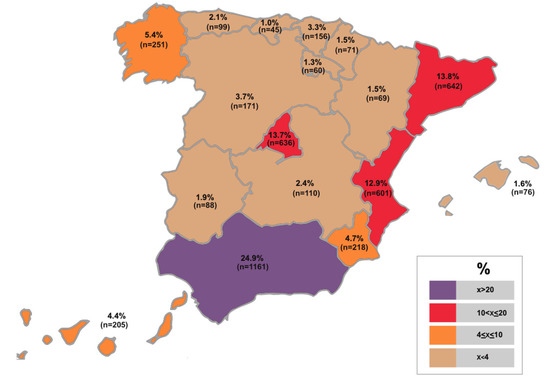
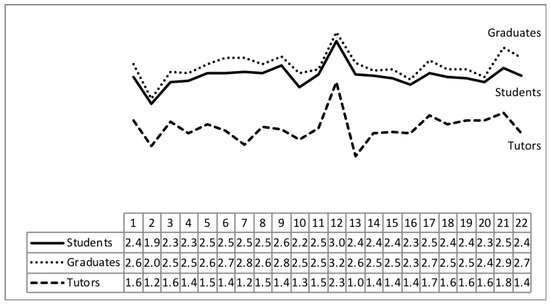
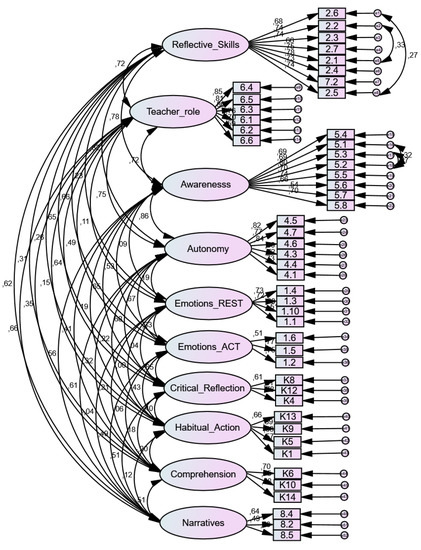
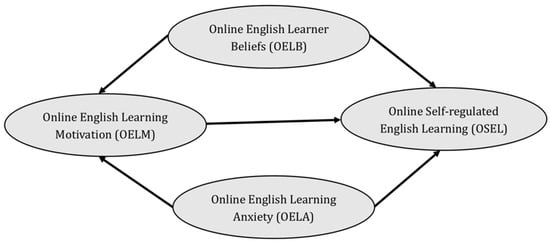
Motivation and Evaluation in Education from the Sustainability Perspective (Closed)
A topical collection in Sustainability (ISSN 2071-1050). This collection belongs to the section "Sustainable Education and Approaches".
Viewed by 89977Editors
Interests: Educational Equity, Educational Evaluation, Reflective Practice, Research Methods in Education, Intercultural Education, Teacher Training. I am committed to working pedagogical practice evidence-informed from the perspective of equity and sustainability
Interests: Educational Evaluation, Evaluation of Professional Profile in Higher Education, Research Methods in Education, Professional Values. I am committed to working in the integral pedagogical practice from the perspective of values, equity and sustainability
Interests: physical education; models-based practice; teaching evaluation
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
One of the main challenges in today's democratic societies is the quality of education promotion and equity for all. In this sense, an education for sustainable development implies offering successful learning opportunities to citizens too. Among others, such perspective reveals implications on the need to give straightforward answers to facilitate the access, the survival, and the academic success of all students in the education system. Hence, education must be led to the promotion of contexts and processes for the empowerment of students. Learners need to "learn to live together" and "learn to learn" autonomously in a world that is continuously changing, diversifying, and subjecting to very different social, economic, cultural, and psychological forces.
Of all the elements involved in the promotion of efficient educational processes, two of them manifest particular relevance. The first educational process is linked to the motivation allowing students themselves to be guided towards well-defined learning outcomes. The second educational process refers to the assessment as a learning activity enabling students to gain consciousness of what and how they learn as acts of metacognition and self-regulation. Both educational elements should not be interpreted as isolated elements but as processes aimed at empowering everyone to be performers and producers agents in self academic, formative, and professional itineraries held in their projects of life in coexistence with others.
The purpose of this Special Issue for Sustainability is the contribution to the scientific debate on the role of motivation and evaluation throughout the teaching-learning process. Consequently, the expectation is the contribution to a more fair, equitable and democratic society. Factors, as mentioned earlier, assume providing students with the necessary skills to be citizens committed to contemporary social challenges through the development of competencies to the adoption and implementation of self-decisions and transitions for a Lifelong-Learning.
Notwithstanding the autonomy of students is a relevant factor, teachers training must be considered necessary as well. A well-trained teacher owns the skills, strategies, and pedagogical resources to stimulate learning motivation and to implement the appropriate formative and shared assessment for learners to acquire meaningful learning. It does not involve mere academic success, but also the measurement of meaningful learning, knowledge transfer, and carried out day-to-day activities.
The present Special Issue for Sustainability encompasses research, studies and educational experiences on the contributions of motivation and evaluation in coherence with current educational challenges from the sustainability perspective:
- Motivation: the importance of the development of personal identity in relation to social learning. Only people with a construction of personal identity can engage with the social challenges of a society.
- Evaluation for successful learning for all: learning that makes students reflect on their commitment to learning and mobilize to act in favor of social transformation.
Consequently, the proposals can be linked to Early Childhood Education, Primary Education, Secondary Education, or Higher Education. Because of its impact and contribution for a better understanding of the Special Issue for Sustainability topic, contributions to informal education environments can be considered as well.
Summing up, accepted academic contributions might be diverse, but always linked to motivation and evaluation from a sustainable perspective, according to the didactic purpose, that should inspire education as an instrument of change and social transformation for the promotion of successful learning processes for all.
Dr. José Sánchez-Santamaría
Dr. Brenda Imelda Boroel Cervantes
Dr. David Hortigüela Alcalá
Guest Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Sustainability is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2400 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- Educational Equity
- Success Education
- Sustainable Education
- Learning Motivation
- Educational Evaluation
- Learn to Learn
- Reflective Thinking
- Professional Development
- Institutional Development
- Citizenship