Intermolecular Interactions in the Formation of Polysaccharide-Gelatin Complexes: A Spectroscopic Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Properties of Gelatin and Polysaccharides
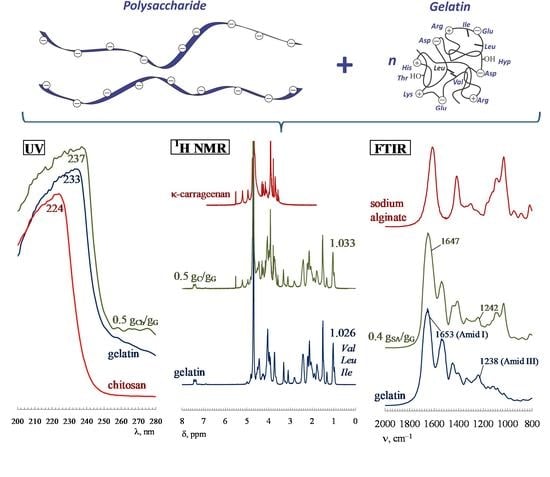
3. The Role of Electrostatic Interactions, Hydrogen Bonds and Hydrophobic Interactions
4. Changes in the Secondary Structure of Gelatin upon Complex Formation with Polysaccharides
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Turgeon, S.L.; Laneuville, S.I. Protein + Polysaccharide Coacervates and Complexes: From Scientific Background to their Application as Functional Ingredients in Food Products. In Modern Biopolymer Science; Kasapis, S., Norton, I.T., Eds.; Elsevier: London, UK, 2009; pp. 327–363. [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt, C.; Turgeon, S.L. Protein/polysaccharide complexes and coacervates in food systems. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 167, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gentile, L. Protein–polysaccharide interactions and aggregates in food formulations. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 48, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izumrudov, V.A. Self-assembly and molecular ‘recognition’ phenomena in solutions of (bio)polyelectrolyte complexes. Russ. Chem. Rev. 2008, 77, 381–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, C.; Sanchez, C.; Desobry-Banon, S.; Hardy, J. Structure and technofunctional properties of protein-polysaccharide complexes: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 1998, 38, 689–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Li, A.; Li, D.; Guo, Y.; Sun, L. Applications of mixed polysaccharide-protein systems in fabricating multi-structures of binary food gels—A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 109, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, A.; Rajendran, S.R.; He, Q.S.; Bazinet, L.; Udenigwe, C.C. Encapsulation of food protein hydrolysates and peptides: A review. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 79270–79278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortés-Morales, E.A.; Mendez-Montealvo, G.; Velázquez, G. Interactions of the molecular assembly of polysaccharide-protein systems as encapsulation materials. A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 295, 102398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Huang, Q. Assembly of protein–polysaccharide complexes for delivery of bioactive ingredients: A perspective paper. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 1344–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Wang, H.; Li, S.; Song, C.; Zhang, S.; Ren, J.; Udenigwe, C.C. Maillard-Type Protein–Polysaccharide Conjugates and Electrostatic Protein–Polysaccharide Complexes as Delivery Vehicles for Food Bioactive Ingredients: Formation, Types, and Applications. Gels 2022, 8, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alipal, J.; Mohd Pu’ad, N.A.S.; Lee, T.C.; Nayan, N.H.M.; Sahari, N.; Basri, H.; Idris, M.I.; Abdullah, H.Z. A review of gelatin: Properties, sources, process, applications, and commercialisation. Mater. Today-Proc. 2021, 42, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Tu, Z.; Shangguan, X.; Sha, X.; Wang, H.; Zhang, L.; Bansal, N. Fish gelatin modifications: A comprehensive review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 86, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Guillen, M.C.; Gimenez, B.; Lopez-Caballero, M.E.; Montero, M.P. Functional and bioactive properties of collagen and gelatin from alternative sources: A review. Food Hydrocoll. 2011, 25, 1813–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haug, I.J.; Draget, K.I. Gelatin. In Handbook of Hydrocolloids, 2nd ed.; Phillips, G.O., Williams, P.A., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009; pp. 142–163. [Google Scholar]
- Karim, A.A.; Bhat, R. Fish gelatin: Properties, challenges, and prospects as an alternative to mammalian gelatins. Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 563–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.-D.; Huang, J.-J.; Wu, J.-L.; Cai, X.-X.; Tian, Y.-Q.; Rao, P.-F.; Huang, J.-L.; Wang, S.-Y. Fabrication, interaction mechanism, functional properties, and applications of fish gelatin-polysaccharide composites: A review. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 122, 107106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derkach, S.R.; Voron’ko, N.G.; Kuchina, Y.A.; Kolotova, D.S. Modified Fish Gelatin as an Alternative to Mammalian Gelatin in Modern Food Technologies. Polymers 2020, 12, 3051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dille, M.J.; Hattrem, M.N.; Draget, K.I. Bioactively filled gelatin gels; challenges and opportunities. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 76, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Astrain, C.; Guaresti, O.; González, K.; Santamaria-Echart, A.; Eceiza, A.; Corcuera, M.A.; Gabilondo, N. Click gelatin hydrogels: Characterization and drug release behaviour. Mater. Lett. 2016, 182, 134–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, X.T.; Rioux, L.-E.; Turgeon, S.L. Formation and functional properties of protein–polysaccharide electrostatic hydrogels in comparison to protein or polysaccharide hydrogels. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 239, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derkach, S.R.; Voron’ko, N.G.; Kuchina, Y.A.; Kolotova, D.S.; Gordeeva, A.M.; Faizullin, D.A.; Gusev, Y.A.; .Zuev, Y.F.; Makshakova, O.N. Molecular structure and properties of κ-carrageenan-gelatin gels. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 197, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenova, M. Protein–polysaccharide associative interactions in the design of tailor-made colloidal particles. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 28, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anvari, M.; Joyner, H.S. Effect of fish gelatin-gum arabic interactions on structural and functional properties of concentrated emulsions. Food Res. Int. 2017, 102, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khemissi, H.; Bassani, H.P.; Aschi, A.; Capron, I.; Benyahia, L.; Nicolai, T. Exploiting Complex Formation between Polysaccharides and Protein Microgels To Influence Particle Stabilization of W/W Emulsions. Langmuir 2018, 34, 11806–11813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derkach, S.; Zhabyko, I.; Voron’ko, N.; Maklakova, A.; Dyakina, T. Stability and the rheological properties of concentrated emulsions containing gelatin–κ-carrageenan polyelectrolyte complexes. Colloids Surf. A 2015, 483, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, E. Interfacial structure and stability of food emulsions as affected by protein–polysaccharide interactions. Soft Matter 2008, 4, 932–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Hossen, A.; Zeng, Y.; Dai, J.; Li, S.; Qin, W.; Liu, Y. Gelatin-based composite films and their application in food packaging: A review. J. Food Eng. 2022, 313, 110762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doublier, J.-L.; Garnier, C.; Renarda, D.; Sanchez, C. Protein-polysaccharide interactions. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2000, 5, 202–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Li, L.; Inoue, C.; Lundin, L.; Appelqvist, I. Associative and Segregative Phase Separations of Gelatin/κ-Carregeenan Aqueous Mixtures. Langmuir 2006, 22, 9532–9537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonov, Y.A.; Goncalves, M.P. Phase separation in aqueous gelatin–κ-carrageenan systems. Food Hydrocoll. 1999, 13, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razzak, M.A.; Kim, M.; Chung, D. Elucidation of aqueous interactions between fish gelatin and sodium alginate. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 148, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lee, J.; Wang, Y.-W.; Huang, Q. Composition and rheological properties of β-lactoglobulin/pectin coacervates: Effects of salt concentration and initial protein/polysaccharide ratio. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 992–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabek, J.F. Experimental Methods in Polymer Chemistry: Physical Principles and Applications; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA; p. 888.
- Drago, R.S. Physical Methods for Chemists, 2nd ed.; Saunders College Publishing: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1992; p. 769. [Google Scholar]
- Silverstein, R.M.; Vebster, F.X.; Kiemle, D.J. Spectrometric Identification of Organic Compounds, 7th ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2005; p. 532. [Google Scholar]
- Kabanov, V.A. Polyelectrolyte complexes in solution and in a bulk. Russ. Chem. Rev. 2005, 74, 3–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, B.P.; Tsianou, M. From polyelectrolyte complexes to polyelectrolyte multilayers: Electrostatic assembly, nanostructure, dynamics, and functional properties. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 244, 71–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siyawamwaya, M.; Choonara, Y.E.; Bijukumar, D.; Kumar, P.; Du Toit, L.C.; Pillay, V. A Review: Overview of Novel Polyelectrolyte Complexes as Prospective Drug Bioavailability Enhancers. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2015, 64, 955–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meka, V.S.; Sing, M.K.G.; Pichika, M.R.; Nali, S.R.; Kolapalli, V.R.M.; Kesharwani, P. A comprehensive review on polyelectrolyte complexes. Drug Discov. Today 2017, 22, 1697–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kizilay, E.; Kayitmazer, A.B.; Dubin, P.L. Complexation and coacervation of polyelectrolytes with oppositely charged colloids. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 167, 24–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veis, A. The Macromolecular Chemistry of Gelatin; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1964; p. 478. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, D. Fish Gelatin: Molecular Interactions and Applications. In Biopolymer-Based Formulations. Biomedical and Food Applications; Pal, K., Banerjee, I., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 67–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derkach, S.R.; Kolotova, D.S.; Voron’ko, N.G.; Obluchinskaya, E.D.; Malkin, A.Y. Rheological Properties of Fish Gelatin Modified with Sodium Alginate. Polymers 2021, 13, 743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acevedo, C.A.; Diaz-Calderon, P.; Lopez, D.; Enrione, J. Assessment of gelatin–chitosan interactions in films by a chemometrics approach. CyTA—J. Food 2015, 13, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohammed, A.S.; Naveed, M.; Jost, N. Polysaccharides; Classification, Chemical Properties, and Future Perspective Applications in Fields of Pharmacology and Biological Medicine (A Review of Current Applications and Upcoming Potentialities). J. Polym. Environ. 2021, 29, 2359–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero, P.; Carpena, M.; García-Oliveira, P.; Echave, J.; Soria-Lopez, A.; García-Pérez, P.; Fraga-Corral, M.; Cao, H.; Nie, S.; Xiao, J.; et al. Seaweed polysaccharides: Emerging extraction technologies, chemical modifications and bioactive properties. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 2021; 1–29, published online. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phawaphuthanon, N.; Yu, D.; Ngamnikom, P.; Shin, I.-S.; Chung, D. Effect of fish gelatine-sodium alginate interactions on foam formation and stability. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 88, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sow, L.C.; Toh, N.Z.Y.; Wong, C.W.; Yang, H. Combination of sodium alginate with tilapia fish gelatin for improved texture properties and nanostructure modification. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 94, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, L.; Li, B.; Zhang, K.; Chu, X.; Hou, H. Physical properties and antioxidant activity of gelatin-sodium alginate edible films with tea polyphenols. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 118, 1377–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, C.; Liu, H.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, L. Blend Films from sodium alginate and gelatin solutions. J. Macromol. Sci. A 2001, 38, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Jia, H.; Cheng, Q.; Pan, F.; Jiang, Z. Sodium alginate-gelatin polyelectrolyte complex membranes with both high water vapor permeance and high permselectivity. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 375, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derkach, S.R.; Voron’ko, N.G.; Sokolan, N.I.; Kolotova, D.S.; Kuchina, Y.A. Interactions between gelatin and sodium alginate: UV and FTIR studies. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2019, 41, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, J.; Liu, J.; Yong, H.; Liu, Y.; Qin, Y.; Liu, J. Development of active packaging based on chitosan-gelatin blend films functionalized with Chinese hawthorn (Crataegus pinnatifida) fruit extract. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 140, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Qin, W.; Dai, J.; Zhang, Q.; Lee, K.; Liu, Y. Physicochemical properties of gelatin films containing tea polyphenol-loaded chitosan nanoparticles generated by electrospray. Mater. Des. 2020, 185, 108277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.F.; Rezaei, M.; Zandi, M.; Ghavi, F.F. Preparation and functional properties of fish gelatin–chitosan blend edible films. Food Chem. 2013, 136, 1490–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staroszczyk, H.; Sztuka, K.; Wolska, J.; Wojtasz-Pajak, A.; Kolodziejska, I. Interactions of fish gelatin and chitosan in uncrosslinked and crosslinked with EDC films: FT-IR study. Spectrochim. Acta A 2014, 117, 707–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Qiu, D.; Cosgrove, T.; Denbow, M.L. A small-angle neutron scattering and rheology study of the composite of chitosan and gelatin. Colloids Surf. B 2009, 70, 254–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uranga, J.; Etxabide, A.; Cabezudo, S.; de la Caba, K.; Guerrero, P. Valorization of marine-derived biowaste to develop chitin/fish gelatin products as bioactive carriers and moisture scavengers. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 706, 135747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anvari, M.; Joyner (Melito), H.S. Effect of fish gelatin and gum arabic interactions on concentrated emulsion large amplitude oscillatory shear behavior and tribological properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 79, 518–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Tu, Z.; Shangguan, X.; Wang, H.; Zhang, L.; Bansal, N. Characteristics of fish gelatin-anionic polysaccharide complexes and their applications in yoghurt: Rheology and tribology. Food Chem. 2020, 343, 128413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Tu, Z.; Zou, Z.; Shangguan, X.; Wang, H.; Bansal, N. Glycosylated fish gelatin emulsion: Rheological, tribological properties and its application as model coffee creamers. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 102, 105552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, L.C.; Barbosa, J.R.; da Conceição, S.; Ribeiro, A.; de Vasconcelos, M.A.M.; de Aguiar, B.A.; da Silva Pereira, G.V.; Albuquerque, G.A.; da Silva, F.N.L.; Crizel, R.L.; et al. Improvement of the characteristics of fish gelatin—gum arabic through the formation of the polyelectrolyte complex. Carbohyd. Polym. 2019, 223, 115068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Anvari, M.; Pan, C.-H.; Chung, D. Characterisation of interactions between fish gelatin and gum arabic in aqueous solutions. Food Chem. 2012, 135, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sow, L.C.; Chong, N.J.M.; Liao, Q.X.; Yang, H. Effects of κ-carrageenan on the structure and rheological properties of fish gelatin. J. Food Eng. 2018, 239, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Zhang, B.; Qiao, D.; Yan, X.; Zhao, S.; Jia, C.; Niu, M.; Xu, Y. Addition of κ-carrageenan increases the strength and chewiness of gelatin-based composite gel. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 128, 107565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pranoto, Y.; Lee, C.M.; Park, N.J. Characterization of fish gelatin films added with gellan and κ-carrageenan. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2007, 40, 766–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derkach, S.R.; Ilyin, S.O.; Maklakova, A.A.; Kulichikhin, V.G.; Malkin, A.Y. The rheology of gelatin hydrogels modified by κ-carrageenan. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 63, 612–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voron’ko, N.G.; Derkach, S.R.; Vovk, M.A.; Tolstoy, P.M. Formation of κ-carrageenan-gelatin polyelectrolyte complexes studied by 1H NMR, UV spectroscopy and kinematic viscosity measurements. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 151, 1152–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohajer, S.; Rezaei, M.; Hosseini, S.F. Physico-chemical and microstructural properties of fish gelatin/agar bio-based blend films. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 157, 784–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jridi, M.; Abdelhedi, O.; Salem, A.; Kechaou, H.; Nasri, M.; Menchari, Y. Physicochemical, antioxidant and antibacterial properties of fish gelatin-based edible films enriched with orange peel pectin: Wrapping application. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 103, 105688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Tu, Z.; Sha, X.; Wang, H.; Hu, Y.; Hu, Z. Gelling properties and interaction analysis of fish gelatin–low-methoxyl pectin system with different concentrations of Ca2+. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 132, 109826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sow, L.C.; Tan, S.J.; Yang, H. Rheological properties and structure modification in liquid and gel of tilapia skin gelatin by the addition of low acyl gellan. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 90, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petcharat, T.; Benjakul, S.; Hemar, Y. Improvement of Gel Properties of Fish Gelatin Using Gellan. Int. J. Food Eng. 2017, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, B.; Zhang, K.; Li, J.; Hou, H. Novel hard capsule prepared by tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) scale gelatin and konjac glucomannan: Characterization, and in vitro dissolution. Carbohyd. Polym. 2019, 206, 254–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imeson, A.P. Carrageenan and Furcellaran. In Handbook of Hydrocolloids, 2nd ed.; Phillips, G.O., Williams, P.A., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009; pp. 164–185. [Google Scholar]
- De Araujo, C.A.; Noseda, M.D.; Cipriani, T.R.; Goncalves, A.G.; Duarte, M.E.R.; Ducatti, D.R.B. Selective sulfation of carrageenans and the influence of sulfate regiochemistry on anticoagulant properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 91, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Usov, A.I. Polysaccharides of the red algae. Adv. Carbohydr. Chem. Biochem. 2011, 65, 115–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knutsen, S.H.; Myslabodski, D.E.; Larsen, B.; Usov, A.I. A modified system of nomenclature for red algal galactans. Bot. Mar. 1994, 37, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draget, K.I. Alginates. In Handbook of Hydrocolloids, 2nd ed.; Phillips, G.O., Williams, P.A., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009; pp. 807–828. [Google Scholar]
- Sellimi, S.; Younes, I.; Ben Ayed, H.; Maalej, H.; Montero, V.; Rinaudo, M.; Dahia, M.; Mechichi, T.; Hajji, M.; Nasri, M. Structural, physicochemical and antioxidant properties of sodium alginate isolated from a Tunisian brown seaweed. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 72, 1358–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voron’ko, N.G.; Derkach, S.R.; Kuchina, Y.A.; Sokolan, N.I.; Kuranova, L.K.; Obluchinskaya, E.D. Influence of added gelatin on the rheological properties of a Fucus vesiculosus extract. Food Biosci. 2019, 29, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dettmar, P.W.; Strugala, V.; Richardson, J.C. The key role alginates play in health. Food Hydrocoll. 2011, 24, 263–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rioux, L.E.; Turgeon, S.L.; Beaulieu, M. Characterization of polysaccharides extracted from brown seaweeds. Carbohydr. Polym. 2007, 69, 530–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzzarelli, R.A.A.; Muzzarelli, C. Chitin and Chitosan Hydrogels. In Handbook of Hydrocolloids, 2nd ed.; Phillips, G.O., Williams, P.A., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009; pp. 849–888. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Xue, C.; Mao, X. Chitosan: Structural modification, biological activity and application. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 4532–4546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younes, I.; Rinaudo, M. Chitin and Chitosan Preparation from Marine Sources. Structure, Properties and Applications. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 1133–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Santos, V.P.; Marques, N.S.S.; Maia, P.C.S.V.; de Lima, M.A.B.; de Oliveira Franco, L.; de Campos-Takaki, G.M. Seafood Waste as Attractive Source of Chitin and Chitosan Production and Their Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derkach, S.R.; Kuchina, Y.A.; Kolotova, D.S.; Voron’ko, N.G. Polyelectrolyte Polysaccharide-gelatin Complexes: Rheology and Structure. Polymers 2020, 12, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dawson, R.M.C.; Elliott, D.C.; Elliott, W.H.; Jones, K.M. Data for Biochemical Research, 3rd ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1986; p. 592. [Google Scholar]
- Lundblad, R.L.; Macdonald, F.M. Handbook of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 4th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010; p. 1098. [Google Scholar]
- Voron’ko, N.G.; Derkach, S.R.; Kuchina, Y.A.; Sokolan, N.I. The chitosan-gelatin (bio)polyelectrolyte complexes formation in an acidic medium. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 138, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voron’ko, N.G.; Derkach, S.R.; Vovk, M.A.; Tolstoy, P.M. Complexation of κ-carrageenan with gelatin in the aqueous phase analysed by 1H NMR kinetics and relaxation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 169, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, V.J. Gelation of Polysaccharides. In Functional Properties of Food Macromolecules; Hill, S.E., Ledward, D.A., Mitchell, J.R., Eds.; Aspen Publishers: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 1998; pp. 143–226. [Google Scholar]
- Djabourov, M.; Leblond, J.; Papon, P. Gelation of aqueous gelatin solutions. I. Structural investigation. J. Phys. Fr. 1988, 49, 319–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Velde, F.; Knutsen, S.H.; Usov, A.I.; Rollema, H.S.; Cerezo, A.S. 1H and 13C high resolution NMR spectroscopy of carrageenans: Application in research and industry. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2002, 13, 73–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebaaly, C.; Karaki, N.; Chahine, N.; Evidente, A.; Yassine, A.; Habib, J.; Kanaan, H. Polysaccharides of the red algae «Pterocladia» growing on the Lebanese coast: Isolation, structural features with antioxidant and anticoagulant activities. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 2, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kravchenko, A.O.; Anastyuk, S.D.; Isakov, V.V.; Sokolova, E.V.; Glazunov, V.P.; Yermak, I.M. Structural peculiarities of polysaccharide from sterile form of Far Eastern red alga Ahnfeltiopsis flabelliformis. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 111, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finer, E.G.; Franks, F.; Phillips, M.C.; Suggetty, A. Gel formation from solutions of single chain gelatin. Biopolymers 1975, 14, 1995–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, P.; Gross, S. High-resolution proton magnetic resonance studies of gelatin solution and gels. J. Photogr. Sci. 1975, 23, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naryshkina, Y.P.; Volkov, V.Y.; Dolinnyi, A.I.; Izmailova, V.N. Investigation of gelatin gel-formation processes by high-resolution nuclear magnetic resonance method. Colloid J. Russ. 1982, 44, 322–326. [Google Scholar]
- Rodin, V.V.; Izmailova, V.N. NMR method in the study of the interfacial adsorption layer of gelatin. Colloids Surf. A 1996, 106, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, L.-C.; Huang, Q.-Y.; Ding, W.; Xiao, X.-H.; Zhang, H.-Y.; Xiong, L.-X. Fish gelatin: The novel potential applications. J. Funct. Food. 2019, 63, 103581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Zhou, K.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Xie, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, H.; Yang, T.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, B. Collagen and its derivatives: From structure and properties to their applications in food industry. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 131, 107748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Te Nijenhuis, K. Thermoreversible network. Adv. Polym. Sci. 1997, 130, 1–235. [Google Scholar]
- Norton, I.T.; Morris, E.R.; Rees, D.A. Lyotropic effects of simple anions of the conformation and interactions of kappa-carrageenan. Carbohydr. Res. 1984, 134, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochas, C.; Taravel, F.-R.; Turquois, T.N.m.r. studies of synergistic kappa carrageenan–carob galactomannan gels. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 1990, 12, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuart, B. Infrared Spectroscopy: Fundamentals and Applications; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2004; p. 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Saidi, G.S.; Al-Alawi, A.; Rahman, M.S.; Guizani, N. Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopic study of extracted gelatin from shaari (Lithrinus microdon) skin: Effects of extraction conditions. Int. Food Res. J. 2012, 19, 1167–1173. [Google Scholar]
- Muyonga, J.N.; Cole, C.G.B.; Dyodu, K.G. Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy study of acid soluble collagen and gelatin from skin and bones of young and adult Nile perch (Lates niloticus). Food Chem. 2004, 86, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aloglu, A.K.; Harrington, P.B. Differentiation of Bovine, Porcine, and Fish Gelatins by Attenuated Total Reflectance Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (ATR-FTIRS) Coupled with Pattern Recognition. J. AOAC Int. 2018, 101, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prystupa, D.A.; Donald, A.M. Infrared study of gelatin conformations in the gel and sol states. Polym. Gels Netw. 1996, 4, 87–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Sun, R.; Ding, M.; Li, L.; Tao, N.; Wang, X.; Zhong, J. Commercial cold-water fish skin gelatin and bovine bone gelatin: Structural, functional, and emulsion stability differences. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 125, 109207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhutani, U.; Laha, A.; Mitra, K.; Majumdar, S. Sodium Alginate and Gelatin Hydrogels: Viscosity Effect on Hydrophobic Drug Release. Mater. Lett. 2016, 164, 76–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, N.; Maji, T.K. Genipin crosslinked microcapsules of gelatin A and κ-carrageenan polyelectrolyte complex for encapsulation of Neem (Azadirachta Indica A. Juss.) seed oil. Polym. Bull. 2010, 65, 347–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartori, C.; Finch, D.S.; Ralph, B.; Gilding, K. Determination of the cation content of alginate thin films by FTi.r. spectroscopy. Polymer 1997, 38, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Wang, Q.; Du, Y. Alginate/gelatin blend films and their properties for drug control release. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 280, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saarai, A.; Kasparkova, V.; Sedlacek, T.; Saha, P. On the development and characterization of crosslinked sodium alginate/gelatine hydrogels. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. 2013, 18, 152–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muzzarelli, R.A.A.; Rocchetti, R.; Stanic, V.; Wecks, M. Methods for the Determination of the Degree of Acetylation of Chitin and Chitosan. In Chitin Handbook; Muzzarelli, R.A.A., Peter, M.G., Eds.; Atec Edizioni: Grottammare, Italy, 1997; pp. 109–119. [Google Scholar]
- Natarajan, N.; Shashirekha, V.; Noorjahan, S.E.; Rameshkumar, M.; Rose, C.; Sastry, T.P. Fibrin–Chitosan-gelatin Composite Film: Preparation and Characterization. J. Macromol. Sci. A 2005, 42, 945–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, M.; Erboz, E. Determination of critical gelation conditions of κ-carrageenan by vicosimetric and FTIR analyses. Food Res. Int. 2010, 43, 1361–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakimets, I.; Wellner, N.; Smith, A.C.; Wilson, R.H.; Farhat, I.; Mitchell, J. Mechanical properties with respect to water content of gelatin films in glassy state. Polymer 2005, 46, 12577–12585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Guillen, M.C.; Lopez-Caballero, M.E.; Aleman, A.; Lopez de Lacey, A.; Gimenez, B.; Montero, P. Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Peptide Fractions from Squid and Tuna Skin Gelatin. In Sea By-Products as Real Material: New Ways of Application; Le Bihan, E., Ed.; Transworld Research Network: Trivandrum, Kerala, India, 2010; pp. 89–115. [Google Scholar]
- Derkatch, S.R.; Voron’ko, N.G.; Izmailova, V.N. Solubilization of oleophilic compounds in gelatin solutions containing surfactant. Colloids Surf. A 2003, 223, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Amino Acid Residue | Chemical Designation | Structure Formula | Number of Amino Acid Residues per 1000 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mammalian Gelatin | Fish Gelatin | |||||
| [41] | [14] | [15] | [43] | |||
| Glycine | Gly |  | 336.5 | 335 | 358 | 326 |
| Lysine | Lys |  | 24.8 | 28 | 26 | 18 |
| Hydroxylysine | Hyl |  | 5.2 | 4 | 6 | – |
| Histidine | His |  | 4.8 | 4 | 8 | 12 |
| Arginine | Arg |  | 47.9 | 48 | 51 | 48 |
| Aspartic acid | Asp |  | 47.3 | 46 | 51 | 49 |
| Glutamic acid | Glu |  | 72.1 | 72 | 74 | 72 |
| Serine | Ser |  | 39.2 | 33 | 63 | 65 |
| Threonine | Thr |  | 16.6 | 18 | 25 | 26 |
| Hydroxyproline | Hyp |  | 94.1 | 93 | 55 | 65 |
| Tyrosine | Tyr |  | 4.6 | 1 | 3 | 5 |
| Alanine | Ala |  | 106.6 | 117 | 108 | 112 |
| Valine | Val |  | 19.5 | 22 | 18 | 21 |
| Leucine | Leu |  | 24.0 | 24 | 20 | 25 |
| Isoleucine | Ile |  | 11.3 | 11 | 11 | 13 |
| Proline | Pro |  | 129.0 | 124 | 95 | 123 |
| Phenylalanine | Phe |  | 12.6 | 14 | 12 | 16 |
| Methionine | Met |  | 3.9 | 4 | 16 | 3 |
| Gelatin Type and Sources | Polysaccharides | Study Methods | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cold water fish skin (cod, pollock, and haddock) | Sodium alginate | Interfacial Tensiometry; Electrophoresis combined with Phase Analysis Light Scattering; Dynamic Light Scattering | [47] |
| Tilapia skin | Sodium alginate | Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy; Atomic Force Microscopy; Dynamic Light Scattering; Phase Analysis Light Scattering; FT-IR Spectroscopy | [48] |
| Cold water fish skin (cod, pollock, and haddock) | Sodium alginate | Turbidimetric acid titration; Laser Doppler Electrophoresis combined with Phase Analysis Light Scattering; Dynamic Light Scattering; Confocal Scanning Laser Microscopy | [31] |
| Tilapia skin (260–270 Bloom) | Sodium alginate | FT-IR Spectroscopy | [49] |
| Bovine skin (Mw = 5 × 104 Da) | Sodium alginate | FT-IR Spectroscopy; Wide-angle X-ray Diffraction; Scanning Electron Microscopy; Thermogravimetric Analysis; Differential Thermal Analysis | [50] |
| Porcine skin (Type A, 300 Bloom) | Sodium alginate | Scanning Electron Microscope; FT-IR spectroscopy; X-ray Diffraction; Differential Scanning Calorimetry; Positron Annihilation Lifetime Spectroscopy | [51] |
| Cold-water fish (pI 7.6, Mw = 13 × 104 Da) | Sodium alginate | UV spectroscopy; Rheology | [43] |
| Bovine skin (Type B, 225 Bloom) | Sodium alginate | FT-IR spectroscopy; UV spectroscopy | [52] |
| Cold water fish skin (Mw = 6 × 104 Da) | Chitosan (90% deacetylated) | FT-IR Spectroscopy; X-ray Diffraction; Scanning Electron Microscopy | [53] |
| Grass carp | Chitosan (95% deacetylated) | FT-IR Spectroscopy; Scanning Electron Microscopy | [54] |
| Bovine skin (Type B, 225 Bloom); Salmon skin | Chitosan | High Performance Liquid Chromatography; Differential Scanning Calorimetry | [44] |
| Cold water fish skin | Chitosan (75–85% deacetylated) | Differential Scanning Calorimetry; FT-IR Spectroscopy | [55] |
| Baltic cod skin | Chitosan (73% deacetylated) | Attenuated Total Reflectance Fourier Transformation Infrared (ATR FT-IR) Spectroscopy | [56] |
| Bovine skin (pI 4.9) | Chitosan (85% deacetylated) | Rheology; Small-angle Neutron Scattering | [57] |
| Fish skin (Type A, 240 Bloom) | β-chitin | FT-IR spectroscopy; Scanning Electron Microscopy | [58] |
| Cold water fish skin (Type B, pI 4.81) | Gum arabic | Rheology; Confocal Scanning Laser Microscopy | [23,59] |
| Bovine skin (Type A, 150 Bloom) Cold water fish skin (Type A) | Gum arabic; κ-Carrageenan | Electrophoresis; Rheology | [60] |
| Grass carp scales | Gum arabic | Intrinsic Fluorescence; UV-Visible Absorption Spectroscopy | [61] |
| Piramutaba skin | Gum arabic | High Performance Liquid Chromatograph; FT-IR Spectroscopy; Gel Electrophoresis SDS-PAGE; Scanning Electron Microscopy | [62] |
| Cold water fish skin | Gum arabic | Laser Doppler Electrophoresis combined with Phase Analysis Light Scattering; Turbidity; Dynamic Light Scattering | [63] |
| Bovine skin (Type B, 225 Bloom) | κ-Carrageenan | Turbidimetric Titration | [25] |
| Bovine skin (Type B, 225 Bloom) | κ-Carrageenan | ATR-FTIR Spectroscopy; Rheology | [21] |
| Pig skin (Type B) | κ-Carrageenan | Turbidity; Differential Scanning Calorimetry; Confocal Scanning Laser Microscopy; Phase Analysis Light Scattering | [29,30] |
| Tilapia skin (180 Bloom) | κ-Carrageenan | UV Spectroscopy; Dynamic Light Scattering; Atomic Force Microscopy; Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy; FT-IR Spectroscopy | [64] |
| Bovine skin (240 Bloom) | κ-Carrageenan; Konjac glucomannan | Scanning Electron Microscopy; X-ray Diffraction; FTIR Spectroscopy; Rheology; Differential Scanning Calorimetry; Texture Profile Analysis | [65] |
| Tilapia fish skin (200 Bloom) | κ-Carrageenan; Gellan | Scanning Electron Microscopy; FT-IR Spectroscopy; Differential Scanning Calorimetry | [66] |
| Bovine skin (Type B, 225 Bloom) | κ-Carrageenan | UV spectroscopy; Rheology; FT-IR Spectroscopy; 1H NMR Spectroscopy | [21,67,68] |
| Cold water fish skin | Agar | UV Spectroscopy; FT-IR Spectroscopy with Attenuated Total Reflection (FTIR-ATR); Atomic Force Microscopy; Scanning Electron Microscopy | [69] |
| Grey triggerfish skin | Pectin | FT-IR Spectroscopy; Differential Scanning Calorimetry; Scanning Electron Microscopy | [70] |
| Tilapia fish skin (pI 9.58, 260–270 Bloom) | Pectin (low-methoxyl) | Spectrophotometry; Rheology; FT-IR Spectroscopy; Scanning Electron Microscopy | [71] |
| Tilapia skin (180 Bloom) | Gellan (low acyl) | Dynamic Light Scattering; Phase Analysis Light Scattering; Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy; Rheology; FT-IR Spectroscopy | [72] |
| Tilapia skin (240 Bloom) | Gellan (low acyl) | Scanning Electron Microscopy; Rheology | [73] |
| Tilapia scale, (250 Bloom) | Konjac glucomannan | FT-IR Spectroscopy; Scanning Electron Microscopy; Rheology | [74] |
| Wavenumber of Absorption Band, cm−1 | Absorption Band | Band Assignment |
|---|---|---|
| Gelatin | ||
| 3401 | Amide A | Stretching vibrations of N–H and O–H groups |
| 1653 | Amide I | Stretching vibrations of C=O and C–N groups |
| 1541 | Amide II | Deformation vibrations of N–H groups and stretching vibrations of C–N groups |
| 1238 | Amide III | Stretching vibrations of N–H and C–N groups |
| 1165 | Stretching vibrations of COOH groups of Glu and Asp in gelatin | |
| Sodium alginate | ||
| 3447 | Amide A | Stretching vibrations of O–H groups |
| 1616 | Asymmetric stretches of COOH groups | |
| 1418 | Symmetric stretches of COOH groups | |
| 1300 | Stretching vibrations of C=O groups | |
| 1092 | Mannuronic units | |
| 1032 | Guluronic units | |
| 820 | α-Configuration of the guluronic units | |
| κ-Carrageenan | ||
| 3420 | Amide A | Stretching vibrations of O–H groups |
| 1263 | Vibration of ester sulfate groups | |
| 928 | 3,6-anhydro-α-D-galactopyranose units | |
| 848 | 4-sulfo-β-D-galactopyranose units | |
| Chitosan | ||
| 3439 | Amide A | Stretching vibrations of N–H and O–H groups |
| 1653 | Amide I | Stretching vibrations of N–H and C=O groups |
| 1560 | Amide II | Stretching vibrations of N–H, C–N and C–C groups |
| 1408 | Asymmetric and symmetric stretches of CH2 groups | |
| 1261 | Amide III | Stretching vibrations of N–H and C–N groups |
| 1074 | Skeletal C–O groups | |
| 1025 | Skeletal C–O groups | |
| 854 | β-Glycosidic bonds | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Derkach, S.R.; Voron’ko, N.G.; Kuchina, Y.A. Intermolecular Interactions in the Formation of Polysaccharide-Gelatin Complexes: A Spectroscopic Study. Polymers 2022, 14, 2777. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14142777
Derkach SR, Voron’ko NG, Kuchina YA. Intermolecular Interactions in the Formation of Polysaccharide-Gelatin Complexes: A Spectroscopic Study. Polymers. 2022; 14(14):2777. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14142777
Chicago/Turabian StyleDerkach, Svetlana R., Nikolay G. Voron’ko, and Yulia A. Kuchina. 2022. "Intermolecular Interactions in the Formation of Polysaccharide-Gelatin Complexes: A Spectroscopic Study" Polymers 14, no. 14: 2777. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14142777