Journal Description
Telecom
Telecom
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on communications and networks published quarterly online by MDPI. FITCE Hellas - Hellenic Branch of FITCE is affiliated with Telecom and its members receive a discount on the article processing charge.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within ESCI (Web of Science), Scopus, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: CiteScore - Q2 (Computer Networks and Communications)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 26.1 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 12.8 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2023).
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review and reviewer names are published annually in the journal.
Latest Articles
Feature-Selection-Based DDoS Attack Detection Using AI Algorithms
Telecom 2024, 5(2), 333-346; https://doi.org/10.3390/telecom5020017 - 17 Apr 2024
Abstract
►
Show Figures
SDN has the ability to transform network design by providing increased versatility and effective regulation. Its programmable centralized controller gives network administration employees more authority, allowing for more seamless supervision. However, centralization makes it vulnerable to a variety of attack vectors, with distributed
[...] Read more.
SDN has the ability to transform network design by providing increased versatility and effective regulation. Its programmable centralized controller gives network administration employees more authority, allowing for more seamless supervision. However, centralization makes it vulnerable to a variety of attack vectors, with distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks posing a serious concern. Feature selection-based Machine Learning (ML) techniques are more effective than traditional signature-based Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) at identifying new threats in the context of defending against distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks. In this study, NGBoost is compared with four additional machine learning (ML) algorithms: convolutional neural network (CNN), Stochastic Gradient Descent (SGD), Decision Tree, and Random Forest, in order to assess the effectiveness of DDoS detection on the CICDDoS2019 dataset. It focuses on important measures such as F1 score, recall, accuracy, and precision. We have examined NeTBIOS, a layer-7 attack, and SYN, a layer-4 attack, in our paper. Our investigation shows that Natural Gradient Boosting and Convolutional Neural Networks, in particular, show promise with tabular data categorization. In conclusion, we go through specific study results on protecting against attacks using DDoS. These experimental findings offer a framework for making decisions.
Full article
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
Simple Compact UWB Vivaldi Antenna Arrays for Breast Cancer Detection
by
Sahar Saleh, Tale Saeidi and Nick Timmons
Telecom 2024, 5(2), 312-332; https://doi.org/10.3390/telecom5020016 - 08 Apr 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
In this study, at ultra-wideband (UWB) frequency band (3.1–10.6 GHz), we propose the use of compact 2:1 and 3:1 nonuniform transmission line Wilkinson power dividers (NTL WPDs) as feeding networks for simple 2 × 1 linear UWB Vivaldi tapered and nonuniform slot antenna
[...] Read more.
In this study, at ultra-wideband (UWB) frequency band (3.1–10.6 GHz), we propose the use of compact 2:1 and 3:1 nonuniform transmission line Wilkinson power dividers (NTL WPDs) as feeding networks for simple 2 × 1 linear UWB Vivaldi tapered and nonuniform slot antenna (VTSA and VNSA) arrays. The 2:1 and 3:1 tapered transmission line (TTL) WPDs are designed and tested in this work as benchmarks for NTL WPDs. The VTSA array provides measured S11 < −10.28 dB at 2.42–11.52 GHz, with a maximum gain of 8.61 dBi, which is 24.39% higher than the single element. Using the VNSA array, we achieve 52% compactness and 6.76% bandwidth enhancement, with good measured results of S11 < −10.2 dB at 3.24–13 GHz and 15.11% improved gain (8.14 dBi) compared to the VNSA single element. The findings show that the NTL and Vivaldi nonuniform slot profile antenna (VNSPA) theories are successful at reducing the size of the UWB WPD and VTSA without sacrificing performance. They also emphasize the Vivaldi antenna’s compatibility with other circuits. These compact arrays are ideal for high-resolution medical applications like breast cancer detection (BCD) because of their high gain, wide bandwidth, directive stable radiation patterns, and low specific absorption rate (SAR). A simple BCD simulation scenario is addressed in this work. Detailed parametric studies are performed on the two arrays for impedance-matching enhancement. The computer simulation technology (CST) software is used for the simulation. Hardware measurement results prove the validity of the proposed arrays.
Full article
Figure 1
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
Horn Antenna on Chip Operating at 180 GHz Using the SiGe CMOS Process
by
Ming-An Chung, Zi-Yu Huang and Yu-Hsun Chen
Telecom 2024, 5(2), 296-311; https://doi.org/10.3390/telecom5020015 - 08 Apr 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This article proposes a chip antenna on millimeter-Waves. This antenna combined with TSMC 180 nm SiGe CMOS technology has the advantage of being small in size and is suitable for wireless communications. The multilayer architecture Horn antenna implemented on M4–M6 can meet both
[...] Read more.
This article proposes a chip antenna on millimeter-Waves. This antenna combined with TSMC 180 nm SiGe CMOS technology has the advantage of being small in size and is suitable for wireless communications. The multilayer architecture Horn antenna implemented on M4–M6 can meet both process reliability specifications and radiation performance. The results of the simulation show that the maximum gain is −4.2 dBi. The return loss measurement results are almost consistent with the simulation results, and the bandwidth range is 177.4–183 GHz. This article first describes the antenna production process and measurement results, analyses the impact of the parameters on the antenna, and further compares it with other designs. The excellence of this article is that it proposes a design that solves the problem of large millimeter wave loss and successfully reduces the area. At the same time, this article can contribute to readers’ future optimization and continued research directions, and at the same time contribute simulation and measurement trends to let readers understand the stability of CMOS chip antenna simulation and measurement.
Full article
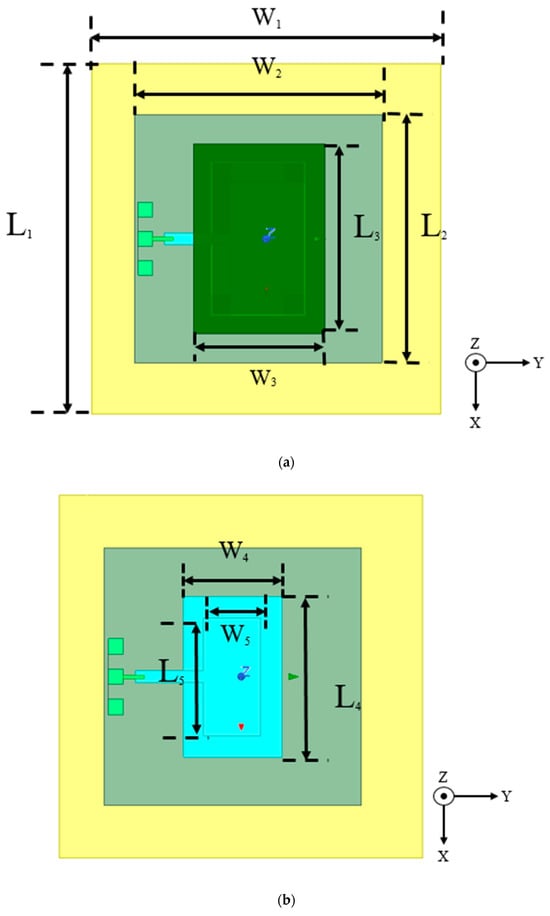
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Optimization of Signal Detection Using Deep CNN in Ultra-Massive MIMO
by
Chittapon Keawin, Apinya Innok and Peerapong Uthansakul
Telecom 2024, 5(2), 280-295; https://doi.org/10.3390/telecom5020014 - 29 Mar 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This paper addresses the evolving landscape of communication technology, emphasizing the pivotal role of 5G and the emerging 6G networks in accommodating the increasing demand for high-speed and accurate data transmission. We delve into the advancements in 5G technology, particularly the implementation of
[...] Read more.
This paper addresses the evolving landscape of communication technology, emphasizing the pivotal role of 5G and the emerging 6G networks in accommodating the increasing demand for high-speed and accurate data transmission. We delve into the advancements in 5G technology, particularly the implementation of millimeter wave (mmWave) frequencies ranging from 30 to 300 GHz. These advancements are instrumental in enhancing applications requiring massive data transmission and reception, facilitated by massive MIMO (multiple input multiple output) systems. Looking towards the future, this paper forecasts the necessity for faster data transmission technologies, shifting the focus toward the development of 6G networks. These future networks are projected to employ ultra-massive MIMO systems in the terahertz band, operating within 0.1–10 THz frequency ranges. A significant part of our research is dedicated to exploring advanced signal detection techniques, helping to mitigate the impact of interference and improve accuracy in data transmission and enabling more efficient communication, even in environments with high levels of noise, and including zero forcing (ZF) and minimum mean square error (MMSE) methods, which form the cornerstone of our proposed approach. Additionally, signal detection contributes to the development of new communication technologies such as 5G and 6G, which require a high data transmission efficiency and rapid response speeds. The core contribution of this study lies in the application of deep learning to signal detection in ultra-massive MIMO systems, a critical component of 6G technology. We compare this approach with existing ELMx-based machine learning methods, focusing on algorithmic efficiency and computational performance. Our comparative analysis included the regularized extreme learning machine (RELM) and the outlier robust extreme learning machine (ORELM), juxtaposed with ZF and MMSE methods. Simulation results indicated the superiority of our convolutional neural network for signal detection (CNN-SD) over the traditional ELMx-based, ZF, and MMSE methods, particularly in terms of channel capacity and bit error rate. Furthermore, we demonstrate the computational efficiency and reduced complexity of the CNN-SD method, underscoring its suitability for future expansive MIMO systems.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Analysis of Carrier Aggregation as a Diversity Technique for Improved Spectral Efficiency and Secrecy Performance in Mobile Communications
by
Paul Ushiki Adamu and Miguel López-Benítez
Telecom 2024, 5(1), 255-279; https://doi.org/10.3390/telecom5010013 - 19 Mar 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Carrier aggregation (CA) was introduced in mobile communication systems in response to the demand for higher network capacity. CA was conceived as a technique to achieve higher data rates by aggregating multiple blocks of spectrum from the same or different frequency bands. This
[...] Read more.
Carrier aggregation (CA) was introduced in mobile communication systems in response to the demand for higher network capacity. CA was conceived as a technique to achieve higher data rates by aggregating multiple blocks of spectrum from the same or different frequency bands. This work explores a different point of view, where CA is employed not as a way to increase capacity through using more bandwidth, but as a diversity technique in order to increase the spectral efficiency of the existing spectrum, and therefore, achieve higher capacity without needing additional spectrum. A mathematical model and set of closed-form expressions are provided, which can be used to characterise the performance of CA as a diversity technique (in terms of both ergodic capacity and secrecy capacity) and determine the impact of various relevant configuration parameters. The numerical results obtained by evaluating the mathematical expressions derived in this work are in line with our previous simulation studies and demonstrate that CA can be effectively exploited as a diversity technique to improve the capacity and performance of mobile communication systems compared to the case of single-carrier transmission over the same amount of bandwidth.
Full article
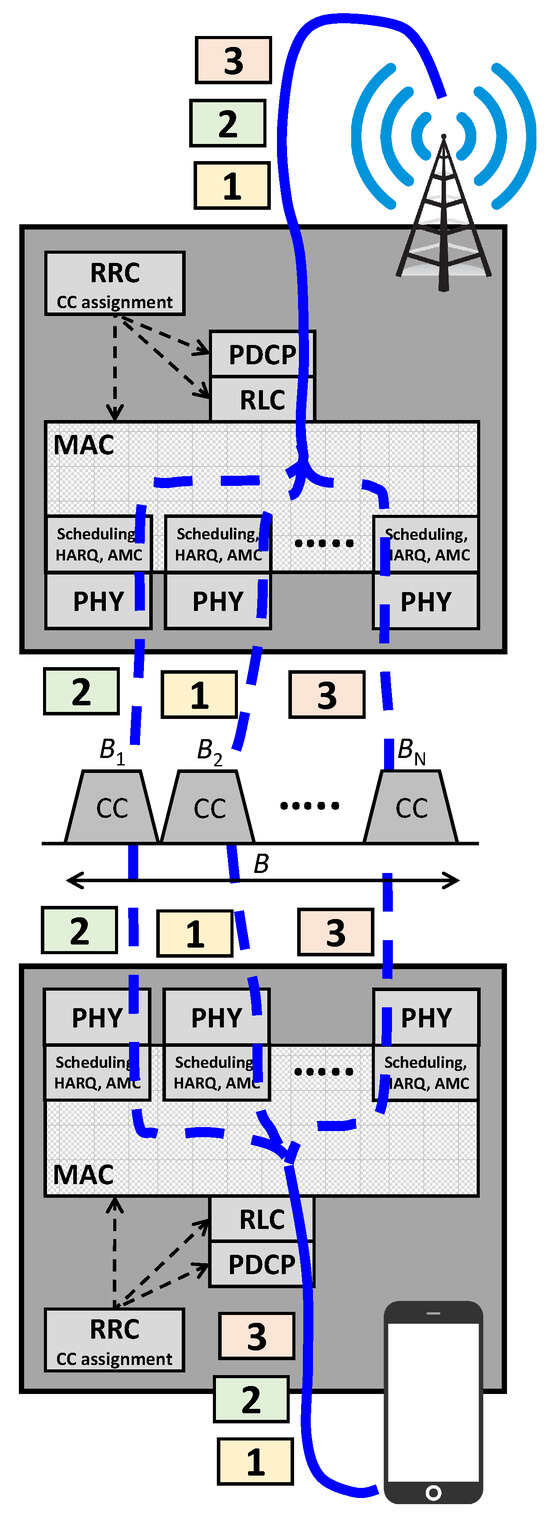
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
TinyGS vs. SatNOGS: A Comparative Analysis of Open-Source Satellite Ground Station Networks
by
João Sá Gomes and Alexandre Ferreira da Silva
Telecom 2024, 5(1), 228-254; https://doi.org/10.3390/telecom5010012 - 07 Mar 2024
Abstract
In recent years, two of the largest open-source ground station (GS) networks capable of enabling Earth–satellite communication have emerged: TinyGS and SatNOGS. These open-source projects enable anyone to build their own GS inexpensively and easily, integrate into a GS network, and receive data
[...] Read more.
In recent years, two of the largest open-source ground station (GS) networks capable of enabling Earth–satellite communication have emerged: TinyGS and SatNOGS. These open-source projects enable anyone to build their own GS inexpensively and easily, integrate into a GS network, and receive data from satellites listed in the database. Additionally, it enables satellite developers to add satellites to the databases of these projects and take advantage of this GS network to receive data from the satellites. This article introduces the TinyGS and SatNOGS projects and conducts a comparative analysis between them. Generally, the TinyGS project seems to have simpler implementation as well as lower associated costs. In a deeper analysis, it was observed that on the 29 July 2023, the TinyGS project had a higher number of online GSs and a more favorable geographic distribution. On the other hand, the SatNOGS project managed to communicate and decode a larger number of satellites up to 29 July 2023. Additionally, in both projects, it was noted that frequencies between 436 and 437 had the highest number of satellites with decoded data. Ultimately, the choice between these projects depends on critical parameters defined by the reader.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Electronic Communications, IOT and Big Data)
►▼
Show Figures
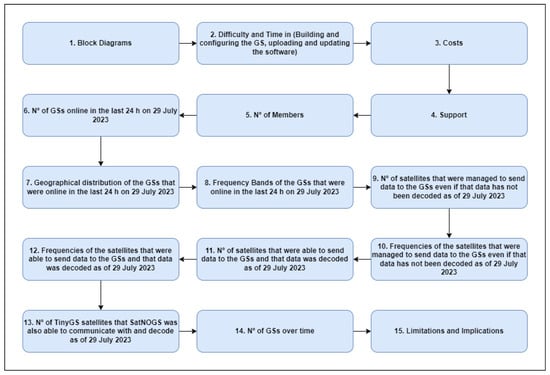
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Transceiver Optimization for Multiuser Multiple-Input Multiple-Output Full-Duplex Amplify-and-Forward Relay Downlink Communications
by
Yunlong Shao and Thomas Aaron Gulliver
Telecom 2024, 5(1), 216-227; https://doi.org/10.3390/telecom5010011 - 06 Mar 2024
Abstract
This paper considers the transceiver design in a multiuser multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) full-duplex (FD) amplify-and-forward (AF) relay downlink communication system, where users simultaneously transmit data via an FD relay node. The design incorporates an imperfect loop interference (LI) cancellation which results in a
[...] Read more.
This paper considers the transceiver design in a multiuser multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) full-duplex (FD) amplify-and-forward (AF) relay downlink communication system, where users simultaneously transmit data via an FD relay node. The design incorporates an imperfect loop interference (LI) cancellation which results in a residual LI. Linear precoders are employed at the sources and relay, and minimum mean-squared-error (MMSE) combiners are employed at the destinations to mitigate the effect of the residual LI. The corresponding design problem is highly nonconvex, so a closed-form solution is intractable. Thus, an iterative method is developed to solve this optimization problem. Simulation results are presented which show that the proposed iterative algorithm provides better performance than the corresponding half-duplex (HD) solution in terms of the achievable rate under residual LI.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Wireless Communication: Applications and Developments)
►▼
Show Figures
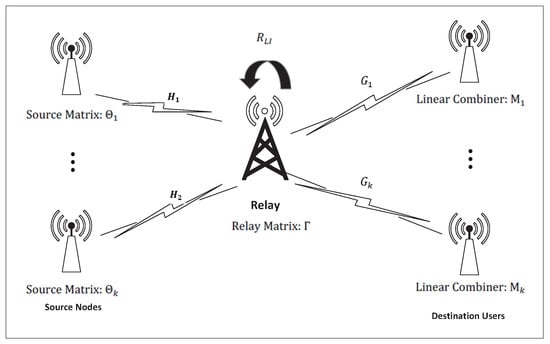
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Maximizing the Downlink Data Rates in Massive Multiple Input Multiple Output with Frequency Division Duplex Transmission Mode Using Power Allocation Optimization Method with Limited Coherence Time
by
Marwah Abdulrazzaq Naser, Munstafa Ismael Salman and Muntadher Alsabah
Telecom 2024, 5(1), 198-215; https://doi.org/10.3390/telecom5010010 - 29 Feb 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The expected development of the future generation of wireless communications systems such as 6G aims to achieve an ultrareliable and low-latency communications (URLLCs) while maximizing the data rates. These requirements push research into developing new advanced technologies. To this end, massive multiple input
[...] Read more.
The expected development of the future generation of wireless communications systems such as 6G aims to achieve an ultrareliable and low-latency communications (URLLCs) while maximizing the data rates. These requirements push research into developing new advanced technologies. To this end, massive multiple input multiple output (MMIMO) is introduced as a promising transmission approach to fulfill these requirements. However, maximizing the downlink-achievable sum rate (DASR) in MMIMO with a frequency division duplex (FDD) transmission mode and limited coherence time (LCT) is very challenging. To address this challenge, this paper proposes a DASR maximization approach using a feasible power allocation optimization method. The proposed approach is based on smartly allocating the total transmit power between the data transmission and training sequence transmission for channel estimation. This can be achieved by allocating more energy to the training signal than the data transmission during the channel estimation process to improve the quality of channel estimation without compromising more training sequence length, thus maximizing the DASR. Additionally, the theory of random matrix approach is exploited to derive an asymptotic closed-form expression for the DASR with a regularized zero-forcing precoder (RZFP), which allows the power optimization process to be achieved without the need for computationally complex Monte Carlo simulations. The results provided in this paper indicate that a considerable enhancement in the DASR performance is achieved using the proposed power allocation method in comparison with the conventional uniform power allocation method.
Full article
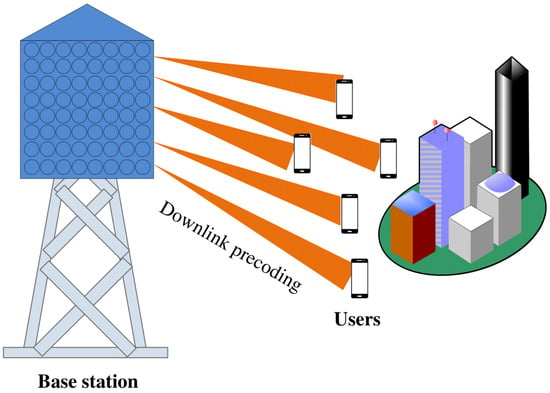
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Dual Data Streaming on Tropospheric Communication Links Based on the Determination of Beam Pointing Dynamics Using a Modified Ray-Based Channel Model
by
Amit Garg, Ranjan Mishra, Ashok Kumar Kalra and Ankush Kapoor
Telecom 2024, 5(1), 176-197; https://doi.org/10.3390/telecom5010009 - 16 Feb 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Tropospheric systems are widely used by military forces as they provide long-distance, real-time communication. Slow-fading propagation loss reduces link availability and limits its data-carrying capacity. Beam pointing dynamics provides knowledge of favorable heights at different times of the day in different seasons and
[...] Read more.
Tropospheric systems are widely used by military forces as they provide long-distance, real-time communication. Slow-fading propagation loss reduces link availability and limits its data-carrying capacity. Beam pointing dynamics provides knowledge of favorable heights at different times of the day in different seasons and a useful steering range. Beam steering, based on the beam pointing dynamics of the link, can overcome slow fading. The main contributions of this paper are the derivation of a realistic and accurate tropospheric channel model obtained by making important modifications to Dinc’s ray-based model. This paper also presents a method for determining beam pointing dynamics using the modified model. Beam pointing dynamics for two different links located in India have been determined in this paper using real-world data obtained from the Indian Meteorological Department. Another significant contribution of the paper is presenting the prospect of dual data streaming on tropospheric links using a fixed beam and a dynamically steered beam, based on the examination of beam pointing dynamics obtained for the two links. The main result presented in this paper is the comparison of powers received from the most favorable heights in a steerable beam system with the powers received in conventional fixed-beam systems for different days of the year. It has been shown that a higher received power can be achieved with beam steering. Another important result shown is the comparison of the achievable data rates for a single fixed-beam system and a dual-beam (one fixed beam and one dynamically steered beam) system. It has been shown that almost double the data rate is achievable in a dual-beam system. The method for the determination of beam pointing dynamics and the possibility of dual data streaming presented in this paper can significantly enhance the availability and capacity of tropospheric links.
Full article
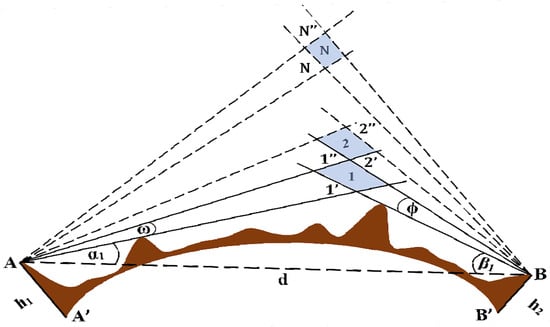
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Modeling and Detection of Attacks in Role-Based Self-Organized Decentralized Wireless Sensor Networks
by
Aleksey Meleshko and Vasily Desnitsky
Telecom 2024, 5(1), 145-175; https://doi.org/10.3390/telecom5010008 - 09 Feb 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This article discusses the modeling and detection of attacks in self-organizing decentralized wireless sensor networks (WSNs) that can be applied to various critical scenarios in practice. Security issues in this type of network have previously been studied to a rather poor extent. In
[...] Read more.
This article discusses the modeling and detection of attacks in self-organizing decentralized wireless sensor networks (WSNs) that can be applied to various critical scenarios in practice. Security issues in this type of network have previously been studied to a rather poor extent. In particular, existing attack detection approaches and algorithms do not rely on the properties of self-organization and decentralization, which an attacker is able to exploit to compromise the network and its services. We propose, first, a model of a self-organizing decentralized wireless sensor network; second, a model of the attacks on such networks; third, algorithms for data collection and attack detection; and, finally, a technique for their application. The WSN model represents a formal specification of this type of network, defining the conditions and limitations of network self-organization and decentralization. The model is characterized by a proposed underlying role-based operation of network nodes and a set of their functional states. The proposed attack model covers the possible types of attacks that are relevant to a given type of WSN and are based on the exploitation of the self-organization and decentralization of the network. The developed algorithm for collecting data for attack detection presents specific types of data and their sources. The developed combined attack detection algorithm is formed of actions that detect relevant attacks on self-organizing decentralized WSNs using machine learning methods. The distinctive element of this algorithm is a set of highly specific features that are obtained by analyzing the data collected in the WSN and used to detect attacks. The proposed technique combines the constructed models and algorithms for the sake of tuning and deploying the attack detection module and the effective detection of attacks in practice. This technique specifies the main steps for the joint use of the models and algorithms and the assignment of data collection and detection parameters. The results of the experiments confirm the correctness of the constructed models, algorithms and technique due to the high values of the attack detection quality indicators. Therefore, the practical application of the proposed apparatus will facilitate improvements in the security of self-organizing decentralized WSNs. Experimental research has confirmed the practical applicability of our proposed solutions. In particular, it has shown that the proposed algorithms and the detection technique can detect both attacks implemented through the exploitation of the network’s properties of decentralization/self-organization and common variations in these attacks (i.e., without exploiting the decentralization property). In general, the experimental results expose a high quality of detection, with an f1-score equal to 0.99.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Underlay Loosely Coupled Model for Public Safety Networks Based on Device-to-Device Communication
by
Wajdi Elleuch
Telecom 2024, 5(1), 122-144; https://doi.org/10.3390/telecom5010007 - 01 Feb 2024
Abstract
In several emergency situations, during natural or human-caused disasters, frontline responders need to be able to communicate and collaborate to properly carry out relief missions. Some countries build their national Public Safety Mobile Broadband based on cellular LTE technology to provide fast, safe,
[...] Read more.
In several emergency situations, during natural or human-caused disasters, frontline responders need to be able to communicate and collaborate to properly carry out relief missions. Some countries build their national Public Safety Mobile Broadband based on cellular LTE technology to provide fast, safe, and secure emergency services. However, in several emergency situations, cellular antennas can be overloaded or partially damaged in a manner that affects group communication services. In the last few years, direct device-to-device (D2D) communications have been proposed by the 3GPP as an underlay of long-term evolution (LTE) networks based on proximity, reuse, and hop gains. This paper focuses on a loosely coupled model based on direct D2D communication in a public safety context. Many scenarios related to user membership and network management are detailed. Both the “less cost” and “optimized tree” approaches are proposed and implemented, and their performance is evaluated in terms of the network update number and the resulting average Channel Quality Indicator (CQI). Other optimization approaches, with different CQI thresholds and optimization interval parameters, are simulated to compare their performance with the “optimized tree” approach. By conducting simulations that combine a CQI threshold = 1 and optimization interval = 2 s, it becomes possible to keep an average CQI level close to the “optimized tree” approach, while the costs related to network updates significantly decrease by almost 35%. Other simulations are also carried out to measure the bandwidth required by the control messages between the server and active users. It was found that both inbound and outbound traffic on the server side can be well supported with LTE and 5G networks.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Joint Application of Telecom and Internet Services)
►▼
Show Figures
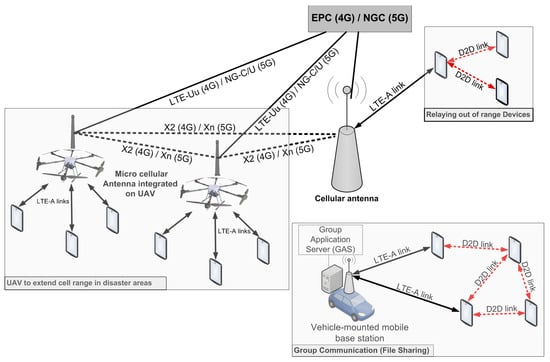
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
An Evaluation Survey of Knowledge-Based Approaches in Telecommunication Applications
by
Georgios P. Koudouridis, Serveh Shalmashi and Reza Moosavi
Telecom 2024, 5(1), 98-121; https://doi.org/10.3390/telecom5010006 - 26 Jan 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The purpose of this survey study is to shed light on the importance of knowledge usage and knowledge-driven applications in telecommunication systems and businesses. To this end, we first define a classification of the different knowledge-based approaches in terms of knowledge representations and
[...] Read more.
The purpose of this survey study is to shed light on the importance of knowledge usage and knowledge-driven applications in telecommunication systems and businesses. To this end, we first define a classification of the different knowledge-based approaches in terms of knowledge representations and reasoning formalisms. Further, we define a set of qualitative criteria and evaluate the different categories for their suitability and usefulness in telecommunications. From the evaluation results, we could conclude that different use cases are better served by different knowledge-based approaches. Further, we elaborate and showcase our findings on three different knowledge-based approaches and their applicability to three operational aspects of telecommunication networks. More specifically, we study the utilization of large language models in network operation and management, the automation of the network based on knowledge-graphs and intent-based networking, and the optimization of the network based on machine learning-based distributed intelligence. The article concludes with challenges, limitations, and future steps toward knowledge-driven telecommunications.
Full article
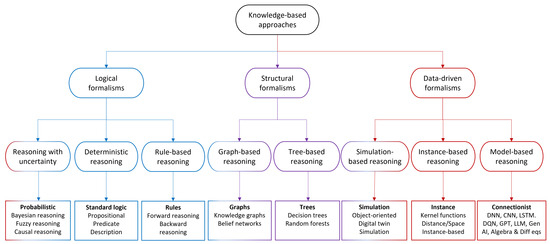
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
6G Goal-Oriented Communications: How to Coexist with Legacy Systems?
by
Mattia Merluzzi, Miltiadis C. Filippou, Leonardo Gomes Baltar, Markus Dominik Mueck and Emilio Calvanese Strinati
Telecom 2024, 5(1), 65-97; https://doi.org/10.3390/telecom5010005 - 24 Jan 2024
Abstract
6G will connect heterogeneous intelligent agents to make them natively operate complex cooperative tasks. When connecting intelligence, two main research questions arise to identify how artificial intelligence and machine learning models behave depending on (i) their input data quality, affected by errors induced
[...] Read more.
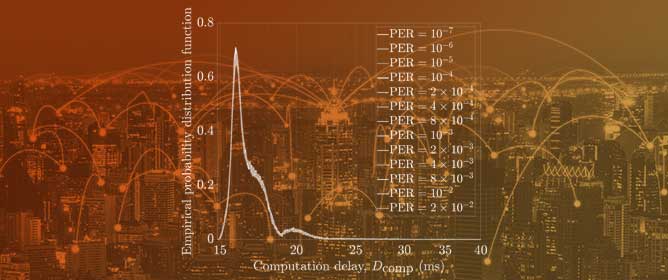
6G will connect heterogeneous intelligent agents to make them natively operate complex cooperative tasks. When connecting intelligence, two main research questions arise to identify how artificial intelligence and machine learning models behave depending on (i) their input data quality, affected by errors induced by interference and additive noise during wireless communication; (ii) their contextual effectiveness and resilience to interpret and exploit the meaning behind the data. Both questions are within the realm of semantic and goal-oriented communications. With this paper, we investigate how to effectively share communication spectrum resources between a legacy communication system (i.e., data-oriented) and a new goal-oriented edge intelligence one. Specifically, we address the scenario of an enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB) service, i.e., a user uploading a video stream to a radio access point, interfering with an edge inference system, in which a user uploads images to a Mobile Edge Host that runs a classification task. Our objective is to achieve, through cooperation, the highest eMBB service data rate, subject to a targeted goal effectiveness of the edge inference service, namely the probability of confident inference on time. We first formalize a general definition of a goal in the context of wireless communications. This includes the goal effectiveness, (i.e., the goal achievability rate, or the probability of achieving the goal), as well as goal cost (i.e., the network resource consumption needed to achieve the goal with target effectiveness). We argue and show, through numerical evaluations, that communication reliability and goal effectiveness are not straightforwardly linked. Then, after a performance evaluation aiming to clarify the difference between communication performance and goal effectiveness, a long-term optimization problem is formulated and solved via Lyapunov stochastic network optimization tools to guarantee the desired target performance. Finally, our numerical results assess the advantages of the proposed optimization and the superiority of the goal-oriented strategy against baseline 5G-compliant legacy approaches, under both stationary and non-stationary communication (and computation) environments.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Next Generation Intelligent Communications and Networks)
►▼
Show Figures
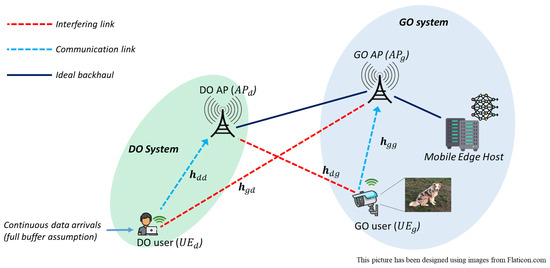
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
5G Physical Layer-Based Procedure to Support Time-Sensitive Networking
by
Faiza Bouchmal, Oscar Carrasco, Yang Fu, Jaime Rodrigo, Jose F. Monserrat and Narcís Cardona
Telecom 2024, 5(1), 49-64; https://doi.org/10.3390/telecom5010004 - 24 Jan 2024
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Deploying 5G in new and diverse use cases, such as Industry 4.0 and factory automation, requires 5G systems to harmonize with the communication technologies used in these industries. To this end, 3GPP Release 16 and Release 17 have made significant progress in integrating
[...] Read more.
Deploying 5G in new and diverse use cases, such as Industry 4.0 and factory automation, requires 5G systems to harmonize with the communication technologies used in these industries. To this end, 3GPP Release 16 and Release 17 have made significant progress in integrating 5G systems with the IEEE 802.1 working group specifications on Time-Sensitive Networking (TSN). This paper explains a method and architecture for supporting TSN over a wireless channel in a 5G network that adds the TSN synchronization function in a Small Cell gNB implementing the TSN Translator function (SC-TT). This TSN-capable small cell provides TSN over the wireless network to synchronize UEs with the Grand Master (GM) using the physical layer signal of the 5G radio frame and the transmission of the GM reference time to provide high-precision synchronization. This paper explores the pivotal role of a Slot Indicator Signal in enhancing synchronization precision, ensuring that the UE-GM synchronization occurs within an exceptionally narrow timeframe as small as 10 ns.
Full article
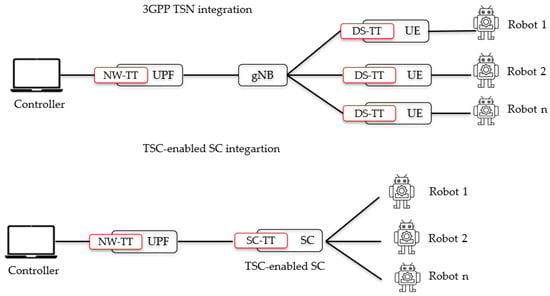
Figure 1
Open AccessCorrection
Correction: Tsakalidis et al. Design and Implementation of a Versatile OpenHAB IoT Testbed with a Variety of Wireless Interfaces and Sensors. Telecom 2023, 4, 597–610
by
Sotirios Tsakalidis, George Tsoulos, Dimitrios Kontaxis and Georgia Athanasiadou
Telecom 2024, 5(1), 48; https://doi.org/10.3390/telecom5010003 - 19 Jan 2024
Abstract
There was an error in the original publication [...]
Full article
Open AccessArticle
An Emergency Message Routing Protocol for Improved Congestion Management in Hybrid RF/VLC VANETs
by
Noha Hassan, Xavier Fernando and Isaac Woungang
Telecom 2024, 5(1), 21-47; https://doi.org/10.3390/telecom5010002 - 25 Dec 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Unexpected traffic incidents cause safety concerns and intense traffic congestion on crowded urban road networks. Vehicular ad-hoc network (VANET)-aided Intelligent Transport Systems (ITS) aim to mitigate these risks through timely dissemination of alert messages. However, conventional Radio frequency (RF) mobile ad-hoc routing protocols
[...] Read more.
Unexpected traffic incidents cause safety concerns and intense traffic congestion on crowded urban road networks. Vehicular ad-hoc network (VANET)-aided Intelligent Transport Systems (ITS) aim to mitigate these risks through timely dissemination of alert messages. However, conventional Radio frequency (RF) mobile ad-hoc routing protocols are ill-suited for dynamic VANET environments due to high mutual interference, packet collisions, high end-to-end delay from frequent route discoveries, and periodic beaconing requirements. Fortunately, the quickly emerging Visible Light Communications (VLC) provide complementary short-range connectivity with high bandwidth and low interference. This paper proposes an efficient adaptive routing protocol for emergency messages in dense VANET scenarios leveraging a hybrid RF/VLC system. When an incident or congestion happens, the source vehicle disseminates the information to the incoming vehicles as quickly as possible using a combination of VLC and RF communication networks. Multi-hop relays extend the connectivity if the direct links are blocked. The coverage area is partitioned into zones based on road segments, intersections, and traffic flows. The Road Side Units (RSU)s are intelligently assigned to zones and they analyze the historical traffic data to characterize each zone and decide a response strategy. We also propose a congestion detection scheme that utilizes traffic simulations to forecast the clearance times under different response strategies. The highest-scoring strategy is selected based on the predicted impacts on travel time, emissions, and driver stress levels. The proposed algorithm adaptively uses the selected strategy to proactively alleviate the predicted congestion through optimized routing and control. Overall, the protocol maximizes safety and efficiency during emergencies by leveraging the hybrid RF/VLC, incorporating real-time congestion forecasting and dynamic rerouting into the response strategies.
Full article
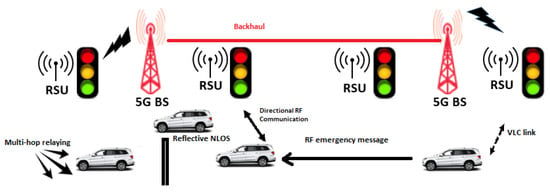
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Smart Detection System of Safety Hazards in Industry 5.0
by
Stavroula Bourou, Apostolos Maniatis, Dimitris Kontopoulos and Panagiotis A. Karkazis
Telecom 2024, 5(1), 1-20; https://doi.org/10.3390/telecom5010001 - 22 Dec 2023
Cited by 1
Abstract
Safety management is a priority to guarantee human-centered manufacturing processes in the context of Industry 5.0, which aims to realize a safe human–machine environment based on knowledge-driven approaches. The traditional approaches for safety management in the industrial environment include staff training, regular inspections,
[...] Read more.
Safety management is a priority to guarantee human-centered manufacturing processes in the context of Industry 5.0, which aims to realize a safe human–machine environment based on knowledge-driven approaches. The traditional approaches for safety management in the industrial environment include staff training, regular inspections, warning signs, etc. Despite the fact that proactive measures and procedures have exceptional importance in the prevention of safety hazards, human–machine–environment coupling requires more sophisticated approaches able to provide automated, reliable, real-time, cost-effective, and adaptive hazard identification in complex manufacturing processes. In this context, the use of virtual reality (VR) can be exploited not only as a means of human training but also as part of the methodology to generate synthetic datasets for training AI models. In this paper, we propose a flexible and adjustable detection system that aims to enhance safety management in Industry 5.0 manufacturing through real-time monitoring and identification of hazards. The first stage of the system contains the synthetic data generation methodology, aiming to create a synthetic dataset via VR, while the second one concerns the training of AI object detectors for real-time inference. The methodology is evaluated by comparing the performance of models trained on both real-world data from a publicly available dataset and our generated synthetic data. Additionally, through a series of experiments, the optimal ratio of synthetic and real-world images is determined for training the object detector. It has been observed that even with a small amount of real-world data, training a robust AI model is achievable. Finally, we use the proposed methodology to generate a synthetic dataset of four classes as well as to train an AI algorithm for real-time detection.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Digitalization, Information Technology and Social Development)
►▼
Show Figures
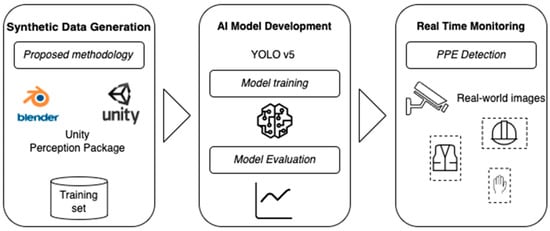
Figure 1
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
Mitigating Timing Side-Channel Attacks in Software-Defined Networks: Detection and Response
by
Faizan Shoaib, Yang-Wai Chow, Elena Vlahu-Gjorgievska and Chau Nguyen
Telecom 2023, 4(4), 877-900; https://doi.org/10.3390/telecom4040038 - 15 Dec 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Software-defined networking (SDN) is an innovative technology that has the potential to enhance the scalability, flexibility, and security of telecommunications networks. The emergence and development of SDNs have introduced new opportunities and challenges in the telecommunications industry. One of the major challenges encountered
[...] Read more.
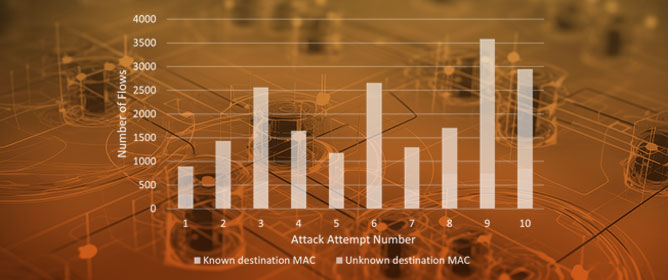
Software-defined networking (SDN) is an innovative technology that has the potential to enhance the scalability, flexibility, and security of telecommunications networks. The emergence and development of SDNs have introduced new opportunities and challenges in the telecommunications industry. One of the major challenges encountered by SDNs is the timing side-channel attacks. These attacks exploit timing information to expose sensitive data, including flow tables, routes, controller types, and ports, which pose a significant threat to communication networks. Existing techniques for mitigating timing side-channel attacks primarily focus on limiting them via network architectural changes. This significantly increases the overhead of SDNs and makes it difficult to identify the origin of the attack. To secure resilient integration of SDN in telecommunications networks, it is necessary to conduct comprehensive research that not only identifies the attack activity, but also formulates an adequate response. In this paper, we propose a detection and response solution for timing side-channel attacks in SDN. We used a machine learning-based approach to detect the probing activity and identify the source. To address the identified timing side-channel attack queries, we propose a response mechanism. This entails devising a feedback-oriented response to counter the identified source, such as blocking or diverting it, while minimising any adverse effects on legitimate network traffic. This methodology is characterised by an automated data-driven approach that enables prompt and effective responses. The architecture of this security solution ensures that it has a minimal impact on network traffic and resource usage as it is designed to be used in conjunction with SDN. The overall design findings show that our detection approach is 94% precise in identifying timing side-channel attacks in SDN when compared with traditional mitigation strategies. Additionally, the response mechanism employed by this approach yielded highly customised and precise responses, resulting in an impressive accuracy score of 97.6%.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
6G Mobile Networks: Key Technologies, Directions, and Advances
by
Ramraj Dangi, Gaurav Choudhary, Nicola Dragoni, Praveen Lalwani, Utkarsh Khare and Souradeep Kundu
Telecom 2023, 4(4), 836-876; https://doi.org/10.3390/telecom4040037 - 01 Dec 2023
Cited by 3
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The exponential growth of the fifth-generation (5G) network gives businesses and universities a chance to turn their attention to the next-generation network. It is widely acknowledged that many IoT devices require more than 5G to send various types of data in real-time. In
[...] Read more.
The exponential growth of the fifth-generation (5G) network gives businesses and universities a chance to turn their attention to the next-generation network. It is widely acknowledged that many IoT devices require more than 5G to send various types of data in real-time. In addition to 5G, several research centres are currently concentrating on 6G, which is expected to produce networks with great quality of service (QoS) and energy efficiency. Future application requirements will necessitate a significant upgrade in mobile network architecture. 6G technologies offer larger networks with lower latency and faster data transmission than 5G networks. This review presents a comprehensive overview of 6G networks which includes the novel architectural changes within 6G networks, recent research insights from diverse institutions, applications within the realm of 6G networks, and the key features associated with them. We also explored various technologies of 6G networks encompassing terahertz, visible light connectivity, blockchain, and symbiotic broadcasting, all of which contribute to the establishment of robust and socially integrated network structures. In this survey, we have focused on 6G network slices and discussed a detailed exploration of security and privacy concerns regarding the potential 6G technologies at the levels of physical infrastructure, connecting protocols, and service provisions, alongside an evaluation of current security strategies.
Full article
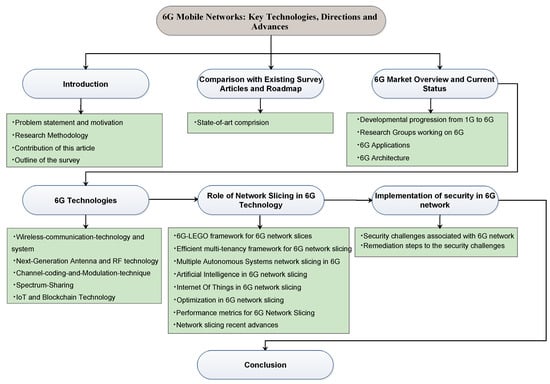
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Performance Improvement Using ICIC for UAV-Assisted Public Safety Networks with Clustered Users during Emergency
by
Abhaykumar Kumbhar
Telecom 2023, 4(4), 816-835; https://doi.org/10.3390/telecom4040036 - 20 Nov 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The application of drones, also known as unmanned aerial vehicles deployed as unmanned aerial base stations (UABSs), has received extensive interest for public safety communications (PSC) to fill the coverage gaps and establish ubiquitous connectivity. In this article, we design a PSC LTE-Advanced
[...] Read more.
The application of drones, also known as unmanned aerial vehicles deployed as unmanned aerial base stations (UABSs), has received extensive interest for public safety communications (PSC) to fill the coverage gaps and establish ubiquitous connectivity. In this article, we design a PSC LTE-Advanced air–ground-based HetNet (AG-HetNet) that is a scenario representation of a geographical area during and after a disaster. As part of the AG-HetNet infrastructure, we have UABSs and ground user equipment (GUE) flocking together in clusters at safe places or evacuation shelters. AG-HetNet uses cell range expansion (CRE), intercell interference coordination (ICIC), and 3D beamforming techniques to ensure ubiquitous connectivity. Through system-level simulations and using a brute-force technique, we evaluate the performance of the AG-HetNet in terms of fifth-percentile spectral efficiency (5pSE) and coverage probability. We compare system-wide 5pSE and coverage probability when UABSs are deployed on a hexagonal grid and for different clustering distributions of GUEs. The results show that reduced power subframes (FeICIC) defined in 3GPP Release-11 can provide practical gains in 5pSE and coverage probability than the 3GPP Release-10 with almost blank subframes (eICIC).
Full article
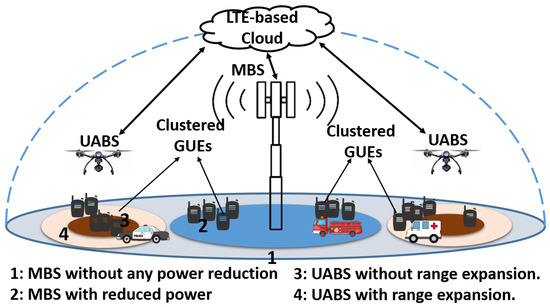
Figure 1
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Applied Sciences, Electronics, Remote Sensing, Sensors, Technologies, Telecom
Recent Advances in PNT Technology with GNSS as the Core and Its Application in Emerging Fields
Topic Editors: Liang Chen, Zhiguo Deng, Guanwen Huang, Huizhong ZhuDeadline: 31 August 2024
Topic in
Coatings, Electronics, Energies, Sensors, Telecom
Condition Monitoring and Diagnostic Methods for Power Equipment in New Energy Power Systems
Topic Editors: Shuaibing Li, Guoqiang Gao, Guochang Li, Yi Cui, Jiefeng Liu, Guangya Zhu, Jin LiDeadline: 15 September 2024
Topic in
Applied Sciences, Electronics, IoT, JSAN, Network, Sensors, Telecom, Technologies
Wireless Energy Harvesting and Power Transfer for Communications and Networks
Topic Editors: Yichuang Sun, Arooj Mubashara Siddiqui, Xiaojing Chen, Oluyomi SimpsonDeadline: 31 December 2024
Topic in
Applied Sciences, Electronics, JSAN, Photonics, Sensors, Telecom
Machine Learning in Communication Systems and Networks, 2nd Edition
Topic Editors: Yichuang Sun, Haeyoung Lee, Oluyomi SimpsonDeadline: 20 July 2025

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Telecom
Joint Application of Telecom and Internet Services
Guest Editors: Arianit Maraj, Dardan MarajDeadline: 31 May 2024
Special Issue in
Telecom
Digitalization, Information Technology and Social Development
Guest Editor: Przemysław Falkowski-GilskiDeadline: 10 June 2024
Special Issue in
Telecom
Advances in Wireless Communication: Applications and Developments
Guest Editor: Mario E. Rivero-AngelesDeadline: 31 July 2024
Special Issue in
Telecom
Performance Criteria for Advanced Wireless Communications
Guest Editor: Seyeong ChoiDeadline: 1 March 2025