Journal Description
Oral
Oral
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on oral health published quarterly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 27.7 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 5.3 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2023).
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
Latest Articles
Experimental Evaluation of a Novel Device to Quantify Canal Cleanliness: An In Vitro Study
Oral 2024, 4(2), 163-172; https://doi.org/10.3390/oral4020013 - 07 Apr 2024
Abstract
►
Show Figures
Endodontic treatments are performed to avoid extractions and maintain the natural dentition. Root canal treatments are undertaken to eliminate or prevent an infection within the root canal system. Chemical and mechanical root canal debridement are the main methods used in endodontics to remove
[...] Read more.
Endodontic treatments are performed to avoid extractions and maintain the natural dentition. Root canal treatments are undertaken to eliminate or prevent an infection within the root canal system. Chemical and mechanical root canal debridement are the main methods used in endodontics to remove necrotic tissue, microorganisms, and microbial byproducts from the canal. However, to date there is no objective method to clinically determine the proper root canal disinfection level and thus proceed with the obturation. Clinicians just rely on their experience and habits or can trust in empirical methods such as the insertion of paper cones inside the canal and then check their appearance after the removal. Even in the in vitro and ex vivo scientific studies there is no objective method to analyze and compare the efficacy of different endodontic chemo-mechanical techniques and materials. The most frequently used method is to visually analyze some areas with a scanning electron microscope (SEM), even if the resulting images are hardly quantifiable and could greatly vary according to the analyzed area. A new device to clinically test the cleanliness of a root canal and display the result in an objective score was recently developed. The device analyzes the luminescence generated by an enzyme cycling method that process the adenosine triphosphate (ATP), adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and adenosine monophosphate (AMP) present in organic residues. The aim of the present in vitro study was to test the efficacy and reliability of this novel device (Endocator) in a controlled in vitro environment, before using it in clinical practice. The device sensitivity was tested on 5 single canal resin blocks. Three consecutive sampling were executed by one operator for each block to test the device repeatability. Results were recorded according to Endoscore (ES) and relative light unit (RLU) scales. Descriptive analysis and comparison between the 5 resin blocks and the 3 consecutive sampling were performed. Only the comparison between the first and third measurements both for ES (p = 0.00115999) and RLU (p = 0.00532749) resulted significant. Endocator was able to determine small variations of canal contamination in a controlled laboratory environment, showing high sensitivity and repeatability.
Full article
Open AccessSystematic Review
Use of Biosensors within the Oral Environment for Systemic Health Monitoring—A Systematic Review
by
Natalie Archer, Sa’ada Ladan, Henry T. Lancashire and Haralampos Petridis
Oral 2024, 4(2), 148-162; https://doi.org/10.3390/oral4020012 - 30 Mar 2024
Abstract
Scientific advances in biosensor technology are leading to the potential of wearable biosensors for salivary biomarker detection. This review aims to identify the current status of intraoral biosensor technology that can be used to monitor systemic diseases. A total of 11 studies were
[...] Read more.
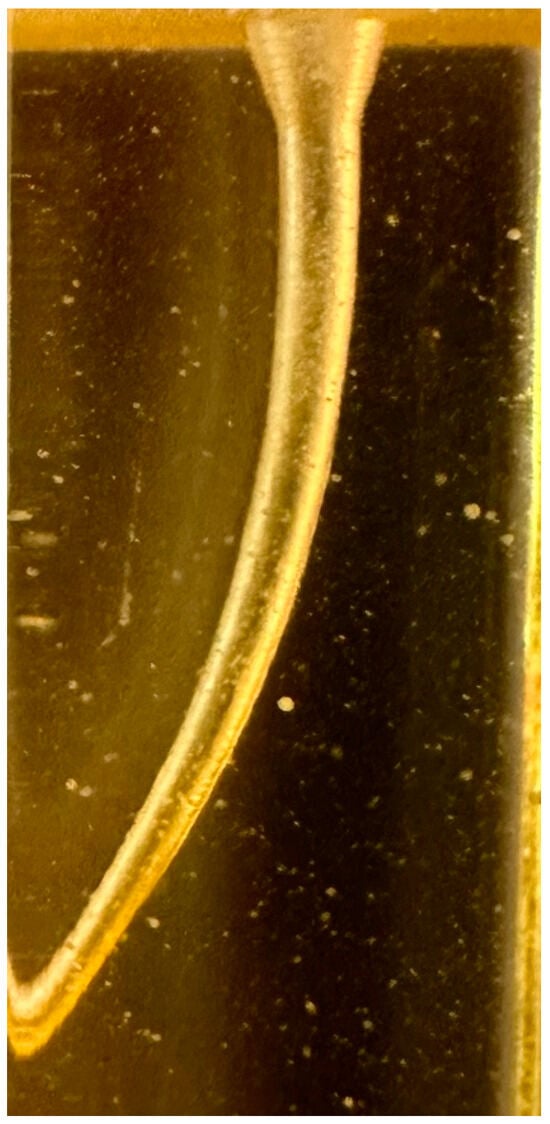
Scientific advances in biosensor technology are leading to the potential of wearable biosensors for salivary biomarker detection. This review aims to identify the current status of intraoral biosensor technology that can be used to monitor systemic diseases. A total of 11 studies were identified for inclusion, which included nine different devices, including modified mouthguards, retainers, toothbrushes, and dental floss. Out of the 11 studies, 8 studied continuous biomarker monitoring, and the remaining 3 were point-of-care applications. A total of seven biomarkers were studied, six of which investigated the intraoral detection of salivary glucose levels using glucose oxidase enzyme. All the sensors demonstrated excellent sensitivity (minimum R = 0.9928) and selectivity. The study designs were proof of concept, with five studies including in vivo components. We concluded that while there are established links between salivary biomarkers and systemic health, there is a lack of mature intraoral biosensor research. Refinement of biosensor design and data analysis is required to improve patient acceptability by promoting more discrete, real-time, low-cost, and wireless devices. Further research that utilises the biosensor technology in large controlled clinical trials will be required to confirm clinical applicability before intraoral biosensor technology can be integrated into routine health monitoring.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Current Issues in Oral Health)
►▼
Show Figures
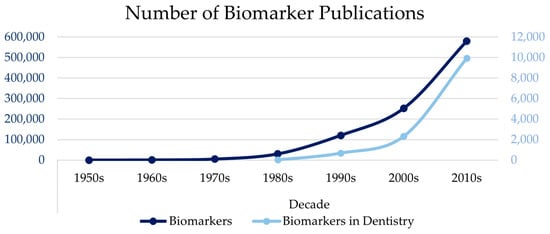
Figure 1
Open AccessCase Report
Hybrid Orthodontics for Aesthetic Deep Bite Correction—Case Series and General Clinical Considerations
by
Akila Aiyar, Giuseppe Scuzzo, Giacomo Scuzzo and Carlalberta Verna
Oral 2024, 4(2), 126-147; https://doi.org/10.3390/oral4020011 - 30 Mar 2024
Abstract
Background: A range of psychosocial and aesthetic factors motivate patients to undergo orthodontic treatment. The appliance choice depends not only on the type of malocclusion, but also on the aesthetic and functional demands of the patients themselves. Nowadays, digital planning enables the manufacture
[...] Read more.
Background: A range of psychosocial and aesthetic factors motivate patients to undergo orthodontic treatment. The appliance choice depends not only on the type of malocclusion, but also on the aesthetic and functional demands of the patients themselves. Nowadays, digital planning enables the manufacture of individualised and customised orthodontic appliances. However, the predictability of movements with aligner treatment has long been under discussion. This article illustrates, through a series of case reports, how a hybrid approach combining individualised aesthetic orthodontic appliances can improve the predictability of tooth movements, thereby providing additional tools for clinicians charged with choosing the best indicated and biomechanically advantageous technique. To this end, three patients with different malocclusions were treated via a hybrid approach involving clear aligners in the upper arch followed by lingual fixed appliances in the upper and lower arches. All patients were treated using ALIAS lingual PSL 0.018 × 0.018-inch slot brackets and in-house 3D-printed aligners. Findings: The hybrid approach combining aligners and fixed lingual appliances led to the successful resolution of all three complex cases in the series without prolonging treatment time. The superimpositions demonstrate the predictability of even traditionally difficult movements. In particular, the Alias PSL lingual system, used from the beginning, enabled good control of both the torque and inclination of the lower incisors. Conclusions: Combining clear aligners and fixed lingual appliances provides a highly efficient means of treating malocclusions aesthetically. In our cases, the aligners offset the lack of bite-plate effect from the lingual brackets and appliances, providing advantageous biomechanics for rotation correction and control of tip, torque and root movements. Understanding how to exploit the strengths of each appliance enables the clinician to treat adult patients efficaciously, efficiently and aesthetically.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Digital Orthodontics: A New Era for Improved Diagnosis and Treatment Options)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
The Most Common Types of Bias in a Human Bitemark Analysis
by
Tayyaba Masood, Scheila Mânica and Hemlata Pandey
Oral 2024, 4(1), 113-125; https://doi.org/10.3390/oral4010010 - 07 Mar 2024
Abstract
Given that some suspected perpetrators were wrongly convicted, a defective bitemark analysis is comparable to dentists’ most crucial clinical decisions regarding assessment. Bias affects human bitemark analysis beyond the limitation of the evidence itself. The aim of this study was to explore the
[...] Read more.
Given that some suspected perpetrators were wrongly convicted, a defective bitemark analysis is comparable to dentists’ most crucial clinical decisions regarding assessment. Bias affects human bitemark analysis beyond the limitation of the evidence itself. The aim of this study was to explore the potential for different types of bias in bitemark analysis and the methods involved in that analysis by conducting a scoping review. Results showed that the 14 articles that explore the topic of bias in bitemark analysis were published from 2006-2022. Publications were from the USA mainly (n = 7), followed by the UK (n = 3), Australia (n = 2), New Zealand, (n = 1) and the Netherlands (n = 1). Of these publications, 36% addressed contextual bias, while 57% acknowledged cognitive bias. According to the findings, preventive measures consist of limiting the availability of unrelated data during research, employing several comparison samples for a more impartial assessment, and repeating the analysis while being blind to past findings. Nevertheless, the physical limitations of the evidence such as distortions are still strongly present.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances of Forensic Dentistry)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Evaluation of Enamel Volume Loss after Exposure to Energy Drinks
by
Karen A. Schulze, Noëlle M. Santucci, Bina Surti, Stefan Habelitz, Mouchumi Bhattacharyya and Warden Noble
Oral 2024, 4(1), 101-112; https://doi.org/10.3390/oral4010009 - 23 Feb 2024
Abstract
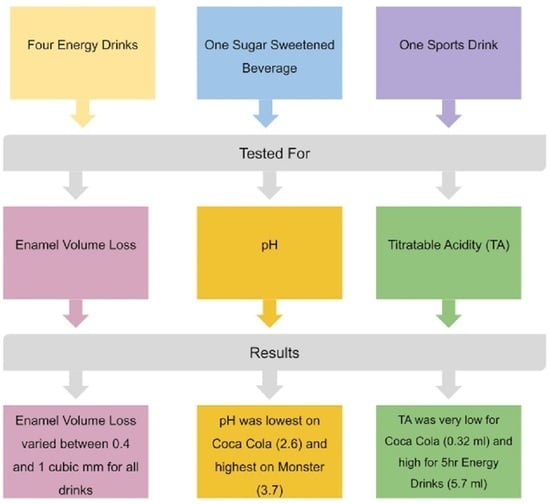
Objectives: This study was conducted to determine the erosive potential of various commercial energy drinks (EDs), sports drinks (SDs), and sugar sweetened beverages (SSBs) and to correlate quantitative changes in tooth enamel volume loss based on the pH and titratable acidity of the
[...] Read more.
Objectives: This study was conducted to determine the erosive potential of various commercial energy drinks (EDs), sports drinks (SDs), and sugar sweetened beverages (SSBs) and to correlate quantitative changes in tooth enamel volume loss based on the pH and titratable acidity of the drinks. Methods: A flat plane on the facial surface of 36 human incisor teeth was created and embedded in sample holders using resin. After pre-scanning with a profilometer (Proscan 2000, Scantron, Ind Products Ltd., Taunton, UK), the six samples per group were immersed for 4 h into either Monster Energy™ (ED), Rockstar™ (ED), Red Bull™ (ED), or 5-h Energy™ (ED) and, for comparison with a sports drink, Gatorade™ (SD) and a sugar sweetened beverage, Coca-Cola® (SSB). After immersion and post-scanning, the quantitative volume loss of the tooth enamel of the 36 samples was calculated (Proscan 3D software V2.1.1.15B), and the pH and titratable acidity (TA) of each drink was determined. Results: All drinks tested caused enamel volume loss. The actual amount varied among the different drinks, from 0.39 mm3 for Red Bull™, up to 1.01 mm3 for Gatorade™. The pH measurements differed for each drink, ranging from 2.6 to 3.7. There was a small reverse correlation of 0.326 between the pH of all drinks and volume loss. Among the energy drinks, titratable acidity was similar and there was only a weak correlation between TA and volume loss (0.319 at p = 0.53). Conclusions: Energy drinks, sugar sweetened beverages, and sport drinks all have the potential to cause enamel tooth surface loss resulting in demineralization. Therefore, the pH of a drink cannot be the sole determinant for choosing a less harmful commercial beverage.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Current Issues in Oral Health)
►▼
Show Figures
Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Teaching of Forensic Dentistry in Khartoum, Sudan
by
Sarah Hag Ali, Ademir Franco, Emilio Nuzzolese and Scheila Mânica
Oral 2024, 4(1), 90-100; https://doi.org/10.3390/oral4010008 - 04 Feb 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Dental professionals assist with legal and criminal matters through the practice of forensic dentistry which has evolved over the past century and is now a crucial component of undergraduate dental education in many nations. The need for formal training in the subject
[...] Read more.
Background: Dental professionals assist with legal and criminal matters through the practice of forensic dentistry which has evolved over the past century and is now a crucial component of undergraduate dental education in many nations. The need for formal training in the subject and its inclusion in dental curricula were acknowledged and addressed in the 1960s and 1970s. Aims: This study aimed to investigate the teaching of forensic dentistry in dental universities of Khartoum, Sudan, and to propose certain topics and teaching criteria to be standardized in forensic dentistry teaching in Sudan. Materials and methods: An observational, descriptive study was conducted, involving all undergraduate dental institutions in Khartoum, Sudan. Institutional websites were searched using the Google search engine to obtain the dental program curricula in English. The curricula were then analyzed to identify the presence of forensic odontology/dentistry teaching. Results: Of the 19 universities included in the study, five (26.3%) teach forensic dentistry in their undergraduate curricula, whereas 12 (63.1%) do not. Two universities (10.6%) indicated the presence of forensic dentistry teaching in their curricula but did not provide actual instruction. The teaching of forensic dentistry mainly occurred during the second, third, and fourth years of the dental program. Three universities considered it an independent subject, while two universities incorporated it into oral and maxillofacial pathology. Four universities provided lectures only, while one university combined lectures and practical sessions. Qualified forensic dentists taught the subject in four universities, while one university had general dentists as instructors. The main topics delivered are: (1) introduction to forensics, (2) human identification, (3) dental age estimation, (4) interpretation of bitemarks, (5) DNA in forensics, and (6) child abuse. Conclusion: Forensic dentistry training is currently undervalued in Sudan due to various limitations. It is recommended that all dental schools in Sudan offer opportunities for students to learn and become acquainted with forensic dentistry as part of their dental programs. The Sudanese Dental Council should establish formal coordination with academic institutions and experienced forensic dentists to ensure the quality and relevance of the proposed modular course within the educational system. Finally, additional topics including dental record-keeping and dental malpractice are suggested for inclusion in the current modules.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Treatment Strategies for Incisors of Children Affected by Molar Incisor Hypomineralization: A Narrative Review
by
Berkant Sezer and Burak Çarıkçıoğlu
Oral 2024, 4(1), 74-89; https://doi.org/10.3390/oral4010007 - 01 Feb 2024
Abstract
Today, molar incisor hypomineralization (MIH), which affects approximately one in seven children, is defined as a hypomineralized developmental enamel defect that often impacts at least one permanent first molar and frequently affects permanent incisors as well. Symptoms and signs include demarcated opacities of
[...] Read more.
Today, molar incisor hypomineralization (MIH), which affects approximately one in seven children, is defined as a hypomineralized developmental enamel defect that often impacts at least one permanent first molar and frequently affects permanent incisors as well. Symptoms and signs include demarcated opacities of various colors, post-eruptive enamel deterioration, atypical caries and restorations, hypersensitivity, tooth loss due to MIH, and difficulty in achieving anesthesia. A detailed review of the scientific literature shows that there are many studies evaluating different treatment approaches for permanent first molars affected by MIH. On the other hand, there are very few scientific studies evaluating treatment approaches for affected incisors in patients with MIH. Most of these studies consist of case reports or series. White/creamy and/or yellow/brown demarcated opacities are commonly observed in affected incisors in patients with MIH. While these opacities increase the susceptibility of enamel to deterioration and dental caries, they also cause aesthetic problems and related psychosocial consequences. Treatment methods, such as resin infiltration, microabrasion, and/or dental bleaching, have been proposed for aesthetic and restorative purposes in affected incisors in patients with MIH. Additionally, various approaches to increase mineral content and relieve hypersensitivity have been recommended. The number of randomized controlled and prospective studies is quite low, but many case reports and case series have been encountered. The purpose of this review was to provide a comprehensive overview of the different treatment management modalities for permanent incisors affected by MIH. As a result, while resin infiltration, dental bleaching, microabrasion, and/or etch–bleach–seal techniques are preferred for aesthetic and restorative purposes in these teeth, it has been observed that agents containing casein phosphopeptide amorphous calcium phosphate, casein phosphopeptide amorphous calcium fluoride phosphate, fluoride, and calcium glycerophosphate increase the mineral content. Additionally, studies have reported that ozone and low-level laser therapy, in addition to these remineralizing agents, reduce hypersensitivity in these teeth. Although the findings of this review indicate that the level of evidence for current approaches is not high, clinicians may prefer one or more of the treatment approaches mentioned in this article based on experience and patient expectations.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Current Issues in Oral Health)
►▼
Show Figures
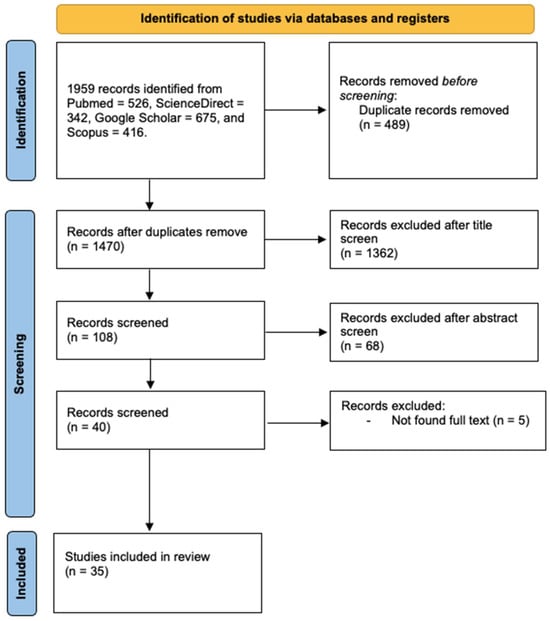
Figure 1
Open AccessFeature PaperReview
Periodontitis and Alzheimer’s Disease: Is There a Connection?
by
William Lundergan, Kavitha Parthasarathy and Navid Knight
Oral 2024, 4(1), 61-73; https://doi.org/10.3390/oral4010006 - 22 Jan 2024
Abstract
The oral health/systemic health connection has been an area of research interest that increased dramatically during the 1990s. Periodontal disease has been associated with a number of systemic conditions, including cardiovascular disease, diabetes, pre-term low-birth-weight infants, respiratory conditions, rheumatoid arthritis, cancer, and Alzheimer’s
[...] Read more.
The oral health/systemic health connection has been an area of research interest that increased dramatically during the 1990s. Periodontal disease has been associated with a number of systemic conditions, including cardiovascular disease, diabetes, pre-term low-birth-weight infants, respiratory conditions, rheumatoid arthritis, cancer, and Alzheimer’s disease. Inflammation is the obvious link that connects periodontal disease with these conditions, but is this association casual or causal? We will address the biologic plausibility, evidence from human studies, evidence from animal studies, and therapeutic interventions as we review the current understanding of the link between periodontitis and Alzheimer’s disease.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Current Issues in Oral Health)
►▼
Show Figures
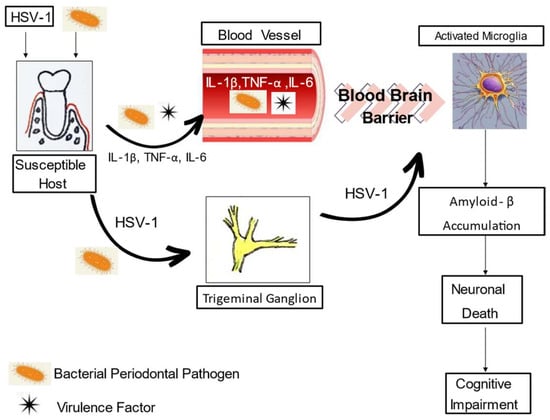
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Intentional Dental Modifications in the African Population
by
Candy Kgabi, Scheila Manica and Hemlata Pandey
Oral 2024, 4(1), 50-60; https://doi.org/10.3390/oral4010005 - 18 Jan 2024
Abstract
(1) This research paper aims to conduct a comprehensive review of the existing scientific literature on intentional dental modifications within the African population. By synthesizing and analysing studies, this paper aims to shed light on the prevalence, cultural significance, and forensic implications of
[...] Read more.
(1) This research paper aims to conduct a comprehensive review of the existing scientific literature on intentional dental modifications within the African population. By synthesizing and analysing studies, this paper aims to shed light on the prevalence, cultural significance, and forensic implications of intentional dental modifications. (2) A scoping review was conducted according to PRISMA for Scoping Reviews and a search performed in June 2023 on the three electronic databases Scopus, PubMed, and Web of Science. (3) The search resulted in 30 studies and showed that intentional dental modifications, also referred to as nontherapeutic dental modifications, are prevalent across the African population for reasons linked to traditional medicine, ethnic affiliation, and individualism, with the highest-reported modification being infant oral mutilation at 53%, followed by tooth filing at 10%, and others such as lip plates, diastema piercings, dental avulsion, dental tattooing, crowns, and oral piercings. (4) The quality and quantity of the available literature on intentional dental modifications in the African population is limited due to bias in reporting, as most studies are those of individuals with severe health complications. The data gathered from this study could further aid in the analysis and identification of nontherapeutic dental modifications, be used in profiling, and assist in the estimation of population affiliation.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances of Forensic Dentistry)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Effectiveness of Bioactive Toothpastes against Dentin Hypersensitivity Using Evaporative and Tactile Analyses: A Randomized Clinical Trial
by
Roberta Caroline Bruschi Alonso, Letícia de Oliveira, Jaqueline Alves Batista Silva, Williane Bernadete Bezerra dos Santos, Lúria Ribeiro de Souza Laranja Ferreira, Ricardo Danil Guiraldo, Fabiano Vieira Vilhena and Paulo Henrique Perlatti D’Alpino
Oral 2024, 4(1), 36-49; https://doi.org/10.3390/oral4010004 - 10 Jan 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The objective of this study was to investigate and compare the effectiveness of toothpastes containing bioactives to relieve dentin hypersensitivity with that of a commercial desensitizing toothpaste containing REFIX technology, associated or not with a calcium booster. In this double-blind, randomized, parallel-group, multi-center
[...] Read more.
The objective of this study was to investigate and compare the effectiveness of toothpastes containing bioactives to relieve dentin hypersensitivity with that of a commercial desensitizing toothpaste containing REFIX technology, associated or not with a calcium booster. In this double-blind, randomized, parallel-group, multi-center clinical trial, thirty-two volunteers diagnosed with dentin hypersensitivity and qualified to participate were randomized into four groups: (1) Colgate Sensitive Pro-Relief; (2) Sensodyne Repair & Relief; (3) Regenerador Sensitive; and (4) Regenerador Sensitive, associated with a calcium booster. Evaporative and tactile tests were used to check for dentin hypersensitivity in the test subjects. The participants brushed their teeth with one of the toothpastes, and dentin hypersensitivity was immediately tested using a visual analogue scale (VAS), in which the pain was rated on a scale of 0 to 10. Dentin hypersensitivity was measured after one week and after one month of the subjects continuing to use the toothpaste three times per day. Data were statistically analyzed with a non-parametric Friedman test for dependent data (α = 0.05). All toothpastes reduced dentin hypersensitivity. In the evaporative test, Sensodyne Protect & Repair and Regenerador Sensitive, associated with the calcium booster, exhibited faster and more effective results in reducing pain caused by dentin hypersensitivity, even after the first use. Colgate Sensitive Pro-Relief was effective only after one week of use. All toothpastes performed well in the tactile test for treating dentin hypersensitivity, and their performance improved over time. Sensodyne Repair & Protect presented the highest overall pain remission after one month (84.6%). The bioactive toothpastes reduced, to a different extent, the tooth hypersensitivity reported by the volunteers. Sensodyne Repair & Relief and Regenerador Sensitive, associated or not with a calcium booster, presented faster and more effective results in reducing pain caused by dentin hypersensitivity.
Full article
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Future Prospects and Challenges in Additive Manufacturing for Complete Dentures: A Narrative Review
by
Mariya Dimitrova, Angelina Vlahova, Yavor Kalachev, Rada Kazakova and Saverio Capodiferro
Oral 2024, 4(1), 23-35; https://doi.org/10.3390/oral4010003 - 26 Dec 2023
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The utilization of computer-assisted design and computer-assisted manufacturing (CAD/CAM) techniques in the creation of complete dentures (CDs) has piqued the interest of many people. This article seeks to provide a comprehensive, critical, and objective analysis of the current knowledge of CDs and related
[...] Read more.
The utilization of computer-assisted design and computer-assisted manufacturing (CAD/CAM) techniques in the creation of complete dentures (CDs) has piqued the interest of many people. This article seeks to provide a comprehensive, critical, and objective analysis of the current knowledge of CDs and related technology. The aim of this study is to assess existing literature concerning 3D-printed complete dentures, covering aspects like innovative biomaterials, manufacturing methods and processes, workflow, and clinical effectiveness. The design of the current study included an initial review of 172 titles, an appraisal of abstracts, and finally a selection of articles for rigorous textual analysis. Inconsistencies discovered throughout the selection process were amicably resolved through discourse, culminating in the identification of 65 items. The publications retrieved from a thorough search of the PubMed, Scopus, and Embase databases spanned the years 1994 to 2023. Contemporary digital technology provides evident advantages, but its successful incorporation necessitates meticulous preparation. In the realm of dental healthcare, the digital workflow showcases versatility and a range of applications.
Full article
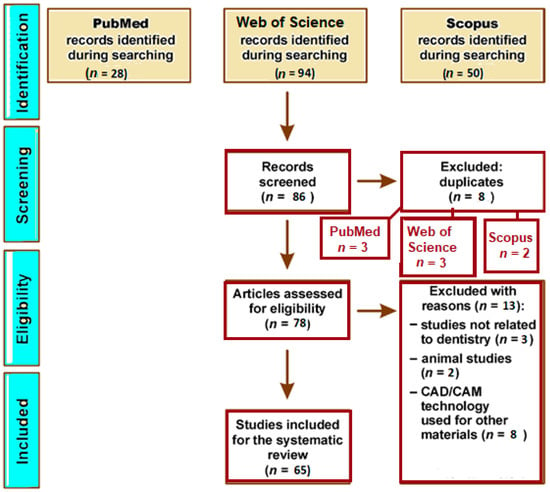
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Zirconia Implants: A Mapping Review
by
Steven J. Sadowsky
Oral 2024, 4(1), 9-22; https://doi.org/10.3390/oral4010002 - 25 Dec 2023
Abstract
The advent of zirconia ceramics with excellent mechanical, biomechanical, and optical properties has made them attractive metal-free substitutes for titanium implants. Both animal and human studies have documented shortcomings with titanium implants. A mapping review of the current literature on three iterations of
[...] Read more.
The advent of zirconia ceramics with excellent mechanical, biomechanical, and optical properties has made them attractive metal-free substitutes for titanium implants. Both animal and human studies have documented shortcomings with titanium implants. A mapping review of the current literature on three iterations of zirconia implant designs has been challenging due to heterogeneous success data and limited follow-up. Zirconia implants hold promise for a new generation of dental implants, but technical developments are needed for design and material enhancements that will need to be validated by long-term rigorous studies.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Current Issues in Oral Health)
►▼
Show Figures
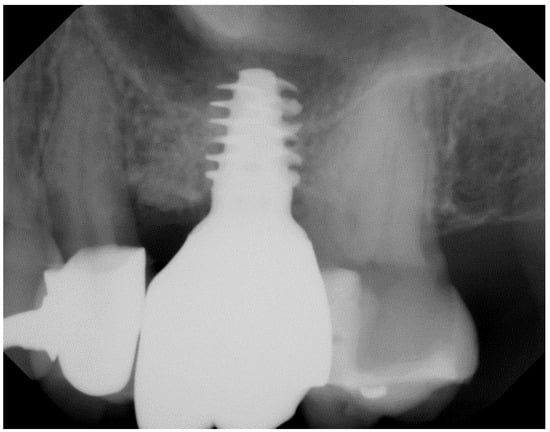
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Use of Fine Arts to Enhance Visualization and Describing Skills in a First-Year Dental Anatomy Course: A Qualitative Study
by
Geetha Siddanna, Bradley Smith, Andrea Mantesso, Vidya Ramaswamy, Tracy de Peralta and Elisabeta Karl
Oral 2024, 4(1), 1-8; https://doi.org/10.3390/oral4010001 - 21 Dec 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
(1) Background: In this qualitative study, we investigated the implementation of an art-based observation workshop as a tool to improve visualization and interpretation skills in a cohort of first-year dental students (N = 109) in a dental anatomy course. (2) Methods: The art
[...] Read more.
(1) Background: In this qualitative study, we investigated the implementation of an art-based observation workshop as a tool to improve visualization and interpretation skills in a cohort of first-year dental students (N = 109) in a dental anatomy course. (2) Methods: The art workshop was held once for a total of 60 min in the pre-clinical simulation laboratory, which is the regular teaching setting for the dental anatomy course. Visualization and interpretation skills were assessed before (pre-test) and after the art-based observation workshop (post-test). The pre- and post-tests contained five images that guided students to describe dental anatomy images. The pre- and post-test had different but similar images. Dental students accessed the pre- and post-tests on CANVAS and recorded their answers. After that, the audio recording files were analyzed and compared to determine the frequency of use of dental anatomy-specific nomenclature while answering the pre- and post-test. (3) Results: Our results demonstrate that students used dental anatomy-specific nomenclature more frequently after the intervention. (4) Conclusions: we have concluded that students’ use of dental anatomy nomenclature in the first-year dental anatomy curriculum is enhanced following an art-based intervention in a regular dental simulation laboratory.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessCase Report
Idiopathic Mandibular Osteosclerosis: A Case of Complex Diagnosis
by
Alexandre Perez, Avigaïl Mamane and Tommaso Lombardi
Oral 2023, 3(4), 572-579; https://doi.org/10.3390/oral3040046 - 11 Dec 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The purpose of this study is to report a case of idiopathic osteosclerosis of the mandible and to discuss the differential diagnosis of this lesion. A 17-year-old female was referred to the University Hospital of Geneva by her orthodontist following the fortuitous finding
[...] Read more.
The purpose of this study is to report a case of idiopathic osteosclerosis of the mandible and to discuss the differential diagnosis of this lesion. A 17-year-old female was referred to the University Hospital of Geneva by her orthodontist following the fortuitous finding of a radio-opaque lesion in the right posterior mandible at the apex of tooth 44. Intraoral clinical examination revealed no abnormalities of the oral mucosa. Tooth 44 was asymptomatic and reacted positively to the sensitivity test. The orthopantomogram revealed a well-defined unilocular radiodense lesion, surrounded by a thin radiolucent border, measuring 10 × 33 mm, located in the IV quadrant, related to the apex of tooth 44. Differential diagnoses mainly included cementoblastoma, focal cemento-osseous dysplasia, ossifying fibroma, condensing osteitis and idiopathic osteosclerosis. The biopsy material allowed a diagnosis of idiopathic osteosclerosis. The proposed treatment was therefore a “wait and see” approach. After 2 years of follow-up, the patient was asymptomatic, and healing was complete without any neurosensory complications. Our case underlines the differential diagnosis complexity of radio-opaque lesions associated with teeth.
Full article
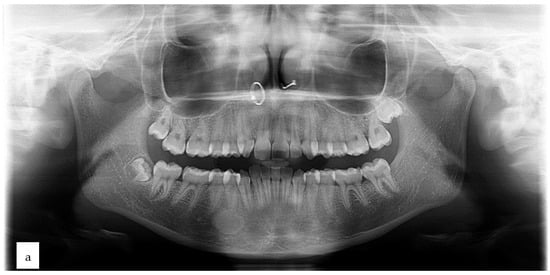
Figure 1
Open AccessFeature PaperEditor’s ChoiceReview
Diagnostic and Prognostic Predictors for the Success of Pulpotomy in Permanent Mature Posterior Teeth with Moderate to Severe Pulpitis: A Scoping Review
by
Helen McHugh, Patricia P. Wright, Christine I. Peters and Ove A. Peters
Oral 2023, 3(4), 545-571; https://doi.org/10.3390/oral3040045 - 27 Nov 2023
Cited by 2
Abstract
A partial or complete pulpotomy is a type of vital pulp therapy (VPT) that aims to remove the inflamed, infected pulp, leaving behind healthy, vital pulp that is capable of healing. VPT has gained renewed popularity as a treatment option in permanent mature
[...] Read more.
A partial or complete pulpotomy is a type of vital pulp therapy (VPT) that aims to remove the inflamed, infected pulp, leaving behind healthy, vital pulp that is capable of healing. VPT has gained renewed popularity as a treatment option in permanent mature posterior teeth with irreversible, moderate to severe pulpitis; its high success rates matching that of root canal treatment (RCT). There is currently no consensus regarding diagnostic and prognostic predictors of success of pulpotomies for managing such cases. Therefore, we conducted a scoping review to identify and analyze how these factors affect the outcome of treatment. A literature search using the PRISMA guidelines was undertaken using PubMed and Scopus on 7 July 2023. A total of 22 studies met the inclusion criteria and were qualitatively analyzed by two reviewers. The following diagnostic and prognostic factors were recognized and discussed; presenting signs and symptoms, periapical diagnosis, bleeding time, indicators of inflammation (bleeding time, concentration of inflammatory biomarkers), patient age and medical status, the depth, activity and location of caries, and restorative factors. Based on the studies assessed, there is limited evidence to support their prognostic value. Further research is necessary to identify solid predictors of outcome.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Current Issues in Oral Health)
►▼
Show Figures
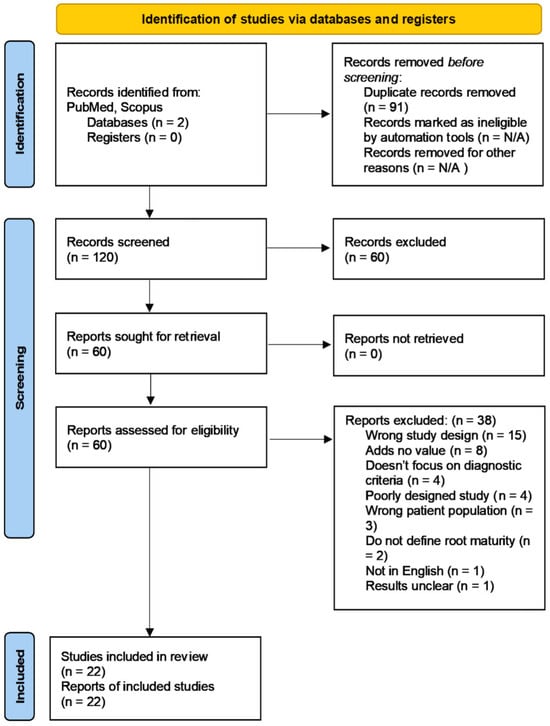
Figure 1
Open AccessOpinion
Skeletal Anchorage in Treating Skeletal Class II Malocclusion in Growing Patients Using the Herbst Appliance
by
Antonio Manni, Stefano Pera, Giorgio Gastaldi, Andrea Boggio and Mauro Cozzani
Oral 2023, 3(4), 539-544; https://doi.org/10.3390/oral3040044 - 27 Nov 2023
Abstract
Skeletal Class II is a common malocclusion affecting the Caucasian population and characterized, in most cases, by a convex profile and mandibular retrusion. Therefore, the treatment plan often requires the use of functional appliances to promote mandibular advancement. In particular, the Herbst appliance
[...] Read more.
Skeletal Class II is a common malocclusion affecting the Caucasian population and characterized, in most cases, by a convex profile and mandibular retrusion. Therefore, the treatment plan often requires the use of functional appliances to promote mandibular advancement. In particular, the Herbst appliance is recommended because of its efficiency and minimal need for compliance. However, in addition to skeletal favorable effects, undesired dental compensations could prematurely reduce the overjet needed for a proper orthopedic outcome. The combination of this appliance with skeletal anchorage and elastic ligatures in the lower or both, in the upper and the lower arch, enables effective control of unfavorable tooth movements, improving the therapeutic potential of such a treatment. These improvements have significantly shifted the main focus on facial aesthetics rather than dental occlusion, with the creation of innovative treatment protocols and a new diagnostic approach to Class II malocclusion.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Exclusive Papers of the Editorial Board Members of Oral)
►▼
Show Figures
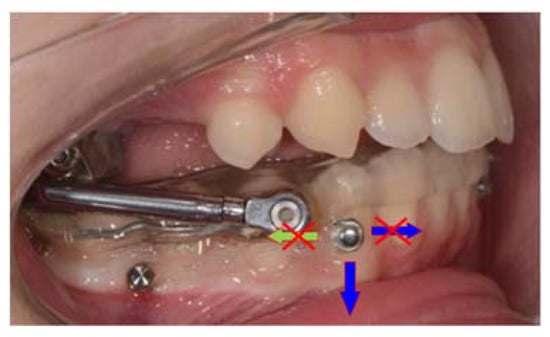
Figure 1
Open AccessEditor’s ChoiceArticle
Role of Glutathione in Neutrophil Chemotaxis in Periodontitis
by
Nurul Iman Binti Badlishah Sham and Melissa M. Grant
Oral 2023, 3(4), 526-538; https://doi.org/10.3390/oral3040043 - 23 Nov 2023
Abstract
Periodontitis is a common non-communicable inflammatory disease that leads to the destruction of periodontal tissues and tooth loss. Initiated by the plaque biofilm, there is a strong innate immune response with an abundance of neutrophils in the periodontium of affected individuals. Previous reports
[...] Read more.
Periodontitis is a common non-communicable inflammatory disease that leads to the destruction of periodontal tissues and tooth loss. Initiated by the plaque biofilm, there is a strong innate immune response with an abundance of neutrophils in the periodontium of affected individuals. Previous reports have shown that the intracellular concentration of glutathione in peripheral blood neutrophils from periodontitis patients and the chemotactic ability of these cells are compromised. Furthermore, other studies have described that in oxidative stress conditions neutrophil chemotaxis is aberrant and causes the glutathionylation of F-actin, a key player in chemotaxis. In this study, the effects of glutathione-modulating compounds were assessed in neutrophils isolated from healthy donors, showing that the perturbation of glutathione homeostasis decreases the chemotaxis of neutrophils. Following this, the intracellular glutathione status and chemotactic ability of neutrophils isolated from periodontitis patients was compared to that of age- and sex-matched controls. A decrease in glutathione and chemotactic ability were confirmed. Finally, the proteome of these neutrophils was explored, demonstrating a change in the abundance of proteins involved in glutathione homeostasis. Together these data suggest that peripheral blood neutrophils from periodontitis patients are compromised in their ability to cope with oxidative stress and move.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Current Issues in Oral Health)
►▼
Show Figures
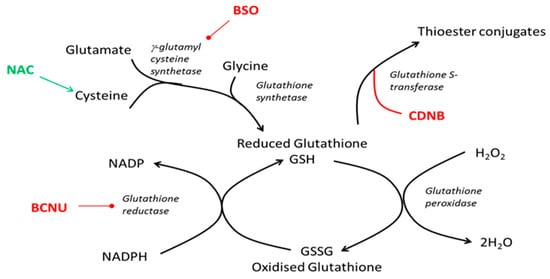
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Dental Age Estimation Methods Tested in a Sample of the Pakistani Population: Cross-Sectional Study
by
Amber Khan, Scheila Manica and Ademir Franco
Oral 2023, 3(4), 511-525; https://doi.org/10.3390/oral3040042 - 20 Nov 2023
Abstract
Forensic dentistry is still an emerging field in Pakistan. The lack of scientific literature on the topic may lead to difficulties in situations where age estimation has a significant part such as in criminal and civil litigation. In mass disasters such as earthquakes
[...] Read more.
Forensic dentistry is still an emerging field in Pakistan. The lack of scientific literature on the topic may lead to difficulties in situations where age estimation has a significant part such as in criminal and civil litigation. In mass disasters such as earthquakes and accidents, the correct investigation of the chronological age can be less troublesome if population-specific evidence is available. This is the rationale that justifies dedicated dental age estimation studies. This cross-sectional study aimed to test the time efficiency, validity and applicability of four dental age estimation methods: two invasive (Bang and Ramm and Lamendin) and two non-invasive (Kvaal and Cameriere) in an adult Pakistani population. A total of 37 teeth collected from a dental hospital in Islamabad, Pakistan, were used. Teeth included the central and lateral incisors, canines, and first and second premolars of males and females. Results were calculated using a Microsoft Office 2007 excel spreadsheet. Overall, Kvaal’s method mean absolute error between chronological and estimated ages (MAE: 12.33) showed the highest variation and Bang and Ramm showed more accurate results in comparison with other methods (MAE: 4.80). It was both time-efficient and practical to use. It can be stated that these were preliminary cross-sectional outcomes and that studies with larger samples are necessary.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances of Forensic Dentistry)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1
Open AccessPerspective
Improving Patient Experience through Meaningful Engagement: The Oral Health Patient’s Journey
by
Shamiso Chakaipa, Sarah J. Prior, Sue Pearson and Pieter J. van Dam
Oral 2023, 3(4), 499-510; https://doi.org/10.3390/oral3040041 - 08 Nov 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Healthcare organisations around the world have embraced the valuable role that patient experience plays in the improvement of health care delivery. Engaging with patients is a vital component of understanding how to deliver safe, high-quality, respectful health care that is person-centred and efficient.
[...] Read more.
Healthcare organisations around the world have embraced the valuable role that patient experience plays in the improvement of health care delivery. Engaging with patients is a vital component of understanding how to deliver safe, high-quality, respectful health care that is person-centred and efficient. In oral health services, patient experience is historically predominantly reported as challenging, which is most commonly associated with past traumatic experience with poor oral health treatment. Additionally, the high out-of-pocket costs associated with oral health treatment can mean that people disengage with these services, thereby worsening their oral health conditions. Consequently, oral health has an enormous task to reduce the negative perceptions and experiences. This demands innovative and subtle ways to navigate and address patient and service challenges. Exploring and acknowledging the myriad of historical challenges that exist for oral health patients and utilising these experiences to support change will ensure person-centred improvements are designed and implemented. Therefore, this perspective paper defines patient experience and proposes how oral health patient experience can be improved using the concept of meaningful engagement with a focus on the Australian context. We identified two important concepts that impact oral health patient experience and explored how these concepts may play a role in improving oral health services through improved patient experience. The first concept is person, patient, and user which focusses on general patient experience journey in a general health care setting. The second concept is preservice, current service, and post service which relates to an oral health patient’s experience journey in an oral health service setting. Our findings suggest that the practitioner–patient relationship and use of technology are central to patient engagement to improve patient experience.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Effects of Ceramic Translucency and Thickness on Polymerization of a Photosensitive Resin Cement
by
Abdullah Barazanchi, Jaafar Abduo, Yvonne Min-Joo Lee, Min-Suk Lee and Kai Chun Li
Oral 2023, 3(4), 490-498; https://doi.org/10.3390/oral3040040 - 30 Oct 2023
Abstract
We investigated the effects of lithium disilicate ceramic thickness and translucency on the degree of polymerization of light-cured resin cement using the measure of hardness. Lithium disilicate specimens of three translucencies (low, medium and high) were prepared to four thicknesses (0.5, 1.0, 2.0
[...] Read more.
We investigated the effects of lithium disilicate ceramic thickness and translucency on the degree of polymerization of light-cured resin cement using the measure of hardness. Lithium disilicate specimens of three translucencies (low, medium and high) were prepared to four thicknesses (0.5, 1.0, 2.0 and 3.0 mm). A light-cured resin cement was cured through each of the ceramic specimens using a handheld curing light for 50 s. A 3D printed jig was used to achieve a uniform thickness of the resin cement. Directly cured resin cement was used as the control. Hardness was measured using nano-indentation to determine the degree of polymerization of the resin cement. Two-way ANOVA and Tukey post hoc tests were used to evaluate interaction between translucency and thickness. Hardness values from control specimens were assessed using the two-tailed t-test with the Bonferroni approach. The translucency of the specimens significantly influenced the hardness (p < 0.001), where a negative linear relationship between cement hardness and ceramic thickness was present for low translucency and high translucency. However, at a 0.5 mm thickness, all specimens showed similar hardness regardless of the translucency. The translucency of ceramics affected the hardness, and hence polymerization, of light-cure resin cement. However, the effect of increased thickness was a more significant factor.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Dental Composite Materials)
►▼
Show Figures
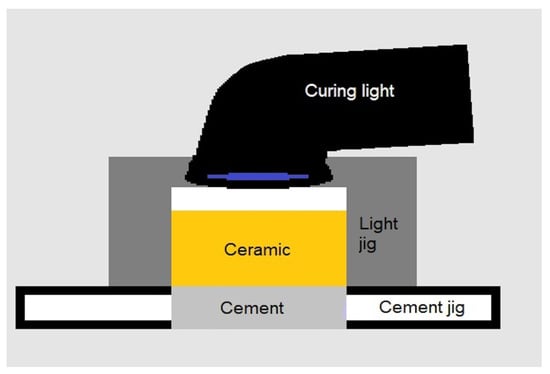
Figure 1
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Dentistry Journal, Healthcare, JCM, JPM, Oral
Advances in Dental Health
Topic Editors: Sabina Saccomanno, Gianni GallusiDeadline: 9 November 2024
Topic in
Biomedicines, JPM, Oral, Pharmaceuticals, Pharmaceutics
Personalized Drug Formulations
Topic Editors: Diego Romano Perinelli, Florentina LupascuDeadline: 31 January 2025

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Oral
Editorial Board Members' Collection Series: Oral Health Management for Special Care Patients
Guest Editors: Hiromitsu Morita, Yoko Iwase-Saito, Ourania Nicolatou-GalitisDeadline: 20 April 2024
Special Issue in
Oral
Oral Health in the Global South
Guest Editors: Zuhair Natto, Kehinde Kazeem Kanmodi, Lawrence Achilles NnyanziDeadline: 20 May 2024
Special Issue in
Oral
Current Issues in Oral Health
Guest Editor: Nejat DüzgüneşDeadline: 25 August 2024
Special Issue in
Oral
Digital Orthodontics: A New Era for Improved Diagnosis and Treatment Options
Guest Editor: Riccardo NuceraDeadline: 20 September 2024
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Oral
Oral and Systemic Health: Border Dentistry and the Borders of Dental Practice
Collection Editors: Giuseppina Campisi, Marco Mascitti
Topical Collection in
Oral
Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw (MRONJ): Current Practice, New Tools and Future Trends
Collection Editors: Vittorio Fusco, Giacomo Oteri, Umberto Romeo, Rodolfo Mauceri, Alberto Bedogni
Topical Collection in
Oral
Synthesis, Testing and Mechanical Behavior of Dental Biomaterials at Different Clinical Parameters
Collection Editors: Joao Paulo Tribst, Eugenio Pedullà