Electrical Technologies
A topical collection in Technologies (ISSN 2227-7080).
Viewed by 28775
Share This Topical Collection
Editors
 Prof. Dr. Valeri Mladenov
Prof. Dr. Valeri Mladenov
 Prof. Dr. Valeri Mladenov
Prof. Dr. Valeri Mladenov
E-Mail
Website
Collection Editor
Department Theoretical Electrical Engineering, Technical University of Sofia, Kliment Ohridski St. 8, 1000 Sofia, Bulgaria
Interests: electrical engineering; electronics; artificial intelligence; neural networks; power systems; applied mathematics; signal processing
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
 Dr. Vasiliki Vita
Dr. Vasiliki Vita
 Dr. Vasiliki Vita
Dr. Vasiliki Vita
E-Mail
Website
Collection Editor
Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering Educators, School of Pedagogical and Technological Education (ASPETE), N. Heraklion Attikis, 141 21 Athens, Greece
Interests: transmission and distribution grids; electric vehicles; distributed generation; energy storage, energy markets; artificial intelligence
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
We are happy to announce a new Topical Collection (TC) of the MDPI journal Technologies, focused on electrical technologies. Electrical technologies are technologies that use electrical power and electronic devices to perform various tasks in different industries. This field includes a broad spectrum of technologies, including power generation and distribution, electronics, telecommunications, and automation.
The purpose of the proposed TC on Electrical Technologies is to provide a wide-ranging view of recent advances in the area. The topics of interest for this SI include, but are not limited to:
- Power generation from a variety of sources, including fossil fuels, nuclear energy, hydroelectric power, wind power, and solar power and distribution. Producing electricity and transporting it to homes, businesses, and industries.
- The study of electronic devices and their applications. Design and manufacturing of electronic devices such as computers, televisions, smart phones, and other consumer electronics.
- Transmitting information over a distance through electronic means, such as telephones, radios, and the internet. Wired and wireless networks, satellite systems, and mobile devices.
- The use of electronic and computerized systems to control and monitor industrial processes. This includes robotics, programmable logic controllers (PLCs), and other technologies used in manufacturing and other industrial applications.
- Renewable energy. Generation of energy from sources that are replenished naturally over time, such as solar, wind, and geothermal. Reduction in reliance on fossil fuels and movement towards more sustainable energy sources.
Prof. Dr. Valeri Mladenov
Dr. Vasiliki Vita
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Technologies is an international peer-reviewed open access monthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript.
The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 1600 CHF (Swiss Francs).
Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's
English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- power generation
- microgrids
- smart grids
- electronic devices
- micro-electronics
- power electron-ics
- telecommunications
- control and automation
- renewable energy
- stability
- reliability
- optimi-zation
Published Papers (15 papers)
Open AccessReview
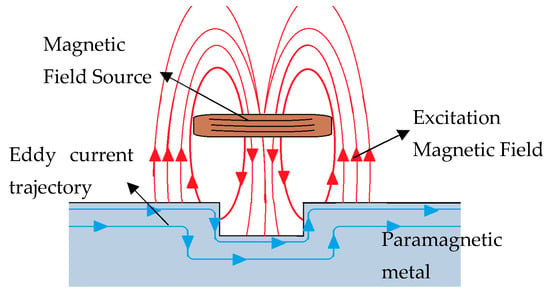
Past, Present, and Future of New Applications in Utilization of Eddy Currents
by
Nestor O. Romero-Arismendi, Juan C. Olivares-Galvan, Jose L. Hernandez-Avila, Rafael Escarela-Perez, Victor M. Jimenez-Mondragon and Felipe Gonzalez-Montañez
Viewed by 844
Abstract
Eddy currents are an electromagnetic phenomenon that represent an inexhaustible source of inspiration for technological innovations in the 21st century. Throughout history, these currents have been a subject of research and technological development in multiple fields. This article delves into the fascinating world
[...] Read more.
Eddy currents are an electromagnetic phenomenon that represent an inexhaustible source of inspiration for technological innovations in the 21st century. Throughout history, these currents have been a subject of research and technological development in multiple fields. This article delves into the fascinating world of eddy currents, revealing their physical foundations and highlighting their impact on a wide range of applications, ranging from non-destructive evaluation of materials to levitation phenomena, as well as their influence on fields as diverse as medicine, the automotive industry, and aerospace. The nature of eddy currents has stimulated the imaginations of scientists and engineers, driving the creation of revolutionary technologies that are transforming our society. As we progress through this article, we will cover the main aspects of eddy currents, their practical applications, and challenges for future works.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
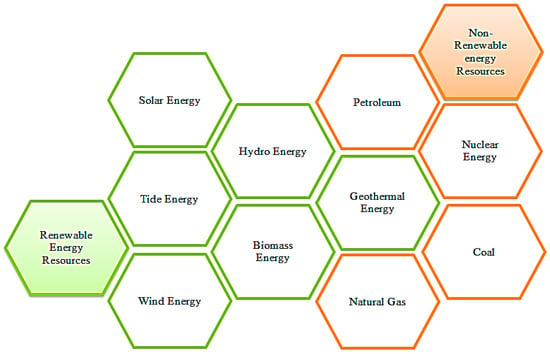
Performance Assessment of Different Sustainable Energy Systems Using Multiple-Criteria Decision-Making Model and Self-Organizing Maps
by
Satyabrata Dash, Sujata Chakravarty, Nimay Chandra Giri, Umashankar Ghugar and Georgios Fotis
Viewed by 886
Abstract
The surging demand for electricity, propelled by the widespread adoption of intelligent grids and heightened consumer interaction with electricity demand and pricing, underscores the imperative for precise prognostication of optimal power plant utilization. To confront this challenge, a dataset centered on issue-centric power
[...] Read more.
The surging demand for electricity, propelled by the widespread adoption of intelligent grids and heightened consumer interaction with electricity demand and pricing, underscores the imperative for precise prognostication of optimal power plant utilization. To confront this challenge, a dataset centered on issue-centric power plans is meticulously crafted. This dataset encapsulates pivotal facets indispensable for attaining sustainable power generation, including meager gas emissions, installation cost, low maintenance cost, elevated power generation, and copious resource availability. The selection of an optimal power plant entails a multifaceted decision-making process, demanding a systematic approach. Our research advocates the amalgamation of multiple-criteria decision-making (MCDM) models with self-organizing maps to gauge the efficacy of diverse sustainable energy systems. The examination discerns solar energy as the preeminent MCDM criterion, securing the apex position with a score of 83.4%, attributable to its ample resource availability, considerable energy generation, nil greenhouse gas emissions, and commendable efficiency. Wind and hydroelectric power closely trail, registering scores of 75.3% and 74.5%, respectively, along with other energy sources. The analysis underscores the supremacy of the renewable energy sources, particularly solar and wind, in fulfilling sustainability objectives and scrutinizing factors such as cost, resource availability, and the environmental impact. The proposed methodology empowers stakeholders to make judicious decisions, accentuating facets that are required for more sustainable and resilient power infrastructure.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
Angle Calculus-Based Thrust Force Determination on the Blades of a 10 kW Wind Turbine
by
José Rafael Dorrego-Portela, Adriana Eneida Ponce-Martínez, Eduardo Pérez-Chaltell, Jaime Peña-Antonio, Carlos Alberto Mateos-Mendoza, José Billerman Robles-Ocampo, Perla Yazmin Sevilla-Camacho, Marcos Aviles and Juvenal Rodríguez-Reséndiz
Viewed by 1306
Abstract
In this article, the behavior of the thrust force on the blades of a 10 kW wind turbine was obtained by considering the characteristic wind speed of the Isthmus of Tehuantepec. Analyzing mechanical forces is essential to efficiently and safely design the different
[...] Read more.
In this article, the behavior of the thrust force on the blades of a 10 kW wind turbine was obtained by considering the characteristic wind speed of the Isthmus of Tehuantepec. Analyzing mechanical forces is essential to efficiently and safely design the different elements that make up the wind turbine because the thrust forces are related to the location point and the blade rotation. For this reason, the thrust force generated in each of the three blades of a low-power wind turbine was analyzed. The angular position (
) of each blade varied from 0° to 120°, the blades were segmented (r), and different wind speeds were tested, such as cutting, design, average, and maximum. The results demonstrate that the thrust force increases proportionally with increasing wind speed and height, but it behaves differently on each blade segment and each angular position. This method determines the angular position and the exact blade segment where the smallest and the most considerable thrust force occurred. Blade 1, positioned at an angular position of 90°, is the blade most affected by the thrust force on P15. When the blade rotates 180°, the thrust force decreases by 9.09 N; this represents a 66.74% decrease. In addition, this study allows the designers to know the blade deflection caused by the thrust force. This information can be used to avoid collision with the tower. The thrust forces caused blade deflections of 10% to 13% concerning the rotor radius used in this study. These results guarantee the operation of the tested generator under their working conditions.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
An Optimum Load Forecasting Strategy (OLFS) for Smart Grids Based on Artificial Intelligence
by
Asmaa Hamdy Rabie, Ahmed I. Saleh, Said H. Abd Elkhalik and Ali E. Takieldeen
Viewed by 1210
Abstract
Recently, the application of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in many areas of life has allowed raising the efficiency of systems and converting them into smart ones, especially in the field of energy. Integrating AI with power systems allows electrical grids to be smart enough
[...] Read more.
Recently, the application of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in many areas of life has allowed raising the efficiency of systems and converting them into smart ones, especially in the field of energy. Integrating AI with power systems allows electrical grids to be smart enough to predict the future load, which is known as Intelligent Load Forecasting (ILF). Hence, suitable decisions for power system planning and operation procedures can be taken accordingly. Moreover, ILF can play a vital role in electrical demand response, which guarantees a reliable transitioning of power systems. This paper introduces an Optimum Load Forecasting Strategy (OLFS) for predicting future load in smart electrical grids based on AI techniques. The proposed OLFS consists of two sequential phases, which are: Data Preprocessing Phase (DPP) and Load Forecasting Phase (LFP). In the former phase, an input electrical load dataset is prepared before the actual forecasting takes place through two essential tasks, namely feature selection and outlier rejection. Feature selection is carried out using Advanced Leopard Seal Optimization (ALSO) as a new nature-inspired optimization technique, while outlier rejection is accomplished through the Interquartile Range (IQR) as a measure of statistical dispersion. On the other hand, actual load forecasting takes place in LFP using a new predictor called the Weighted K-Nearest Neighbor (WKNN) algorithm. The proposed OLFS has been tested through extensive experiments. Results have shown that OLFS outperforms recent load forecasting techniques as it introduces the maximum prediction accuracy with the minimum root mean square error.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
A Comprehensive Performance Analysis of a 48-Watt Transformerless DC-DC Boost Converter Using a Proportional–Integral–Derivative Controller with Special Attention to Inductor Design and Components Reliability
by
Kuldeep Jayaswal, D. K. Palwalia and Josep M. Guerrero
Viewed by 1359
Abstract
In this research paper, a comprehensive performance analysis was carried out for a 48-watt transformerless DC-DC boost converter using a Proportional–Integral–Derivative (PID) controller through dynamic modeling. In a boost converter, the optimal design of the magnetic element plays an important role in efficient
[...] Read more.
In this research paper, a comprehensive performance analysis was carried out for a 48-watt transformerless DC-DC boost converter using a Proportional–Integral–Derivative (PID) controller through dynamic modeling. In a boost converter, the optimal design of the magnetic element plays an important role in efficient energy transfer. This research paper emphasizes the design of an inductor using the Area Product Technique (APT) to analyze factors such as area product, window area, number of turns, and wire size. Observations were made by examining its response to changes in load current, supply voltage, and load resistance at frequency levels of 100 and 500 kHz. Moreover, this paper extended its investigation by analyzing the failure rates and reliability of active and passive components in a 48-watt boost converter, providing valuable insights about failure behavior and reliability. Frequency domain analysis was conducted to assess the controller’s stability and robustness. The results conclusively underscore the benefits of incorporating the designed PID controller in terms of achieving the desired regulation and rapid response to disturbances at 100 and 500 kHz. The findings emphasize the outstanding reliability of the inductor, evident from the significantly low failure rates in comparison to other circuit components. Conversely, the research also reveals the inherent vulnerability of the switching device (MOSFET), characterized by a higher failure rate and lower reliability. The MATLAB
® Simulink platform was utilized to investigate the results.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
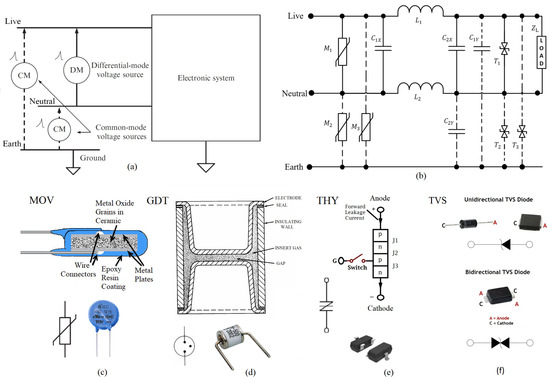
Laplace Transform-Based Modelling, Surge Energy Distribution, and Experimental Validation of a Supercapacitor Transient Suppressor
by
Sadeeshvara Silva Thotabaddadurage
Viewed by 1865
Abstract
The discovery of the transient-surge-withstanding capability of electrochemical dual-layer capacitors (EDLCs) led to the development of a unique, commercially beneficial circuit topology known as a supercapacitor transient suppressor (STS). Despite its low component count, the new design consists of a transient-absorbing magnetic core
[...] Read more.
The discovery of the transient-surge-withstanding capability of electrochemical dual-layer capacitors (EDLCs) led to the development of a unique, commercially beneficial circuit topology known as a supercapacitor transient suppressor (STS). Despite its low component count, the new design consists of a transient-absorbing magnetic core which takes the form of a coupled inductor placed between the AC-main- and load-side varistors. With an introduction to the structural features of metal oxide varistors (MOVs), gas tubes, thyristors, and EDLCs, this research presents a frequency (
S)-domain analysis of an STS circuit to accurately model the surge propagation through its coupled inductor. Transient energy distribution trends among STS components are estimated in this paper, with an emphasis on peak energies absorbed and dissipated by the various inductive, capacitive, and resistive circuit elements. Moreover, this study reveals STS transient-mode test waveforms validated by a standard lightning surge simulator with supporting simulation plots based on LTSpice numerical techniques. Both experimental and simulation results are consistent, with the analytical findings showing 90% of the peak transient propagating through the primary coil, whereas only 10% is shared into the secondary coil of the coupled inductor. In addition, it is proven that the two STS MOVs dissipate over 50% of the transient energy for a standard 6 kV/3 kA combinational surge, while the magnetic core absorbs over 20% of the energy. All test procedures conducted during this research adhere to IEEE C62.41/IEC 61000-4-5 standards.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
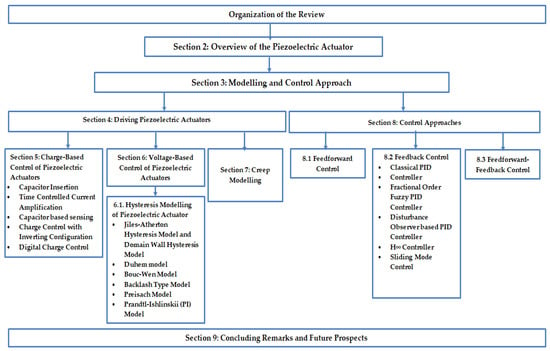
Application of Modeling and Control Approaches of Piezoelectric Actuators: A Review
by
Mithun Kanchan, Mohith Santhya, Ritesh Bhat and Nithesh Naik
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 2313
Abstract
Piezoelectric actuators find extensive application in delivering precision motion in the micrometer to nanometer range. The advantages of a broader range of motion, rapid response, higher stiffness, and large actuation force from piezoelectric actuators make them suitable for precision positioning applications. However, the
[...] Read more.
Piezoelectric actuators find extensive application in delivering precision motion in the micrometer to nanometer range. The advantages of a broader range of motion, rapid response, higher stiffness, and large actuation force from piezoelectric actuators make them suitable for precision positioning applications. However, the inherent nonlinearity in the piezoelectric actuators under dynamic working conditions severely affects the accuracy of the generated motion. The nonlinearity in the piezoelectric actuators arises from hysteresis, creep, and vibration, which affect the performance of the piezoelectric actuator. Thus, there is a need for appropriate modeling and control approaches for piezoelectric actuators, which can model the nonlinearity phenomenon and provide adequate compensation to achieve higher motion accuracy. The present review covers different methods adopted for overcoming the nonlinearity issues in piezoelectric actuators. This review highlights the charge-based and voltage-based control methods that drive the piezoelectric actuators. The survey also includes different modeling approaches for the creep and hysteresis phenomenon of the piezoelectric actuators. In addition, the present review also highlights different control strategies and their applications in various types of piezoelectric actuators. An attempt is also made to compare the piezoelectric actuator’s different modeling and control approaches and highlight prospects.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Modern DC–DC Power Converter Topologies and Hybrid Control Strategies for Maximum Power Output in Sustainable Nanogrids and Picogrids—A Comprehensive Survey
by
Anupama Ganguly, Pabitra Kumar Biswas, Chiranjit Sain and Taha Selim Ustun
Cited by 4 | Viewed by 2403
Abstract
Sustainable energy exhibited immense growth in the last few years. As compared to other sustainable sources, solar power is proved to be the most feasible source due to some unanticipated characteristics, such as being clean, noiseless, ecofriendly, etc. The output from the solar
[...] Read more.
Sustainable energy exhibited immense growth in the last few years. As compared to other sustainable sources, solar power is proved to be the most feasible source due to some unanticipated characteristics, such as being clean, noiseless, ecofriendly, etc. The output from the solar power is entirely unpredictable since solar power generation is dependent on the intensity of solar irradiation and solar panel temperature. Further, these parameters are weather dependent and thus intermittent in nature. To conquer intermittency, power converters play an important role in solar power generation. Generally, photovoltaic systems will eventually suffer from a decrease in energy conversion efficiency along with improper stability and intermittent properties. As a result, the maximum power point tracking (MPPT) algorithm must be incorporated to cultivate maximum power from solar power. To make solar power generation reliable, a proper control technique must be added to the DC–DC power converter topologies. Furthermore, this study reviewed the progress of the maximum power point tracking algorithm and included an in-depth discussion on modern and both unidirectional and bidirectional DC–DC power converter topologies for harvesting electric power. Lastly, for the reliability and continuity of the power demand and to allow for distributed generation, this article also established the possibility of integrating solar PV systems into nanogrids and picogrids in a sustainable environment. The outcome of this comprehensive survey would be of strong interest to the researchers, technologists, and the industry in the relevant field to carry out future research.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessCommunication
FPGA-Based Implementation of a New 3-D Multistable Chaotic Jerk System with Two Unstable Balance Points
by
Sundarapandian Vaidyanathan, Esteban Tlelo-Cuautle, Khaled Benkouider, Aceng Sambas and Brisbane Ovilla-Martínez
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 1278
Abstract
Mechanical jerk systems have applications in several areas, such as oscillators, microcontrollers, circuits, memristors, encryption, etc. This research manuscript reports a new 3-D chaotic jerk system with two unstable balance points. It is shown that the proposed mechanical jerk system exhibits multistability with
[...] Read more.
Mechanical jerk systems have applications in several areas, such as oscillators, microcontrollers, circuits, memristors, encryption, etc. This research manuscript reports a new 3-D chaotic jerk system with two unstable balance points. It is shown that the proposed mechanical jerk system exhibits multistability with coexisting chaotic attractors for the same set of system constants but for different initial states. A bifurcation analysis of the proposed mechanical jerk system is presented to highlight the special properties of the system with respect to the variation of system constants. A field-programmable gate array (FPGA) implementation of the proposed mechanical jerk system is given by synthesizing the discrete equations that are obtained by applying one-step numerical methods. The hardware resources are reduced by performing pipeline operations, and, finally, the paper concludes that the experimental results of the proposed mechanical jerk system using FPGA-based design show good agreement with the MATLAB simulations of the same system.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
An Extensive Critique on Smart Grid Technologies: Recent Advancements, Key Challenges, and Future Directions
by
Sonam Dorji, Albert Alexander Stonier, Geno Peter, Ramya Kuppusamy and Yuvaraja Teekaraman
Cited by 7 | Viewed by 4277
Abstract
Given the various aspects of climate change and the growing demand for energy, energy efficiency and environmental protection have become major concerns worldwide. If not taken care of, energy demand will become unmanageable due to technological growth in cities and nations. The solution
[...] Read more.
Given the various aspects of climate change and the growing demand for energy, energy efficiency and environmental protection have become major concerns worldwide. If not taken care of, energy demand will become unmanageable due to technological growth in cities and nations. The solution to the global energy crisis could be an advanced two-way digital power flow system that is capable of self-healing, interoperability, and predicting conditions under various uncertainties and is equipped with cyber protections against malicious attacks. The smart grid enables the integration of renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and energy storage into the grid. Therefore, the perception of the smart grid and the weight given to it by researchers and policymakers are of utmost importance. In this paper, the studies of many researchers on smart grids are examined in detail. Based on the literature review, various principles of smart grids, the development of smart grids, functionality of smart grids, technologies of smart grids with their characteristics, communication of smart grids, problems in the implementation of smart grids, and possible future studies proposed by various researchers have been presented.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessCommunication
Analysis of Redundancy Techniques for Electronics Design—Case Study of Digital Image Processing
by
Padmanabhan Balasubramanian
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 1571
Abstract
Electronic circuits/systems operating in harsh environments such as space are likely to experience faults or failures due to the impact of high-energy radiation. Given this, to overcome any faults or failures, redundancy is usually employed as a hardening-by-design approach. Moreover, low power and
[...] Read more.
Electronic circuits/systems operating in harsh environments such as space are likely to experience faults or failures due to the impact of high-energy radiation. Given this, to overcome any faults or failures, redundancy is usually employed as a hardening-by-design approach. Moreover, low power and a small silicon footprint are also important considerations for space electronics since these translate into better energy efficiency, less system weight, and less cost. Therefore, the fault-tolerant design of electronic circuits and systems should go hand in hand with the optimization of design metrics, especially for resource-constrained electronics such as those used in space systems. A single circuit or system (also called a simplex implementation) is not fault-tolerant as it may become a single point of failure and is not used for a space application. As an alternative, a triple modular redundancy (TMR) implementation, which uses three identical copies of a circuit or system and a voter to perform majority voting of the circuits and systems outputs, may be used. However, in comparison with a simplex implementation, a TMR implementation consumes about 200% more area and dissipates 200% more power when circuits or systems are triplicated. To mitigate the area and power overheads of a TMR implementation compared to a simplex implementation, researchers have suggested alternative redundancy approaches such as selective TMR (STMR) insertion, partially approximate TMR (PATMR), fully approximate TMR (FATMR), and majority voting-based reduced precision redundancy (VRPR). Among these, VRPR appears to be promising, especially for inherently error-tolerant applications such as digital image/video/audio processing, which is relevant to space systems. However, the alternative redundancy approaches mentioned are unlikely to be suitable for the implementation of control logic. In this work, we analyze various redundancy approaches and evaluate the performance of TMR and VRPR for a digital image processing application. We provide MATLAB-based image processing results corresponding to TMR and VRPR and physical implementation results of functional units based on TMR and VRPR using a 28-nm CMOS technology.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
An Efficient Smart Pharmaceutical Packaging Technology Framework to Assess the Quality of Returned Medication through Non-Intrusively Recording Storage Conditions after Dispensation
by
James Gerrans, Parastou Donyai, Katherine Finlay and R. Simon Sherratt
Viewed by 2109
Abstract
Medicine waste is a global issue, with economic, environmental, and social consequences that are only predicted to worsen. A structured review of the literature on medicine reuse revealed that there is a lack of technological applications addressing the key concerns raised by pharmaceutical
[...] Read more.
Medicine waste is a global issue, with economic, environmental, and social consequences that are only predicted to worsen. A structured review of the literature on medicine reuse revealed that there is a lack of technological applications addressing the key concerns raised by pharmaceutical stakeholders on the safety and feasibility of redispensing medication. A basis and guidelines for solutions aiming at enabling medicine reuse were devised by exploring a conceptual model of a Circular Pharmaceutical Supply Chain (CPSC), discussing concerns raised within the literature and identifying methods to influence the public and pharmaceutical companies. SPaRAS, a novel system to validate the storage conditions and streamline the assessment of returned medicines, is proposed. The Smart Packaging System (SPS) will record the storage conditions of medication while in patient care. The companion Returns Assessment System (RAS) will efficiently communicate with the SPS through RFID, configure the sensors within the SPS to the needs of its assigned medicine and assess the returns against tailored eligibility criteria. The increased safety and efficiency provided by SPaRAS addresses the concerns of large pharmaceutical companies and the public, offering a method to reuse previously owned medication and reduce the effects of unnecessary medicine waste.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessEditor’s ChoiceArticle
Utilization of Artificial Neural Networks for Precise Electrical Load Prediction
by
Christos Pavlatos, Evangelos Makris, Georgios Fotis, Vasiliki Vita and Valeri Mladenov
Cited by 11 | Viewed by 1697
Abstract
In the energy-planning sector, the precise prediction of electrical load is a critical matter for the functional operation of power systems and the efficient management of markets. Numerous forecasting platforms have been proposed in the literature to tackle this issue. This paper introduces
[...] Read more.
In the energy-planning sector, the precise prediction of electrical load is a critical matter for the functional operation of power systems and the efficient management of markets. Numerous forecasting platforms have been proposed in the literature to tackle this issue. This paper introduces an effective framework, coded in Python, that can forecast future electrical load based on hourly or daily load inputs. The framework utilizes a recurrent neural network model, consisting of two simpleRNN layers and a dense layer, and adopts the Adam optimizer and tanh loss function during the training process. Depending on the size of the input dataset, the proposed system can handle both short-term and medium-term load-forecasting categories. The network was extensively tested using multiple datasets, and the results were found to be highly promising. All variations of the network were able to capture the underlying patterns and achieved a small test error in terms of root mean square error and mean absolute error. Notably, the proposed framework outperformed more complex neural networks, with a root mean square error of 0.033, indicating a high degree of accuracy in predicting future load, due to its ability to capture data patterns and trends.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Geographical Dependence of Open Hardware Optimization: Case Study of Solar Photovoltaic Racking
by
Shafquat Rana, Nicholas Vandewetering, Jadyn Powell, Jonathan Álvarez Ariza and Joshua M. Pearce
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 2632
Abstract
Open-source technological development is well-known for rapid innovation and providing opportunities to reduce costs and thus increase accessibility for a wide range of products. This is done through distributed manufacturing, in which products are produced close to end users. There is anecdotal evidence
[...] Read more.
Open-source technological development is well-known for rapid innovation and providing opportunities to reduce costs and thus increase accessibility for a wide range of products. This is done through distributed manufacturing, in which products are produced close to end users. There is anecdotal evidence that these opportunities are heavily geographically dependent, with some locations unable to acquire components to build open hardware at accessible prices because of trade restrictions, tariffs, taxes, or market availability. Supply chain disruptions during the COVID-19 pandemic exacerbated this and forced designers to pivot towards a la carte-style design frameworks for critical system components. To further develop this phenomenon, a case study of free and open-source solar photovoltaic (PV) racking systems is provided. Two similar open-source designs made from different materials are compared in terms of capital costs for their detailed bill of materials throughout ten locations in North, Central and South America. The differences in economic optimization showed that the costs of wood-based racks were superior in North America and in some South American countries, while metal was less costly in Central and South America. The results make it clear that open hardware designs would be best to allow for local optimization based on material availability in all designs.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessEditor’s ChoiceArticle
Photovoltaic Inverter Reliability Study through SiC Switches Redundant Structures
by
Ignacio Villanueva, Nimrod Vázquez, Joaquín Vaquero, Claudia Hernández, Héctor López-Tapia and Rene Osorio-Sánchez
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 1640
Abstract
Reliability is a very important issue in power electronics; however, sometimes it is not considered, studied, or analyzed. At present, renewables have become more popular, and more complex setups are required to drive this type of system. In the specific case of inverters
[...] Read more.
Reliability is a very important issue in power electronics; however, sometimes it is not considered, studied, or analyzed. At present, renewables have become more popular, and more complex setups are required to drive this type of system. In the specific case of inverters in photovoltaic systems, the user’s safety, quality, reliability, and the system’s useful life must be guaranteed. In this paper, the reliability of a full bridge inverter is predicted by calculating metrics such as failure rates and Mean Time Between Failures. Reliability is obtained using different types of structures for SiC MOSFETs: serial systems, active parallel redundant systems, and passive parallel redundant systems. Finally, the reliability study shows that a system with a passive parallel redundant structure is more reliable and has a higher useful life compared to the other structures.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures