Dermatopathology, Volume 9, Issue 2 (June 2022) – 14 articles
Malignant melanoma (MM) is derived through malignant transformation of pigment-producing cells in human skin. Highly differentiated melanoma cells usually maintain their pigment-producing function and, hence, immunohistochemically express melanocytic markers.
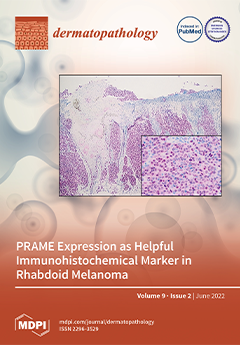
Rhabdoid melanoma, a rare, dedifferentiated variant of MM, is characterized by the potential loss of conventional melanocytic markers. Since rhabdoid differentiation is associated with poor prognosis, immunohistochemical clues for accurate diagnosis are highly desirable. A relatively new marker molecule is PRAME (preferentially expressed antigen in melanoma), an antigen that is expressed in multiple malignant tumors, including MM.
In four new cases of primary rhabdoid melanomas, consistent nuclear positivity for PRAME underlines a possible immunohistochemical clue in the diagnosis of this rare entity. View this paper
- Issues are regarded as officially published after their release is announced to the table of contents alert mailing list.
- You may sign up for e-mail alerts to receive table of contents of newly released issues.
- PDF is the official format for papers published in both, html and pdf forms. To view the papers in pdf format, click on the "PDF Full-text" link, and use the free Adobe Reader to open them.