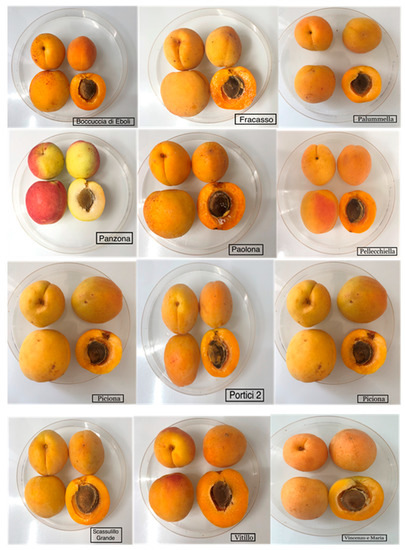
Nutritive Value, Polyphenolic Content, and Bioactive Constitution of Green, Red and Flowering Plants-Volume II
A topical collection in Horticulturae (ISSN 2311-7524). This collection belongs to the section "Postharvest Biology, Quality, Safety, and Technology".
Viewed by 21924Editor
Interests: horticultural crops; microgreens; protected cultivation; hydroponics; plant biostimulants; nutrient eustress; biofortification; space farming; nutrient recovery from urine
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
Plants, including vegetables, are an essential element of the human diet, considering their dense nutritional content, concomitant with low-calorie values and bioactive content that could assist in boosting nutritional quality and food security. Plants are exhibiting a colossal rebound in the context of healthier lifestyles, especially as functional foods empowered with bioactive phytochemicals. Impelled by nature’s endowment as suppliers of healthier nutritional foods, a prominent orientation towards plant consumption is thriving. Plants synthesize uncountable “ecochemichals” via secondary metabolism, which command medical and socio-economic significance. Among these secondary metabolites, phenolic compounds are of prime interest and are largely present in medicinal plants, herbs, vegetables, and flowers. These metabolites are at the helm of the bitterness, color, and scent of plants, and are correlated to the beneficial health qualities expressed by the antioxidant capacity. The accretion of these health-promoting phytochemicals depends chiefly on the genetic material and the maturity harvest stage, but notwithstanding the main role that is played by the pre-harvest factors, i.e., eustress, fertilization, irrigation, light, and other agronomic practices.
This Special issue of Horticulturae will gather scientific research that explores innovations or recent studies in boosting plant nutritional qualities including vegetables, herbs, and flowers. Therefore, any review, scientific research, short note, or opinion article that deals with the phytochemical content of plants and boosting methods is appreciated for submission.
Dr. Christophe El-Nakhel
Collection Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Horticulturae is an international peer-reviewed open access monthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2200 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- secondary metabolites
- phytochemicals
- beneficial stress
- functional food
- pre-harvest factors
- specialty crops
- fruit and leafy vegetables