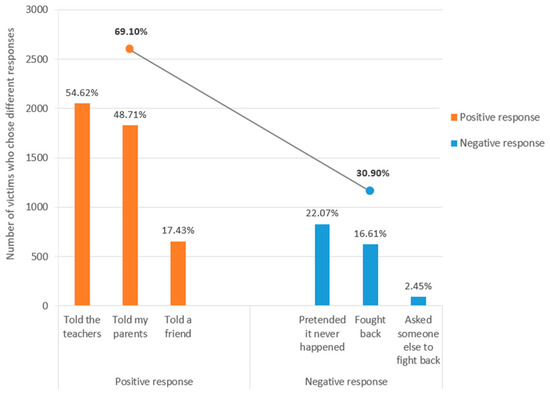
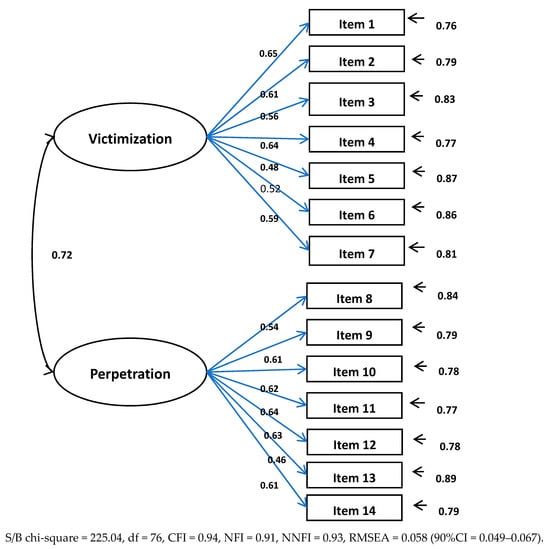
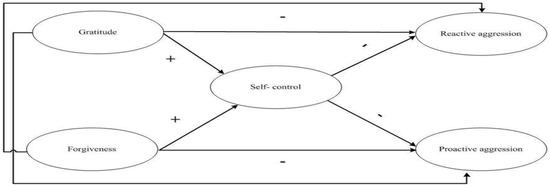
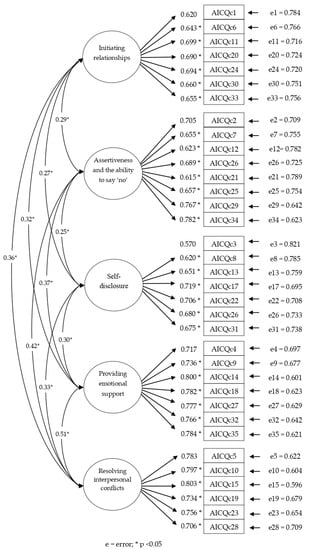
Bullying, Cyberbullying, Dating Violence, and Cyber Dating Violence in Adolescence
A topical collection in International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health (ISSN 1660-4601). This collection belongs to the section "Behavioral and Mental Health".
Viewed by 121311Editor
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
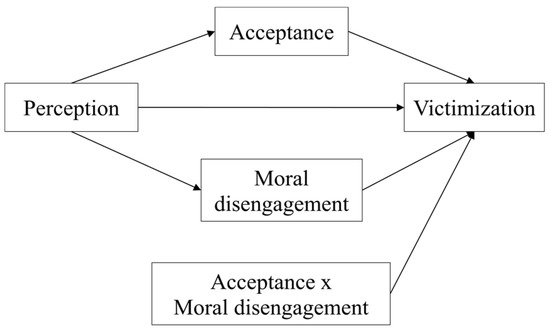
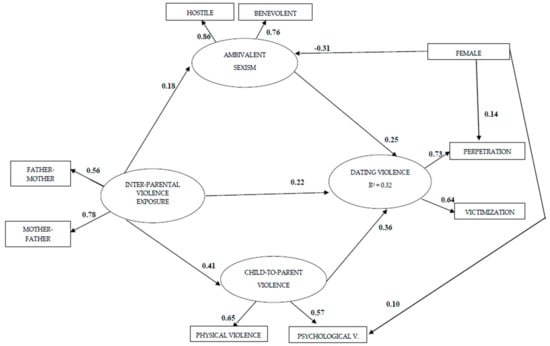
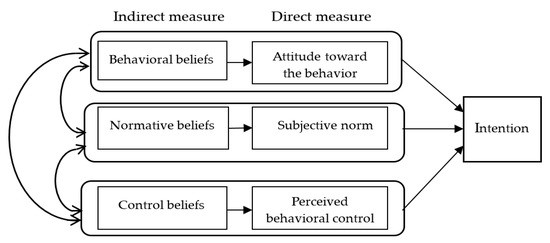
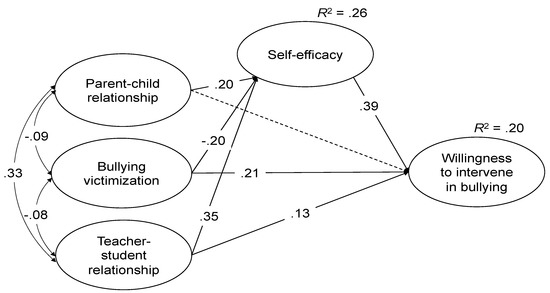
This Special Issue seeks to deepen our knowledge about bullying and teen dating violence, the individual and social variables related to them, the links between these two types of violence, and their expansion into the virtual world. Bullying is a public health problem that affects a large number of adolescents, and the current use of new technologies means that many peer aggressions move quickly from the real world to the virtual world. Bullying and cyberbullying have common risk factors and are strongly related, although they have shown some differences in their characteristics. Teen dating violence, a relevant problem with serious psychosocial consequences, is also related to bullying. Teen dating violence shows a high prevalence, and adolescents frequently extend aggressions in the context of romantic relationships to the virtual world. Moreover, adolescents’ involvement in cyber dating violence is growing.
In this Special Issue, we invite authors to contribute research focused on variables linked to these types of violence, relationships between bullying and cyberbullying, common protective and risk factors, and links between teen dating violence and cyber dating violence and between cyberbullying and cyber dating violence. Any research focused on only one of these types of violence (bullying, cyberbullying, teen dating violence, and cyber dating violence) will also be considered. Some aspects that could be analyzed are the following: risk and protective factors, psychosocial consequences, different roles (victim, aggressor, victim-aggressor), assessment, and evidence-based intervention programs. Other forms of online and offline peer aggression will also be considered.
Dr. María-Jesús Cava
Collection Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health is an international peer-reviewed open access monthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2500 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- Adolescence
- Bullying
- Cyberbullying
- Peer aggression
- School violence
- Teen dating violence
- Cyber dating violence/Cyber dating abuse
- Psychosocial adjustment
- Risk and protective factors
- Assessment
- Prevention