Project Risk Assessment and Corporate Behavior: Creating Knowledge for Sustainable Business (Closed)
A topical collection in Sustainability (ISSN 2071-1050). This collection belongs to the section "Economic and Business Aspects of Sustainability".
Viewed by 49416Editor
2. CTS Uninova, 2829-516 Caparica, Portugal
Interests: project management; risk management
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
In today’s turbulent and unpredictable business landscape, if organizations want to achieve a sustainable competitive advantage, they must prioritize performance and innovation. The business environment has changed radically in recent years, and this change will certainly continue.
Nowadays, the importance of projects is overwhelming, and their importance will grow in the future. In this context, projects emerge as a way for organizations to implement their strategic objectives in order to respond to a need, opportunity, or threat in an efficient way. Furthermore, organizations alone do not always hold the necessary resources to enhance performance. Therefore, organizations often engage in collaborative projects, where they interact with business partners, customers, universities, and scientific and public institutions, and through the exchange of ideas, resources, and technologies facilitate the achievement of individual and collective goals. Indeed, certain authors and researchers argue that, among many other factors, the ability of an organization to develop projects is central to an organization’s success.
It must be stated that not all organizations have production; however, all organizations have projects. The risk is the probability of a specified uncertain event occurring and the consequences. Any factor that affects the performance of a project can be a source of risk for an organization.
The risk arises when this effect has an uncertain and significant impact on an organization’s competitiveness. In this context, the management of risk in projects and its corporate impact is currently one of the main topics of interest for researchers and practitioners working in the area of project management.
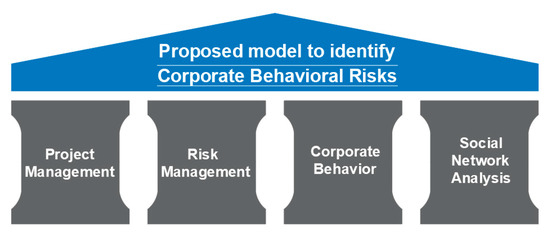
This Special Issue will focus on symbioses between Project Risk Assessment and Corporate Behavior in order to support organizational sustainability. Contributions concerning theoretical approaches as well as case studies are welcome.
Prof. Dr. António Abreu
Guest Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Sustainability is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2400 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- Sustainable project
- Project sustainability management
- Sustainability metrics
- Strategies of Mitigation
- Technologies to support sustainable project management
- Project sustainability and organizational Behavior
- Challenges for risk management in projects
- Risk management process
- Risk analyses Tools
- Risk evaluation tools
- Collaborative project
- Simulation
- Cases studies