Sustainable Consumption and Production
A topical collection in Sustainability (ISSN 2071-1050). This collection belongs to the section "Environmental Sustainability and Applications".
Viewed by 80728Editors
Interests: sustainable consumption and production, circular economy, life cycle assessment, sustainability indicators, education for sustainable development, sustainable cities
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
We are preparing a Special Issue in the research field of sustainable consumption and production.
The Bundtland report, published in 1987, generally defined sustainabile development and framed the future of a global society. Furthermore, the Agenda 21 as a deliverable of the United Nation Earth Summit in 1992 paved a way for sustainable consumption and production. Following those, a success at the global level was perceived, in terms of reducing the usage of toxic chemicals, changing consumption patters and resource usage, as well as innovations from engineering and technology perspectives (Kovačič Lukman et al., 2016). However, challenges in sustainable consumption and production still exist in 2020, especially when considering reaching Sustainable Development Goal No. 12. and the European Union Green Deal, emphasizing research, innovations, and technology improvements in a context of environmental, economic, societal, and policy dimensions.
Thus, we are inviting all authors of relevant research domains to submit high-level original research, state-of-the-art reviews or evidenced-based case studies, contributing to theoretical understanding and practical implementation of sustainable consumption and production, from various perspecives: engineering, technology, environmental, and societal. The papers should address but are not limited to:
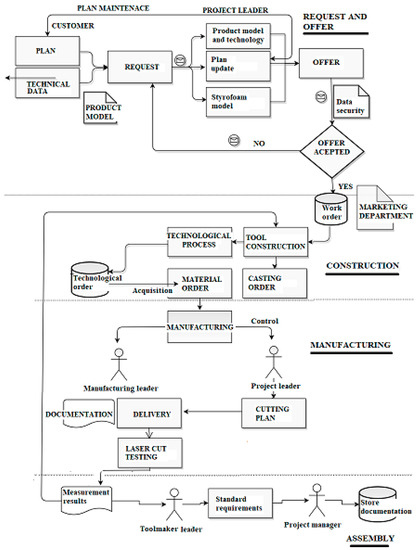
- Sustainable production and resource efficiency, including innovative and sustainable manufacturing processes, products and service design;
- Life cycle assessment and management, sustainability assessment of production systems;
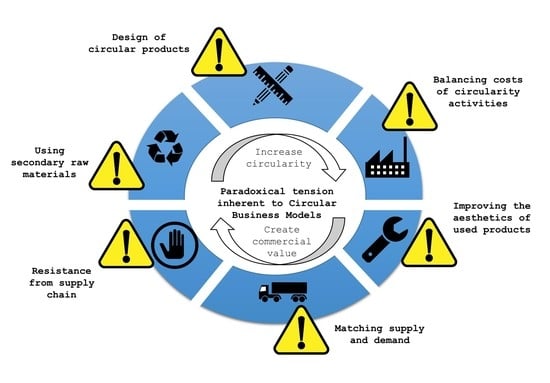
- Ciruclar economy, including innovative business models;
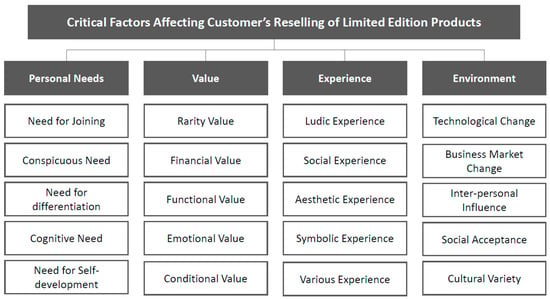
- Sustainable consumption at various levels: individual, organizational, city;
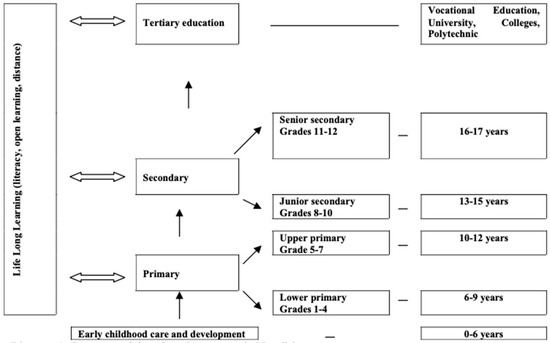
- New educational initiatives in sustainable consumption and production.
Prof. Dr. Rebeka Kovačič Lukman
Dr. Damjan Krajnc
Guest Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Sustainability is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2400 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- Sustainable production and resource efficiency
- Life cycle assessment and management
- Ciruclar economy, including innovative business models
- Sustainable consumption at various levels: individual, organizational, city
- New educational initiatives in sustainable consumption and production
- Innovative and sustainable manufacturing processes
- Products and service design
- Sustainability assessment of production systems
- Innovative business models