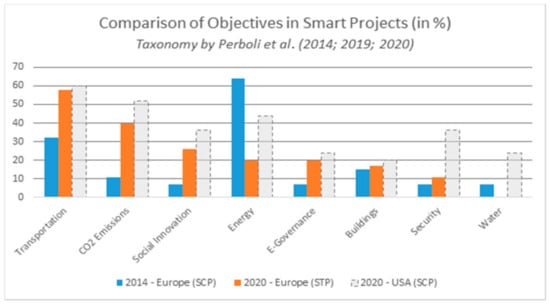
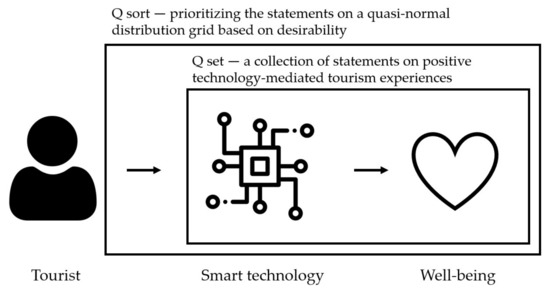
Sustainable Innovation in Tourism and Hospitality
A topical collection in Sustainability (ISSN 2071-1050). This collection belongs to the section "Tourism, Culture, and Heritage".
Viewed by 23519Editors
2. Alliance for Innovators and Researchers in Tourism and Hospitality (AIRTH)
Interests: tourism innovation; service design; e-tourism
Interests: best practices for binational education; quality of life and community engagement; sustainable development and social inclusion; tourism development and social responsibility
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
Innovation is becoming increasingly important in tourism and hospitality, both following and dictating trends such as globalization, digitization and sustainability. More recently, the new reality imposed by Covid-19 weakened the tourism and hospitality sector while, at the same time, questioning and sharpening its sustainable development goals and priorities. The objectives of this Special Issue are therefore twofold. Firstly, we would like to present state-of-the-art scientific analyses, both empirical and theoretical, of sustainable innovation responses to current and future trends and threats. Secondly, at the same time, we wish to devote as much attention as possible to studies focusing on innovation in the tourism and hospitality sector that address the sustainability aspects of all areas, and not just those which are ecological.
More precisely, with our first objective, we are interested in the changing patterns of global trends and their impacts on sustainable innovation in the tourism and hospitality sector, including the pre-/mid-/post-Covid-19 influences on sustainable innovation behavior, approaches, dynamics and outcomes of all or selected stakeholders in the tourism and hospitality sector. Tourism organizations tend to perform better in terms of environmental and economic sustainability, compared to a generally lower commitment to the social dimension of sustainability. Underperformance in the social component of sustainability among tourism organizations can result, among other things, from misconceptions of authenticity or unclear guidelines on social sustainability as opposed to increasingly adopted environmental sustainability policies. For our second objective, we encourage authors to consider innovative approaches to integrating social sustainability, beyond the economic and environmental dimensions, within the overall performance of tourism organizations.
Dr. Dejan Krizaj
Dr. Vinod Sasidharan
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Sustainability is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2400 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- tourism innovation
- sustainable development
- social sustainability
- tourism trends