Renewable Energy Technologies towards Food-Energy-Water Security Nexus
A special issue of Sustainability (ISSN 2071-1050). This special issue belongs to the section "Energy Sustainability".
Deadline for manuscript submissions: closed (30 November 2023) | Viewed by 6441
Special Issue Editors
Interests: electrical engineering; industrial engineering; control systems engineering; fuzzy logic; neural network
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: design and control of special motor drive, and its applications in Electric Vehicle (EV); renewable energy generation
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: electrical drives for home appliances, industrial and automotive applications; sensorless and advanced control algorithms
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: control systems of electric drives; hybrid powertrains; real-time communications
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Special Issue Information
Dear Colleagues,
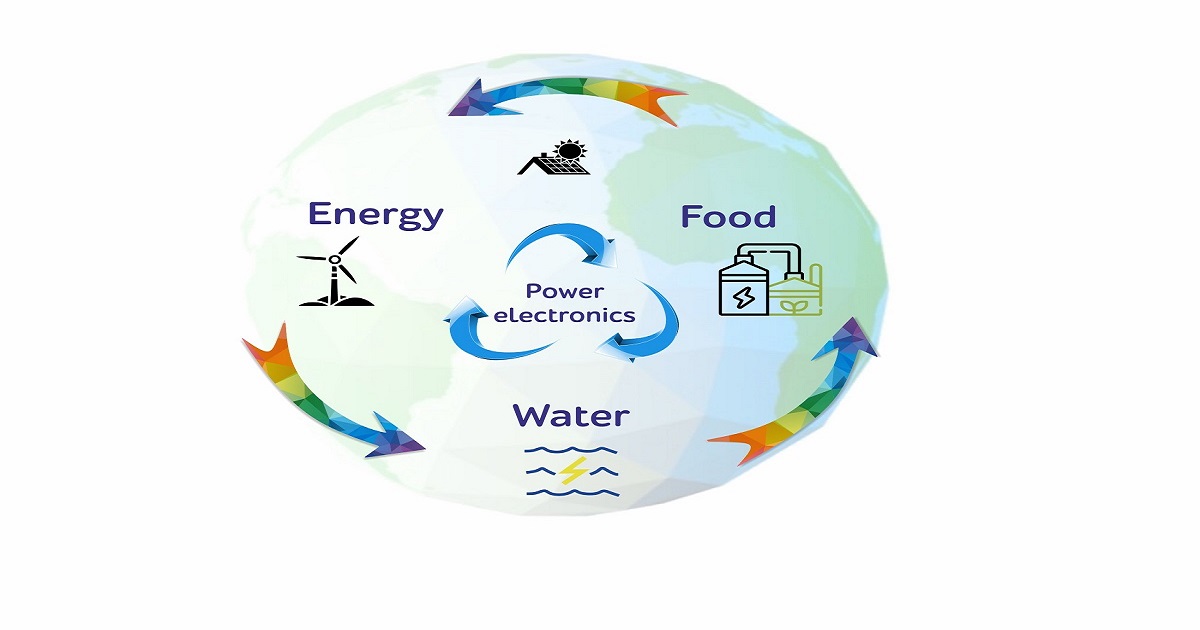
One of the greatest problems facing humanity today is sustainably delivering electrical energy, water, and food security. Food and water security are provided by the generation of energy from renewable energy sources, such as wind turbines, solar panels, wave energy sources, biohydrogen, and hydropower systems. This Special Issue aims to connect scientists from various research fields to discuss the vision for a Water–Energy–Food ecosystem.
We are pleased to invite you to share your research and submit manuscripts in the field of industrial development and energy evolution for an upcoming Special Issue of Sustainability. This Special Issue aims to open a debate on how the ecosystems that provide us with natural resources and the human activities that impact upon them could be controlled responsibly. Today's society is characterized by a high demand for electrical energy, and our direction of development must be focused on renewable energy resources whose uses affect the food ecosystem. The main key in the transformation of electrical energy lies in the strategic decisions we will take regarding natural resources, which require careful monitoring and appropriate interaction.
In this Special Issue, original research articles and reviews are welcome. We are seeking to achieve a multifaceted discussion on the management and use of energy, land, and water, energy efficiency control system development, distributed energy system design, renewable energy systems, food production as it relates to energy and water, and the latest developments in the area of anaerobic digester outputs.
Prof. Dr. Galina Demidova
Prof. Dr. Hao Chen
Dr. Anton Dianov
Dr. Aleksey S. Anuchin
Guest Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the special issue website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Sustainability is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2400 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- wind energy
- solar energy
- inverters
- wave power
- hydropower
- control systems
- agro-food industry
- biogas
- biohydrogen
- anaerobic digestion








