Journal Description
IoT
IoT
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on Internet of Things (IoT) published quarterly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions
- High Visibility: indexed within ESCI (Web of Science), Scopus, EBSCO, and other databases.
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 23.3 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 5.5 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2023).
- Journal Rank: CiteScore - Q1 (Computer Science (miscellaneous))
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
Latest Articles
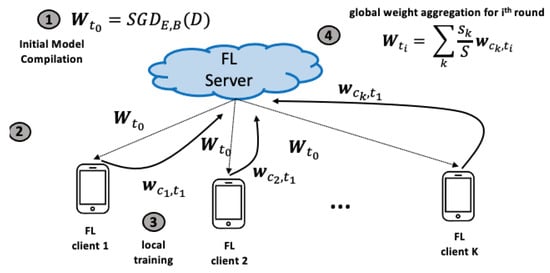
FedMon: A Federated Learning Monitoring Toolkit
IoT 2024, 5(2), 227-249; https://doi.org/10.3390/iot5020012 - 11 Apr 2024
Abstract
Federated learning (FL) is rapidly shaping into a key enabler for large-scale Artificial Intelligence (AI) where models are trained in a distributed fashion by several clients without sharing local and possibly sensitive data. For edge computing, sharing the computational load across multiple clients
[...] Read more.
Federated learning (FL) is rapidly shaping into a key enabler for large-scale Artificial Intelligence (AI) where models are trained in a distributed fashion by several clients without sharing local and possibly sensitive data. For edge computing, sharing the computational load across multiple clients is ideal, especially when the underlying IoT and edge nodes encompass limited resource capacity. Despite its wide applicability, monitoring FL deployments comes with significant challenges. AI practitioners are required to invest a vast amount of time (and labor) in manually configuring state-of-the-art monitoring tools. This entails addressing the unique characteristics of the FL training process, including the extraction of FL-specific and system-level metrics, aligning metrics to training rounds, pinpointing performance inefficiencies, and comparing current to previous deployments. This work introduces FedMon, a toolkit designed to ease the burden of monitoring FL deployments by seamlessly integrating the probing interface with the FL deployment, automating the metric extraction, providing a rich set of system, dataset, model, and experiment-level metrics, and providing the analytic means to assess trade-offs and compare different model and training configurations.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Cloud and Edge Computing Systems for IoT)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Enhancing Automatic Modulation Recognition for IoT Applications Using Transformers
by
Narges Rashvand, Kenneth Witham, Gabriel Maldonado, Vinit Katariya, Nishanth Marer Prabhu, Gunar Schirner and Hamed Tabkhi
IoT 2024, 5(2), 212-226; https://doi.org/10.3390/iot5020011 - 09 Apr 2024
Abstract
Automatic modulation recognition (AMR) is vital for accurately identifying modulation types within incoming signals, a critical task for optimizing operations within edge devices in IoT ecosystems. This paper presents an innovative approach that leverages Transformer networks, initially designed for natural language processing, to
[...] Read more.
Automatic modulation recognition (AMR) is vital for accurately identifying modulation types within incoming signals, a critical task for optimizing operations within edge devices in IoT ecosystems. This paper presents an innovative approach that leverages Transformer networks, initially designed for natural language processing, to address the challenges of efficient AMR. Our Transformer network architecture is designed with the mindset of real-time edge computing on IoT devices. Four tokenization techniques are proposed and explored for creating proper embeddings of RF signals, specifically focusing on overcoming the limitations related to the model size often encountered in IoT scenarios. Extensive experiments reveal that our proposed method outperformed advanced deep learning techniques, achieving the highest recognition accuracy. Notably, our model achieved an accuracy of 65.75 on the RML2016 and 65.80 on the CSPB.ML.2018+ dataset.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Cloud and Edge Computing Systems for IoT)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Development of a Multi-Radio Device for Dry Container Monitoring and Tracking
by
Mariano Falcitelli, Misal, Sandro Noto and Paolo Pagano
IoT 2024, 5(2), 187-211; https://doi.org/10.3390/iot5020010 - 02 Apr 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Maritime shipping companies have identified continuous tracking of intermodal containers as a key tool for increasing shipment reliability and generating important economies of scale. Equipping all dry containers with an Internet-connected tracking device is a need in the global shipping market that is
[...] Read more.
Maritime shipping companies have identified continuous tracking of intermodal containers as a key tool for increasing shipment reliability and generating important economies of scale. Equipping all dry containers with an Internet-connected tracking device is a need in the global shipping market that is still waiting to be met. This paper presents the methods and tools to build and test a prototype of a Container Tracking Device (CTD) that integrates NB-IoT, BLE Mesh telecommunication and low-power consumption technologies for the massive deployment of the IoT. The work was carried out as part of a project to build the so-called “5G Global Tracking System”, enabling several different logistic applications relying on massive IoT, M2M standard platforms, as well as satellite networks to collect data from dry containers when the vessel is in open sea. Starting from a preliminary phase, in which state-of-the-art technologies, research approaches, industrial initiatives and developing standards were investigated, a prototype version of the CTD has been designed, verified and developed as the first fundamental step for subsequent industrial engineering. The results of specific tests are shown: after verifying that the firmware is capable of handling the various functions of the device, a special focus is devoted to the power consumption measurements of the CTD to size the battery pack.
Full article
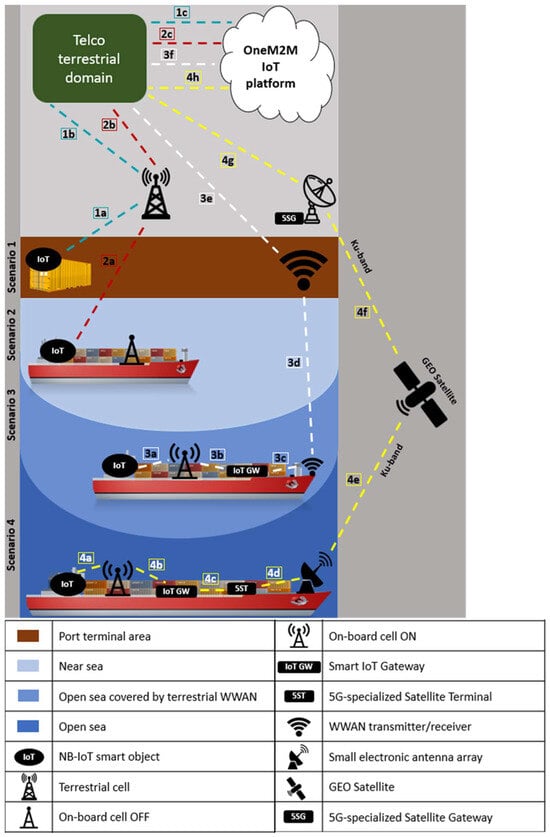
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Integration of Smart Cane with Social Media: Design of a New Step Counter Algorithm for Cane
by
Mohamed Dhiaeddine Messaoudi, Bob-Antoine J. Menelas and Hamid Mcheick
IoT 2024, 5(1), 168-186; https://doi.org/10.3390/iot5010009 - 14 Mar 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This research introduces an innovative smart cane architecture designed to empower visually impaired individuals. Integrating advanced sensors and social media connectivity, the smart cane enhances accessibility and encourages physical activity. Three meticulously developed algorithms ensure accurate step counting, swing detection, and proximity measurement.
[...] Read more.
This research introduces an innovative smart cane architecture designed to empower visually impaired individuals. Integrating advanced sensors and social media connectivity, the smart cane enhances accessibility and encourages physical activity. Three meticulously developed algorithms ensure accurate step counting, swing detection, and proximity measurement. The smart cane’s architecture comprises the platform, communications, sensors, calculation, and user interface layers, providing comprehensive assistance for visually impaired individuals. Hardware components include an audio–tactile interaction module, input command module, microphone integration, local storage, step count module, cloud integration, and rechargeable battery. Software v1.9.7 components include Facebook Chat API integration, Python Facebook API integration, fbchat library integration, and Speech Recognition library integration. Overall, the proposed smart cane offers a comprehensive solution to enhance mobility, accessibility, and social engagement for visually impaired individuals. This study represents a significant stride toward a more inclusive society, leveraging technology to create meaningful impact in the lives of those with visual impairments. By fostering socialization and independence, our smart cane not only improves mobility but also enhances the overall well-being of the visually impaired community.
Full article
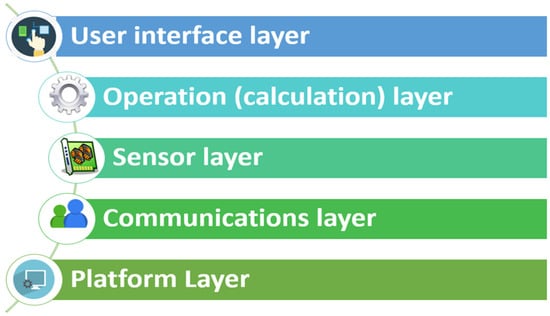
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A Wearable Internet of Things Device for Noninvasive Remote Monitoring of Vital Signs Related to Heart Failure
by
Sheikh Muhammad Asher Iqbal, Mary Ann Leavitt, Imadeldin Mahgoub and Waseem Asghar
IoT 2024, 5(1), 155-167; https://doi.org/10.3390/iot5010008 - 12 Mar 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Cardiovascular disease is one of the leading causes of death in the world. Heart failure is a cardiovascular disease in which the heart is unable to pump sufficient blood to fulfill the body’s requirements and can lead to fluid overload. Traditional solutions are
[...] Read more.
Cardiovascular disease is one of the leading causes of death in the world. Heart failure is a cardiovascular disease in which the heart is unable to pump sufficient blood to fulfill the body’s requirements and can lead to fluid overload. Traditional solutions are not adequate to address the progression of heart failure. Herein, we report a body-mounted wearable sensor to monitor the parameters related to heart failure. These include heart rate, blood oxygen saturation, thoracic impedance, and activity status. The device is compact and wearable and measures the parameters continuously in real time. The device is an Internet of Things (IoT) device connected with a cloud-based database enabling the parameters to be visualized on a mobile application.
Full article
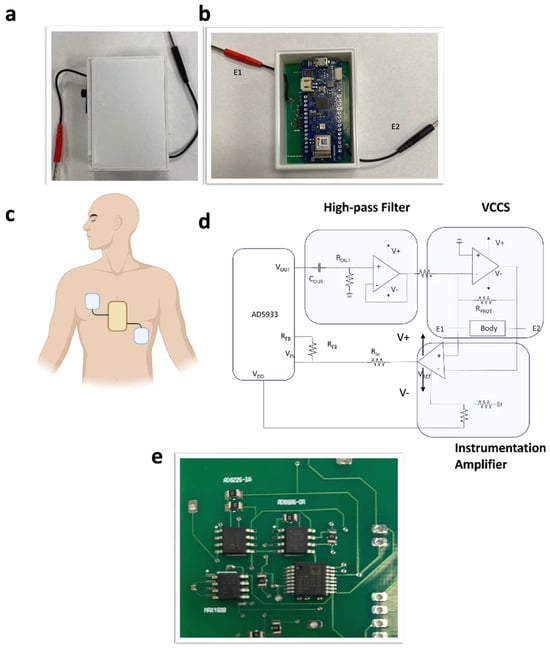
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Analyzing Threats and Attacks in Edge Data Analytics within IoT Environments
by
Poornima Mahadevappa, Redhwan Al-amri, Gamal Alkawsi, Ammar Ahmed Alkahtani, Mohammed Fahad Alghenaim and Mohammed Alsamman
IoT 2024, 5(1), 123-154; https://doi.org/10.3390/iot5010007 - 05 Mar 2024
Abstract
Edge data analytics refers to processing near data sources at the edge of the network to reduce delays in data transmission and, consequently, enable real-time interactions. However, data analytics at the edge introduces numerous security risks that can impact the data being processed.
[...] Read more.
Edge data analytics refers to processing near data sources at the edge of the network to reduce delays in data transmission and, consequently, enable real-time interactions. However, data analytics at the edge introduces numerous security risks that can impact the data being processed. Thus, safeguarding sensitive data from being exposed to illegitimate users is crucial to avoiding uncertainties and maintaining the overall quality of the service offered. Most existing edge security models have considered attacks during data analysis as an afterthought. In this paper, an overview of edge data analytics in healthcare, traffic management, and smart city use cases is provided, including the possible attacks and their impacts on edge data analytics. Further, existing models are investigated to understand how these attacks are handled and research gaps are identified. Finally, research directions to enhance data analytics at the edge are presented.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Cloud and Edge Computing Systems for IoT)
►▼
Show Figures
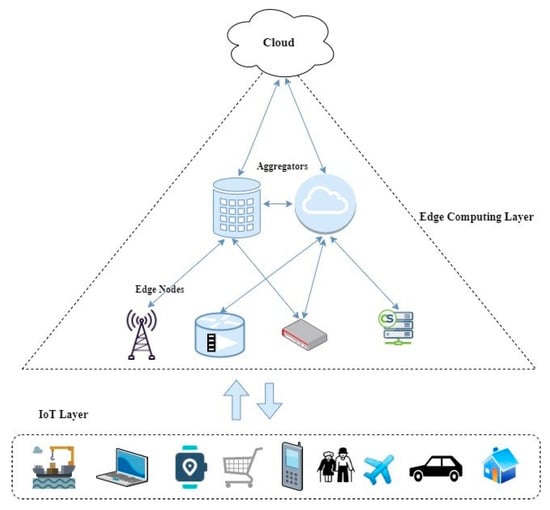
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A Reference Design Model to Manage Consent in Data Subjects-Centered Internet of Things Devices
by
Pankaj Khatiwada, Bian Yang, Jia-Chun Lin, Godfrey Mugurusi and Stian Underbekken
IoT 2024, 5(1), 100-122; https://doi.org/10.3390/iot5010006 - 06 Feb 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Internet of Things (IoT) devices have changed how billions of people in the world connect and interact with each other. But, as more people use IoT devices, many questions arise about how these devices handle private data and whether they properly ask for
[...] Read more.
Internet of Things (IoT) devices have changed how billions of people in the world connect and interact with each other. But, as more people use IoT devices, many questions arise about how these devices handle private data and whether they properly ask for permission when using it. Due to information privacy regulations such as the EU’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), which requires companies to seek permission from data subjects (DS) before using their data, it is crucial for IoT companies to obtain this permission correctly. However, this can be really challenging in the IoT world because people often find it difficult to interact with and manage multiple IoT devices under their control. Also, the rules about privacy are not always clear. As such, this paper proposes a new model to improve how consent is managed in the world of IoT. The model seeks to minimize “consent fatigue” (when people get tired of always being asked for permission) and give DS more control over how their data are shared. This includes having default permission settings, being able to compare similar devices, and, in the future, using AI to give personalized advice. The model allows users to easily review and change their IoT device permissions if previous conditions are not met. It also emphasizes the need for easily understandable privacy rules, clear communication with users, and robust tracking of consent for data usage. By using this model, companies that provide IoT services can do a better job of protecting user privacy and managing DS consent. In addition, companies can more easily comply with data protection laws and build stronger relationships with their customers.
Full article
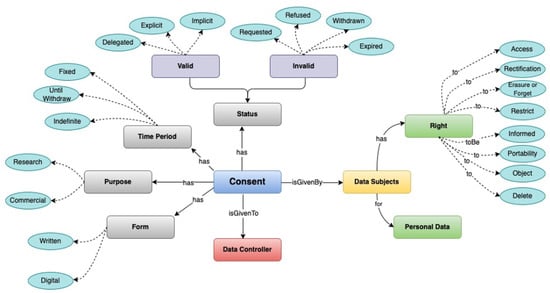
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Development and Assessment of Internet of Things-Driven Smart Home Security and Automation with Voice Commands
by
Paniti Netinant, Thitipong Utsanok, Meennapa Rukhiran and Suttipong Klongdee
IoT 2024, 5(1), 79-99; https://doi.org/10.3390/iot5010005 - 01 Feb 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
With the rapid rise of digitalization in the global economy, home security systems have become increasingly important for personal comfort and property protection. The collaboration between humans, the Internet of Things (IoT), and smart homes can be highly efficient. Interaction considers convenience, efficiency,
[...] Read more.
With the rapid rise of digitalization in the global economy, home security systems have become increasingly important for personal comfort and property protection. The collaboration between humans, the Internet of Things (IoT), and smart homes can be highly efficient. Interaction considers convenience, efficiency, security, responsiveness, and automation. This study aims to develop and assess IoT-based home security systems utilizing passive infrared (PIR) sensors to improve user interface, security, and automation controls using voice commands and buttons across different communication protocols. The proposed system incorporates controls for lighting and intrusion monitoring, as well as assessing both the functionality of voice commands and the precision of intruder detection via the PIR sensors. Intelligent light control and PIR intruder detection with a variable delay time for response detection are unified into the research methodology. The test outcomes examine the average effective response time in-depth, revealing performance distinctions among wireless fidelity (Wi-Fi) and fourth- and fifth-generation mobile connections. The outcomes illustrate the reliability of voice-activated light control via Google Assistant, with response accuracy rates of 83 percent for Thai voice commands and 91.50 percent for English voice commands. Moreover, the Blynk mobile application provided exceptional precision regarding operating light-button commands. The PIR motion detectors have a one hundred percent detection accuracy, and a 2.5 s delay is advised for PIR detection. Extended PIR detection delays result in prolonged system response times. This study examines the intricacies of response times across various environmental conditions, considering different degrees of mobile communication quality. This study ultimately advances the field by developing an IoT system prepared for efficient integration into everyday life, holding the potential to provide improved convenience, time-saving effectiveness, cost-efficiency, and enhanced home security protocols.
Full article
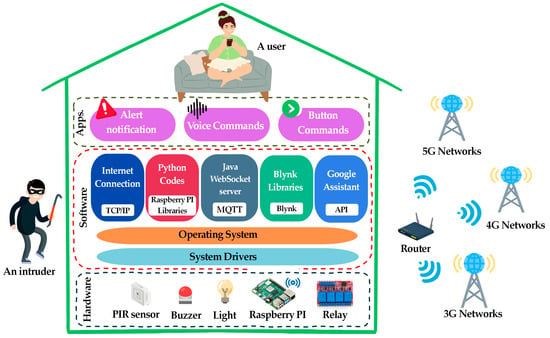
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Utilizing an Internet of Things (IoT) Device, Intelligent Control Design, and Simulation for an Agricultural System
by
Sairoel Amertet Finecomess, Girma Gebresenbet and Hassan Mohammed Alwan
IoT 2024, 5(1), 58-78; https://doi.org/10.3390/iot5010004 - 31 Jan 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
In an agricultural system, finding suitable watering, pesticides, and soil content to provide the right nutrients for the right plant remains challenging. Plants cannot speak and cannot ask for the food they require. These problems can be addressed by applying intelligent (fuzzy logic)
[...] Read more.
In an agricultural system, finding suitable watering, pesticides, and soil content to provide the right nutrients for the right plant remains challenging. Plants cannot speak and cannot ask for the food they require. These problems can be addressed by applying intelligent (fuzzy logic) controllers to IoT devices in order to enhance communication between crops, ground mobile robots, aerial robots, and the entire farm system. The application of fuzzy logic in agriculture is a promising technology that can be used to optimize crop yields and reduce water usage. It was developed based on language and the air properties in agricultural fields. The entire system was simulated in the MATLAB/SIMULINK environment with Cisco Packet Tracer integration. The inputs for the system were soil moisture sensors, temperature sensors, and humidity sensors, and the outputs were pump flow, valve opening, water level, and moisture in the sounding. The obtained results were the output of the valve opening, moisture in the sounding, pump flow rate, outflow, water level, and ADH values, which are 10.00000013 rad/s, 34.72%, 4.494%, 0.025 m3/s, 73.31 cm3, and 750 values, respectively. The outflow rate increase indicates that water is being released from the tanks, and the control signal fluctuates, indicating that the valve is opening.
Full article
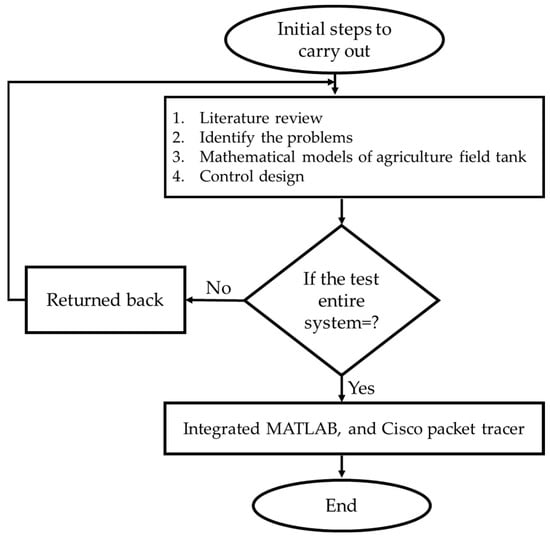
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A Testbed Platform to Support an IoT City Lab
by
Carlo Impagliazzo, Muriel Cabianca, Maria Laura Clemente, Giuliana Siddi Moreau, Matteo Vocale and Lidia Leoni
IoT 2024, 5(1), 35-57; https://doi.org/10.3390/iot5010003 - 24 Jan 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This paper describes the development activity that has been carried out for a living laboratory for the city of Cagliari aimed at functioning as a learning center for local SMEs willing to improve their skills in IoT and create applications that will be
[...] Read more.
This paper describes the development activity that has been carried out for a living laboratory for the city of Cagliari aimed at functioning as a learning center for local SMEs willing to improve their skills in IoT and create applications that will be integrated in an open innovation ecosystem. The many users belonging to the various SMEs involved in the project required an ICT laboratory with a platform that could manage them and provide a multi-tenant environment for the development of IoT applications. The architecture also had to be scalable and interoperable, and the resulting platform had to collect many kinds of data from sensors or other data sources, elaborate them, and show georeferenced information on a 3D satellite interactive view along with statistics on side panels. This work was based on a platform already developed by CRS4 for a previous project. Preserving the concept of the decision-making tool for Smart Cities, almost every component was redesigned, and, in this paper, we describe the new solutions that have been implemented. Starting from the former structure, further features were added in a novel way in order to offer an enhanced framework that can deal with the activities of the laboratory, exploiting the scalability of the open-source systems involved, their robustness and flexibility, and leveraging domain standards. In this article, the main challenges involved in the development of the platform are described, as well as the solutions that have been implemented so far.
Full article
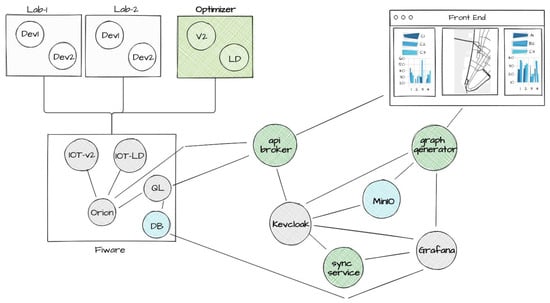
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Enhancing IoT Data Security: Using the Blockchain to Boost Data Integrity and Privacy
by
Ali Eghmazi, Mohammadhossein Ataei, René Jr Landry and Guy Chevrette
IoT 2024, 5(1), 20-34; https://doi.org/10.3390/iot5010002 - 10 Jan 2024
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a technology that can connect billions of devices or “things” to other devices (machine to machine) or even to people via an existing infrastructure. IoT applications in real-world scenarios include smart cities, smart houses, connected appliances, shipping,
[...] Read more.
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a technology that can connect billions of devices or “things” to other devices (machine to machine) or even to people via an existing infrastructure. IoT applications in real-world scenarios include smart cities, smart houses, connected appliances, shipping, monitoring, smart supply chain management, and smart grids. As the number of devices all over the world is increasing (in all aspects of daily life), huge amounts of data are being produced as a result. New issues are therefore arising from the use and development of current technologies, regarding new applications, regulation, cloud computing, security, and privacy. The blockchain has shown promise in terms of securing and preserving the privacy of users and data, in a decentralized manner. In particular, Hyperledger Fabric v2.x is a new generation of blockchain that is open source and offers versatility, modularity, and performance. In this paper, a blockchain as a service (BaaS) application based on Hyperledger Fabric is presented to address the security and privacy challenges associated with the IoT. A new architecture is introduced to enable this integration, and is developed and deployed, and its performance is analyzed in real-world scenarios. We also propose a new data structure with encryption based on public and private keys for enhanced security and privacy.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A Distributed Lightweight PUF-Based Mutual Authentication Protocol for IoV
by
Mona Alkanhal, Abdulaziz Alali and Mohamed Younis
IoT 2024, 5(1), 1-19; https://doi.org/10.3390/iot5010001 - 30 Dec 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
In recent times, the advent of innovative technological paradigms like the Internet of Things has paved the way for numerous applications that enhance the quality of human life. A remarkable application of IoT that has emerged is the Internet of Vehicles (IoV), motivated
[...] Read more.
In recent times, the advent of innovative technological paradigms like the Internet of Things has paved the way for numerous applications that enhance the quality of human life. A remarkable application of IoT that has emerged is the Internet of Vehicles (IoV), motivated by an unparalleled surge of connected vehicles on the roads. IoV has become an area of significant interest due to its potential in enhancing traffic safety as well as providing accurate routing information. The primary objective of IoV is to maintain strict latency standards while ensuring confidentiality and security. Given the high mobility and limited bandwidth, vehicles need to have rapid and frequent authentication. Securing Vehicle-to-Roadside unit (V2R) and Vehicle-to-Vehicle (V2V) communications in IoV is essential for preventing critical information leakage to an adversary or unauthenticated users. To address these challenges, this paper proposes a novel mutual authentication protocol which incorporates hardware-based security primitives, namely physically unclonable functions (PUFs) with Multi-Input Multi-Output (MIMO) physical layer communications. The protocol allows a V2V and V2R to mutually authenticate each other without the involvement of a trusted third-party (server). The protocol design effectively mitigates modeling attacks and impersonation attempts, where the accuracy of predicting the value of each PUF response bit does not exceed 54%, which is equivalent to a random guess.
Full article
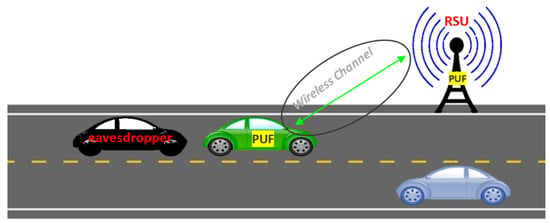
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A Systematic Approach to Long-Term Storage of Documents Using Digital Twin Technologies
by
Alexander Solovyev and Ivan Tarkhanov
IoT 2023, 4(4), 610-627; https://doi.org/10.3390/iot4040026 - 04 Dec 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The article discusses the modeling of the use of digital twin technologies (a digital twin) for the task of organizing long-term storage of various types of documents. A digital twin in this respect differs from a digital copy, which has no connection with
[...] Read more.
The article discusses the modeling of the use of digital twin technologies (a digital twin) for the task of organizing long-term storage of various types of documents. A digital twin in this respect differs from a digital copy, which has no connection with the real original object. A review of the problem was carried out. We argue that, despite the active use of digital twin technology in various areas, its applications in the area of long-term storage of documents remain limited. At the same time, the task of increasing the durability of documents during long-term storage remains important and largely unresolved. The complexity of solving the problem of long-term storage of documents is considered, and a formal statement of the problem of long-term storage using digital twin technologies is carried out. Destructive factors that affect long-term storage documents and significantly reduce their durability have been identified. A system of indicators has been developed to assess the durability (preservation) of documents. The modeling of the use of digital twin technology in the organization of long-term preservation within the framework of Industry 4.0 was carried out. In the course of modeling, the goals and the strategies of long-term storage were established. Primary mathematical models for controlling destructive factors as well as technological solutions for digital twin long-term storage are proposed. It is assumed that the key part of this technology is the Industrial Internet of Things. The effectiveness of the use of digital twin technologies for solving the problem was assessed. The spheres of application and further ways of research are determined.
Full article
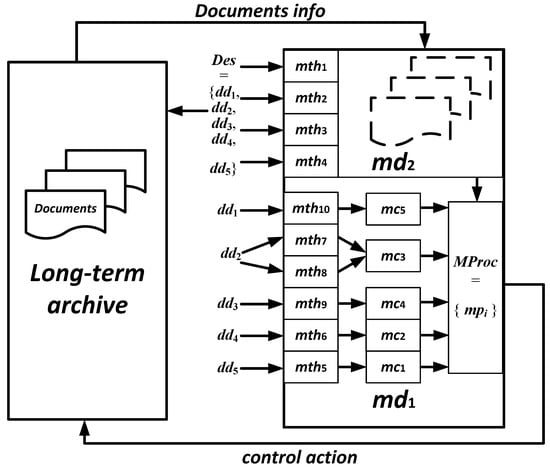
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Decentralised IOTA-Based Concepts of Digital Trust for Securing Remote Driving in an Urban Environment
by
Juhani Latvakoski, Vesa Kyllönen and Jussi Ronkainen
IoT 2023, 4(4), 582-609; https://doi.org/10.3390/iot4040025 - 29 Nov 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The novel contribution of this research is decentralised IOTA-based concepts of digital trust for securing remote driving in an urban environment. The conceptual solutions are studied and described, and respective experimental solutions are developed relying on digital identities, public key cryptography with a
[...] Read more.
The novel contribution of this research is decentralised IOTA-based concepts of digital trust for securing remote driving in an urban environment. The conceptual solutions are studied and described, and respective experimental solutions are developed relying on digital identities, public key cryptography with a decentralised approach using decentralised identifiers (DIDs) and verifiable credentials (VCs), and an IOTA-based distributed ledger. The provided digital trust solutions were validated by executing them according to the remote driving scenario but with a simulated vehicle and simulated remote driving system. The hybrid simulation mainly focused on the validation of functional, causal temporal correctness, feasibility, and capabilities of the provided solutions. The evaluations indicate that the concepts of digital trust fulfil the purpose and contribute towards making remote driving more trustable. A supervisory stakeholder was used as a verifier, requiring a set of example verifiable credentials from the vehicle and the remote driver, and accepting them to the security control channel. The separation of control and data planes from each other was found to be a good solution because the delays caused by required security control can be limited to the initiation of the remote driving session without causing additional delays in the actual real-time remote driving control data flow. The application of the IOTA Tangle as the verifiable data registry was found to be sufficient for security control purposes. During the evaluations, the need for further studies related to scalability, application of wallets, dynamic trust situations, time-sensitive behaviour, and autonomous operations, as well as smart contract(s) between multiple stakeholders, were detected. As the next step of this research, the provided digital trust solutions will be integrated with a vehicle, remote driving system and traffic infrastructure for evaluation of the performance, reliability, scalability, and flexibility in real-world experiments of remote driving of an electric bus in an urban environment.
Full article
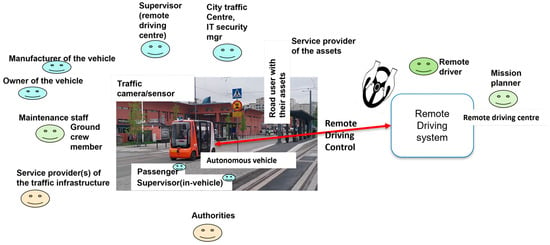
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A Smart Fire Detector IoT System with Extinguisher Class Recommendation Using Deep Learning
by
Tareq Khan
IoT 2023, 4(4), 558-581; https://doi.org/10.3390/iot4040024 - 25 Nov 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Fires kill and injure people, destroy residences, pollute the air, and cause economic loss. The damage of the fire can be reduced if we can detect the fire early and notify the firefighters as soon as possible. In this project, a novel Internet
[...] Read more.
Fires kill and injure people, destroy residences, pollute the air, and cause economic loss. The damage of the fire can be reduced if we can detect the fire early and notify the firefighters as soon as possible. In this project, a novel Internet of Things (IoT)-based fire detector device is developed that automatically detects a fire, recognizes the object that is burning, finds out the class of fire extinguisher needed, and then sends notifications with location information to the user and the emergency responders smartphones within a second. This will help firefighters to arrive quickly with the correct fire extinguisher—thus, the spread of fire can be reduced. The device detects fire using a thermal camera and common objects using a red-green-blue (RGB) camera with a deep-learning-based algorithm. When a fire is detected, the device sends data using the Internet to a central server, and it then sends notifications to the smartphone apps. No smoke detector or fire alarm is available in the literature that can automatically suggest the class of fire extinguisher needed, and this research fills this gap. Prototypes of the fire detector device, the central server for the emergency responder’s station, and smartphone apps have been developed and tested successfully.
Full article
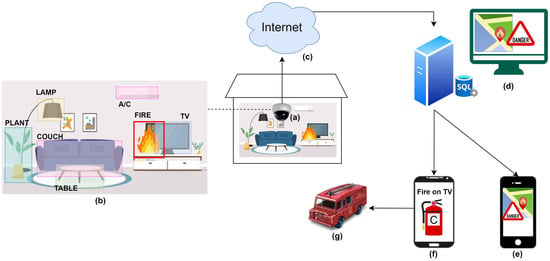
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Constraint-Aware Federated Scheduling for Data Center Workloads
by
Meghana Thiyyakat, Subramaniam Kalambur and Dinkar Sitaram
IoT 2023, 4(4), 534-557; https://doi.org/10.3390/iot4040023 - 08 Nov 2023
Abstract
The use of data centers is ubiquitous, as they support multiple technologies across domains for storing, processing, and disseminating data. IoT applications utilize both cloud data centers and edge data centers based on the nature of the workload. Due to the stringent latency
[...] Read more.
The use of data centers is ubiquitous, as they support multiple technologies across domains for storing, processing, and disseminating data. IoT applications utilize both cloud data centers and edge data centers based on the nature of the workload. Due to the stringent latency requirements of IoT applications, the workloads are run on hardware accelerators such as FPGAs and GPUs for faster execution. The introduction of such hardware alongside existing variations in the hardware and software configurations of the machines in the data center, increases the heterogeneity of the infrastructure. Optimal job performance necessitates the satisfaction of task placement constraints. This is accomplished through constraint-aware scheduling, where tasks are scheduled on worker nodes with appropriate machine configurations. The presence of placement constraints limits the number of suitable resources available to run a task, leading to queuing delays. As federated schedulers have gained prominence for their speed and scalability, we assess the performance of two such schedulers, Megha and Pigeon, within a constraint-aware context. We extend our previous work on Megha by comparing its performance with a constraint-aware version of the state-of-the-art federated scheduler Pigeon, PigeonC. The results of our experiments with synthetic and real-world cluster traces show that Megha reduces the 99th percentile of job response time delays by a factor of 10 when compared to PigeonC. We also describe enhancements made to Megha’s architecture to improve its scheduling efficiency.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Cloud and Edge Computing Systems for IoT)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A Novel Internet of Things-Based System for Ten-Pin Bowling
by
Ilias Zosimadis and Ioannis Stamelos
IoT 2023, 4(4), 514-533; https://doi.org/10.3390/iot4040022 - 31 Oct 2023
Abstract
Bowling is a target sport that is popular among all age groups with professionals and amateur players. Delivering an accurate and consistent bowling throw into the lane requires the incorporation of motion techniques. Consequently, this research presents a novel IoT Cloud-based system for
[...] Read more.
Bowling is a target sport that is popular among all age groups with professionals and amateur players. Delivering an accurate and consistent bowling throw into the lane requires the incorporation of motion techniques. Consequently, this research presents a novel IoT Cloud-based system for providing real-time monitoring and coaching services to bowling athletes. The system includes two inertial measurement units (IMUs) sensors for capturing motion data, a mobile application, and a Cloud server for processing the data. First, the quality of each phase of a throw is assessed using a Dynamic Time Warping (DTW)-based algorithm. Second, an on-device-level technique is proposed to identify common bowling errors. Finally, an SVM classification model is employed for assessing the skill level of bowler athletes. We recruited nine right-handed bowlers to perform 50 throws wearing the two sensors and using the proposed system. The results of our experiments suggest that the proposed system can effectively and efficiently assess the quality of the throw, detect common bowling errors, and classify the skill level of the bowler.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Machine Learning in Internet of Things)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Internet-of-Things Edge Computing Systems for Streaming Video Analytics: Trails Behind and the Paths Ahead
by
Arun A. Ravindran
IoT 2023, 4(4), 486-513; https://doi.org/10.3390/iot4040021 - 24 Oct 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The falling cost of IoT cameras, the advancement of AI-based computer vision algorithms, and powerful hardware accelerators for deep learning have enabled the widespread deployment of surveillance cameras with the ability to automatically analyze streaming video feeds to detect events of interest. While
[...] Read more.
The falling cost of IoT cameras, the advancement of AI-based computer vision algorithms, and powerful hardware accelerators for deep learning have enabled the widespread deployment of surveillance cameras with the ability to automatically analyze streaming video feeds to detect events of interest. While streaming video analytics is currently largely performed in the cloud, edge computing has emerged as a pivotal component due to its advantages of low latency, reduced bandwidth, and enhanced privacy. However, a distinct gap persists between state-of-the-art computer vision algorithms and the successful practical implementation of edge-based streaming video analytics systems. This paper presents a comprehensive review of more than 30 research papers published over the last 6 years on IoT edge streaming video analytics (IE-SVA) systems. The papers are analyzed across 17 distinct dimensions. Unlike prior reviews, we examine each system holistically, identifying their strengths and weaknesses in diverse implementations. Our findings suggest that certain critical topics necessary for the practical realization of IE-SVA systems are not sufficiently addressed in current research. Based on these observations, we propose research trajectories across short-, medium-, and long-term horizons. Additionally, we explore trending topics in other computing areas that can significantly impact the evolution of IE-SVA systems.
Full article
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
IoT-Applicable Generalized Frameproof Combinatorial Designs
by
Bimal Kumar Roy and Anandarup Roy
IoT 2023, 4(3), 466-485; https://doi.org/10.3390/iot4030020 - 21 Sep 2023
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Secret sharing schemes are widely used to protect data by breaking the secret into pieces and sharing them amongst various members of a party. In this paper, our objective is to produce a repairable ramp scheme that allows for the retrieval of a
[...] Read more.
Secret sharing schemes are widely used to protect data by breaking the secret into pieces and sharing them amongst various members of a party. In this paper, our objective is to produce a repairable ramp scheme that allows for the retrieval of a share through a collection of members in the event of its loss. Repairable Threshold Schemes (RTSs) can be used in cloud storage and General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) protocols. Secure and energy-efficient data transfer in sensor-based IoTs is built using ramp-type schemes. Protecting personal privacy and reinforcing the security of electronic identification (eID) cards can be achieved using similar schemes. Desmedt et al. introduced the concept of frameproofness in 2021, which motivated us to further improve our construction with respect to this framework. We introduce a graph theoretic approach to the design for a well-rounded and easy presentation of the idea and clarity of our results. We also highlight the importance of secret sharing schemes for IoT applications, as they distribute the secret amongst several devices. Secret sharing schemes offer superior security in lightweight IoT compared to symmetric key encryption or AE schemes because they do not disclose the entire secret to a single device, but rather distribute it among several devices.
Full article
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Challenges and Opportunities in the Internet of Intelligence of Things in Higher Education—Towards Bridging Theory and Practice
by
Raafat George Saadé, Jun Zhang, Xiaoyong Wang, Hao Liu and Hong Guan
IoT 2023, 4(3), 430-465; https://doi.org/10.3390/iot4030019 - 14 Sep 2023
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The application of the Internet of Things is increasing in momentum as advances in artificial intelligence exponentially increase its integration. This has caused continuous shifts in the Internet of Things paradigm with increasing levels of complexity. Consequently, researchers, practitioners, and governments continue facing
[...] Read more.
The application of the Internet of Things is increasing in momentum as advances in artificial intelligence exponentially increase its integration. This has caused continuous shifts in the Internet of Things paradigm with increasing levels of complexity. Consequently, researchers, practitioners, and governments continue facing evolving challenges, making it more difficult to adapt. This is especially true in the education sector, which is the focus of this article. The overall purpose of this study is to explore the application of IoT and artificial intelligence in education and, more specifically, learning. Our methodology follows four research questions. We first report the results of a systematic literature review on the Internet of Intelligence of Things (IoIT) in education. Secondly, we develop a corresponding conceptual model, followed thirdly by an exploratory pilot survey conducted on a group of educators from around the world to get insights on their knowledge and use of the Internet of Things in their classroom, thereby providing a better understanding of issues, such as knowledge, use, and their readiness to integrate IoIT. We finally present the application of the IoITE conceptual model in teaching and learning through four use cases. Our review of publications shows that research in the IoITE is scarce. This is even more so if we consider its application to learning. Analysis of the survey results finds that educators, in general, are lacking in their readiness to innovate with the Internet of Things in learning. Use cases highlight IoITE possibilities and its potential to explore and exploit. Challenges are identified and discussed.
Full article

Figure 1
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
AI, Algorithms, Computers, IoT, Mathematics
Modeling and Practice for Trustworthy and Secure Systems
Topic Editors: Ali Safaa Sadiq Al Shakarchi, Houbing Song, Ahmad Fadhil Yusof, Sushil Kumar, Omprakash KaiwartyaDeadline: 31 August 2024
Topic in
Applied Sciences, Electronics, IoT, Materials, Robotics, Sensors, Machines
Smart Production in Terms of Industry 4.0 and 5.0
Topic Editors: Iwona Paprocka, Cezary Grabowik, Jozef HusarDeadline: 31 October 2024
Topic in
Applied Sciences, Electronics, IoT, JSAN, Network, Sensors, Telecom, Technologies
Wireless Energy Harvesting and Power Transfer for Communications and Networks
Topic Editors: Yichuang Sun, Arooj Mubashara Siddiqui, Xiaojing Chen, Oluyomi SimpsonDeadline: 31 December 2024
Topic in
Energies, Sensors, Electronics, Smart Cities, IoT
IoT for Energy Management Systems and Smart Cities, 2nd Volume
Topic Editors: Antonio Cano-Ortega, Francisco Sánchez-SutilDeadline: 30 April 2025

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
IoT
Beyond 5G: Evolution of IoT with Intelligent Wireless Communication
Guest Editors: Lopamudra Kundu, Amiya Nayak, Xingqin LinDeadline: 15 May 2024
Special Issue in
IoT
6G Optical Internet of Things (OIoT) for Sustainable Smart Cities
Guest Editors: Geetika Aggarwal, Arooj Mubashara SiddiquiDeadline: 15 December 2024