Circular Economy Approaches for Lifecycles of Products and Services
A topical collection in Sustainability (ISSN 2071-1050). This collection belongs to the section "Sustainable Products and Services".
Viewed by 46781Editors
Interests: circular economy; sustainable technology; sustainable production and consumption; sustainable design and manufacture
Interests: sustainability; ICT; internet of things; sustainable production and consumption; industrial engineering; control
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
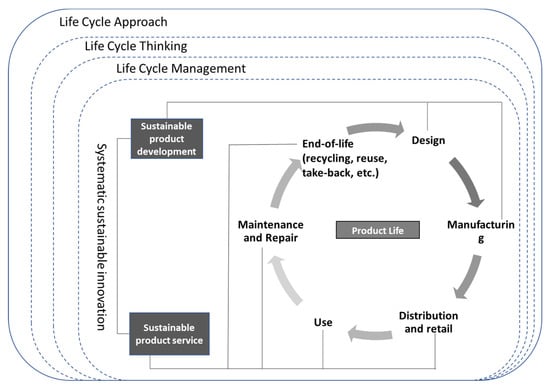
There has been an increasing demand to implement circular economy approaches in the development of products and services through product life cycle. To facilitate implementation, sustainability technologies play important roles covering environmental, social and economic perspectives. To meet the demand, the project “a circular economy approach for lifecycles of products and services (CIRC4Life)” http://www.circ4life.eu has been in operation since May 2018 and will conclude at the end of October 2021 with total project budget 7.3 million euros. The CIRC4Life project is supported by the European Commission’s Horizon 2020 programme, which involves 17 international teams.
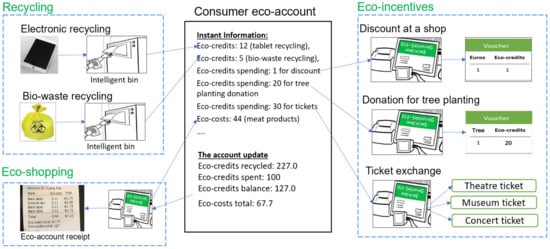
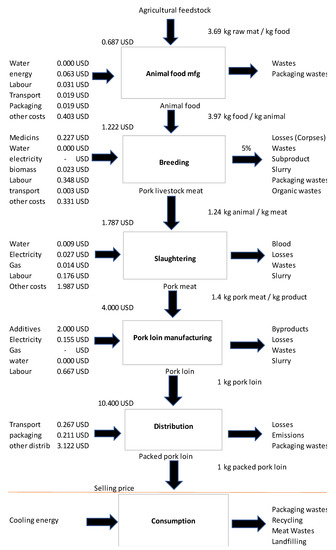
The CIRC4Life project develops three circular economy business models (CEBMs): the co-creation of products and services, sustainable consumption, and collaborative recycling/reuse. The CEBMs are demonstrated in four industrial sectors: LED lighting products, vegetable farming, meat supply chain and bio-waste recycling, and computer tablet recycling and reuse. The CEBMs and demonstrators are supported by various sustainability technologies, including information and communication technology (ICT), traceability, environmental and social life cycle assessments, sustainable design and manufacture, eco-accounting, eco-shopping and eco-incentives, decision-making tools, online data mining, living lab approaches, and more, which can be found on the project Website mentioned above.
In order to further develop and implement circular economy approaches and sustainability, to share the CIRC4Life project achievements and to promote the research outcome in the research areas, this Topical Collection calls for papers focused on, but not limited to, the following topics:
- Circular economy and sustainability methods/technologies
- Circular economy approaches for products and services;
- Circular economy business models;
- Sustainability technologies and their industrial application;
- Sustainability and circular economy through product life cycle;
- Methodologies for environmentally friendly product development;
- Environmental life cycle assessment. Social life cycle assessment. Three bottom lines of sustainability;
- Product environmental footprint, environmental product declaration, product carbon footprint, life cycle analysis methods, lifecycle inventory data;
- Eco-labelling and environmental labelling.
- Circular economy and sustainability implementation
- Sustainable production and consumption;
- Eco-design and eco-manufacture;
- Product supply chain/value chain with sustainability;
- Methods and applications of Eco-accounting, eco-cost, eco-credit, eco-shopping and eco-incentives;
- Climate change resilience, and green-house gas emission adaptation and mitigation;
- Sustainable built and environment;
- Low carbon emission buildings and sustainable construction;
- Renewable energy;
- End-of-life product treatment. Remanufacture, recycle and reuse. WEEE treatment. Bio-waste treatment;
- Sustainable product services, leasing services, product maintenance;
- Sustainable technology for vegetable farming and the meat supply chain;
- Co-creation and living labs for circular economy.
- Development and support for circular economy and sustainability
- Traceability, control, condition monitoring and related technologies for circular economy and sustainability;
- Sustainability and circular economy supported by ICT technologies such as smart computing, internet of things, mobile technology, big data, cloud computing, internet technology, blockchain, etc;
- ICT infrastructure for sustainability;
- Online data mining consumer preferences from e-commerce websites;
- Green computing;
- Decision-making systems for sustainability;
- Policy alignment for circular economy and sustainability;
- Education and training for circular economy and sustainability;
- Public awareness of circular economy and sustainability;
- Literature review for circular economy and sustainability;
- Other issues/fields related to circular economy and sustainability.
Prof. Dr. Daizhong Su
Dr. Wenjie Peng
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Sustainability is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2400 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- circular economy
- sustainability
- sustainable technology
- product life cycle
- products and services
- sustainable production and consumption
- information and communication technology (ICT)
- computing
- traceability
- policy
- recycle
- reuse
- re-manufacture