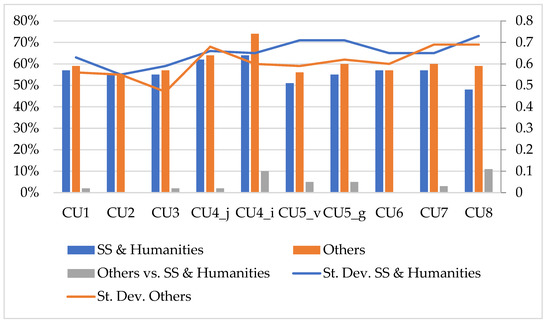
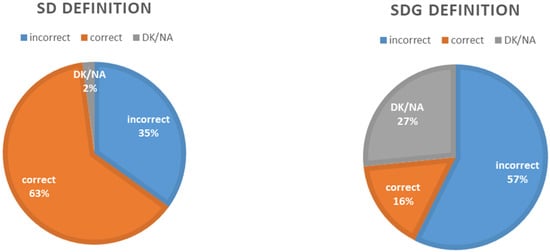
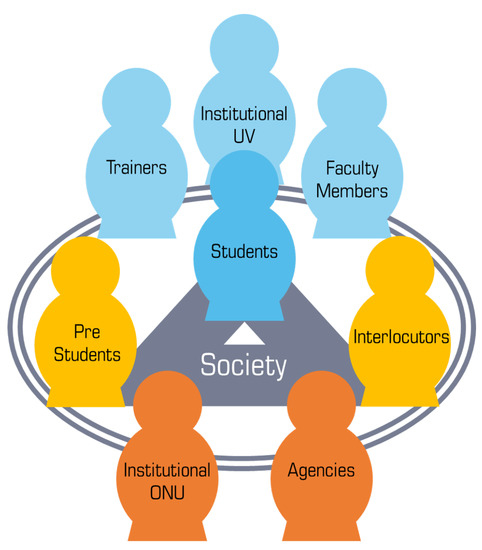
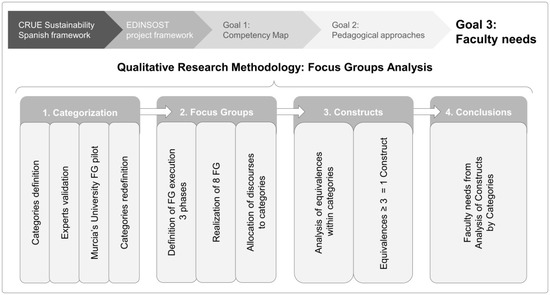
Education for Sustainable Development in Higher Education
A topical collection in Sustainability (ISSN 2071-1050). This collection belongs to the section "Sustainable Education and Approaches".
Viewed by 115936Editors
Interests: education for sustainable development; innovation in engineering education; ethics and sustainability in engineering education; neuroeducation; curriculum design
Interests: sustainability education in engineering; pedagogical innovation in engineering education; circular design education; education in design engineering
Interests: sustainability education in engineering; pedagogical innovation in engineering education; transdisciplinarity in engineering; challenge-based education in engineering
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
Education for sustainable Development (ESD) plays a key role in Higher Education degrees. University students must learn to think long-term and understand that in order to achieve a better world, they must situate their future professional activities within the framework of sustainable solutions. To this end, future graduates must be aware of the complexities of the social environment in which they are developing their work, and of the need to harmonize short-term improvements with sustainable development based on the long term. ESD is essential for the training of agents of change and transformation that can promote policies, strategies, and methods that enable a more sustainable future to be built.
ESD has mainly been addressed in Higher Education in three different ways: (1) introducing specific sustainability subjects into the curriculum, (2) including learning objectives related to sustainability in technical subjects, and (3) applying the criterion of sustainability in the final degree thesis.
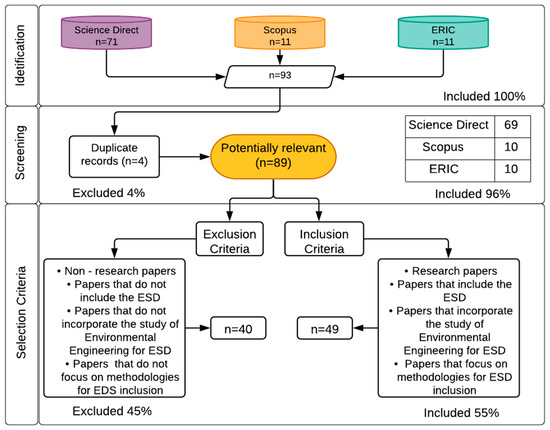
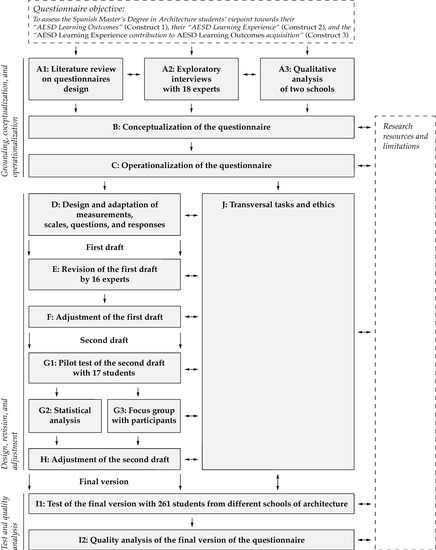
This Topical Collection will gather original research in the field of ESD in Higher Education focused on introducing ESD in Higher Education curricula, assessing students’ sustainability competencies, and evaluating the impacts of ESD in people's daily lives.
Suitable topics include but are not limited to the following:
- introducing ethics in Higher Education;
- deontological principles related to sustainability in Higher Education;
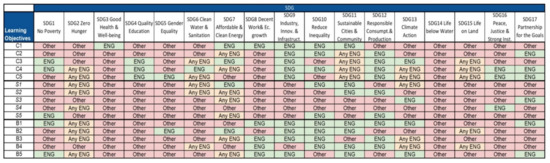
- developing Sustainable Development Goals (SDG) in Higher Education subjects;
- developing SDG in bachelor's and master's theses,
- how to reduce the human carbon footprint thanks to Higher Education;
- how to improve people's daily lives through Higher Education;
- accessibility, ergonomics and security in technological solutions;
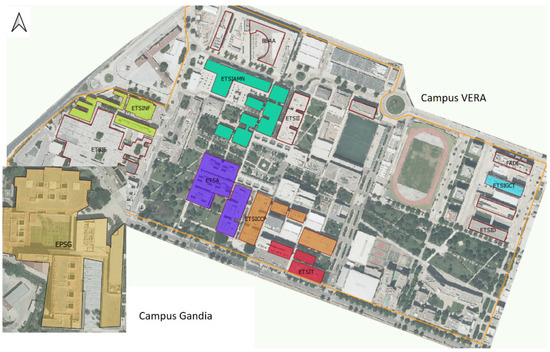
- living labs and campus labs for sustainability education in universities
- teaching methodologies to introduce sustainability and social commitment in Higher Education.
- inter- and transdisciplinarity for sustainability in higher education
Dr. Fermin Sanchez-Carracedo
Dr. Jordi Segalàs Coral
Dr. Gemma Tejedor
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Sustainability is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2400 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- introducing ESD and SDG in Higher Education curricula
- instruments for assessing ESD in Higher Education
- sustainability in final degree projects
- ethics and deontological principles in Higher Education
- encouraging research and dissemination of sustainable development knowledge
- pedagogical approaches to ESD