Oxidative Stress and Metabolite Signaling in the Heart and Cancer
A special issue of Antioxidants (ISSN 2076-3921). This special issue belongs to the section "Health Outcomes of Antioxidants and Oxidative Stress".
Deadline for manuscript submissions: 8 July 2024 | Viewed by 170
Special Issue Editors
Interests: intermediate metabolite signaling on: intracardiac cell-cell cross-talk between cardiomyocytes and non-cardiomyocytes; metabolomic signaling; spatial metabolomics; metabolite-protein interactions; post-translational modifications by intermediate metabolites; endoplasmic reticulum stress; oxidative stress; nitrosative stress
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: genetics; epigenetics; gene expression; cardiac hypertrophy; arterial hypertension and atherosclerosis
Special Issue Information
Dear Colleagues,
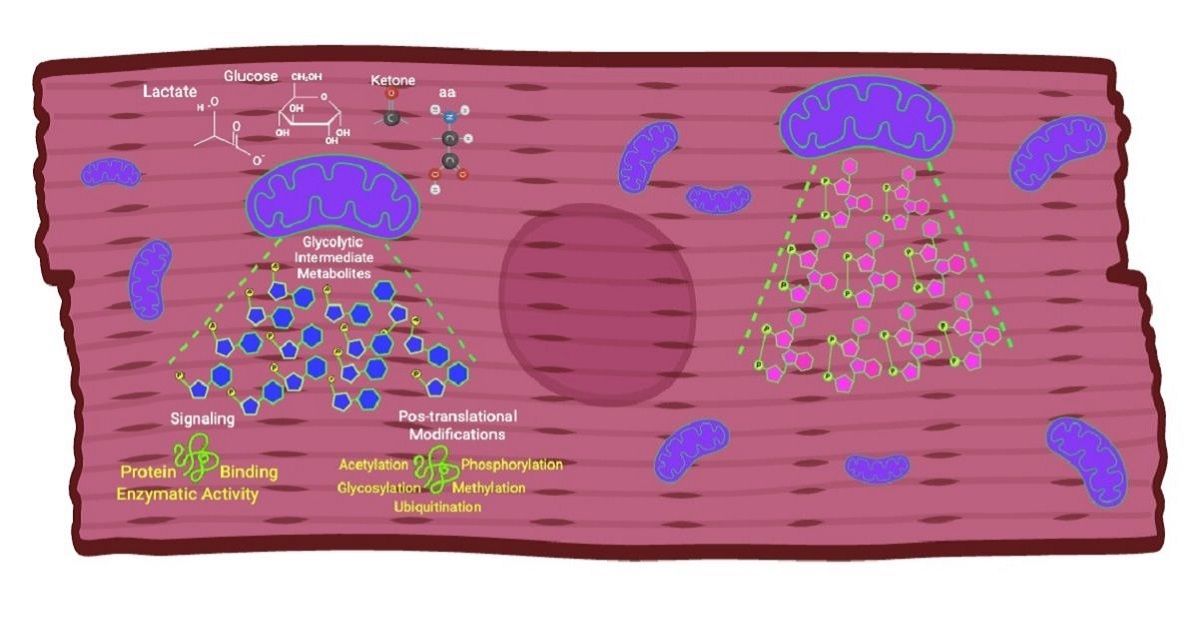
Nutrient catabolism via oxidative phosphorylation affects intracellular signaling in the heart and has been extensively studied. Metabolic remodeling inducing nitrosative/oxidative stress processes has also been under investigation. However, how intermediate metabolites generated from this catabolism affect signaling and post-translational modifications remains largely unexplored. During diseases, heart metabolic remodeling toward glycolysis is accompanied by changes in levels of glycolytic intermediate metabolites, and its post-translational modifications appear to be globally reduced. Still, the functional consequences of these modifications are unknown. Intermediate metabolites can bind to proteins and affect enzymatic activity or subcellular localization. Under various conditions, glucose, lactate, ketones, and amino acids are used as cardiac fuel, and the impact of these large fuel fluxes through intermediate metabolic pathways on cardiac function is even less studied. This Special Issue plans to give an overview of the most recent advances in the field of intra/extracellular metabolite signaling and nitro-oxidative programs in cancer and cardiovascular diseases to understand and translate intermediate metabolite levels into new potential therapies. Nutrient catabolism via oxidative phosphorylation affects intracellular signaling in the heart and has been extensively studied. Metabolic remodeling inducing nitrosative/oxidative stress processes has also been under investigation. However, how intermediate metabolites generated from this catabolism affect signaling and post-translational modifications remains largely unexplored. During diseases, heart metabolic remodeling toward glycolysis is accompanied by changes in levels of glycolytic intermediate metabolites, and its post-translational modifications appear to be globally reduced. Still, the functional consequences of these modifications are unknown. Intermediate metabolites can bind to proteins and affect enzymatic activity or subcellular localization. Under various conditions, glucose, lactate, ketones, and amino acids are used as cardiac fuel, and the impact of these large fuel fluxes through intermediate metabolic pathways on cardiac function is even less studied.
This Special Issue plans to give an overview of the most recent advances in the field of intra/extracellular metabolite signaling and nitro-oxidative programs in cancer and cardiovascular diseases to understand and translate intermediate metabolite levels into new potential therapies.
Dr. Amarylis Claudine Bonito A. Wanschel
Dr. Roberto Schreiber
Dr. Konstantinos E. Hatzistergos
Guest Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the special issue website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Antioxidants is an international peer-reviewed open access monthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2900 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- cardiovascular (dys)-function
- cardiac signaling
- oxidative stress
- nitrosative stress
- superoxide
- hydrogen peroxide
- hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha
- hypoxia
- glycolysis
- oxidative phosphorylation
- fatty acids
- glucose
- ER-stress







