Marine Harmful Algae
A special issue of Journal of Marine Science and Engineering (ISSN 2077-1312). This special issue belongs to the section "Marine Biology".
Deadline for manuscript submissions: closed (31 January 2023) | Viewed by 14571
Special Issue Editor
Interests: Harmful Algal Blooms (HABs); marine toxins; dinoflagellates; diatoms; ichthyotoxicity; proteomics; marine phytoplankton and their associations with water quality; Relationship between HAB species and bacteria
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Special Issue Information
Dear Colleagues,
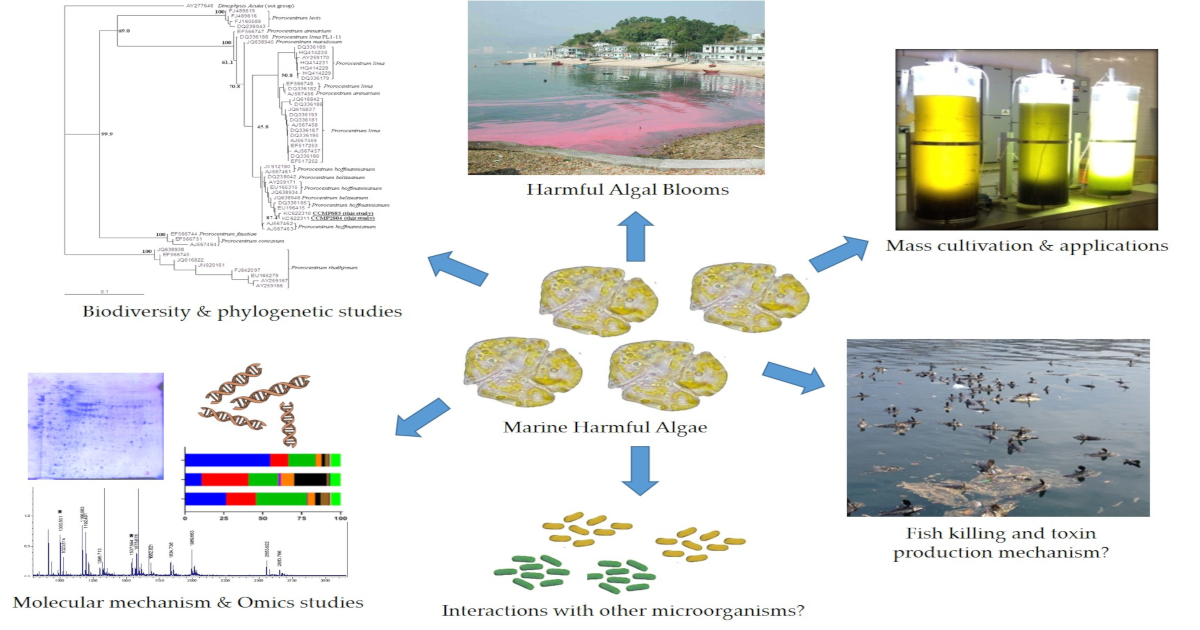
Microalgae, also referred to as phytoplankton or planktonic algae, are single-celled photosynthetic organisms usually found in marine environments. The biodiversity of microalgae is enormous. They are the primary producer in the aquatic food web, providing an essential ecological function for all aquatic life. However, some of these microalgae species are harmful and responsible for causing harmful algal blooms (HABs). HABs can cause serious negative impacts on the economy, fishery/seafood industry, environment, and even recreational activities. It should be stressed that some of these causative agents produce toxins that can cause human illness and even death. These biotoxins can be accumulated in seafood. Such contaminations of seafood with biotoxins could negatively affect the shellfish and aquaculture industries. Therefore, there is an urgent need to understand the mechanism of the cause of algal bloom and toxin biosynthesis by the harmful algae. With modern and new technologies available today, e.g., different omics techniques, more of such underlying mechanisms and molecular pathways will be disclosed. This Special Issue aims to promote knowledge and publish new findings on all types of researches related to marine harmful algae. Topics of interest include but are not limited to the following:
- The distribution, biodiversity and phylogenetic studies of harmful algae;
- The occurrence, ecology, physiology, toxicology of harmful algal blooms;
- The control and mitigation of harmful algal blooms;
- Toxin production and ichthyotoxicity of harmful microalgae;
- Allelopathic interactions between harmful algae and other microorganisms;
- Applications of marine harmful algae;
- Molecular mechanism and omics research in harmful algae;
- Rapid identification methods for harmful microalgae.
Research and review articles, as well as case studies, regarding recent advances related to marine harmful algae are welcome.
Prof. Dr. Wang Fat Fred Lee
Guest Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the special issue website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering is an international peer-reviewed open access monthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2600 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- allelopathic interactions
- dinoflagellates
- diatoms
- harmful algal blooms (HABs)
- ichthyotoxicity
- marine toxins
- mitigation of HABs
- omics
- rapid identification methods





