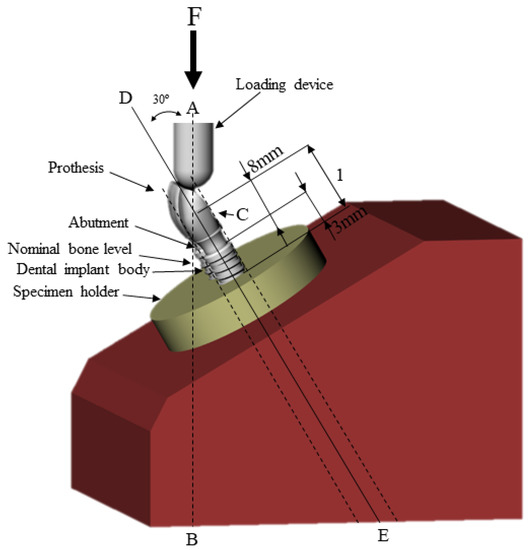
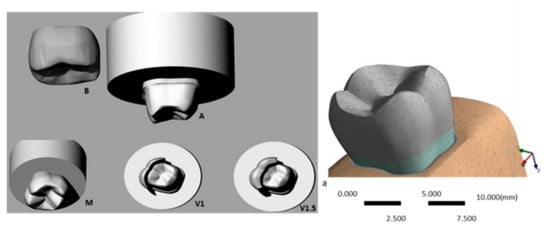
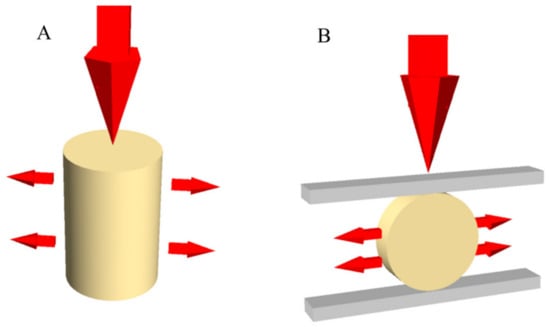
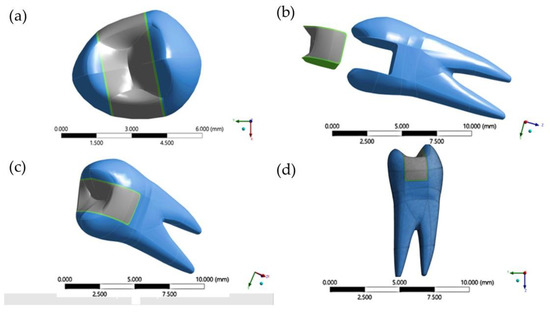
Synthesis, Testing and Mechanical Behavior of Dental Biomaterials at Different Clinical Parameters
A topical collection in Oral (ISSN 2673-6373).
Viewed by 20755Editors
Interests: dental materials; adhesive dentistry; biomechanics; finite element analysis; dental implants; prosthetic dentistry; dental ceramics; fatigue; dental restoration failure
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: endodontics; restorative dentistry; dental materials; oral surgery
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
Although the oral environment can present an unfriendly effect on dental biomaterials, the synergy collaboration of many studies from different fields, such as material sciences, biology, chemistry and mechanics, has allowed us to provide durable dental treatments and positive life quality improvements for our patients using dental biomaterials applied in many ways.
Currently, dental biomaterials can be developed with unique microstructure, be susceptible to specific surface treatments, with an isotropic behavior and sometimes viscoelastic performance present. The overall performance of the dental treatment can be affected by the use of smart materials in terms of durability and mechanical resistance, as well as by the processing methods, clinical parameters, and laboratorial techniques applied during oral rehabilitation.
Dental biomaterials, in general, are extremely important to dentistry today and allow us to recover missing biological tissues with a proper biomimetic concept and adequate esthetics. Nevertheless, the dental biomaterial properties related to their durability, mechanical, and long-term behavior should be known before applicability in the human body can be achieved.
This topical collection focuses on the development of synthesis, testing, and evaluation of the mechanical behavior of dental biomaterials at different clinical parameters.
The topics of interest include but are not limited to:
Indirect materials for prosthetic dentistry;
Resin composites and cements for restorative dentistry;
Post-endodontic treatment performance;
Rehabilitation with endosseous implants;
Post-and-core dental treatments;
Fractography of contemporary dental materials;
Oral trauma prevention and treatment with biomaterials;
Clinical and laboratory research of basic and applied performance of dental materials.
Dr. Joao Paulo Tribst
Prof. Dr. Eugenio Pedullà
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Oral is an international peer-reviewed open access quarterly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 1000 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- dental biomaterials
- dental implants
- biomechanics
2021
Planned Papers
The below list represents only planned manuscripts. Some of these manuscripts have not been received by the Editorial Office yet. Papers submitted to MDPI journals are subject to peer-review.