic Sciences, Healthcare, JCM, JPM
Ethical, Legal and Forensic Issues regarding Vulnerable Populations
Topic Editors: Stavroula Papadodima, Flora BacopoulouDeadline: 19 September 2024
Topic in
Electronics, Eng, Forensic Sciences, Forests, Geosciences, Heritage, Infrastructures, Remote Sensing
Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR) Techniques and Applications
Topic Editors: Pier Matteo Barone, Alastair Ruffell, Carlotta FerraraDeadline: 31 October 2024

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Forensic Sciences
Study in Forensic Pathology
Guest Editor: Massimiliano EspositoDeadline: 30 April 2024
Special Issue in
Forensic Sciences
The Role of Forensic Geology in Criminal Investigations
Guest Editors: Alastair Ruffell, Pier Matteo Barone, Rosa Maria Di Maggio, Laurance Donnelly, Mariano MercurioDeadline: 1 June 2024
Special Issue in
Forensic Sciences
The Analysis and Interpretation of the Mechanisms and Signs of Asphyxiation in Cadavers: A Challenge for the Forensic Pathologist
Guest Editors: Matteo Antonio Sacco, Isabella AquilaDeadline: 15 June 2024
Special Issue in
Forensic Sciences
Imaging Wound Ballistics – Taking Full Advantage of the Electromagnetic Spectrum: 2nd Edition
Guest Editors: Dominic Gascho, Sören KottnerDeadline: 30 June 2024
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Forensic Sciences
The Rise of Forensic Anthropology and Documented Human Osteological Collections
Collection Editors: Francisca Alves Cardoso, Vanessa Campanacho, Claudia Regina Plens