Journal Description
Pediatric Reports
Pediatric Reports
is an international, scientific, peer-reviewed open access journal on all aspects of pediatrics, published quarterly online by MDPI (from Volume 12 Issue 3 - 2020). The Italian Society of Pediatric Psychology (SIPPed) is affiliated with Pediatric Reports and the members receive discounts of the article processing charge.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, ESCI (Web of Science), PubMed, PMC, Embase, and other databases.
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 32.4 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 7.6 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2023).
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
Impact Factor:
1.1 (2022);
5-Year Impact Factor:
1.1 (2022)
Latest Articles
The Burden of Not Doing
Pediatr. Rep. 2024, 16(2), 327-328; https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric16020028 (registering DOI) - 25 Apr 2024
Abstract
The cultural and professional growth of a physician is a long process, spanning over more than 10 years [...]
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Predictive Value of Neutrophil-to-Monocyte Ratio, Lymphocyte-to-Monocyte Ratio, C-Reactive Protein, Procalcitonin, and Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha for Neurological Complications in Mechanically Ventilated Neonates Born after 35 Weeks of Gestation
by
Daniela Mariana Cioboata, Marioara Boia, Aniko Maria Manea, Oana Cristina Costescu, Sergiu Costescu, Florina Marinela Doandes, Zoran Laurentiu Popa and Dorel Sandesc
Pediatr. Rep. 2024, 16(2), 313-326; https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric16020027 (registering DOI) - 24 Apr 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This prospective study investigated the association between elevated neutrophil-to-monocyte ratio (NMR), lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio (LMR), C-reactive protein (CRP), procalcitonin, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) and the risk of developing neurological complications in mechanically ventilated neonates. The aim was to evaluate these biomarkers’ predictive value
[...] Read more.
This prospective study investigated the association between elevated neutrophil-to-monocyte ratio (NMR), lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio (LMR), C-reactive protein (CRP), procalcitonin, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) and the risk of developing neurological complications in mechanically ventilated neonates. The aim was to evaluate these biomarkers’ predictive value for neurological complications. Within a one-year period from January to December 2022, this research encompassed neonates born at ≥35 weeks of gestational age who required mechanical ventilation in the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) from the first day of life. Biomarkers were measured within the first 24 h and at 72 h. Sensitivity, specificity, and area under the curve (AUC) values were calculated for each biomarker to establish the best cutoff values for predicting neurological complications. The final analysis included a total of 85 newborns, of which 26 developed neurological complications and 59 without such complications. Among the studied biomarkers, TNF-alpha at >12.8 pg/mL in the first 24 h demonstrated the highest predictive value for neurological complications, with a sensitivity of 82%, specificity of 69%, and the highest AUC (0.574, p = 0.005). At 72 h, TNF-alpha levels greater than 14.3 pg/mL showed further increased predictive accuracy (sensitivity of 87%, specificity of 72%, AUC of 0.593, p < 0.001). The NMR also emerged as a significant predictor, with a cutoff value of >5.3 yielding a sensitivity of 78% and specificity of 67% (AUC of 0.562, p = 0.029) at 24 h, and a cutoff of >6.1 showing a sensitivity of 76% and specificity of 68% (AUC of 0.567, p = 0.025) at 72 h. Conversely, CRP and procalcitonin showed limited predictive value at both time points. This study identifies TNF-alpha and NMR as robust early predictors of neurological complications in mechanically ventilated neonates, underscoring their potential utility in guiding early intervention strategies. These findings highlight the importance of incorporating specific biomarker monitoring in the clinical management of at-risk neonates to mitigate the incidence of neurological complications.
Full article
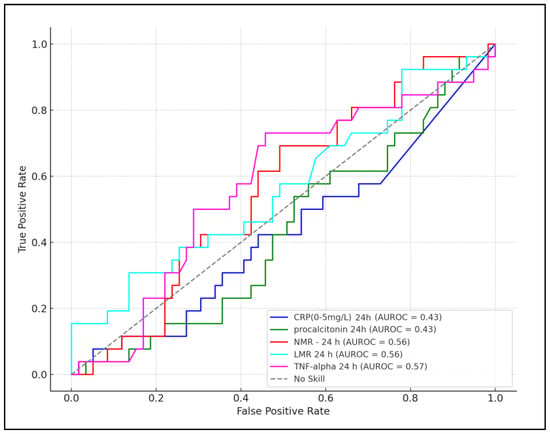
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Predictors of Corporal Punishment during the COVID-19 Pandemic
by
Robert D. Sege, Eliza Loren Purdue, Dina Burstein, Phyllis Holditch Niolon, Lori Lyn Price, Ye Chen, Elizabeth A. Swedo, Tammy Piazza Hurley, Kavita Prasad and Bart Klika
Pediatr. Rep. 2024, 16(2), 300-312; https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric16020026 - 19 Apr 2024
Abstract
Although current policies discourage the use of corporal punishment (CP), its use is still widespread in the US. The objective of this study was to assess the proportion of parents who used CP during the pandemic and identify related risk and protective factors.
[...] Read more.
Although current policies discourage the use of corporal punishment (CP), its use is still widespread in the US. The objective of this study was to assess the proportion of parents who used CP during the pandemic and identify related risk and protective factors. We analyzed results of a nationwide cross-sectional internet panel survey of 9000 US caregivers who responded in three waves from November 2020 to July 2021. One in six respondents reported having spanked their child in the past week. Spanking was associated with intimate partner violence and the use of multiple discipline strategies and not significantly associated with region or racial self-identification. Parents who spanked sought out more kinds of support, suggesting an opportunity to reduce spanking through more effective parenting resources. Additionally, these results suggest that parents who report using CP may be at risk for concurrent domestic violence.
Full article
Open AccessEditorial
Metabolic-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD): A New Term for a More Appropriate Therapy in Pediatrics?
by
Mosca Antonella, Andrea Pietrobattista and Giuseppe Maggiore
Pediatr. Rep. 2024, 16(2), 288-299; https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric16020025 - 10 Apr 2024
Abstract
The term “non-alcoholic fatty liver disease” (NAFLD) has been, for a long time, used to describe the spectrum of liver lesions encompassing steatosis, steatohepatitis (NASH), and steatotic cirrhosis [...]
Full article
Open AccessArticle
The Impact of Prenatal Alcohol Exposure on the Autonomic Nervous System and Cardiovascular System in Rats in a Sex-Specific Manner
by
Michał Jurczyk, Magdalena Król, Aleksandra Midro, Katarzyna Dyląg, Magdalena Kurnik-Łucka, Kamil Skowron and Krzysztof Gil
Pediatr. Rep. 2024, 16(2), 278-287; https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric16020024 - 09 Apr 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder (FASD) is a consequence of prenatal alcohol exposure (PAE) associated with a range of effects, including dysmorphic features, prenatal and/or postnatal growth problems, and neurodevelopmental difficulties. Despite advances in treatment methods, there are still gaps in knowledge that
[...] Read more.
Background: Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder (FASD) is a consequence of prenatal alcohol exposure (PAE) associated with a range of effects, including dysmorphic features, prenatal and/or postnatal growth problems, and neurodevelopmental difficulties. Despite advances in treatment methods, there are still gaps in knowledge that highlight the need for further research. The study investigates the effect of PAE on the autonomic system, including sex differences that may aid in early FASD diagnosis, which is essential for effective interventions. Methods: During gestational days 5 to 20, five pregnant female Wistar rats were orally administered either glucose or ethanol. After 22 days, 26 offspring were born and kept with their mothers for 21 days before being isolated. Electrocardiographic recordings were taken on the 29th and 64th day. Heart rate variability (HRV) parameters were collected, including heart rate (HR), standard deviation (SD), standard deviation of normal-to-normal intervals (SDNN), and the root mean square of successive differences between normal heartbeats (RMSSD). Additionally, a biochemical analysis of basic serum parameters was performed on day 68 of the study. Results: The study found that PAE had a significant impact on HRV. While electrolyte homeostasis remained mostly unaffected, sex differences were observed across various parameters in both control and PAE groups, highlighting the sex-specific effects of PAE. Specifically, the PAE group had lower mean heart rates, particularly among females, and higher SDNN and RMSSD values. Additionally, there was a shift towards parasympathetic activity and a reduction in heart rate entropy in the PAE group. Biochemical changes induced by PAE were also observed, including elevated levels of alanine transaminase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST), especially in males, increased creatinine concentration in females, and alterations in lipid metabolism. Conclusions: PAE negatively affects the development of the autonomic nervous system, resulting in decreased heart rate and altered sympathetic activity. PAE also induces cardiovascular abnormalities with sex-specific effects, highlighting a relationship between PAE consequences and sex. Elevated liver enzymes in the PAE group may indicate direct toxic effects, while increased creatinine levels, particularly in females, may suggest an influence on nephrogenesis and vascular function. The reduced potassium content may be linked to hypothalamus–pituitary–adrenal axis overactivity.
Full article
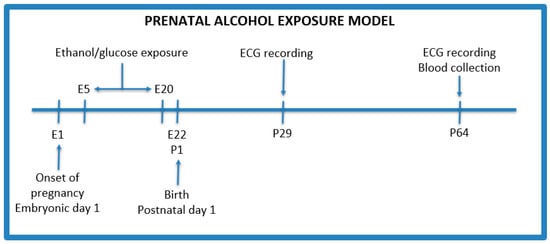
Figure 1
Open AccessCase Report
High-Altitude Pulmonary Edema in Two Pediatric Patients with Pre-Existing Lung Disease
by
Ali Alsuheel Asseri, Marei Assiri, Norah Alshehri, Noha Saad Alyazidi, Ahmed Alasmari, Saud Q. Alshabab and Nada Abdullah Asiri
Pediatr. Rep. 2024, 16(2), 271-277; https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric16020023 - 05 Apr 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: The illnesses associated with changes in barometric pressure can be classified into three types: acute mountain sickness, high-altitude pulmonary edema (HAPE), and high-altitude cerebral edema. HAPE is a rare form of pulmonary edema that occurs in susceptible individuals after arriving at altitudes
[...] Read more.
Background: The illnesses associated with changes in barometric pressure can be classified into three types: acute mountain sickness, high-altitude pulmonary edema (HAPE), and high-altitude cerebral edema. HAPE is a rare form of pulmonary edema that occurs in susceptible individuals after arriving at altitudes over 2500 m above sea level (m). Only a few studies have reported classical HAPE among children with underlying cardiopulmonary comorbidities. In this study, we report two pediatric cases of classical HAPE that occurred immediately upon arriving at Abha city (with an average elevation of 2270 m above sea level). Notably, both patients possessed underlying chronic lung diseases, raising crucial questions about susceptibility factors and the early onset manifestations of HAPE. Case: Two pediatric cases of HAPE are presented. The first patient, with a medical history of repaired right congenital diaphragmatic hernia and subsequent right lung hypoplasia, developed HAPE following their ascent to a high altitude. The second patient, diagnosed with diffuse lung disease of unknown etiology, experienced HAPE after a rapid high-altitude ascent. Both patients resided in low-altitude areas prior to ascent. The initial emergency room assessment revealed that both patients had severe hypoxia with respiratory distress that mandated the initiation of respiratory support and 100% oxygen therapy. They required intensive care unit admission, improved after 5 days of hospitalization, and were sent home in good condition. Conclusion: HAPE is a complex, potentially life-threatening high-altitude illness with diverse clinical presentations and variable risk factors. This case report sheds light on a potential predisposition factor—pre-existing lung disease—in children experiencing severe HAPE. While further validation is crucial, this valuable insight opens doors for improved preventative strategies and informed medical decisions for children with pre-existing lung conditions traveling to high altitudes.
Full article
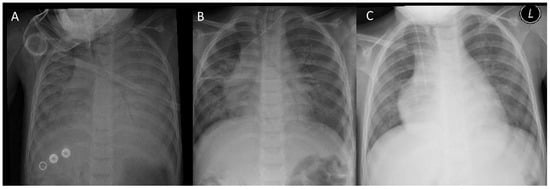
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Effects of Two Online Mindfulness-Based Interventions for Early Adolescents for Attentional, Emotional, and Behavioral Self-Regulation
by
Bárbara Porter, Cristian Oyanadel, Ignacio Betancourt, Frank C. Worrell and Wenceslao Peñate
Pediatr. Rep. 2024, 16(2), 254-270; https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric16020022 - 29 Mar 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
(1) Background: Mindfulness-based interventions (MBIs) have shown interesting preliminary effects on self-regulation processes in early adolescence. However, programs have typically combined different types of interventions with no understanding of the specific effect of each intervention type on attentional, emotional, and behavioral regulation. The
[...] Read more.
(1) Background: Mindfulness-based interventions (MBIs) have shown interesting preliminary effects on self-regulation processes in early adolescence. However, programs have typically combined different types of interventions with no understanding of the specific effect of each intervention type on attentional, emotional, and behavioral regulation. The objective of this research was to evaluate the effect of two MBIs—one focused on classic attentional practices and another focused on the recognition and expression of emotions—on attentional, emotional, and behavioral self-regulation in early adolescents. (2) Method: An experimental paradigm was used. A sample of 74 children aged between 8 and 12 years old were randomly assigned to three experimental conditions: (1) an MBI with a focus on attentional practices, (2) an MBI with a focus on recognition and expression of emotions, and (3) a control group. The interventions lasted 8 weeks, with a weekly, 1 h online synchronous session plus home practices. Children were evaluated before starting the intervention and at the end of the 8-week period. The assessed outcomes were (1) mindfulness; (2) emotional regulation; (3) attentional regulation, and (4) behavioral regulation. (3) Results: Children who participated in both intervention programs increased their mindfulness and emotional and behavioral regulation scores. Only children who participated in the MBI with a focus on attention showed significant changes in their ability to self-regulate attention. (4) Conclusions: The use of online MBIs, with attention to external and internal stimuli practices, can be a good strategy to strengthen self-regulation skills for attention, emotions, and behavior in early adolescence.
Full article
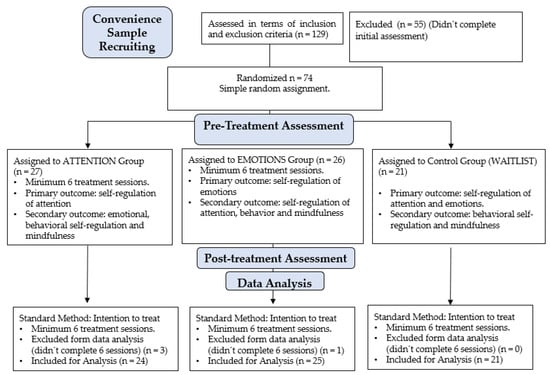
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Control of Dental Caries in Children and Adolescents Using Fluoride: An Overview of Community-Level Fluoridation Methods
by
América Patricia Pontigo-Loyola, Martha Mendoza-Rodriguez, Rubén de la Rosa-Santillana, Maria Gracia Rivera-Pacheco, Horacio Islas-Granillo, Juan Fernando Casanova-Rosado, María de Lourdes Márquez-Corona, José de Jesús Navarrete-Hernández, Carlo Eduardo Medina-Solís and David J. Manton
Pediatr. Rep. 2024, 16(2), 243-253; https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric16020021 - 27 Mar 2024
Abstract
The maintenance of oral health is a crucial aspect of general well-being; however, a significant proportion of the worldwide population experiences a range of oral diseases. Dental caries is a highly prevalent non-communicable disease globally, especially in children and adolescents. Fluoride is involved
[...] Read more.
The maintenance of oral health is a crucial aspect of general well-being; however, a significant proportion of the worldwide population experiences a range of oral diseases. Dental caries is a highly prevalent non-communicable disease globally, especially in children and adolescents. Fluoride is involved in the control of dental caries, primarily by decreasing the critical pH for dental hard tissue dissolution and decreasing enamel solubility. Due to the substantial data supporting the efficacy of fluoride in controlling dental caries, many community-level fluoridation initiatives have been devised and executed as global public health preventive interventions. These initiatives encompass the fluoridation of water, salt, and milk. Water fluoridation is considered safe and effective when fluoride levels are maintained within the recommended range (0.6 to 1.1 mg/L). Salt fluoridation has a cariostatic potential similar to that of water fluoridation, and a fluoride concentration of 250 micrograms per gram in salt is not associated with an increased risk of developing dental fluorosis. However, there is currently an effort to reduce the consumption of table salt in order to mitigate the harmful effects of excessive salt consumption. It has been hypothesized that fluoride food supplementation, such as fluoridated milk, is associated with a decrease in caries experience in permanent teeth; however, the effect is not clear in primary teeth. Public-level fluoride interventions are more cost-effective than the operative care of caries lesions and limit the burden of care. The administration of fluorides should be conducted using safe methods, limiting ingestion, and adhering to the guidelines set by international and national health agencies in each country. This is particularly important when considering children with developing dentitions. Fluoride is an important tool in the control of dental caries, but it is crucial to combine it with good oral hygiene, a healthy diet, and regular visits to a dental professional to maintain long-term oral health.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Two versus Three Infusion Regimens of N-Acetylcysteine for Acetaminophen Overdose
by
Shadi Tamur, Bader Alyahya, Faisal Alsani, Ammar Abdulraheem Bahauddin, Maryam Aljaid, Sultan Al-Malki, Ahmad Alzahrani, Abdullah Khayat, Anwar Shams and Dominic S. Chalut
Pediatr. Rep. 2024, 16(1), 232-242; https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric16010020 - 20 Mar 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Acetaminophen overdose is a common clinical condition, often leading to liver toxicity. Current treatments involve the three-infusion N-Acetylcysteine (NAC) regimen (FDA-labeled), which may be complex, time-consuming, and need to be changed. An alternative uses two infusions instead, which offers possible advantages regarding
[...] Read more.
Background: Acetaminophen overdose is a common clinical condition, often leading to liver toxicity. Current treatments involve the three-infusion N-Acetylcysteine (NAC) regimen (FDA-labeled), which may be complex, time-consuming, and need to be changed. An alternative uses two infusions instead, which offers possible advantages regarding simplicity and administration errors. This study sought to compare the respective efficacies and safety outcomes when treating acute acetaminophen overdose among children and adolescents. Methods: At Montreal Children’s Hospital, a retrospective study was conducted comparing pre-2003 FDA-labelled three-infusion NAC therapy with a two-infusion regimen. Information was collected regarding patient demographics, NAC administration details, errors, rates of hepatotoxicity, and adverse reactions, and the statistical test Chi-square test was employed to obtain the results. Results: A total of 126 patients met the inclusion criteria. Of these patients, 65 received a two-infusion regimen, and 61 patients received the FDA-labeled regimen. The two-infusion group experienced significantly fewer administration errors (4 errors vs. 23 errors; p < 0.001), while the rates of hepatotoxicity between them were similar. There were no instances of liver transplantation or mortality due to either regimen. Adverse reactions occurred equally frequently between both regimens with no discernible difference—the meantime to administer NAC was 9 h for the two-infusion regimen and 8.5 h for FDA-labeled regimen groups, respectively. Three cases of hepatitis were successfully treated with timely NAC therapy, and no liver transplantation or mortality occurred. Adverse reactions, including anaphylactoid reactions, were observed in both groups but were resolved when temporarily stopped and restarted at a slower infusion rate. Conclusions: The two-infusion NAC regimen proved similar efficacy at protecting liver damage and improving patient outcomes compared to its FDA-labeled three-stage counterpart, with significantly fewer administration errors for this version of NAC treatment, suggesting potential advantages in terms of safety and simplicity. Future research should investigate larger cohorts and more variables to validate these results further and optimize the management of acetaminophen overdose cases; further investigation should focus on dosing strategies, personalized approaches, and long-term patient care in this context.
Full article
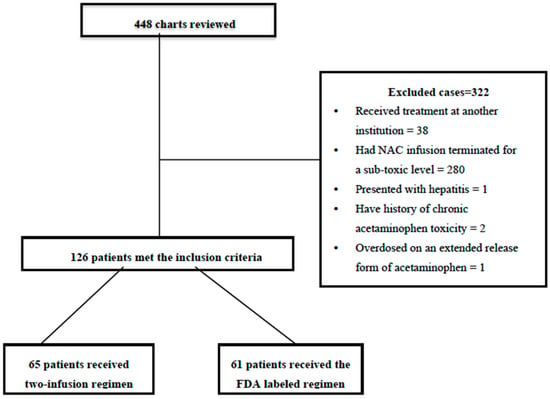
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
School Medical Service: Strategies to Promote Psycho-Physiological Well-Being
by
Francesco Tafuri and Francesca Latino
Pediatr. Rep. 2024, 16(1), 214-231; https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric16010019 - 19 Mar 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Schools represent the ideal setting for educating children about the acquisition of active lifestyles seen not only from a health point of view but also from psycho-pedagogical and social perspectives. Based on evidence from scientific literature, there is a need to include physical
[...] Read more.
Schools represent the ideal setting for educating children about the acquisition of active lifestyles seen not only from a health point of view but also from psycho-pedagogical and social perspectives. Based on evidence from scientific literature, there is a need to include physical activity in school routines, especially in primary schools, where the habits learned by children stay with them in their later years and adulthood. With the support of the school medicine service, schools become a favorable context for planning health education sessions aimed at students, with particular reference to prevention. Within teaching, it is necessary to consider the motor area as a fundamental tool for acquiring correct lifestyles, facilitating cognitive development, inclusiveness, and psycho-emotional and socio-relational factors. Schools can play a fundamental role, becoming the key to promoting physical activity at different times of the day, such as during class hours (with active breaks), during breaks, before and after lessons, and by integrating movement into teaching. This review is the result of an in-depth overview of the available literature on the relationship of schools with health and health promotion from a preventive perspective, with awareness of how the issue is being approached and the need for further future reflections that will go hand in hand with the coming changes.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Pediatric Lemierre’s Syndrome: A Comprehensive Literature Review
by
Salvatore Lavalle, Edoardo Masiello, Salvatore Cocuzza, Piero Pavone, Alessandra Di Nora, Christian Calvo-Henriquez, Jerome Rene Lechien, Miguel Mayo Yanez, Andrea Praticò, Manuela Ceccarelli, Giannicola Iannella, Annalisa Pace, Federica Maria Parisi, Giuseppe Magliulo and Antonino Maniaci
Pediatr. Rep. 2024, 16(1), 201-213; https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric16010018 - 18 Mar 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Lemierre syndrome is a rare, potentially fatal complication of oropharyngeal infections characterized by septic thrombophlebitis of the internal jugular vein. It primarily affects healthy adolescents and young adults. Its incidence declined after the antibiotic era, but it may have resurged in recent
[...] Read more.
Background: Lemierre syndrome is a rare, potentially fatal complication of oropharyngeal infections characterized by septic thrombophlebitis of the internal jugular vein. It primarily affects healthy adolescents and young adults. Its incidence declined after the antibiotic era, but it may have resurged in recent decades, likely due to judicious antibiotic use and increasing bacterial resistance. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are imperative to prevent significant morbidity and mortality. Methods: Lemierre syndrome has been called “the forgotten disease,” with a reported incidence of around 3.6 cases per million. The mean age at presentation is around 20 years old, though it can occur at any age. Lemierre Syndrome follows an oropharyngeal infection, most commonly pharyngitis, leading to septic thrombophlebitis of the internal jugular vein. F. necrophorum is the classic pathogen, though other organisms are being increasingly isolated. Metastatic infections, especially pulmonary, are common complications. Contrast-enhanced CT of the neck confirming internal jugular vein thrombosis is the gold standard for diagnosis. Long-course broad-spectrum IV antibiotics covering anaerobes are the mainstays of the disease’s treatment. Anticoagulation may also be considered. Mortality rates are high without treatment, but most patients recover fully with appropriate therapy. Conclusions: Lemierre syndrome should be suspected in patients with prolonged pharyngitis followed by unilateral neck swelling and fevers. Early diagnosis and prompt antibiotic therapy are key, given the potential for disastrous outcomes if untreated. An increased awareness of Lemierre syndrome facilitates its timely management.
Full article
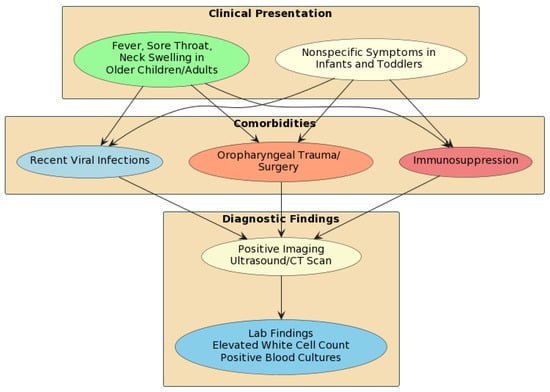
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Suprapubic and Transurethral Bladder Access for Voiding Cystourethrography in Pediatric Male Patients
by
Wiebke Schlötelburg, Clemens Benoit, Mandy Kasper, Bernhard Petritsch, Andreas Max Weng, Thorsten Alexander Bley and Simon Veldhoen
Pediatr. Rep. 2024, 16(1), 190-200; https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric16010017 - 13 Mar 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Purpose: To compare suprapubic access (SPA) and transurethral catheterization (TUC) in voiding cystourethrogram (VCUG). Methods: Retrospective single-center evaluation of 311 VCUG performed in male patients under 12 years of age. Two study groups were built based on the bladder access method. TUC was
[...] Read more.
Purpose: To compare suprapubic access (SPA) and transurethral catheterization (TUC) in voiding cystourethrogram (VCUG). Methods: Retrospective single-center evaluation of 311 VCUG performed in male patients under 12 years of age. Two study groups were built based on the bladder access method. TUC was performed in 213 patients, whereas 98 received SPA. The groups were compared regarding the procedural switch rate, the complication rate, radiation parameters, the amount of contrast media applied and the examination quality. Complications were graded in minor (contrast leakage, premature termination of the examination) and major (fever, urinary tract infection, bladder perforation). Fluoroscopy time and radiation parameters were compared. Examination quality was assessed based on the satisfactory acquisition of fluoroscopic images using a four-point Likert scale. Results: In 9% of the SPA examinations a method switch to TUC was necessary. The minor complication rate was 1.9% for TUC and 35.7% for SPA (p < 0.001). The major complication rate was 0.9% for TUC and 2% for SPA (p > 0.05). Mean fluoroscopy time and radiation dose were significantly lower in TUC (TUC, 26 ± 19 s, 0.6 ± 1.2 µGy·m2; SPA, 38 ± 33 s, 1.7 ± 2.9 µGy·m2; p = 0.01/0.001). There was no significant difference regarding the amount of contrast media applied (TUC, 62 ± 40 mL; SPA, 66 ± 41 mL; p > 0.05) and the examination quality with full diagnostic quality achieved in 88% of TUC and 89% of SPA examinations (p > 0.05). Conclusions: As TUC provides significantly lower radiation exposure and less periprocedural complications, it should be the primary bladder access route for VCUG in pediatric male patients.
Full article
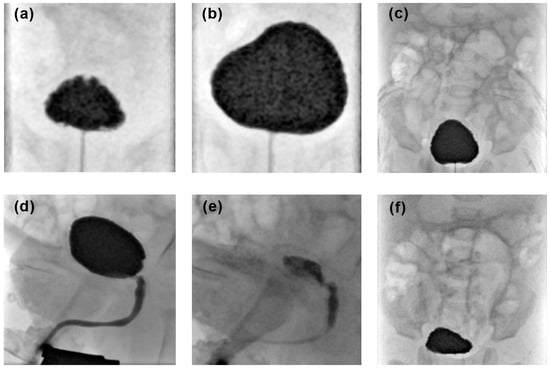
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A Comparison of Parent Reports, the Mental Synthesis Evaluation Checklist (MSEC) and the Autism Treatment Evaluation Checklist (ATEC), with the Childhood Autism Rating Scale (CARS)
by
Rebecca Netson, Andriane Schmiedel Fucks, Andressa Schmiedel Sanches Santos, Lucas Ernesto Pavoski Poloni, Nilson Noboru Nacano, Elielton Fucks, Katarina Radi, William E. Strong, Alice Aparecida Carnaval, María Russo, Rohan Venkatesh and Andrey Vyshedskiy
Pediatr. Rep. 2024, 16(1), 174-189; https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric16010016 - 11 Mar 2024
Abstract
This study compares two parent reports, the Mental Synthesis Evaluation Checklist (MSEC) and the Autism Treatment Evaluation Checklist (ATEC), with the Childhood Autism Rating Scale (CARS). The ATEC consists of four subscales, as follows: (1) expressive language, (2) sociability, (3) sensory awareness, and
[...] Read more.
This study compares two parent reports, the Mental Synthesis Evaluation Checklist (MSEC) and the Autism Treatment Evaluation Checklist (ATEC), with the Childhood Autism Rating Scale (CARS). The ATEC consists of four subscales, as follows: (1) expressive language, (2) sociability, (3) sensory awareness, and (4) health. The MSEC is complementary to the ATEC in measuring complex language comprehension. The parents of 143 autistic children, from 2 to 22 years of age (mean 6.7 ± 5.1 years), completed the MSEC and the ATEC questionnaires and a clinician assessed their CARS score. The CARS score correlated strongly with all parent reports, the complex language comprehension MSEC (r = 0.60, p < 0.0001), expressive language (r = 0.66, p < 0.0001), sociability (r = 0.58, p < 0.0001), sensory awareness (r = 0.71, p < 0.0001), and health (r = 0.53, p < 0.0001), as well as the total ATEC score (r = 0.75, p < 0.0001). The strongest correlation was between the CARS score and the composite of all five parent-reported scores (total ATEC + MSEC, r = 0.77, p < 0.0001). These results suggest a high fidelity of the MSEC and ATEC parent reports and especially of their composite score, total ATEC + MSEC.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Pediatric Psychology)
►▼
Show Figures
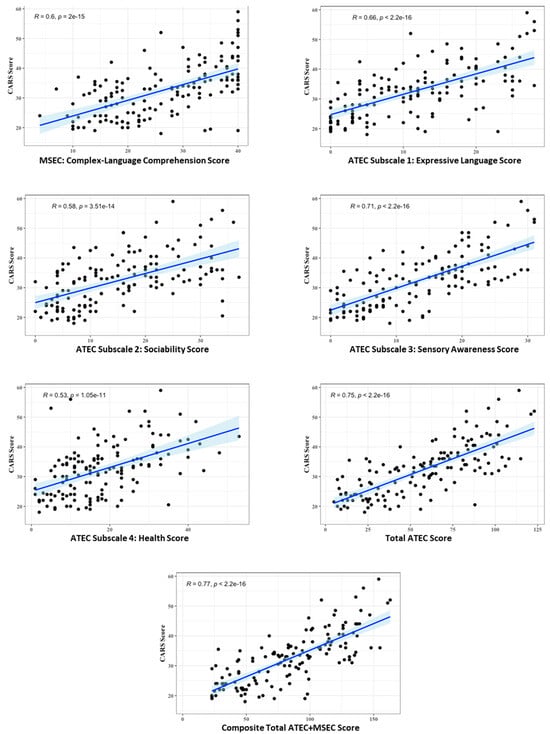
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Awareness of Child Abuse and Neglect: A Prospective Interventional Study among Schoolteachers from Andhra Pradesh
by
Anuja Singaraju, Venkata Ratna Kumar Rudravaram, Sivakumar Nuvvula and Sreekanth Kumar Mallineni
Pediatr. Rep. 2024, 16(1), 163-173; https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric16010015 - 27 Feb 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Aim: To assess the awareness of schoolteachers from Andhra Pradesh towards child abuse and neglect (CAN) through pre- and post-educational intervention (audiovisual aid) questionnaires. Materials and methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted with 300 schoolteachers using a 12-item questionnaire that was created using
[...] Read more.
Aim: To assess the awareness of schoolteachers from Andhra Pradesh towards child abuse and neglect (CAN) through pre- and post-educational intervention (audiovisual aid) questionnaires. Materials and methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted with 300 schoolteachers using a 12-item questionnaire that was created using the standard focus group discussion method. Baseline awareness of CAN was assessed using the questionnaire. Subsequently, all the schoolteachers were educated regarding the various types of CAN and the process of reporting CAN using an audiovisual aid. The same questionnaire was re-administered to all the teachers immediately after the intervention and after three months. The data were statistically analyzed using Fisher’s exact test to compare the frequency and distribution of responses among the study participants at various intervals. Results: A statistically significant difference (p value < 0.05) was observed in the awareness of the schoolteachers regarding CAN compared to the baseline and immediately after the intervention. However, there was no statistically significant difference (p value > 0.05) between immediately after the intervention and three months. Conclusion: There is a need to have awareness among schoolteachers concerning CAN. However, after education through audiovisual aids, teachers’ awareness of CAN has been improved.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Clinical, Immunological and Inflammatory Characteristics among Mexican Children with Different Subtypes of Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis: Exploring the Correlation between Anti-Cyclic Citrullinated Peptide (anti-CCP) and Rheumatoid Factor (RF)
by
Hayde Guadalupe Hernández-Huirache, Dagoberto Armenta-Medina and Edel Rafael Rodea-Montero
Pediatr. Rep. 2024, 16(1), 151-162; https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric16010014 - 07 Feb 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Introduction: Juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA) is the most common chronic rheumatic disease in childhood, affecting one to four of every 1000 children worldwide. It is characterized by joint inflammation lasting more than six weeks in children under 16 years. The aim of this
[...] Read more.
Introduction: Juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA) is the most common chronic rheumatic disease in childhood, affecting one to four of every 1000 children worldwide. It is characterized by joint inflammation lasting more than six weeks in children under 16 years. The aim of this study was to estimate the frequency of JIA subtypes in the Mexican patient population; compare clinical, immunological and inflammation markers by JIA subtype; and examine the correlation between these variables. Methods: We conducted a cross-sectional study of 50 patients with JIA (2–15 years). We estimated the frequency of each JIA subtype, assessed and compared the immunological characteristics (RF, ANA and anti-CCP) by JIA subtype at the time of diagnosis using Kruskal–Wallis or chi-square tests, and calculated Spearman correlation coefficients between the assessments. Results: Our analysis included 50 patients, 29 (58%) girls and 21 (42%) boys, aged at the time of diagnosis 10.56 ± 3.99 years. The frequencies of JIA subtypes were RF-seropositive polyarthritis (34%), RF-seronegative polyarthritis (28%), systemic arthritis (16%), oligoarthritis (14%) and arthritis-related enthesitis (8%). We found a significant association between sex and JIA subtype (p = 0.014). There was a significant difference in anti-CCP levels by JIA subtype (p < 0.001). We also detected positive correlations between RF and anti-CCP (r = 0.63, p < 0.001) and between age and anti-CCP (r = 0.29, p = 0.041). Conclusions: Our study suggests that the frequency of the polyarticular subtypes of JIA is higher in Mexican children compared to other populations. Our findings highlight the importance of considering the presence of anti-CCP and RF as important criteria when deciding on treatment for JIA patients as elevated levels of these antibodies may indicate early forms of adult rheumatoid arthritis.
Full article
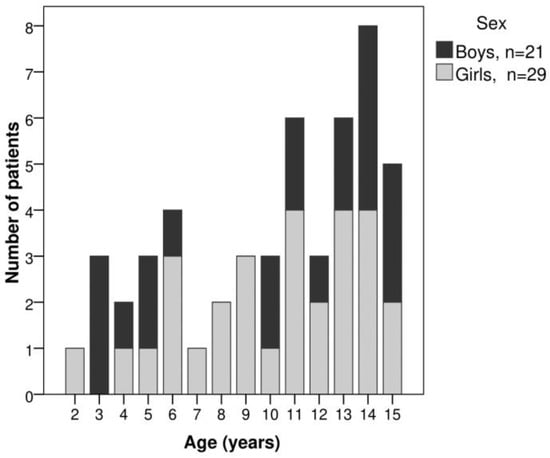
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
The Ongoing Impact of COVID-19 on Pediatric Obesity
by
Domenico Iacopetta, Alessia Catalano, Jessica Ceramella, Michele Pellegrino, Maria Marra, Elisabetta Scali, Maria Stefania Sinicropi and Stefano Aquaro
Pediatr. Rep. 2024, 16(1), 135-150; https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric16010013 - 02 Feb 2024
Abstract
In the developed world, pediatric obesity (PO) has been a major health concern since the last century, and this condition may lead to detrimental life-long physical and mental comorbidities. Currently, its prevalence has increased in low- and middle-income countries and in many high-income
[...] Read more.
In the developed world, pediatric obesity (PO) has been a major health concern since the last century, and this condition may lead to detrimental life-long physical and mental comorbidities. Currently, its prevalence has increased in low- and middle-income countries and in many high-income countries. Thus, the provision of effective and tailored care for children and their families has become vital. The social consequences of the COVID-19 pandemic are known everywhere, and among these, it has been argued that the COVID-19 pandemic has had a major impact on PO. Overall, the growth of PO over the last decade has been enhanced by the pandemic. During the COVID-19 pandemic, children, adolescents and young adults gained weight as the pediatric population dealt with sedentary lifestyles and changes in food habits. In this review, we want to highlight the impact that the COVID-19 pandemic had on PO.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Pediatric Psychology)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
The Concept of Child-Centred Care in Healthcare: A Scoping Review
by
Bernie Carter, Sarah Young, Karen Ford and Steven Campbell
Pediatr. Rep. 2024, 16(1), 114-134; https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric16010012 - 01 Feb 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Although child-centred care is increasingly referred to within the nursing literature, a clear definition of child-centred care and clarity around the concept is yet to be achieved. The objectives of this review were to examine the following: (1) What constitutes the concept of
[...] Read more.
Although child-centred care is increasingly referred to within the nursing literature, a clear definition of child-centred care and clarity around the concept is yet to be achieved. The objectives of this review were to examine the following: (1) What constitutes the concept of child-centred care in healthcare? (2) How has the concept of child-centred care developed? (3) What is the applicability of child-centred care and what are its limitations? (4) How does the concept of child-centred care benefit and inform children’s healthcare? In total, 2984 papers were imported for screening, and, following the removal of duplicates and screening, 21 papers were included in the scoping review. The findings suggest that child-centred care is an emerging, ambiguous poorly defined concept; no clear consensus exists about what constitutes child-centred care. Although it seems antithetical to argue against child-centred care, little robust evidence was identified that demonstrates the impact and benefit of child-centred care. If child-centred care is to be a sustainable, convincing model to guide practice and compete with other models of care, it needs to establish robust evidence of its effectiveness, the impact on children and their families, as well as the wider impacts on the healthcare system.
Full article
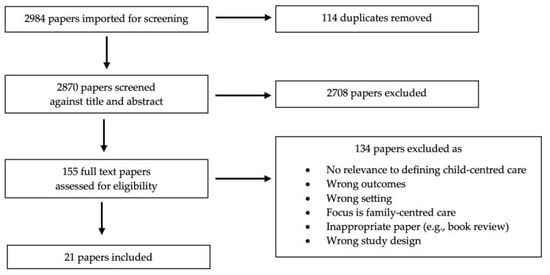
Figure 1
Open AccessEditorial
Pediatric Autoimmune Hepatitis
by
Silvia Nastasio, Marco Sciveres, Paola Francalanci and Giuseppe Maggiore
Pediatr. Rep. 2024, 16(1), 110-113; https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric16010011 - 01 Feb 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Pediatric autoimmune hepatitis (PAIH) is a rare necro-inflammatory disease of the liver of unknown etiology thought to derive from the dysregulation of the immune response upon exposure to environmental triggers in genetically predisposed individuals [...]
Full article
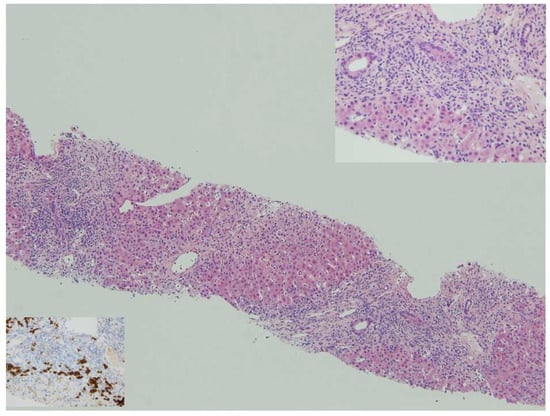
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Is the Over-the-Head Technique an Alternative for Infant CPR Performed by a Single Rescuer? A Randomized Simulation Study with Lifeguards
by
Silvia Aranda-García, Silvia San Román-Mata, Martín Otero-Agra, Antonio Rodríguez-Núñez, María Fernández-Méndez, Rubén Navarro-Patón and Roberto Barcala-Furelos
Pediatr. Rep. 2024, 16(1), 100-109; https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric16010010 - 29 Jan 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
(1) Objective: The objective was to evaluate the quality of cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR, chest compressions and ventilations) when performed by a lone first responder on an infant victim via the over-the-head technique (OTH) with bag-mask ventilation in comparison with the standard lateral technique
[...] Read more.
(1) Objective: The objective was to evaluate the quality of cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR, chest compressions and ventilations) when performed by a lone first responder on an infant victim via the over-the-head technique (OTH) with bag-mask ventilation in comparison with the standard lateral technique (LAT) position. (2) Methods: A randomized simulation crossover study in a baby manikin was conducted. A total of 28 first responders performed each of the techniques in two separate CPR tests (15:2 chest compressions:ventilations ratio), each lasting 5 min with a 15 min resting period. Quality CPR parameters were assessed using an app connected to the manikin. Those variables were related to chest compressions (CC: depth, rate, and correct CC point) and ventilation (number of effective ventilations). Additional variables included perceptions of the ease of execution of CPR. (3) Results: The median global CPR quality (integrated CC + V) was 82% with OTH and 79% with LAT (p = 0.94), whilst the CC quality was 88% with OTH and 80% with LAT (p = 0.67), and ventilation quality was 85% with OTH and 85% with LAT (p = 0.98). Correct chest release was significantly better with OTH (OTH: 92% vs. LAT: 62%, p < 0.001). There were no statistically significant differences in the remaining variables. Ease of execution perceptions favored the use of LAT over OTH. (4) Conclusions: Chest compressions and ventilations can be performed with similar quality in an infant manikin by lifeguards both with the standard recommended position (LAT) and the alternative OTH. This option could give some advantages in terms of optimal chest release between compressions. Our results should encourage the assessment of OTH in some selected cases and situations as when a lone rescuer is present and/or there are physical conditions that could impede the lateral rescue position.
Full article
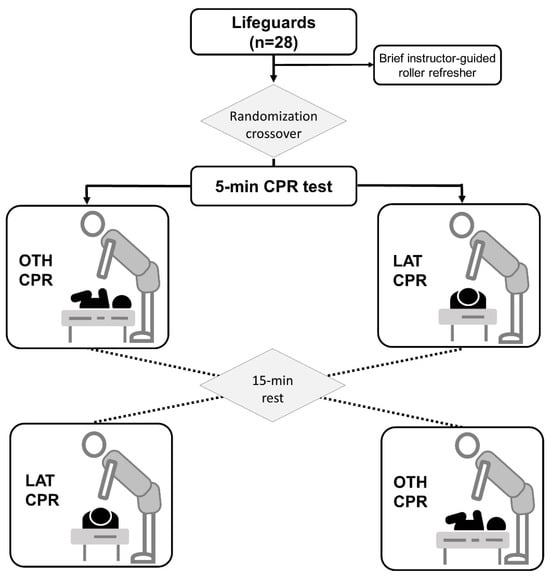
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Motion and Form Perception in Childhood-Onset Schizophrenia
by
Szabolcs Kéri and Oguz Kelemen
Pediatr. Rep. 2024, 16(1), 88-99; https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric16010009 - 15 Jan 2024
Abstract
(1) Background: Childhood-onset schizophrenia (COS) is a rare type of psychotic disorder characterized by delusions, hallucinations, grossly disorganized behavior, and poor psychosocial functioning. The etiology of COS is unknown, but neurodevelopmental factors are likely to play a critical role. A potential neurodevelopmental anomaly
[...] Read more.
(1) Background: Childhood-onset schizophrenia (COS) is a rare type of psychotic disorder characterized by delusions, hallucinations, grossly disorganized behavior, and poor psychosocial functioning. The etiology of COS is unknown, but neurodevelopmental factors are likely to play a critical role. A potential neurodevelopmental anomaly marker is the dorsal visual system dysfunction, which is implicated in motion perception, spatial functions, and attention. (2) Methods: To elucidate the role of the dorsal visual system in COS, we investigated 21 patients with COS and 21 control participants matched for age, sex, education, IQ, and parental socioeconomic status. Participants completed a motion and form coherence task, during which one assesses an individual’s ability to detect the direction of motion within a field of moving elements or dots and to recognize a meaningful form or object from a set of fragmented or disconnected visual elements, respectively. (3) Results: The patients with COS were impaired in both visual tasks compared to the control participants, but the evidence for the deficit was more substantial for motion perception than for form perception (form: BF10 = 27.22; motion: BF10 = 6.97 × 106). (4) Conclusions: These results highlight the importance of dorsal visual stream vulnerability in COS, a potential marker of neurodevelopmental anomalies.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Pediatric Psychology)
►▼
Show Figures
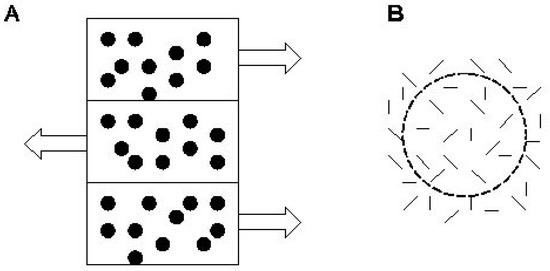
Figure 1
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Pediatric Reports
Global Neonatal Screening: Expanding Horizons in Diagnostic Technologies
Guest Editor: Victoria KainDeadline: 10 September 2024
Special Issue in
Pediatric Reports
Modern Solutions for Diagnosis and Treatment Planning in Pediatric Dentistry and Orthodontics
Guest Editors: Antonino Lo Giudice, Rosalia Leonardi, Vincenzo RonsivalleDeadline: 31 January 2025
Special Issue in
Pediatric Reports
Mental Health and Psychiatric Disorders of Children and Adolescents
Guest Editor: Artemis K. TsitsikaDeadline: 30 April 2025
Special Issue in
Pediatric Reports
Pediatric Cancers Risk Factors and Prevention
Guest Editor: Paraskevi A FaraziDeadline: 16 June 2025
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Pediatric Reports
COVID-19: What Happens in Pediatric Research in the Era of Pandemic
Collection Editor: Maurizio Aricò





