Preparation of Nanocellulose-Based Aerogel and Its Research Progress in Wastewater Treatment
Abstract
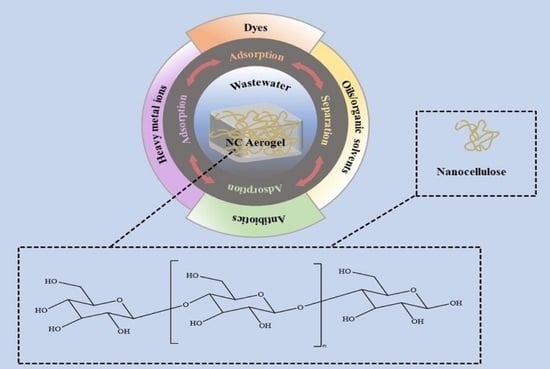
:1. Introduction
2. Preparation of a Nanocellulose-Based Aerogel
2.1. Preparation of Nanocellulose
2.2. Gelation of Nanocellulose
2.3. Solvent Substitution of Nanocellulose Wet Gel
2.4. Drying of Nanocellulose Wet Gel
3. Application of Nanocellulose-Based Aerogel in Wastewater Treatment
3.1. Adsorption of Dyes
3.2. Adsorption of Heavy Metal Ions
3.3. Adsorption of Antibiotics
3.4. Oil-Water Separation and Adsorption of Organic Solvents
4. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Garrick, D.E.; Hall, J.W.; Dobson, A.; Damania, R.; Grafton, R.Q.; Hope, R.; Hepburn, C.; Bark, R.; Boltz, F.; De Stefano, L. Valuing water for sustainable development. Science 2017, 358, 1003–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdellatif, F.H.H.; Abdellatif, M.M. Bio-based i-carrageenan aerogels as efficient adsorbents for heavy metal ions and acid dye from aqueous solution. Cellulose 2020, 27, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janani, R.; Gurunathan, B.; Sivakumar, K.; Varjani, S.; Ngo, H.H.; Gnansounou, E. Advancements in heavy metals removal from effluents employing nano-adsorbents: Way towards cleaner production. Environ. Res. 2022, 203, 111815. [Google Scholar]
- Lima, E.C. Removal of emerging contaminants from the environment by adsorption. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 150, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Bhatia, D.; Sharma, N.R.; Singh, J.; Kanwar, R.S. Biological methods for textile dye removal from wastewater: A review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 47, 1836–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, M.; Saha, R. Dyes and their removal technologies from wastewater: A critical review. Intell. Environ. Data Monit. Pollut. Manag. 2021, 2021, 127–160. [Google Scholar]
- Hokkanen, S.; Bhatnagar, A.; Sillanpää, M. A review on modification methods to cellulose-based adsorbents to improve adsorption capacity. Water Res. 2016, 91, 156–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahfoudhi, N.; Boufi, S. Nanocellulose as a novel nanostructured adsorbent for environmental remediation: A review. Cellulose 2017, 24, 1171–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanpour, M.; Hatami, M. Application of three dimensional porous aerogels as adsorbent for removal of heavy metal ions from water/wastewater: A review study. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 284, 102247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Ma, W.; Han, D.; Gan, S.; Dong, X.; Niu, L. Convenient recycling of 3D AgX/graphene aerogels (X= Br, Cl) for efficient photocatalytic degradation of water pollutants. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 3767–3773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-González, C.A.; Alnaief, M.; Smirnova, I. Polysaccharide-based aerogels—Promising biodegradable carriers for drug delivery systems. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 86, 1425–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kistler, S.S. Coherent expanded aerogels and jellies. Nature 1931, 127, 741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-G.; Zhu, Y.-J.; Xiong, Z.-C.; Wu, J.; Chen, F. Bioinspired ultralight inorganic aerogel for highly efficient air filtration and oil–water separation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 13019–13027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Ran, Y.; Xi, J.; Wang, J. Polymeric hybrid aerogels and their biomedical applications. Soft Matter 2020, 16, 9160–9175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, L.; Si, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wang, X.; Yu, J.; Ding, B. Ultralight, superelastic and bendable lashing-structured nanofibrous aerogels for effective sound absorption. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 2289–2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, M.; Wang, H.; Yan, N.; Cai, Z.; Yu, Y. Ultralight, hydrophobic, anisotropic bamboo-derived cellulose nanofibrils aerogels with excellent shape recovery via freeze-casting. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 208, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Xie, Y.; Liang, H.; Wang, Y.; Ge, T.; Song, Y.; Wang, M.; Li, Q.; Yu, H.; Fan, Z. Lightweight, flexible, thermally-stable, and thermally-insulating aerogels derived from cotton nanofibrillated cellulose. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 9202–9210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.; Heo, S.; Foo, M.; Chew, I.M.; Yoo, C. An insight into nanocellulose as soft condensed matter: Challenge and future prospective toward environmental sustainability. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 1309–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kargarzadeh, H.; Mariano, M.; Gopakumar, D.; Ahmad, I.; Thomas, S.; Dufresne, A.; Huang, J.; Lin, N. Advances in cellulose nanomaterials. Cellulose 2018, 25, 2151–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Zhao, J.; Wu, X.; Yao, W.; Guo, H.; Ji, D.; Yu, Q.; Luo, L.; Li, X.; Zhang, L. Extraction of Corn Bract Cellulose by the Ammonia-Coordinated Bio-Enzymatic Method. Polymers 2022, 15, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abitbol, T.; Rivkin, A.; Cao, Y.; Nevo, Y.; Abraham, E.; Ben-Shalom, T.; Lapidot, S.; Shoseyov, O. Nanocellulose, a tiny fiber with huge applications. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2016, 39, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bian, H.; Luo, J.; Wang, R.; Zhou, X.; Ni, S.; Shi, R.; Fang, G.; Dai, H. Recyclable and reusable maleic acid for efficient production of cellulose nanofibrils with stable performance. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 20022–20031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badshah, M.; Ullah, H.; Khan, S.A.; Park, J.K.; Khan, T. Preparation, characterization and in-vitro evaluation of bacterial cellulose matrices for oral drug delivery. Cellulose 2017, 24, 5041–5052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picheth, G.F.; Pirich, C.L.; Sierakowski, M.R.; Woehl, M.A.; Sakakibara, C.N.; de Souza, C.F.; Martin, A.A.; da Silva, R.; de Freitas, R.A. Bacterial cellulose in biomedical applications: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 104, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, H.; Dong, M.; Chen, L.; Zhou, X.; Wang, R.; Jiao, L.; Ji, X.; Dai, H. On-demand regulation of lignocellulosic nanofibrils based on rapid fractionation using acid hydrotrope: Kinetic study and characterization. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 9569–9577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, H.; Chen, L.; Dong, M.; Wang, L.; Wang, R.; Zhou, X.; Wu, C.; Wang, X.; Ji, X.; Dai, H. Natural lignocellulosic nanofibril film with excellent ultraviolet blocking performance and robust environment resistance. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 166, 1578–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Saito, T.; Isogai, A. Aerogels with 3D ordered nanofiber skeletons of liquid-crystalline nanocellulose derivatives as tough and transparent insulators. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 10394–10397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibi, Y.; Lucia, L.A.; Rojas, O.J. Cellulose nanocrystals: Chemistry, self-assembly, and applications. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 3479–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemm, D.; Kramer, F.; Moritz, S.; Lindström, T.; Ankerfors, M.; Gray, D.; Dorris, A. Nanocelluloses: A new family of nature-based materials. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 5438–5466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorgieva, S.; Trček, J. Bacterial cellulose: Production, modification and perspectives in biomedical applications. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakutsah, K.; Aht-Ong, D. Facile isolation of cellulose nanofibers from water hyacinth using water-based mechanical defibrillation: Insights into morphological, physical, and rheological properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 145, 64–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, J.; Zhu, E.; Zhu, H.; Liu, D.; Cai, H.; Xiong, C.; Yang, Q.; Shi, Z. Dye adsorption performance of nanocellulose beads with different carboxyl group content. Cellulose 2022, 30, 1623–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Liu, Y.; Chen, G. A comparative study on the starch-based biocomposite films reinforced by nanocellulose prepared from different non-wood fibers. Cellulose 2019, 26, 2425–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Liu, X.; Qu, J.; Yang, S.; Wang, A.; Wang, C.; Wei, B.; Xu, J.; Ni, Y. Preparation and characterization of lignin-containing cellulose nanofibril from poplar high-yield pulp via TEMPO-mediated oxidation and homogenization. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 6131–6139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Wu, Q.; Ren, S.; Lei, T. Comparison of highly transparent all-cellulose nanopaper prepared using sulfuric acid and TEMPO-mediated oxidation methods. Cellulose 2015, 22, 1123–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coseri, S.; Biliuta, G.; Simionescu, B.C.; Stana-Kleinschek, K.; Ribitsch, V.; Harabagiu, V. Oxidized cellulose—Survey of the most recent achievements. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 93, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlsson, D.O.; Lindh, J.; Nyholm, L.; Strømme, M.; Mihranyan, A. Cooxidant-free TEMPO-mediated oxidation of highly crystalline nanocellulose in water. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 52289–52298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriksson, M.; Henriksson, G.; Berglund, L.; Lindström, T. An environmentally friendly method for enzyme-assisted preparation of microfibrillated cellulose (MFC) nanofibers. Eur. Polym. J. 2007, 43, 3434–3441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhena, T.C.; John, M.J. Cellulose nanomaterials: New generation materials for solving global issues. Cellulose 2020, 27, 1149–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibi, Y.; Dufresne, A. Highly filled bionanocomposites from functionalized polysaccharide nanocrystals. Biomacromolecules 2008, 9, 1974–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wu, X.; Yuan, X.; Yang, X.; Guo, H.; Yao, W.; Ji, D.; Li, X.; Zhang, L. Nanocellulose and Cellulose Making with Bio-Enzymes from Different Particle Sizes of Neosinocalamus Affinis. Coatings 2022, 12, 1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.-M.; Yu, H.-Y.; Wang, D.-C.; Mao, Z.-H.; Yao, J.; Tam, K.C. Facile and green synthesis of carboxylated cellulose nanocrystals as efficient adsorbents in wastewater treatments. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 18067–18075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Yuan, X.; Zhao, J.; Ji, D.; Guo, H.; Yao, W.; Li, X.; Zhang, L. Study on the effects of different pectinase/cellulase ratios and pretreatment times on the preparation of nanocellulose by ultrasound-assisted bio-enzyme heat treatment. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 5149–5157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rana, A.K.; Frollini, E.; Thakur, V.K. Cellulose nanocrystals: Pretreatments, preparation strategies, and surface functionalization. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 182, 1554–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zhang, F.; Zhong, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Gao, P.; Tian, F.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, R.; Cullen, P.J. Emerging Food Packaging Applications of Cellulose Nanocomposites: A Review. Polymers 2022, 14, 4025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kargupta, W.; Seifert, R.; Martinez, M.; Olson, J.; Tanner, J.; Batchelor, W. Sustainable production process of mechanically prepared nanocellulose from hardwood and softwood: A comparative investigation of refining energy consumption at laboratory and pilot scale. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 171, 113868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellebracht, N.C.; Jones, C.W. Amine functionalization of cellulose nanocrystals for acid–base organocatalysis: Surface chemistry, cross-linking, and solvent effects. Cellulose 2018, 25, 6495–6512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeasmin, M.S.; Mondal, M.I.H. Synthesis of highly substituted carboxymethyl cellulose depending on cellulose particle size. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 80, 725–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patoary, M.K.; Farooq, A.; Zaarour, B.; Liu, L. Phosphorylated cellulose nanofibrils: Structure-morphology-rheology relationships. Cellulose 2021, 28, 4105–4117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.; Liu, R.; Duan, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, Q. A simultaneous strategy for the preparation of acetylation modified cellulose nanofiber/polypropylene composites. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 277, 118744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, K.; Saito, Y.; Akiyoshi, M.; Endo, T.; Matsunaga, T. Preparation and characterization of nitrocellulose nanofiber. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 2021, 46, 962–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henschen, J.; Li, D.; Ek, M. Preparation of cellulose nanomaterials via cellulose oxalates. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 213, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhan, P.; Liu, N.; Wu, Z. Preparation of nanocellulose from steam exploded poplar wood by enzymolysis assisted sonication. Mater. Res. Express 2020, 7, 035010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, P.; Wu, Z.; Xing, C.; Zhang, Q.; Wei, Z.; Nie, S. Effect of enzymatic treatment on the thermal stability of cellulose nanofibrils. Cellulose 2019, 26, 7717–7725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, S.; Zhang, K.; Lin, X.; Zhang, C.; Yan, D.; Liang, H.; Wang, S. Enzymatic pretreatment for the improvement of dispersion and film properties of cellulose nanofibrils. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 181, 1136–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kassab, Z.; Syafri, E.; Tamraoui, Y.; Hannache, H.; El Achaby, M. Characteristics of sulfated and carboxylated cellulose nanocrystals extracted from Juncus plant stems. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 154, 1419–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasheed, M.; Jawaid, M.; Parveez, B.; Zuriyati, A.; Khan, A. Morphological, chemical and thermal analysis of cellulose nanocrystals extracted from bamboo fibre. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 160, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatenholm, P.; Klemm, D. Bacterial nanocellulose as a renewable material for biomedical applications. MRS Bull. 2010, 35, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevanic, J.S.; Joly, C.; Mikkonen, K.S.; Pirkkalainen, K.; Serimaa, R.; Rémond, C.; Toriz, G.; Gatenholm, P.; Tenkanen, M.; Salmén, L. Bacterial nanocellulose-reinforced arabinoxylan films. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2011, 122, 1030–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salari, M.; Khiabani, M.S.; Mokarram, R.R.; Ghanbarzadeh, B.; Kafil, H.S. Preparation and characterization of cellulose nanocrystals from bacterial cellulose produced in sugar beet molasses and cheese whey media. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 122, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Xu, S.; Ge, X.; Tan, L.; Liu, T. Low-cost and highly efficient production of bacterial cellulose from sweet potato residues: Optimization, characterization, and application. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 196, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Geng, B.; Chen, Y.; Wang, H. Review on the aerogel-type oil sorbents derived from nanocellulose. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 49–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, L.-Y.; Weng, Y.-X.; Wang, Y.-Z. Cellulose aerogels: Synthesis, applications, and prospects. Polymers 2018, 10, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Sun, B.; Yuan, Z.; Liu, Y. Regenerated cellulose microgel: A promising reinforcing agent and gelator for soft matter. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2021, 3, 4101–4108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, H.; Fei, Y.; Cheng, J.; Wang, C.; Zhang, J.; Niu, C.; Fu, Q.; Cheng, J.; Lu, L. Green Preparation of Durian Rind-Based Cellulose Nanofiber and Its Application in Aerogel. Molecules 2022, 27, 6507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaheed, N.; Javanshir, S.; Esmkhani, M.; Dekamin, M.G.; Naimi-Jamal, M.R. Synthesis of nanocellulose aerogels and Cu-BTC/nanocellulose aerogel composites for adsorption of organic dyes and heavy metal ions. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 18553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heath, L.; Thielemans, W. Cellulose nanowhisker aerogels. Green Chem. 2010, 12, 1448–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Wu, Y.; Han, M.; You, J.; Jia, C.; Kim, J. Aerogel nanoarchitectonics based on cellulose nanocrystals and nanofibers from eucalyptus pulp: Preparation and comparative study. Cellulose 2022, 29, 817–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.; Sathwane, M.; Chhajed, M.; Verma, C.; Grohens, Y.; Seantier, B.; Agrawal, A.K.; Maji, P.K. Surfactant Assisted In Situ Synthesis of Nanofibrillated Cellulose/Polymethylsilsesquioxane Aerogel for Tuning Its Thermal Performance. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2023, 44, 2200628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.Y.; Liang, H.W.; Hu, B.C.; Yu, S.H. Emerging carbon-nanofiber aerogels: Chemosynthesis versus biosynthesis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 15646–15662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Shamshina, J.L.; Berton, P.; Gurau, G.; Rogers, R.D. Hydrogels based on cellulose and chitin: Fabrication, properties, and applications. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 53–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, M.; Li, Y.; Yu, H.-Y.; Li, Z.; Cao, Y.; Chen, X. Construction of nanocellulose aerogels with mechanical flexibility and pH-responsive properties via a cross-linker structure design strategy. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 9951–9960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, J.-Q.; Xie, K.-Y.; Li, Z.; Zuo, X.; Guo, W.; Chen, Q.-Y.; Li, H.; Fei, C.; Lu, M.-H. Multifunctional ultralight nanocellulose aerogels as excellent broadband acoustic absorption materials. J. Mater. Sci. 2023, 58, 971–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surapolchai, W.; Schiraldi, D.A. The effects of physical and chemical interactions in the formation of cellulose aerogels. Polym. Bull. 2010, 65, 951–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Grishkewich, N.; Liu, L.; Wang, C.; Tam, K.C.; Liu, S.; Mao, Z.; Sui, X. Construction of functional cellulose aerogels via atmospheric drying chemically cross-linked and solvent exchanged cellulose nanofibrils. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 366, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Lv, P.; Feng, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, H.; Alfred, M.; Wei, Q. Biomass-derived nanocellulose aerogel enable highly efficient immobilization of laccase for the degradation of organic pollutants. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 356, 127311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, M.; Zhang, J. Gas phase synthesis of aminated nanocellulose aerogel for carbon dioxide adsorption. Cellulose 2020, 27, 2953–2958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciftci, D.; Ubeyitogullari, A.; Huerta, R.R.; Ciftci, O.N.; Flores, R.A.; Saldaña, M.D. Lupin hull cellulose nanofiber aerogel preparation by supercritical CO2 and freeze drying. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2017, 127, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Tan, S.; Xu, Z. Anisotropic nanocellulose aerogel loaded with modified uio-66 as efficient adsorbent for heavy metal ions removal. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Sun, M.; Wu, X.; Shi, T.; Chen, H.; Wang, H. Preparation of nanocellulose aerogel from the poplar (Populus tomentosa) catkin fiber. Forests 2019, 10, 749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Guo, X.; Lei, W.; Ding, R.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, H. Facile Preparation of Cellulose Aerogels with Controllable Pore Structure. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, H.; Song, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Zhao, H. Tert-butyl alcohol used to fabricate nano-cellulose aerogels via freeze-drying technology. Mater. Res. Express 2017, 4, 065006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Cranston, E.D. Chemically cross-linked cellulose nanocrystal aerogels with shape recovery and superabsorbent properties. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 6016–6025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, H.; Song, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Zhao, H. Fabrication and characterization of nano-cellulose aerogels via supercritical CO2 drying technology. Mater. Lett. 2016, 183, 179–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Wang, S.; He, C.; Lu, Z.; Huang, J.; Chen, Z. Facilitated fabrication of high strength silica aerogels using cellulose nanofibrils as scaffold. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 147, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Tanna, V.A.; Zhou, Y.; Winter, H.H.; Watkins, J.J.; Carter, K.R. Nanocellulose aerogels inspired by frozen tofu. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 6387–6391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, P.; Duan, Y.; Jiang, M.; Zhang, J. Graphene/cellulose nanocrystals hybrid aerogel with tunable mechanical strength and hydrophilicity fabricated by ambient pressure drying technique. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 16467–16473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pour, G.; Beauger, C.; Rigacci, A.; Budtova, T. Xerocellulose: Lightweight, porous and hydrophobic cellulose prepared via ambient drying. J. Mater. Sci. 2015, 50, 4526–4535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Malfait, W.J.; Guerrero-Alburquerque, N.; Koebel, M.M.; Nyström, G. Biopolymer aerogels and foams: Chemistry, properties, and applications. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 7580–7608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul Khalil, H.; Adnan, A.; Yahya, E.B.; Olaiya, N.; Safrida, S.; Hossain, M.S.; Balakrishnan, V.; Gopakumar, D.A.; Abdullah, C.; Oyekanmi, A. A review on plant cellulose nanofibre-based aerogels for biomedical applications. Polymers 2020, 12, 1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F. Starch based aerogels: Production, properties and applications. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 89, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Ching, Y.C.; Chuah, C.H. Preparation of aerogel beads and microspheres based on chitosan and cellulose for drug delivery: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 170, 751–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rigueto, C.V.T.; Nazari, M.T.; Massuda, L.Á.; Ostwald, B.E.P.; Piccin, J.S.; Dettmer, A. Production and environmental applications of gelatin-based composite adsorbents for contaminants removal: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 2465–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alguacil, F.J.; López, F.A. Organic dyes versus adsorption processing. Molecules 2021, 26, 5440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, D.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, S.; Chen, Q.; Wang, C.; Wu, T.; Xu, M. Adsorptive removal of organic dyes via porous materials for wastewater treatment in recent decades: A review on species, mechanisms and perspectives. Chemosphere 2021, 293, 133464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Pu, J. Facile fabrication of an effective nanocellulose-based aerogel and removal of methylene blue from aqueous system. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 37, 101511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.; Zou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Du, Z.; Cheng, X. Mechanically robust sodium alginate/cellulose nanofibers/polyethyleneimine composite aerogel for effective removal of hexavalent chromium and anionic dyes. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2022, 62, 1927–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Hu, C.; Dichiara, A.B.; Jiang, W.; Gu, J. Cellulose nanofibril/carbon nanomaterial hybrid aerogels for adsorption removal of cationic and anionic organic dyes. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maatar, W.; Boufi, S. Microporous cationic nanofibrillar cellulose aerogel as promising adsorbent of acid dyes. Cellulose 2017, 24, 1001–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yang, J.; Du, H.; Qin, C.; Liu, H. Polydopamine-modified cellulose nanofibril composite aerogel: An effective dye adsorbent. Langmuir 2022, 38, 4164–4174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grishkewich, N.; Li, Y.; Liu, K.; Tam, K.C. Synthesis and characterization of modified cellulose nanofibril organosilica aerogels for the removal of anionic dye. J. Polym. Res. 2022, 29, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.; Wang, F.; Wu, Y.; He, J.; Huang, Y. Aramid nanofibers/bacterial cellulose nanocomposite aerogels for high-efficient cationic dye removal. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2021, 272, 124985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nia, M.H.; Tavakolian, M.; Kiasat, A.R.; van de Ven, T.G. Hybrid aerogel nanocomposite of dendritic colloidal silica and hairy nanocellulose: An effective dye adsorbent. Langmuir 2020, 36, 11963–11974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Dinh, D.M.; Hsieh, Y.-L. Adsorption and desorption of cationic malachite green dye on cellulose nanofibril aerogels. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 173, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhan, Y.; Gong, Y.; Ren, E.; Lan, J.; Guo, R.; Yan, B.; Chen, S.; Lin, S. Development of eco-friendly CO2-responsive cellulose nanofibril aerogels as “green” adsorbents for anionic dyes removal. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 405, 124194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, N.; Huang, L.-Y.; Xiong, Y.-S.; Tian, R.; Yin, J.-Y.; Cao, D.-Y.; Hu, D.-B.; Lu, H.-Q.; Li, W.; Li, K. Micro-mechanism insights into the adsorption of anionic dyes using quaternary ammonium-functionalised chitosan aerogels. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 313, 120855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, J.; Cai, T.; Dai, J.; Yao, L.; Liu, F.; Liu, Y.; Shu, J.; Fan, J.; Peng, H. High strength chitin/chitosan-based aerogel with 3D hierarchically macro-meso-microporous structure for high-efficiency adsorption of Cu (II) ions and Congo red. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 230, 123238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, S.; Mu, M.; Wang, L.; Fan, Y.; Liu, X. Eco-friendly ferrocene-functionalized chitosan aerogel for efficient dye degradation and phosphate adsorption from wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 439, 135605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, C.; Zhang, N.; Hu, C.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, H.; Xing, Y. Preparation of a novel citric acid-crosslinked Zn-MOF/chitosan composite and application in adsorption of chromium (VI) and methyl orange from aqueous solution. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 258, 117644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Zang, G.-L.; Shi, C.; Yu, H.-Q.; Sheng, G.-P. A novel adsorbent TEMPO-mediated oxidized cellulose nanofibrils modified with PEI: Preparation, characterization, and application for Cu (II) removal. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 316, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, Y.; Hu, Y.H. Design, synthesis, and performance of adsorbents for heavy metal removal from wastewater: A review. J. Mater. Chem. A 2022, 10, 1047–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.-Y.; Cui, Z.-M.; Chen, C.-Q.; Song, W.-G.; Cai, W. Ceria hollow nanospheres produced by a template-free microwave-assisted hydrothermal method for heavy metal ion removal and catalysis. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 9865–9870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zito, P.; Shipley, H.J. Inorganic nano-adsorbents for the removal of heavy metals and arsenic: A review. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 29885–29907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, R.; Asthana, A.; Singh, A.K.; Jain, B.; Susan, A.B.H. Adsorption of heavy metal ions by various low-cost adsorbents: A review. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2022, 102, 342–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, B.; Déon, S.; Morin-Crini, N.; Crini, G.; Fievet, P. Polymer-enhanced ultrafiltration for heavy metal removal: Influence of chitosan and carboxymethyl cellulose on filtration performances. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 171, 927–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, B.; Xu, Z.; Liang, P.; Zhang, J.; Christie, P.; Liu, H.; Wu, S.; Liu, X. Three-dimensional macroscopic aminosilylated nanocellulose aerogels as sustainable bio-adsorbents for the effective removal of heavy metal ions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 190, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, L.; Zhang, S.; Qi, F.; Huang, A. Highly stable cellulose nanofiber/polyacrylamide aerogel via in-situ physical/chemical double crosslinking for highly efficient Cu (II) ions removal. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 209, 1922–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Shao, L.; Jia, M. Shape memory and underwater superelastic mof@ cellulose aerogels for rapid and large-capacity adsorption of metal ions. Cellulose 2022, 29, 8243–8254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zuo, K.; Wu, W.; Xu, Z.; Yi, Y.; Jing, Y.; Dai, H.; Fang, G. Shape memory aerogels from nanocellulose and polyethyleneimine as a novel adsorbent for removal of Cu (II) and Pb (II). Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 196, 376–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.-M.; An, Q.-D.; Xiao, Z.-Y.; Zhai, S.-R.; Shi, Z. Polyethylenimine-functionalized cellulose aerogel beads for efficient dynamic removal of chromium (VI) from aqueous solution. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 54039–54052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.-J.; Ban, G.; Kim, H.S.; Jeong, H.S.; Park, M.S. Fabrication of cylindrical 3D cellulose nanofibril (CNF) aerogel for continuous removal of copper (Cu2+) from wastewater. Chemosphere 2021, 278, 130288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; Yang, Z.; Sun, Y.; Wang, C.; Fan, J.; Kang, G.; Zhang, R.; Dong, X.; Li, Y. Nanocellulose-based magnetic hybrid aerogel for adsorption of heavy metal ions from water. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 6709–6718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, C.; Gao, J.; Ren, W.; Xie, Y.; Abdalkarim, S.Y.H.; Wang, S.; Ni, Q.; Yao, J. Fabrication of metal-organic frameworks@ cellulose aerogels composite materials for removal of heavy metal ions in water. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 205, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Y.; Li, W. Nanocellulose aerogel for highly efficient adsorption of uranium (VI) from aqueous solution. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 267, 118233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Tang, C.; Fu, S.; Tam, K.C.; Zong, Y. Cellulose-based aerogel beads for efficient adsorption-reduction-sequestration of Cr (VI). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 216, 860–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahnaz, T.; Sharma, V.; Subbiah, S.; Narayanasamy, S. Multivariate optimisation of Cr (VI), Co (III) and Cu (II) adsorption onto nanobentonite incorporated nanocellulose/chitosan aerogel using response surface methodology. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 36, 101283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Tian, Y.; Kong, L.; Zhang, J.; Zuo, W.; Li, Y.; Cai, G. A novel 3D superelastic polyethyleneimine functionalized chitosan aerogels for selective removal of Cr (VI) from aqueous solution: Performance and mechanisms. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 425, 131722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghiorghita, C.-A.; Lazar, M.M.; Platon, I.-V.; Humelnicu, D.; Doroftei, F.; Dinu, M.V. Feather-weight cryostructured thiourea-chitosan aerogels for highly efficient removal of heavy metal ions and bacterial pathogens. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 235, 123910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Shao, L.; Ruan, Z.; Hu, W.; Lu, L.; Chen, Y. Converting untreated waste office paper and chitosan into aerogel adsorbent for the removal of heavy metal ions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 193, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, Y.; Fu, Z.; Lu, L.; Cheng, J.; Fei, Y. A ‘top modification’strategy for enhancing the ability of a chitosan aerogel to efficiently capture heavy metal ions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 594, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Shang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Cui, S.; Zhong, Y.; Huang, L. Ultra-efficient adsorption of copper ions in chitosan–montmorillonite composite aerogel at wastewater treatment. Cellulose 2021, 28, 7201–7212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eniola, J.O.; Kumar, R.; Barakat, M.A. Adsorptive removal of antibiotics from water over natural and modified adsorbents. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 34775–34788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Song, W.; Lin, H.; Wang, W.; Du, L.; Xing, W. Antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes in global lakes: A review and meta-analysis. Environ. Int. 2018, 116, 60–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, Y.; You, Q.; Wang, Q.; Liao, G.; Wang, D. Highly efficient removal of antibiotics and dyes from water by the modified carbon nanofibers composites with abundant mesoporous structure. Colloids Surf., A 2018, 558, 392–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q.; Fan, B.; Xiong, Y.; Jin, C.; Sun, Q.; Sheng, C. 3D assembly based on 2D structure of cellulose nanofibril/graphene oxide hybrid aerogel for adsorptive removal of antibiotics in water. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yao, Q.; Sheng, C.; Jin, C.; Sun, Q. One-step preparation of graphene oxide/cellulose nanofibril hybrid aerogel for adsorptive removal of four kinds of antibiotics. J. Nanomater. 2017, 2017, 5150613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Song, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.-F.; Yao, J. Construction of a hybrid graphene oxide/nanofibrillated cellulose aerogel used for the efficient removal of methylene blue and tetracycline. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2021, 150, 109839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Zheng, H.; Zeng, T.; Yang, J.; Fang, X.; Zhang, C. Porous carbon aerogel derived from bacterial cellulose with prominent potential for efficient removal of antibiotics from the aquatic matrix. Water Sci. Technol. 2021, 84, 1896–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Yu, H.; Zeng, F.; Li, X.; Sun, J.; Hu, X.; Pan, Q.; Li, C.; Lin, H.; min Su, Z. Polyaniline as interface layers promoting the in-situ growth of zeolite imidazole skeleton on regenerated cellulose aerogel for efficient removal of tetracycline. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 579, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, F.; Li, H.; Chen, C.; Wang, Z.; Liu, X.; Jiang, G.; Cheng, T.; Bai, R.; Song, L. Cattail fibers as source of cellulose to prepare a novel type of composite aerogel adsorbent for the removal of enrofloxacin in wastewater. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 191, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, C.; Chen, G.; Ma, Y.; Du, C.; He, C.; Liu, X.; Jin, X.; Chen, Q.; He, S.; Huang, Y. PVA-assisted CNCs/SiO2 composite aerogel for efficient sorption of ciprofloxacin. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 630, 544–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Dong, P.; Xie, J.; Li, J.; Wu, L.; Yang, S.-T.; Luo, J. Porous graphene oxide–chitosan aerogel for tetracycline removal. Mater. Res. Express 2013, 1, 015601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, Y.; Li, M.; Sun, Y.; Wang, H.; Cui, M.; Xu, W. Adsorption of tetracycline by Nicandra physaloides (L.) Gaertn seed gum and Nicandra physaloides (L.) Gaertn seed gum/Carboxymethyl chitosan aerogel. Environ. Technol. 2022, 43, 4237–4248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Lei, Y.; Khan, M.A.; Wang, F.; Chu, Y.; Lei, W.; Xia, M.; Zhu, S. Adsorption properties, kinetics & thermodynamics of tetracycline on carboxymethyl-chitosan reformed montmorillonite. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 124, 557–567. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, T.; Li, G.; He, Y.; Duan, P. Hybrid carbon nanotubes/graphene/nickel fluffy spheres for fast magnetic separation and efficient removal of organic solvents from water. Mater. Lett. 2019, 254, 440–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motta, F.L.; Stoyanov, S.R.; Soares, J.B. Application of solidifiers for oil spill containment: A review. Chemosphere 2018, 194, 837–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelova, D.; Uzunov, I.; Uzunova, S.; Gigova, A.; Minchev, L. Kinetics of oil and oil products adsorption by carbonized rice husks. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 172, 306–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhlamadi, G.; Goharshadi, E.K. Sustainable and superhydrophobic cellulose nanocrystal-based aerogel derived from waste tissue paper as a sorbent for efficient oil/water separation. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2021, 154, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosli, N.A.; Khairudin, F.A.; Kargarzadeh, H.; Othaman, R.; Ahmad, I. Hydrophobic-oleophilic gamma-irradiated modified cellulose nanocrystal/gelatin aerogel for oil absorption. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 219, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Xu, G.; Xu, Y.; Wang, F.; Shen, H. Ultralight, hydrophobic, sustainable, cost-effective and floating kapok/microfibrillated cellulose aerogels as speedy and recyclable oil superabsorbents. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 406, 124758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Xie, Z.; Chen, Z.; Jiang, H. Hydrophobic and lipophilic cellulose nanocrystal aerogel prepared by methyltrichlorosilane via vapor-phase reaction. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2022, 139, e53045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, A.; Huang, R.; Penkova, A.; Qi, W.; He, Z.; Su, R. Superhydrophobic, elastic and anisotropic cellulose nanofiber aerogels for highly effective oil/water separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 295, 121266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, H.-Y.; Li, H.; Jing, X.; Zhang, Q.; Feng, P.-Y.; He, P.; Liu, Y. Superhydrophobic cellulose nanofibril/silica fiber/Fe3O4 nanocomposite aerogel for magnetically driven selective oil absorption. Cellulose 2020, 27, 8909–8922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Feng, Q.; Chen, C.; Xu, Z. Preparation of antifouling and highly hydrophobic cellulose nanofibers/alginate aerogels by bidirectional freeze-drying for water-oil separation in the ocean environment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 441, 129965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, G.; Zhu, H.; Wang, F.; Xu, G.; Shen, H.; Wang, J. Multiscale kapok/cellulose aerogels for oil absorption: The study on structure and oil absorption properties. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 171, 113902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Gao, C.; Zhou, X.; Du, A.; Naik, N.; Guo, Z. Nanocellulose nanocomposite aerogel towards efficient oil and organic solvent adsorption. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2021, 4, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Shao, C.; Zhou, S.; Yang, J.; Xu, F. Preparation of carbon aerogels from TEMPO-oxidized cellulose nanofibers for organic solvents absorption. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 38220–38230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Han, Y.; Xing, X.; Zhu, H.; Wang, Q.; Wang, X. Preparation of micro-convex rough interface carbon aerogels with cellulose-lithium bromide (LiBr) molten salt hydrate gelled system and application of oil-water separation. Colloids Surf. A 2022, 650, 129624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Fu, Q.; Liu, H.; Gu, H.; Guo, Z. Solvent-free nanoalumina loaded nanocellulose aerogel for efficient oil and organic solvent adsorption. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 581, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhajed, M.; Verma, C.; Singh, S.; Maji, P.K. Synergistic effect of natural rubber for imparting hydrophobicity in nanocellulose aerogel through one-pot synthesis and its application in oil/organic solvent sorption. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 51, 103471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, B.; Qi, B.; Wang, P.; Liu, Y.; Yu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Ren, X. Mechanically Tough and Regenerable Antibacterial Nanofibrillated Cellulose-Based Aerogels for Oil/Water Separation. Langmuir 2022, 38, 10716–10727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Jiang, S.; Li, M.; Wang, N.; Liu, L.; Liu, L.; Ge, A. Superior stable, hydrophobic and multifunctional nanocellulose hybrid aerogel via rapid UV induced in-situ polymerization. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 288, 119370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Yin, M.; Li, L.; Fan, B.; Liu, Y.; Li, R.; Ren, X.; Huang, T.-S.; Kim, I.S. Construction of aerogels based on nanocrystalline cellulose and chitosan for high efficient oil/water separation and water disinfection. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 243, 116461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, S.; Li, Z.; Fan, C.; Chen, J.; Huang, H.; Chen, G.; Liu, S.; Zhou, H.; Liu, R.; Feng, Z. Fast-thermoresponsive carboxylated carbon nanotube/chitosan aerogels with switchable wettability for oil/water separation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 433, 128808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Lin, R.; Lin, C.; He, B.; Zheng, T.; Lu, L.; Cao, Y. An environment-friendly and multi-functional absorbent from chitosan for organic pollutants and heavy metal ion. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 148, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.; Jiang, X.; Wang, J.; Hu, R. Degradable composite aerogel with excellent water-absorption for trace water removal in oil and oil-in-water emulsion filtration. Front. Mater. 2022, 9, 1093164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Category | Source | Preparation Method | Advantages | Disadvantages | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cellulose nanocrystals (CNC) | Cellulose | Acid hydrolysis High-shear mechanical stripping | High specific surface area High mechanical properties Biodegradable | Higher production costs Easy to gather | [28] |
| Cellulose nanofilaments (CNF) | Cellulose | Acid hydrolysis High-shear mechanical stripping Biological preparation chemical oxidative stripping | High specific surface area High mechanical properties Biodegradable Can be prepared into a variety of forms | Higher production costs Easy to gather | [29] |
| Bacterial cellulose (BC) | Natural cellulose material synthesized by microbial growth | Extraction from cultures by chemical and physical methods | Biodegradable Can be prepared in a variety of forms | Higher production cost Poorer mechanical properties | [30] |
| Preparation Method | Advantages | Disadvantages | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mechanical preparation | Simple operation No chemical reagents are required | Limited production capacity Requiring high energy consumption equipment | [38] |
| Chemical preparation | Can precisely control the structure and morphology of the product | The use of chemical reagents is harmful to the human body High environmental impact | [39] |
| Bio-enzyme preparation | The production process is environmentally friendly The prepared nanocellulose has a uniform structure High cellulose decomposition rate | Enzyme preparations are expensive Take a long time to prepare | [40,41] |
| Acid hydrolysis preparation | Low cost Simple and easy to use stable and controllable Quality of finished products | Production environment with acidic wastewater discharge easy to produce by-products Need to treat wastewater and waste acid | [42,43] |
| TEMPO oxidation method preparation | The production process is environmentally friendly The prepared nanocellulose has a uniform structure High cellulose decomposition rate | TEMPO reagents are expensive Take a long time to prepare | [44] |
| Aerogel Category | Source | Adjustability | Mechanical Strength | Renewability | Production Cost | Thermal Stability | Mechanical Properties | Water Resistance | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nanocellulose-based aerogel | Cellulose | High | High | High | Low | Low | High strength High toughness | Good | [90] |
| Starch-based aerogel | Plant starch | Low | Low | Low | Low | Moderate | Moderate | Poor | [91] |
| Chitosan-based aerogel | Chitosan | High | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate | Good | [92] |
| Gelatin-based aerogel | Animal bones | Low | Moderate | Low | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate | Poor | [93] |
| Aerogel Name | Preparation Method | Dyes | Specific Surface Area (m2/g) | Porosity (%) | Density (mg/cm3) | Adsorption Capacity (mg/g) | pH | Number of Cycles | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nanocellulose-based aerogels | |||||||||
| Cu-BTC/NFC aerogel | Freeze-drying | CR | 18.283 | / | / | 39 | / | / | [66] |
| CGS | Freeze-drying | MB | / | 98.7 | 19.9 | 608.4 | 7 | 10 | [96] |
| SCP | Freeze-drying | CR MO | / | / | / | 2007.48 2253.38 | 2–5 | 5 | [97] |
| CNF-GnP | Freeze-drying | MB CR | / | / | / | 1178.5 585.3 | / | 4 | [98] |
| Q-CNF | Freeze-drying | Bule Red Orange | / | 99 | 17.5 | 230 160 560 | / | 20 | [99] |
| PCNF | Freeze-drying | MB | 368.15 | / | 27.2 | 208 | 5 | 5 | [100] |
| DADMAC-MBAA modified CNF-Silica aerogels | Freeze-drying | MO | / | / | / | 186.7 | 5–7 | 3 | [101] |
| ANFs/BC | Freeze-drying | MB | / | / | / | 54.45 | / | / | [102] |
| Silica-cellulose aerogel | Freeze-drying | MB MO | 350 | 93 | 107 | 270 300 | / | / | [103] |
| Cellulose nanofibril-based aerogel | Freeze-drying | MG | 193 | / | / | 212.7 | / | 4 | [104] |
| CO2-responsive cellulose nanofibril aerogel | Freeze-drying | MB NGB MO | 17.97 | / | 21.7 | 598.8 621.1 892.9 | / | 20 | [105] |
| Chitosan-based aerogels | |||||||||
| QCSA | Freeze-drying | CR MO SY | / | / | 60 | 1259.6 607.5 550.2 | 7 | 5 | [106] |
| HPS | Freeze-drying | CR | 123.92 | 98.16 | / | 2074 | 6 | 7 | [107] |
| Fc-CS | Freeze-drying | MB | 5 | / | / | 156.3 | 5–6 | 5 | [108] |
| ZnBDC/CSC | Freeze-drying | MO | 16.5 | / | / | 202 | 5 | 5 | [109] |
| Aerogel Name | Preparation Method | Metal Ions | Specific Surface Area (m2/g) | Porosity (%) | Density (mg/cm3) | Adsorption Capacity (mg/g) | pH | Number of Cycles | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nanocellulose-based aerogels | |||||||||
| APTMs modified TO-NFC | Freeze-drying | Cu (Ⅱ) Cd (Ⅱ) Hg (Ⅱ) | 129.32 | 99.14 | / | 99 124.5 242.1 | 3–7 | / | [116] |
| TOCNF-TMPTAP-APAM | Freeze-drying | Cu (Ⅱ) | / | 99.1 | 14.4 | 240.00 | 6 | 10 | [117] |
| MOF@CA | Freeze-drying | Pb (Ⅱ) Cu (Ⅱ) | / | 99.4–99.5 | 9.8–11.2 | 123.00 70.53 | / | 5 | [118] |
| NFC/PEI hybrid aerogels | Freeze-drying | Pb (Ⅱ) Cu (Ⅱ) | 42.5 | / | / | 357.44 175.44 | 2–5 | 3 | [119] |
| CPA | Freeze-drying | Cr (Ⅵ) | 36.77 | / | / | 229.10 | 2 | 5 | [120] |
| PEI@CNF aerogels | Freeze-drying | Cu (Ⅱ) | 11.48 | / | / | 135.10 | 3–6 | 3 | [121] |
| nanocellulose-Fe3O4 hybrid aerogel | Freeze-drying | Cr (Ⅱ) Pb (Ⅱ) Cu (Ⅱ) | / | 5 | / | 2.20 1.25 0.40 | / | / | [122] |
| UiO-66-NH2@CA | Freeze-drying | Pb (Ⅱ) | / | / | / | 89.40 | / | 5 | [123] |
| CNFs aerogel | Freeze-drying | U (Ⅵ) | 188 | / | / | 440.60 | 5 | [124] | |
| CGP | Freeze-drying | Cr (Ⅵ) | / | / | / | 386.40 | 2 | 5 | [125] |
| Chitosan-based aerogels | |||||||||
| PCA | Freeze-drying | Cr (Ⅵ) | / | / | / | 445.29 | 3 | 10 | [127] |
| CSTU | Freeze-drying | Ag (Ⅰ) Pb (Ⅱ) | 416.64–447.26 | / | 2.1–10.3 | 1.11 mmol/g 0.48 mmol/g | 6 | 5 | [128] |
| WP-CSA | Freeze-drying | Cu (Ⅱ) | / | / | 106 | 156.3 | 2.3–5.5 | / | [129] |
| E-CS aerogel | Freeze-drying | Cu (Ⅱ) Pb (Ⅱ) Cd (Ⅱ) | / | 97.38 | 38.3 | 108.14 143.73 84.62 | 5 | 3 | [130] |
| CS-MMT | Freeze-drying | Cu (Ⅱ) | 14.133 | / | / | 86.95 | 6 | 7 | [131] |
| Aerogel Name | Preparation Method | Antibiotics | Specific Surface Area (m2/g) | Porosity (%) | Adsorption Capacity (mg/g) | pH | Number of Cycles | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nanocellulose-based aerogels | ||||||||
| CNF/GO | Freeze-drying |
Loramphenicol Macrolides Quinolones β-lactams sulfonamides tetracyclines | 97.5 | / | 418.7 291.8 128.3 230.7 227.3 454.6 | 2.0 | 10 | [135] |
| GO-CNF | Freeze-drying |
DXC CTC OTC TC | 89.9 | / |
469.7 396.5 386.5 343.8 | / | 5 | [136] |
| GO/CNF | Freeze-drying | TC | 35 | / | 47.3 | / | 3 | [137] |
| BCCA | Freeze-drying |
CAP NOR SMX | 1505 | / |
525 1926 1264 | 5 | 5 | [138] |
| ZIF-67/PANI/RCA aerogel | Freeze-drying | TC | / | / | 409.55 | 7.0 | 6 | [139] |
| ZCCA | Freeze-drying | ENR | 756.45 | 95 | 172.09 | 2.0–6.0 | 6 | [140] |
| PVA-assisted CNCs/SiO2 aerogel | Freeze-drying | CIP | / | / | 163.34 | 4.0 | / | [141] |
| Chitosan-based aerogels | ||||||||
| PGO-CS | Freeze-drying | TC | 345 | / | 1470 | 9.0–10.0 | 4 | [142] |
| CMC | Freeze-drying | TC | 0.73 | / | 332.23 | 3.0–4.0 | / | [143] |
| CMC-Mt | Freeze-drying | CTC | 119.526 | / | 48.71 | 4.0–7.0 | / | [144] |
| Aerogel Name | Preparation Method | Oil/Organic Solvents | Specific Surface Area (m2/g) | Porosity (%) | Density (mg/cm3) | Adsorption Capacity (g/g) | Water Contact Angle (°) | Number of Cycles | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nanocellulose-based aerogels | |||||||||
| silylated PVA/CNC aerogels | Freeze-drying | Chloroform Dodecane Acetone Ethanol DMF 2-Propanol Etyl acetate Hexane Toluene Xylene Olive oil Cooked oil Sesame oil Motor oil Crude oil Gasoline | 76 | 98.42 | 17 | 69–168 | 154.93 | 20 | [148] |
| γ-irradiated CNC-MTMS/gelatin aerogels | Freeze-drying | Chloroform Crude oil | / | / | 85 | / (It can absorb 430% of its own weight) | 118 | 8 | [149] |
| KCAs | Freeze-drying | Vegetable Oil Motor oil Gasoline Vacuum pump oil Trichloromethane Ethanol DMF | / | 99.58 | 5.1 | 104–190.2 | 140.1 | 10 | [150] |
| MTS-CNC | Freeze-drying | Liquid paraffin oil | 282 | / | / | 60 | 148.5 | 5 | [151] |
| CNF-PDMS | Freeze-drying | Dim ethylb enzene Ethyl acetate Ethanol n-Hexane n-Decane n-Dodecane n-Hexadecane Methylcyclohexane Dichloroethane Toluene Dimethylformamide Petroleum ether THF Petroleum | / | 98.4 | 22.7 | 24–48 | 163.5 | 20 | [152] |
| M-CNF/silica/Fe3O4) | Freeze-drying | DMF DMSO Octane Gasoline Dioxane Toluene Hexane Chloroform | 82.6 | / | 22.3 | 34–58 | 150 | 10 | [153] |
| CNF/SA | Freeze-drying | Flax seed oil Pump oil Used pump oil Olive oil Silicane oil Toluene Acetone Ethanol Hexane Ethylene glycol DMF DMSO | 149.64 | 97.85 | 24.2 | 41.16–88.91 | 144.5 | 20 | [154] |
| KNA | Freeze-drying | vegetable oil | / | 99.5–99.6 | 4.9–6.0 | 141.9 | 147.6 | / | [155] |
| NC/NCS/rGO nanocomposite aerogel | Freeze-drying | Acetone Sesame oil Ethyl acetate Mineral oil Thiophene Pump oil Used pump oil Kerosene Ethanol | / | 99.18 | / | 153.22 159.64 149.60 171.85 139.93 132.47 176.82 128.70 120.34 | 115.26 | / | [156] |
| TOCN carbon aerogel | Freeze-drying and high-temperature carbonization | Gasoline Diesel oil Pump oil Motor oil Sesame oil Chloroform Acetaldehyde Ethanol Toluene Octadecylene Cyclohexane Heptane n-Hexane Acetone Methanol Lactic acid Styrene THF DMF | 249.91 | 99.5 | 8.8 | 110–260 | 139.6 | 5 | [157] |
| CCA | Freeze-drying and high-temperature carbonization | Soybean oil Pump oil Acetone Ethylene glycol Methanol DMF Hexane Ethanol | 79.2 | 98.9–99.2 | 16–23 | 22–55 | >135 | 5 | [158] |
| NC/Al2O3 aerogel | Freeze-drying | Anhydrous ethanol Ethyl acetate Thiophene Cyclohexane Sesame oil Acetone Dichlormethae | 124 | 99.09 | 5.1 | 89.91 93.93 108.07 71.13 64.83 85.19 117.65 | / | / | [159] |
| NLA | Freeze-drying | Crude oil Rexid oil Silicon oil Vacuum pump oil Red oil Hexane Xylene DMF THF DCM Chloroform | / | 98 | 22 | 30–67 | 120.5 | 10 | [160] |
| PAC-g-PEI | Freeze-drying | n-hexane toluene edible oil silicone oil | / | 94 | 67 | / (Separation efficiency over 99%) | / (Oil contact angle is 130.3°–135°) | 50 | [161] |
| P-CNS | Freeze-drying | Dichloromethae Soybean oil Pump oil Chloroform Diesel Motor oil Ethanol Acetone Toluene Hexane Gasoline Octane | 362.7 | 98.9–99.4 | 8.4–12.9 | 100–225 | 133.6–168.4 | 50 | [162] |
| NCC/CS aerogel | Freeze-drying | Methylbenzene Petroleum ether n-Hexane Edible oil Silicone oil Dodecane | / | 97.66 | 40.82 | / (Separation efficiency over 99%) | / (Oil contact angle is 109°–141.1°) | 50 | [163] |
| Chitosan-based aerogels | |||||||||
| PNI-Si@CCNT/CA | Freeze-drying | N-hexane Toluene Trichloromethane Petroleum ether Peanut oil Soybean oil Sunflower oil Olive oil | 2.81 | / | 0.0051 | 23.8 35.3 53.0 42.1 41.0 35.2 32.5 40.8 | / (Oil contact angle is 134°) | 9 | [164] |
| CsA | Freeze-drying | Crude oil Diesel | 28.3 | 97.98 | 28.3 | 41.07 31.07 | / | 3.0–4.0 | [165] |
| (CA/CS/CMC) | Freeze-drying | Chloroform Toluene Acetone Methanol Ethanol | / | 96 | 8.3–63.6 | 27–44 | / | 4.0–7.0 | [166] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, J.; Yuan, X.; Wu, X.; Liu, L.; Guo, H.; Xu, K.; Zhang, L.; Du, G. Preparation of Nanocellulose-Based Aerogel and Its Research Progress in Wastewater Treatment. Molecules 2023, 28, 3541. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28083541
Zhao J, Yuan X, Wu X, Liu L, Guo H, Xu K, Zhang L, Du G. Preparation of Nanocellulose-Based Aerogel and Its Research Progress in Wastewater Treatment. Molecules. 2023; 28(8):3541. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28083541
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Jiaxin, Xushuo Yuan, Xiaoxiao Wu, Li Liu, Haiyang Guo, Kaimeng Xu, Lianpeng Zhang, and Guanben Du. 2023. "Preparation of Nanocellulose-Based Aerogel and Its Research Progress in Wastewater Treatment" Molecules 28, no. 8: 3541. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28083541