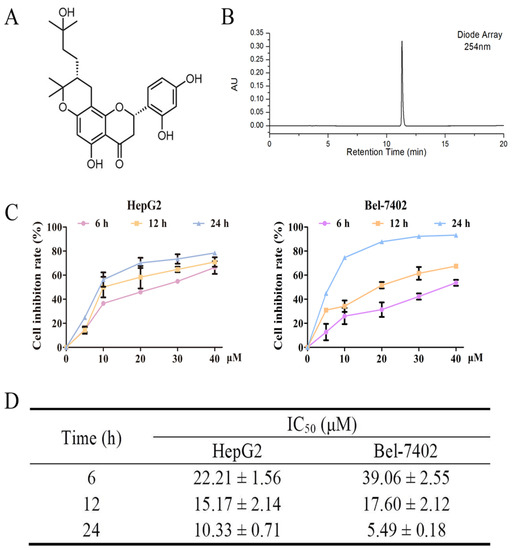
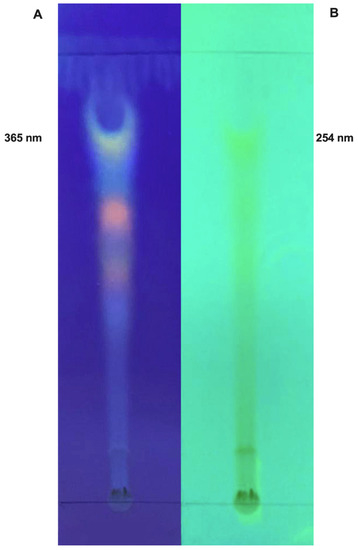
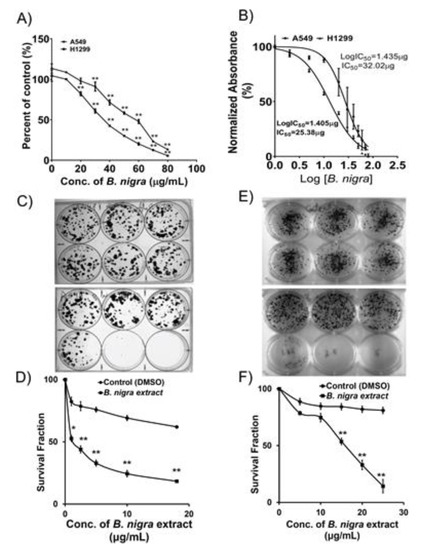
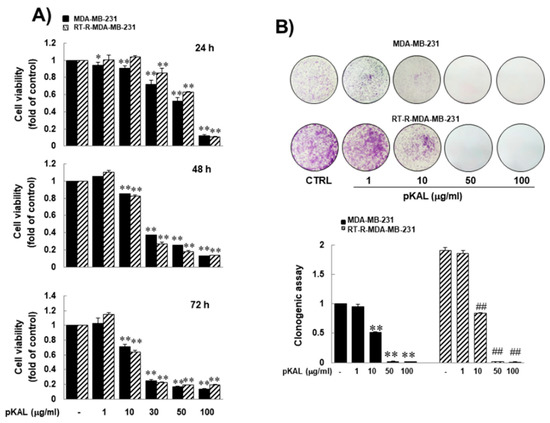
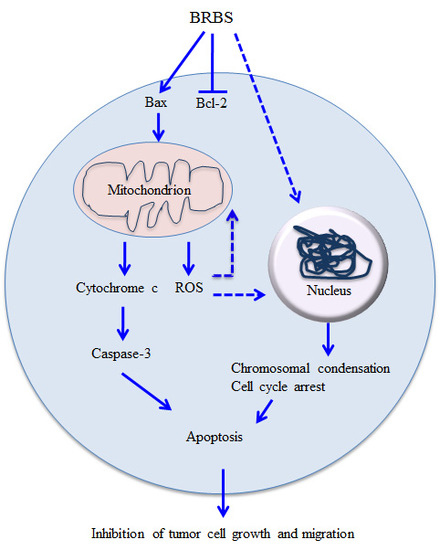
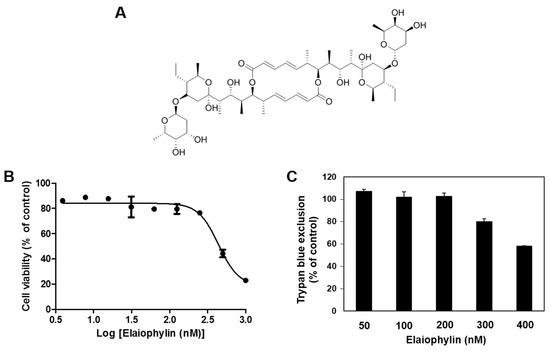
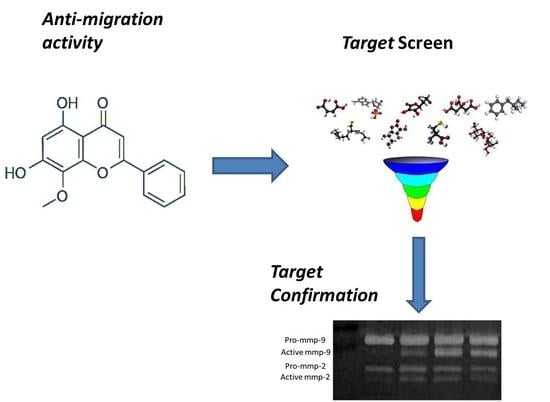
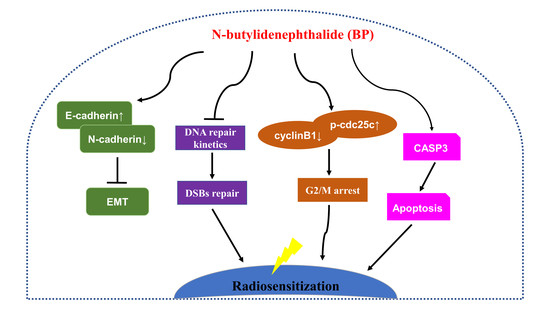
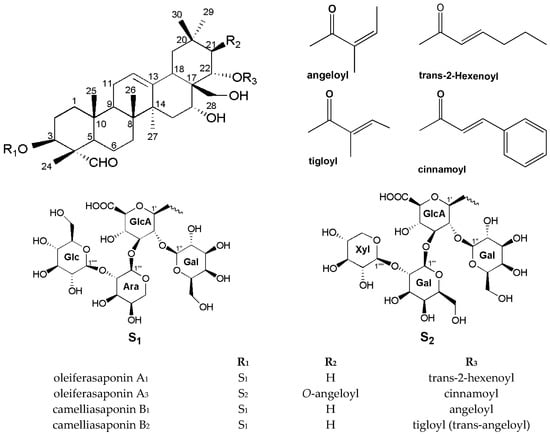
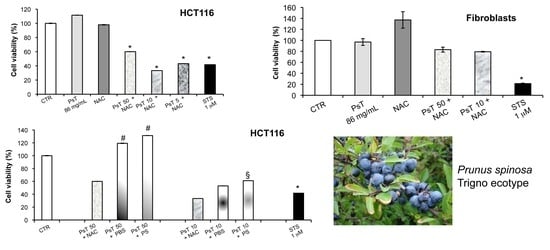
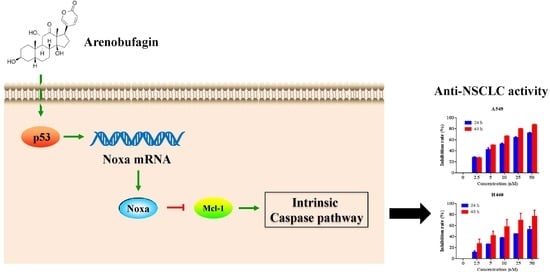
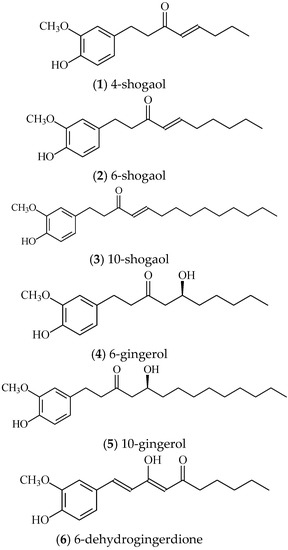
Natural Products: Anticancer Potential and Beyond (Closed)
A topical collection in Molecules (ISSN 1420-3049). This collection belongs to the section "Natural Products Chemistry".
Viewed by 230341Editors
Interests: drug resistance; ABC transporter; tyrosine kinase inhibitor; cancer
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: Biomarkers; Anti-Cancer Drugs; Cancer Chemotherapy; Cancer Biology; Developmental Biology
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: drug discovery; natural products chemistry; organic synthesis; pharmacokinetics; anticancer drug leads; CB2 drug leads
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
In the period of 1981–2010, about 80% of the anticancer drugs approved for clinical use were either natural products or inspired by natural products, highlighting the importance of natural products in cancer treatment. Indeed, many natural products have been introduced into oncological practice and also used as lead compounds for the development of more potent and less toxic anticancer drugs. Many natural product anticancer drugs, including those from plants (e.g., vincristine, paclitaxel, irrinotecan, etoposide, etc.), marine sources (e.g., cytarabine), and microbials (e.g., dactinomycine, doxorubicin, bleomycins, etc.), are currently used in clinics. In this Special Issue, we invite investigators to contribute original research articles, as well as review articles that are related to the application of natural products in the treatment of cancer. We are particularly interested in research that works toward improving the anticancer effects of natural products while reducing their side effects. Potential topics include, but are not limited to:
• The anti-cancer effects of new natural products, and their underlying mechanisms
• Pharmacological interventions for the treatment of cancer in natural products
• The development of new natural products that reverse multi-drug resistance in cancer
• Clinical studies and therapeutic efficacy in anti-cancer natural products.
Prof. Dr. Zhe-Sheng (Jason) Chen
Dr. Dong-Hua Yang
Dr. Mohamed Ali Ibrahim
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Molecules is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2700 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- Natural products
- Anti-cancer
- Chemotherapy
- Drug Resistance
- ABC transporters
- P-glycoprotein
- Breast cancer resistance protein
- Side effects
- Marine drugs
- Plants
- Microbials
- Isolation
- Extracts