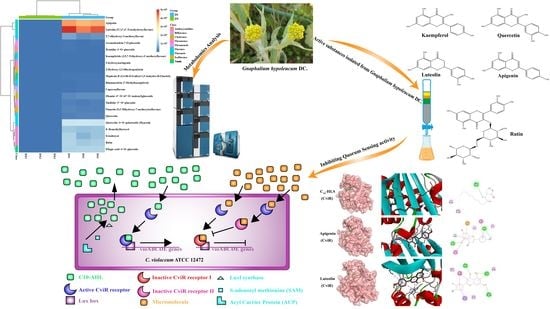
The Derived Components of Gnaphalium hypoleucum DC. Reduce Quorum Sensing of Chromobacterium violaceum
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Metabolome Identification Results of Gnaphalium hypoleucum DC.
2.2. Minimum Inhibitory Concentration of Crude Extracts and Active Compounds against C. violaceum
2.3. Active Compounds from G. hypoleucum DC. Shown an Inhibitory Effect on Violacein Production of C. violaceum
2.4. Anti-Biofilm Activity of Luteolin and Apigenin on C. violaceum
2.5. Reduced Swarming Activity of Luteolin and Apigenin on C. violaceum
2.6. Molecular Docking Prediction
2.7. Apigenin and Luteolin Inhibits Violacein Production through Influencing the Expression of vioABCDE Operon
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Metabolomics Analysis and Active Ingredient Extraction of Gnaphalium hypoleucum DC.
4.2. Determination of Minimum Inhibitory Concentrations
4.3. Anti-QS Activity of Extracts and Compounds Isolated from Gnaphalium hypoleucum DC.
4.4. Anti-Biofilm Activity of Crystal Violet Extracts and Compounds Isolated from G. hypoleucum DC.
4.5. Swimming and Swarming Assays
4.6. SEM Observation
4.7. Molecular Docking Prediction
4.8. Action of Active Compounds on vioABCDE Operon of C. violaceum
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Wu, S.; Liu, J.; Liu, C.; Yang, A.; Qiao, J. Quorum sensing for population-level control of bacteria and potential therapeutic applications. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2020, 77, 1319–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, J.Y.; Chen, T.T.; Tan, X.J.; Chen, T.; Jia, A.Q. The quorum-sensing inhibiting effects of stilbenoids and their potential structure-activity relationship. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 5217–5220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivera, M.L.C.; Hassimotto, N.M.A.; Bueris, V.; Sircili, M.P.; de Almeida, F.A.; Pinto, U.M. Effect of Capsicum Frutescens Extract, Capsaicin, and Luteolin on Quorum Sensing Regulated Phenotypes. J. Food Sci. 2019, 84, 1477–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Yousef, H.M.; Ahmed, A.F.; Al-Shabib, N.A.; Sameen, L.; Khan, R.A.; Rehman, T.; Alsalme, A.; Al-Ajmi, M.F.; Khan, M.S.; Husain, F.M. Onion Peel Ethylacetate Fraction and Its Derived Constituent Quercetin 4’-O-β-D Glucopyranoside Attenuates Quorum Sensing Regulated Virulence and Biofilm Formation. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gemiarto, A.T.; Ninyio, N.N.; Lee, S.W.; Logis, J.; Fatima, A.; Chan, E.W.C.; Lim, C.S.Y. Isoprenyl caffeate, a major compound in manuka propolis, is a quorum-sensing inhibitor in Chromobacterium violaceum. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2015, 108, 491–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Y.Q.; Zeng, H.; Chen, W. Okanin in Coreopsis tinctoria Nutt is a major quorum-sensing inhibitor against Chromobacterium violaceum. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 260, 113017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerreiro, E.; Kavka, J.; Giordano, O.S. 5,8-Dihydroxy-3,6,7-trimethoxyflavone from Gnaphalium gaudichaudianum. Phytochemistry 1982, 21, 2601–2602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.J.; Hu, Y.J.; Xu, P.; Liang, W.Q.; Zhou, J.; Liu, P.G.; Cheng, L.; Pu, J.B. Screening of Potential Xanthine Oxidase Inhibitors in Gnaphalium hypoleucum DC. by Immobilized Metal Affinity Chromatography and Ultrafiltration-Ultra Performance Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry. Molecules 2016, 21, 1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumar, N.; Singh, A.; Sharma, D.K.; Kishore, K. Estimation of wound healing potential of Gnaphalium hypoleucum DC. Int. Res. J. Pharm. 2018, 9, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Xu, N.Y.; Li, Q.R.; Yao, S.; Li, M.; Li, H.R.; Zhang, J.; Chen, D.F. Antiglycemic and anticomplementary potential of an edible plant Gnaphalium hypoleucum DC. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 38, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouedraogo, V.; Sombié, P.; Compaore, M.; Kiendrebeogo, M. African Journal of Microbiology Research Anti-quorum quenching activity of methyl gallate isolated from galls of Guiera senegalensis J. F. Gmel (Combretaceae). Afr. J. Microbil. Res. 2019, 13, 290–297. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-López, M.; García-Contreras, R.; Soto-Hernández, M.; Rodríguez-Zavala, J.; Martínez-Vázquez, M.; Prado-Galbarro, F.J.; Castillo-Juárez, I. Antiquorum Sensing Activity of Seed Oils from Oleaginous Plants and Protective Effect During Challenge with Chromobacterium violaceum. J. Med. Food. 2018, 21, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vattem, D.A.; Mihalik, K.; Crixell, S.H.; Mclean, R. Dietary phytochemicals as quorum sensing inhibitors. Fitoterapia 2007, 78, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Woo, E.R.; Lee, D.G. Apigenin induces cell shrinkage in Candida albicans by membrane perturbation. FEMS Yeast Res. 2018, 18, foy003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Q.; Lu, Y.; Wu, S.Q.; Yao, S.; Zhang, J. Study on the chemical constituents from Gnaphalium hypoleucum. J. Chin. Med. Mater. 2012, 35, 566–568. [Google Scholar]
- Bali, E.B.; Erkan Kübra Türkmen Erdnmez, D.; Salam, N. Comparative Study of Inhibitory Potential of Dietary Phytochemicals Against Quorum Sensing Activity of and Biofilm Formation by Chromobacterium violaceum 12472, and Swimming and Swarming Behaviour of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2019, 57, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Pan, Y.; Li, X.; Jie, J.; Zeng, M. Chemical composition, antimicrobial and anti-quorum sensing activities of pummelo peel flavonoid extract. Ind. Crops Prod. 2017, 109, 862–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quecan, B.X.V.; Santos, J.T.C.; Rivera, M.L.C.; Hassimotto, N.; Pinto, U. Effect of Quercetin Rich Onion Extracts on Bacterial Quorum Sensing. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bodede, O.; Shaik, S.; Chenia, H.; Singh, P.; Moodley, R. Quorum sensing inhibitory potential and in silico molecular docking of flavonoids and novel terpenoids from Senegalia nigrescens. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 216, 134–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharafutdinov, I.S.; Pavlova, A.S.; Khabibrakhmanova, A.M.; Faizova, R.G.; Kurbangalieva, A.R.; Tanaka, K.; Trizna, E.Y.; Baidamshina, D.R.; Bogachev, M.I.; Kayumov, A.R. Targeting Bacillus cereus cells: Increasing efficiency of antimicrobials by the bornyl-possessing 2(5H)-furanone derivative. New Microbiol. 2019, 42, 29–36. [Google Scholar]
- Shehzad, A.; Shahzad, R.; Lee, Y.S. Curcumin: A Potent Modulator of Multiple Enzymes in Multiple Cancers. Enzymes 2014, 36, 149–174. [Google Scholar]
- Vikram, A.; Jayaprakasha, G.K.; Jesudhasan, P.R.; Pillai, S.D.; Patil, B.S. Suppression of bacterial cell-cell signalling, biofilm formation and type III secretion system by citrus flavonoids. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 109, 515–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poli, J.P.; Guinoiseau, E.; de Rocca Serra, D.; Sylvain, S.; Mathieu, P.; Tomi, F.; Quilichini, Y.; Berti, L.; Lorenzi, V. Anti-Quorum Sensing Activity of 12 Essential Oils on Chromobacterium violaceum and Specific Action of cis-cis-p-Menthenolide from Corsican Mentha suaveolens ssp. Insularis. Molecules 2018, 23, 2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kothari, V.; Sharma, S.; Padia, D. Recent research advances on, Chromobacterium violaceum. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2017, 10, 744–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.P.; Zeng, H.; Wan, C.X.; Zhou, Z.B. Amicoumacins from a desert bacterium: Quorum sensing inhibitor against Chromobacterium violaceum. Nat. Prod. Res. 2021, 35, 5508–5512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Rizzoni, E.A.; Sul, S.-Y.; Stephanopoulos, G. Improving metabolic pathway efficiency by statistical model-based multivariate regulatory metabolic engineering. ACS Synth. Biol. 2017, 6, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, Y.M.; Abouwarda, A.M.; Omar, F.A. Effect of kitasamycin and nitrofurantoin at subinhibitory concentrations on quorum sensing regulated traits of C. violaceum. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 2020, 113, 1601–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Li, D.; Huang, X.; Yang, H.; Qiu, Z.; Zou, L.; Liang, Q.; Shi, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wu, S.; et al. Study on antibacterial and quorum-sensing inhibition activities of Cinnamomum camphora leaf essential oil. Molecules 2019, 24, 3792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ravichandran, V.; Zhong, L.; Wang, H.; Yu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Li, A. Virtual Screening and Biomolecular Interactions of CviR-Based Quorum Sensing Inhibitors Against Chromobacterium violaceum. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brango-Vanegas, J.; Costa, G.M.; Ortmann, C.F.; Schenkel, E.P.; Reginatto, F.H.; Ramos, F.A.; Arévalo-Ferro, C.; Castellanos, L. Glycosylflavonoids from Cecropia pachystachya Trecul are quorum sensing inhibitors. Phytomedicine 2014, 21, 670–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.-L.; Chu, Z.-Y.; Liu, G.-M.; Yang, S.-Q.; Zeng, H. The Derived Components of Gnaphalium hypoleucum DC. Reduce Quorum Sensing of Chromobacterium violaceum. Molecules 2022, 27, 4881. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27154881
Li Y-L, Chu Z-Y, Liu G-M, Yang S-Q, Zeng H. The Derived Components of Gnaphalium hypoleucum DC. Reduce Quorum Sensing of Chromobacterium violaceum. Molecules. 2022; 27(15):4881. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27154881
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yu-Long, Zi-Yong Chu, Gui-Min Liu, Sheng-Qiang Yang, and Hong Zeng. 2022. "The Derived Components of Gnaphalium hypoleucum DC. Reduce Quorum Sensing of Chromobacterium violaceum" Molecules 27, no. 15: 4881. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27154881