Nitrogen-Doped Pitch-Based Activated Carbon Fibers with Multi-Dimensional Metal Nanoparticle Distribution for the Effective Removal of NO
Abstract
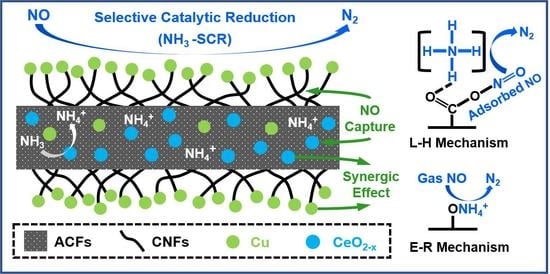
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
3. Experimental
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation and Characterization
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Croisé, C.; Pointecouteau, R.; Akil, J.; Demourgues, A.; Bion, N.; Courtois, X.; Can, F. Insight into the praseodymium effect on the NH3-SCR reaction pathways over W or Nb supported ceria-zirconia based catalysts. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2021, 7, 120563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Ren, S.; Yang, J.; Liu, W.; Su, Z.; Chen, Z.; Wang, M.; Chen, L. NH3 treatment of CeO2 nanorods catalyst for improving NH3-SCR of NO. J. Energy Inst. 2021, 98, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Duan, R.; Liu, W.; Wang, D.; Wang, B.; Xu, Y.; Niu, C.; Shi, J.-W. The insight into the role of CeO2 in improving low-temperature catalytic performance and SO2 tolerance of MnCoCeOx microflowers for the NH3-SCR of NOx. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 510, 145517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, M.; Su, S.; Qian, K.; Liu, L.; Yin, Z.; Hu, S.; Wang, Y.; Xiang, J. Insight into the catalytic performance and NH3 adsorption under high concentration of CO2 and/or H2O conditions on selective catalytic reduction of NO by NH3 over V2O5-WO3/TiO2 catalyst. Fuel 2021, 286, 119478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, S.; Peng, H.; Liu, W.; Mi, Y.; Wang, Z.; Tang, C.; Wu, D.; An, T. Insight into the activity and SO2 tolerance of hierarchically ordered MnFe1-δCoδOx ternary oxides for low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3. J. Catal. 2021, 395, 195–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Cai, S.; Gao, M.; Hasegawa, J.-Y.; Wang, P.; Zhang, J.; Shi, L.; Zhang, D. Selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3 by using novel catalysts: State of the art and future prospects. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 10916–10976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Li, Y.; Xu, Z.; Xiong, J.; Zhu, T. Transformation of functional groups in the reduction of NO with NH3 over nitrogen-enriched activated carbons. Fuel 2018, 223, 312–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, H.; Tu, Y.-T.; Lai, Y.-C.; Lin, C.-C. Reduction of NO with NH3 over carbon catalysts: The effects of treating carbon with H2SO4 and HNO3. Carbon 2001, 39, 575–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lietti, L.; Nova, I.; Forzatti, P. Selective catalytic reduction (SCR) of NO by NH3 over TiO2-supported V2O5-WO3 and V2O5-MoO3 catalysts. Top. Catal. 2000, 11, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Peng, J.; Ge, R.; Wu, S.; Zeng, K.; Huang, H.; Yang, K.; Sun, Z. Research progress on selective catalytic reduction (SCR) catalysts for NOX removal from coal-fired flue gas. Fuel Process. Technol. 2022, 236, 1074324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Li, Z.; Yang, C.; Ma, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Song, K.; Cui, J. Significant promoting effect of La doping on the wide temperature NH3-SCR performance of Ce and Cu modified ZSM-5 catalysts. J. Solid State Chem. 2022, 305, 122700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Chen, G.; Guo, F.; Xie, J. Development of wide-temperature vanadium-based catalysts for selective catalytic reducing of NOX with ammonia: Review. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 353, 507–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaskar, B.; Nishith, V. Preparation of asymmetrically distributed bimetal ceria (CeO2) and copper (Cu) nanoparticles in nitrogen-doped activated carbon micro/nanofibers for the removal of nitric oxide (NO) by reduction. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 436, 218–226. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, L.; Luo, W.; Sun, W.; Yang, J. Efficient nonthermal plasma degradation of toluene over NiO catalyst with limited NOx generation. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2019, 45, 2903–2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, L.; Ma, K.; Zou, W.; Cao, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Tang, C.; Dong, L. Ultra-low loading of copper modified TiO2/CeO2 catalysts for low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NO by NH3. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2017, 207, 366–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Luo, W.; Züttel, A.; Xiong, Y. Synergistic Cu/CeO2 carbon nanofiber catalysts for efficient CO2 electroreduction. Electrochem. Commun. 2020, 114, 106716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Kumar, R.; Sharma, A.; Verma, N. Novel Cu-carbon nanofiber composites for the counter electrodes of dye-sensitized solar cells. Int. J. Energy Res. 2015, 39, 668–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Yi, H.; Tang, X.; Deng, H.; Liu, H. Thermodynamics for the adsorption of SO2, NO and CO2 from flue gas on activated carbon fiber. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 200, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, J.-W.; Park, S.-J.; Ryu, S.-K. Effect of modification with HNO3 and NaOH on metal adsorption by pitch-based activated carbon fibers. Carbon 2001, 39, 1635–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podyacheva, O.Y.; Shmakov, A.; Boronin, A.; Kibis, L.; Koscheev, S.; Gerasimov, E.Y.; Ismagilov, Z. A correlation between structural changes in a Ni-Cu catalyst during decomposition of ethylene/ammonia mixture and properties of nitrogen-doped carbon nanofibers. J. Energy Chem. 2013, 22, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.Y.; Li, Q.; Easton, C.D.; Liu, C.; Wilde, A.L.; Veitch, C.; McDonnell, J. Surface modification of carbon fibres with ammonium cerium nitrate for interfacial shear strength enhancement. Compos. Part B Eng. 2022, 246, 110173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, A.; Zhou, X.; Huang, X.; Ji, L.; Zhou, W.; Luo, S.; Yao, C. Cerium-loaded MnOX/attapulgite catalyst for the low-temperature NH3-selective catalytic reduction. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2017, 49, 230–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Kyotani, T.; Tomita, A. Study on the Carbon-Nitric Oxide Reaction in the Presence of Oxygen. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1994, 33, 2840–2845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matzner, S.; Boehm, H.P. Influence of nitrogen doping on the adsorption and reduction of nitric oxide by activated carbons. Carbon 1998, 36, 1697–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, M.; Liu, Q.; Zhu, B.; Yang, J.; Li, L.; Zhou, Q.; Ren, S. Synergy of KCl and Hgel on selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3 over V2O5–WO3/TiO2 catalysts. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 264, 815–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Yi, Y.; Li, J.; Woo, S.I.; Wang, B.; Cao, X.; Li, Z. A superior catalyst with dual redox cycles for the selective reduction of NOX by ammonia. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 7726–7728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.-T.; Zhen, W.-L.; Pan, W.-G.; Zhou, Y.; Hong, J.-N.; Xu, H.-J.; Jin, Q.; Ding, C.-G.; Guo, S.-Y. Effect of Cu Doping on the SCR Activity of CeO2 Catalyst Prepared by Citric Acid Method. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2014, 20, 1577–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Gao, S.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Z. Selective Catalytic Reduction of NO over Carbon Nanotubes Supported CeO2. Catal. Commun. 2011, 14, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Liu, F.; Ren, L.; Shi, X.; Xiao, F.-S.; He, H. Excellent Performance of One-Pot Synthesized Cu-SSZ-13 Catalyst for the Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOX with NH3. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 566–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Samples | XPS Analysis (at%) | NO Adsorption Ability (%) | NH3-SCR Reactivity | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu2p | Ce3d | Ce3+/ (Ce3+ + Ce4+) | NO Conversion (%) | T (°C) | ||
| N-CNF/ACF@Cu/Ce | 0.48 | 0.22 | 22.30 | 63.08 | 72~81 | 295~495 |
| N-CNF/ACF@Cu | 0.48 | 0.00 | -- | 62.31 | 60~62 | 269~293 |
| N-CNF/ACF@Ce | 0.00 | 0.38 | 21.48 | 40.47 | 67~82 | 296~347 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, S.; Han, Z.; Yang, J.; Chen, X.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, J. Nitrogen-Doped Pitch-Based Activated Carbon Fibers with Multi-Dimensional Metal Nanoparticle Distribution for the Effective Removal of NO. Catalysts 2022, 12, 1192. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12101192
Chang S, Han Z, Yang J, Chen X, Liu J, Liu Y, Li J. Nitrogen-Doped Pitch-Based Activated Carbon Fibers with Multi-Dimensional Metal Nanoparticle Distribution for the Effective Removal of NO. Catalysts. 2022; 12(10):1192. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12101192
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Shengkai, Zhuo Han, Jianxiao Yang, Xuli Chen, Jiahao Liu, Yue Liu, and Jun Li. 2022. "Nitrogen-Doped Pitch-Based Activated Carbon Fibers with Multi-Dimensional Metal Nanoparticle Distribution for the Effective Removal of NO" Catalysts 12, no. 10: 1192. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12101192