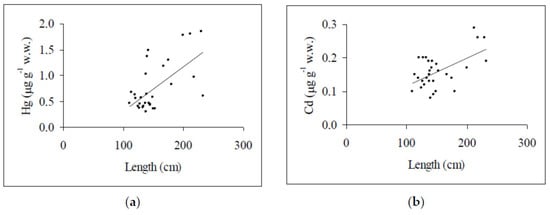
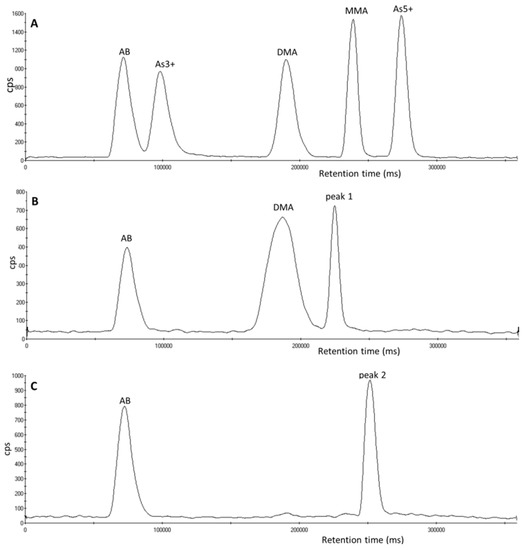
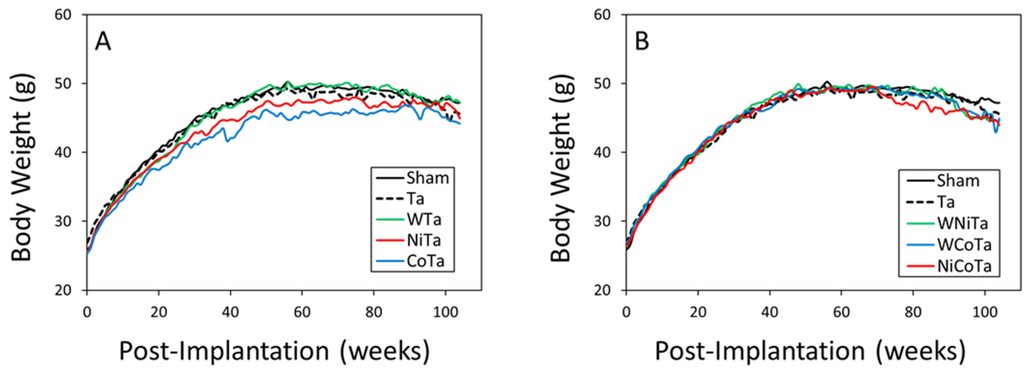
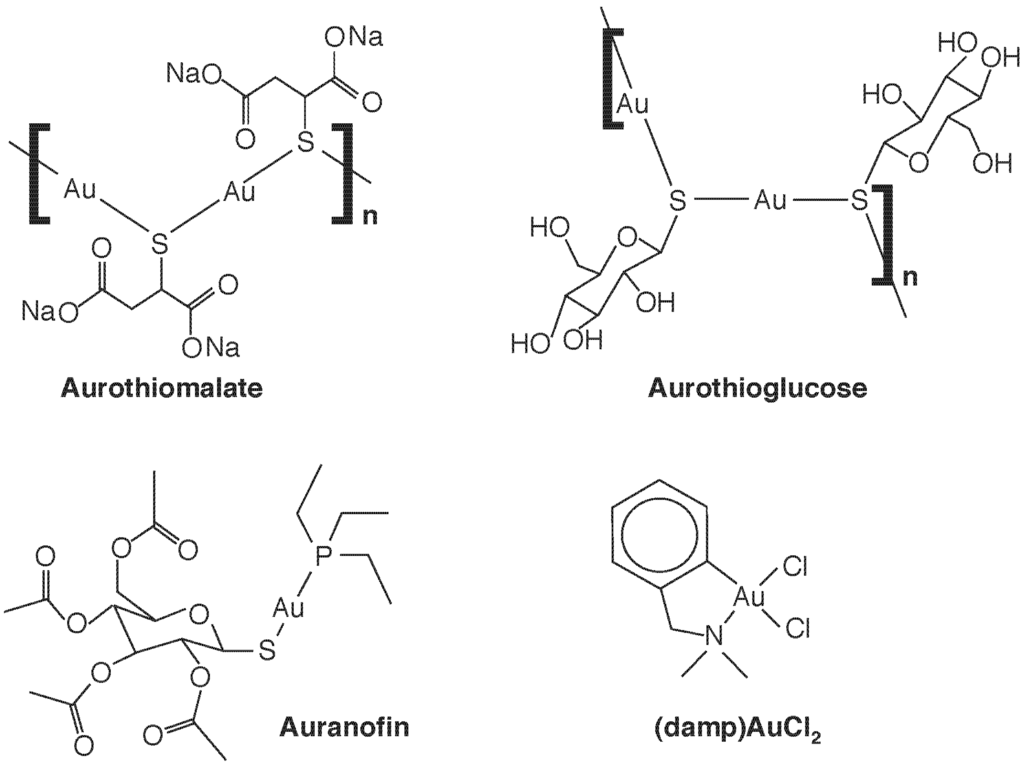
Heavy Metals Toxicology (Closed)
A topical collection in Toxics (ISSN 2305-6304). This collection belongs to the section "Metals and Radioactive Substances".
Viewed by 147365Editor
Interests: neurotoxicology; heavy metals; teratology; behavioral teratology
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
Heavy metals such as lead and mercury continue to effect human and environmental health. Heavy metals not only persist in the environment but continue to be produced and released by mining, manufacturing and environmental processes. Human exposure persists and even expands as humankind develops more manufacturing and mining processes, encroaches on more land area, and develops uses for a wider variety of heavy metals. Progress has been made in understanding the toxicology of metals, prevention has been improved and treatment refined over the years. Despite these advances more research needs to be done.
We invite contributors to this collection of Toxics that will focus on heavy metal toxicology. We invite all papers addressing this problem. Theoretical papers will also be considered. We especially encourage papers examining metal-metal interactions and pharmacologic treatment of heavy metal exposure.
Professor Dr. Wayne Briner
Collection Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts for the topical collection can be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. All papers will be peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on this website. The topical collection considers regular research articles, short communications and review articles. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The article processing charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2600 CHF (Swiss Francs). English correction and/or formatting fees will be charged in certain cases for those articles accepted for publication that require extensive additional formatting and/or English corrections. For further details see here.
Keywords
- heavy metal
- interactions
- chelation
- lead
- mercury
- treatment
- molecular mechanisms
- antagonist