Power System and Sustainability
Share This Topical Collection
Editors
 Dr. Gaetano Zizzo
Dr. Gaetano Zizzo
 Dr. Gaetano Zizzo
Dr. Gaetano Zizzo
E-Mail
Website
Collection Editor
Department of Engineering, University of Palermo, Building 9, 90128 Palermo, Italy
Interests: smart grids; energy blockchain; vehicle-to-grid; demand response; energy services; renewables integration in power system; energy communities
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
 Prof. Dr. Favuzza Salvatore
Prof. Dr. Favuzza Salvatore
 Prof. Dr. Favuzza Salvatore
Prof. Dr. Favuzza Salvatore
E-Mail
Website
Collection Editor
Dipartimento di Ingegneria, Università di Palermo, Viale delle Scienze, Edificio 9, 90128 Palermo, Italy
Interests: power systems analysis; power system protection; distributed generation; power systems modeling; electrical engineering; power generation; energy; renewable energy; electrical power engineering; artificial intelligence
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
Decarbonization, energy efficiency improvements, and grid integration of distributed generation and storage systems are topical issues for power system research in the new century.
Power systems are required to become more and more smart, green, and sustainable, managed by intelligent devices, allowing also the participation of end-users in the energy share.
New regulations and support policies are driving the development of new strategies and devices for making this epochal transformation real.
In this context, we encourage all researchers from relevant domains to submit papers to this Special Issue on “Power Systems and Sustainability”. Contributions on the following themes, but not limited to them, are welcomed:
- Insular Power Systems: Design, operations, planning, economics, efficiency improvement;
- Rural Power Systems: Design, operations, planning, economics, efficiency improvement;
- Life Cycle Assessment of new high efficiency devices and components for power grids;
- Impact of BAC and TBM systems on near zero energy buildings
- Impact of battery storage systems on the generation and distribution efficiency of a microgrid
- ICT for smart grids
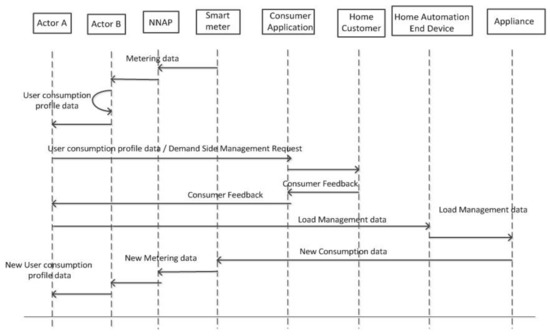
- Demand Side Management and Demand Response
- Multi carrier hubs
- Environmental impact of modern power systems
- Energy storage for mitigating the variability of renewable electricity sources
- Electricity from renewable sources
- Electrical wastes treatment
- Support policies for battery storage systems
Dr. Gaetano Zizzo
Prof. Salvatore Favuzza
Guest Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Sustainability is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript.
The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2400 CHF (Swiss Francs).
Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's
English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- Insular Power Systems
- Rural Power Systems
- Smart Grids Smart Cities
- Renewable Energy
- Electric Energy Storage Systems
- ICT for Smart Grids
- Waste treatment
- Support Policies
- NZEB
- BAC and TBM systems
- LCA
Published Papers (50 papers)
Open AccessArticle
A Dispatching Method for Large-Scale Interruptible Load and Electric Vehicle Clusters to Alleviate Overload of Interface Power Flow
by
Xi Ye, Gan Li, Tong Zhu, Lei Zhang, Yanfeng Wang, Xiang Wang and Hua Zhong
Viewed by 676
Abstract
The study of dispatching methods for large-scale interruptible loads and electric vehicle clusters is of great significance as an optional method to alleviate the problem of overload in interface power flow. In this paper, the distribution model and transfer capacity of large-scale interruptible
[...] Read more.
The study of dispatching methods for large-scale interruptible loads and electric vehicle clusters is of great significance as an optional method to alleviate the problem of overload in interface power flow. In this paper, the distribution model and transfer capacity of large-scale interruptible load and electric vehicle in two dimensions of time and space were firstly introduced. Then, a large-scale interruptible load and electric vehicle dispatching model considering transmission interface power flow balance was established. Finally, a case study was carried out with the city power grid as the research object. Studies show that by dispatching large-scale interruptible load and electric vehicle, the overload rate of interface power flow can be reduced by 12–17%, while the proportion of clean energy generation increased by 4.19%. Large-scale interruptible load and electric vehicles are quite different in terms of the role they play in grid regulation. The regulation cost of electric vehicles is higher than that of large-scale interruptible load, but it also has the advantages of promoting the consumption of clean energy and improving the overall operating economy. Which type of resource should be given priority is based on the actual state of the grid. In addition, the cost of electricity has a significant impact on the load response behavior of electric vehicles. It should be determined according to various factors, such as interface power flow control requirements, regulation costs, and power grid operation costs.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
The Effect of Power Flow Entropy on Available Load Supply Capacity under Stochastic Scenarios with Different Control Coefficients of UPFC
by
Zhongxi Ou, Yuanyuan Lou, Junzhou Wang, Yixin Li, Kun Yang, Sui Peng and Junjie Tang
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 1027
Abstract
With the sharp increase in fluctuant sources in power systems, the deterministic power flow (DPF) calculation has been unable to meet the demands of practical applications; thus, the probabilistic method becomes indispensable for the reliable and stable operation of power systems. This paper
[...] Read more.
With the sharp increase in fluctuant sources in power systems, the deterministic power flow (DPF) calculation has been unable to meet the demands of practical applications; thus, the probabilistic method becomes indispensable for the reliable and stable operation of power systems. This paper adopts the probabilistic power flow (PPF) method, which is a Monte Carlo simulation (MCS) based on the Latin hypercube sampling (LHS) method, to analyze the uncertainties of power systems. Specifically, the available load supply capability (ALSC) based on the branch loading rate is used to analyze the safety margin of the whole system, while the improved power flow entropy is introduced to quantify the equilibrium of power flow distribution. The repeated power flow (RPF) calculation is combined with the PPF method, and, hence, the probabilistic repeated power flow (PRPF) method is proposed to calculate the power flow entropy at the initial state and the probabilistic ALSC. To flexibly control the power flow, the unified power flow controller (UPFC) is added to the AC power system. The different control coefficients of UPFC are set to reveal the relationship between power flow entropy and available load supply capability under the stochastic scenarios. Finally, the modified IEEE14 test system is used to study the adjustment abilities of UPFC. With consideration of uncertainties in the test case, the positive effect of UPFC on the power flow entropy and the probabilistic ALSC under stochastic scenarios is deeply studied.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Fault Diagnostic Methodologies for Utility-Scale Photovoltaic Power Plants: A State of the Art Review
by
Qamar Navid, Ahmed Hassan, Abbas Ahmad Fardoun, Rashad Ramzan and Abdulrahman Alraeesi
Cited by 14 | Viewed by 3134
Abstract
The worldwide electricity supply network has recently experienced a huge rate of solar photovoltaic penetration. Grid-connected photovoltaic (PV) systems range from smaller custom built-in arrays to larger utility power plants. When the size and share of PV systems in the energy mix increases,
[...] Read more.
The worldwide electricity supply network has recently experienced a huge rate of solar photovoltaic penetration. Grid-connected photovoltaic (PV) systems range from smaller custom built-in arrays to larger utility power plants. When the size and share of PV systems in the energy mix increases, the operational complexity and reliability of grid stability also increase. The growing concern about PV plants compared to traditional power plants is the dispersed existence of PV plants with millions of generators (PV panels) spread over kilometers, which increases the possibility of faults occurring and associated risk. As a result, a robust fault diagnosis and mitigation framework remain a key component of PV plants. Various fault monitoring and diagnostic systems are currently being used, defined by calculation of electrical parameters, extracted electrical parameters, artificial intelligence, and thermography. This article explores existing PV fault diagnostic systems in a detailed way and addresses their possible merits and demerits.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Understanding Technology, Fuel, Market and Policy Drivers for New York State’s Power Sector Transformation
by
Mine Isik and P. Ozge Kaplan
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 2522
Abstract
A thorough understanding of the drivers that affect the emission levels from electricity generation, support sound design and the implementation of further emission reduction goals are presented here. For instance, New York State has already committed a transition to 100% clean energy by
[...] Read more.
A thorough understanding of the drivers that affect the emission levels from electricity generation, support sound design and the implementation of further emission reduction goals are presented here. For instance, New York State has already committed a transition to 100% clean energy by 2040. This paper identifies the relationships among driving factors and the changes in emissions levels between 1990 and 2050 using the logarithmic mean divisia index analysis. The analysis relies on historical data and outputs from techno-economic-energy system modeling to elucidate future power sector pathways. Three scenarios, including a business-as-usual scenario and two policy scenarios, explore the changes in utility structure, efficiency, fuel type, generation, and emission factors, considering the non-fossil-based technology options and air regulations. We present retrospective and prospective analysis of carbon dioxide, sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxide emissions for the New York State’s power sector. Based on our findings, although the intensity varies by period and emission type, in aggregate, fossil fuel mix change can be defined as the main contributor to reduce emissions. Electricity generation level variations and technical efficiency have relatively smaller impacts. We also observe that increased emissions due to nuclear phase-out will be avoided by the onshore and offshore wind with a lower fraction met by solar until 2050.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
An Online Novel Two-Layered Photovoltaic Fault Monitoring Technique Based Upon the Thermal Signatures
by
Qamar Navid, Ahmed Hassan, Abbas Ahmad Fardoun and Rashad Ramzan
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 1875
Abstract
The share of photovoltaic (PV) power generation in the energy mix is increasing at a rapid pace with dramatically increasing capacity addition through utility-scale PV power plants globally. As PV plants are forecasted to be a major energy generator in the future, their
[...] Read more.
The share of photovoltaic (PV) power generation in the energy mix is increasing at a rapid pace with dramatically increasing capacity addition through utility-scale PV power plants globally. As PV plants are forecasted to be a major energy generator in the future, their reliable operation remains of primary concern due to a possibility of faults in a tremendously huge number of PV panels involved in power generation in larger plants. The precise detection of nature and the location of the faults along with a prompt remedial mechanism is deemed crucial for smoother power plant operation. The existing fault diagnostic methodologies based on thermal imaging of the panels as well as electrical parameters through inverter possess certain limitations. The current article deals with a novel fault diagnostic technique based on PV panel electrical parameters and junction temperatures that can precisely locate and categorize the faults. The proposed scheme has been tested on a 1.6 kW photovoltaic system for short circuit, open circuit, grounding, and partial shading faults. The proposed method showed improved accuracy compared to thermal imaging on panel scale fault detection, offering a possibility to adapt to the PV plant scale.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
A Review of Clean Electricity Policies—From Countries to Utilities
by
Kaiqi Sun, Huangqing Xiao, Shengyuan Liu, Shutang You, Fan Yang, Yuqing Dong, Weikang Wang and Yilu Liu
Cited by 24 | Viewed by 4911
Abstract
Due to the heavy stress on environmental deterioration and the excessive consumption of fossil resources, the transition of global energy from fossil fuel energy to clean energy has significantly accelerated in recent years. The power industry and policymakers in almost all countries are
[...] Read more.
Due to the heavy stress on environmental deterioration and the excessive consumption of fossil resources, the transition of global energy from fossil fuel energy to clean energy has significantly accelerated in recent years. The power industry and policymakers in almost all countries are focusing on clean energy development. Thanks to progressive clean energy policies, significant progress in clean energy integration and greenhouse gas reduction has been achieved around the world. However, due to the differences in economic structures, clean energy distributions, and development models, clean energy policy scope, focus, and coverage vary between different countries, states, and utilities. This paper aims at providing a policy review for readers to easily obtain clean energy policy information on various clean energies in the U.S. and some other countries. Firstly, this paper reviews and compares some countries’ clean energy policies on electricity. Then, taking the U.S. as an example, this paper introduces the clean energy policies of some representative states and utilities in the U.S in perspectives of renewable energies, electric vehicles, and energy storage.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
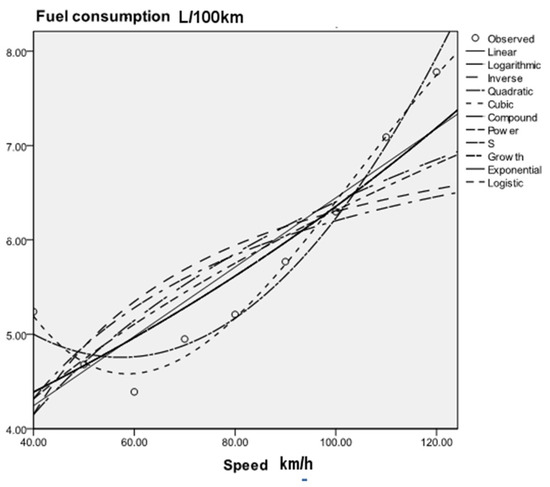
Study on a Prediction Model of Superhighway Fuel Consumption Based on the Test of Easy Car Platform
by
Yong-Ming He, Jia Kang, Yu-Long Pei, Bin Ran and Yu-Ting Song
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 2798
Abstract
To explore the relationship between fuel consumption and speed for a vehicle on a superhighway with a design speed exceeding 120 km/h, the fuel consumption data provided by the Test of Easy Car platform are used to fit the fuel consumption of different
[...] Read more.
To explore the relationship between fuel consumption and speed for a vehicle on a superhighway with a design speed exceeding 120 km/h, the fuel consumption data provided by the Test of Easy Car platform are used to fit the fuel consumption of different models. The fitting results show that the fitting degree of fuel consumption by a cubic curve is the highest, and the correlation coefficient is above 0.95. A fuel consumption cubic curve model of different vehicle types is established by using the fitting parameters to predict the fuel consumption when a vehicle is running at a speed of 130 km/h–180 km/h. The prediction results show that the average fuel consumption of compact vehicles is the lowest when a vehicle is running on a superhighway at speeds of 130 km/h–180 km/h, with values of 8.95 L/100 km–16.26 L/100 km; the average fuel consumption of sport utility vehicles (SUVs) is the highest, with values of 12.65 L/100 km–22.70 L/100 km. The prediction results can be used to estimate the cost of using a superhighway and provide a basis for estimating the feasibility of superhighways.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
A Comparative Analysis of Machine Learning Approaches for Short-/Long-Term Electricity Load Forecasting in Cyprus
by
Davut Solyali
Cited by 71 | Viewed by 6942
Abstract
Estimating the electricity load is a crucial task in the planning of power generation systems and the efficient operation and sustainable growth of modern electricity supply networks. Especially with the advent of smart grids, the need for fairly precise and highly reliable estimation
[...] Read more.
Estimating the electricity load is a crucial task in the planning of power generation systems and the efficient operation and sustainable growth of modern electricity supply networks. Especially with the advent of smart grids, the need for fairly precise and highly reliable estimation of electricity load is greater than ever. It is a challenging task to estimate the electricity load with high precision. Many energy demand management methods are used to estimate future energy demands correctly. Machine learning methods are well adapted to the nature of the electrical load, as they can model complicated nonlinear connections through a learning process containing historical data patterns. Many scientists have used machine learning (ML) to anticipate failure before it occurs as well as predict the outcome. ML is an artificial intelligence (AI) subdomain that involves studying and developing mathematical algorithms to understand data or obtain data directly without relying on a prearranged model algorithm. ML is applied in all industries. In this paper, machine learning strategies including artificial neural network (ANN), multiple linear regression (MLR), adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system (ANFIS), and support vector machine (SVM) were used to estimate electricity demand and propose criteria for power generation in Cyprus. The simulations were adapted to real historical data explaining the electricity usage in 2016 and 2107 with long-term and short-term analysis. It was observed that electricity load is a result of temperature, humidity, solar irradiation, population, gross national income (GNI) per capita, and the electricity price per kilowatt-hour, which provide input parameters for the ML algorithms. Using electricity load data from Cyprus, the performance of the ML algorithms was thoroughly evaluated. The results of long-term and short-term studies show that SVM and ANN are comparatively superior to other ML methods, providing more reliable and precise outcomes in terms of fewer estimation errors for Cyprus’s time series forecasting criteria for power generation.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Research on Green Productivity of Chinese Real Estate Companies—Based on SBM-DEA and TOBIT Models
by
Zhao Yang and Hong Fang
Cited by 16 | Viewed by 3140
Abstract
Apart from promoting social-economic development and increasing social employment, the real estate industry in China has also brought up problems such as high energy consumption and high emissions. Scholars now focus more on energy conservation, emission reduction and sustainable development of real estate
[...] Read more.
Apart from promoting social-economic development and increasing social employment, the real estate industry in China has also brought up problems such as high energy consumption and high emissions. Scholars now focus more on energy conservation, emission reduction and sustainable development of real estate companies in their current research. The data used by this paper are three-year panel data from 2015 to 2018, with observations from 15 representative real estate companies. CO
2 and green credit index are introduced as the undesirable output and the green output of real estate companies respectively. First, with the DEA model and the Malmquist index model, this paper evaluates the green productivity of real estate companies statically and dynamically. The Tobit model is then employed by the author to analyze factors that may affect green productivity. Our results indicate that (1) the green productivities of 15 Chinese real estate companies have improved by various degrees. The average green productivity rises from 0.701 in 2015 to 0.849 in 2018, indicating that the energy utilization rate of enterprises has gradually increased. From the calculation and decomposition of the Malmquist total factor productivity index, we know that technological progress is vital in improving the green productivity of real estate companies. (2) As for the influencing factors, the green productivity is positively related to factors such as policy compliance indicator P, environmental responsibility commitment indicator R, indicator of green innovation capability I, and indicator of green development information disclosure M. The asset-liability ratio on the contrary has a negative impact on green productivity. It’s worth to point out that the green innovation index and green productivity is significantly correlated and the correlation coefficient can be up to 0.636, which implies that the key to improving green productivity is to increase research and development investment.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
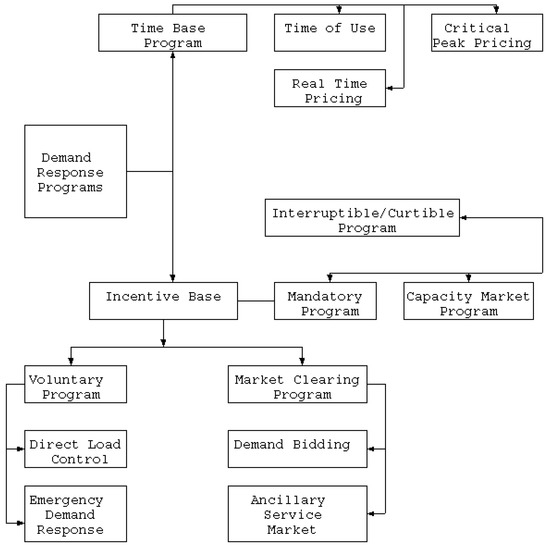
Demand Response Economic Assessment with the Integration of Renewable Energy for Developing Electricity Markets
by
Abdul Conteh, Mohammed Elsayed Lotfy, Oludamilare Bode Adewuyi, Paras Mandal, Hiroshi Takahashi and Tomonobu Senjyu
Cited by 15 | Viewed by 3093
Abstract
Electricity disparity in sub-Saharan Africa is a multi-dimensional challenge that has significant implications on the current socio-economic predicament of the region. Strategic implementation of demand response (DR) programs and renewable energy (RE) integration can provide efficient solutions with several benefits such as peak
[...] Read more.
Electricity disparity in sub-Saharan Africa is a multi-dimensional challenge that has significant implications on the current socio-economic predicament of the region. Strategic implementation of demand response (DR) programs and renewable energy (RE) integration can provide efficient solutions with several benefits such as peak load reduction, grid congestion mitigation, load profile modification, and greenhouse gas emissions reduction. In this research, an incentive and price-based DR programs model using the price elasticity concepts is proposed. Economic analysis of the customer benefit, utility revenue, load factor, and load profile modification are optimally carried out using Freetown (Sierra Leone) peak load demand. The strategic selection index is employed to prioritize relevant DR programs that are techno-economically beneficial for the independent power producers (IPPs) and participating customers. Moreover, optimally designed hybridized grid-connected RE was incorporated using the Genetic Algorithm (GA) to meet the deficit after DR implementation. GA is used to get the optimal solution in terms of the required PV area and the number of BESS to match the net load demand after implementing the DR schemes. The results show credible enhancement in the load profile in terms of peak period reduction as measured using the effective load factor. Moreover, customer benefit and utility revenues are significantly improved using the proposed approach. Furthermore, the inclusion of the hybrid RE supply proves to be an efficient approach to meet the load demand during low peak and valley periods and can also mitigate greenhouse gas emissions.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessEditor’s ChoiceArticle
Multi-Period Generation Expansion Planning for Sustainable Power Systems to Maximize the Utilization of Renewable Energy Sources
by
Qingtao Li, Jianxue Wang, Yao Zhang, Yue Fan, Guojun Bao and Xuebin Wang
Cited by 30 | Viewed by 3467
Abstract
The increasing penetration of renewable energy brings great challenges to the planning and operation of power systems. To deal with the fluctuation of renewable energy, the main focus of current research is on incorporating the detailed operation constraints into generation expansion planning (GEP)
[...] Read more.
The increasing penetration of renewable energy brings great challenges to the planning and operation of power systems. To deal with the fluctuation of renewable energy, the main focus of current research is on incorporating the detailed operation constraints into generation expansion planning (GEP) models. In most studies, the traditional objective function of GEP is to minimize the total cost (including the investment and operation cost). However, in power systems with high penetration of renewable energy, more attention has been paid to increasing the utilization of renewable energy and reducing the renewable energy curtailment. Different from the traditional objective function, this paper proposes a new objective function to maximize the accommodation of renewable energy during the planning horizon, taking into account short-term operation constraints and uncertainties from load and renewable energy sources. A power grid of one province in China is modified as a case study to verify the rationality and effectiveness of the proposed model. Numerical results show that the proposed GEP model could install more renewable power plants and improve the accommodation of renewable energy compared to the traditional GEP model.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
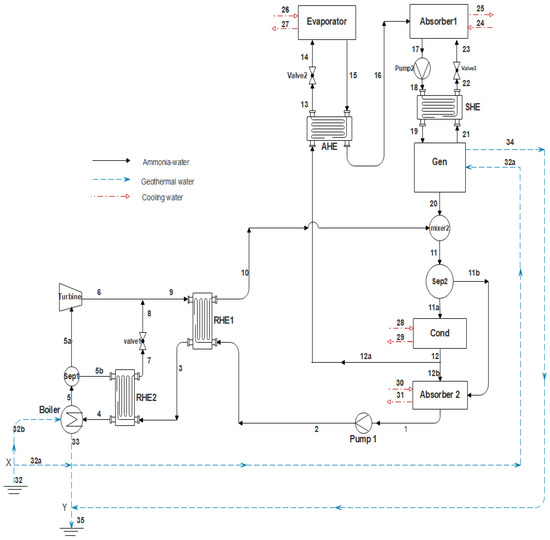
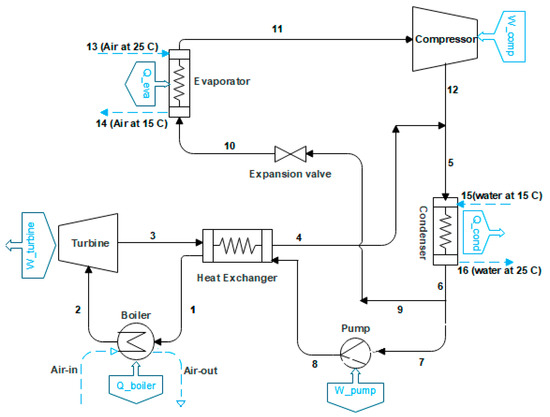
Energy and Cost Analysis and Optimization of a Geothermal-Based Cogeneration Cycle Using an Ammonia-Water Solution: Thermodynamic and Thermoeconomic Viewpoints
by
Nima Javanshir, Seyed Mahmoudi S. M., M. Akbari Kordlar and Marc A. Rosen
Cited by 28 | Viewed by 2378
Abstract
A cogeneration cycle for electric power and refrigeration, using an ammonia-water solution as a working fluid and the geothermal hot water as a heat source, is proposed and investigated. The system is a combination of a
modified Kalina cycle (KC) which produces power
[...] Read more.
A cogeneration cycle for electric power and refrigeration, using an ammonia-water solution as a working fluid and the geothermal hot water as a heat source, is proposed and investigated. The system is a combination of a
modified Kalina cycle (KC) which produces power and an absorption refrigeration cycle (ARC) that generates cooling. Geothermal water is supplied to both the KC boiler and the ARC generator. The system is analyzed from thermodynamic and economic viewpoints, utilizing Engineering Equation Solver (EES) software. In addition, a parametric study is carried out to evaluate the effects of decision parameters on the cycle performance. Furthermore, the system performance is optimized for either maximizing the exergy efficiency (EOD case) or minimizing the total product unit cost (COD case). In the EOD case the exergy efficiency and total product unit cost, respectively, are calculated as 34.7% and 15.8$/GJ. In the COD case the exergy efficiency and total product unit cost are calculated as 29.8% and 15.0$/GJ. In this case, the cooling unit cost,
, and power unit cost,
, are achieved as 3.9 and 11.1$/GJ. These values are 20.4% and 13.2% less than those obtained when the two products are produced separately by the ARC and KC, respectively. The thermoeconomic analysis identifies the more important components, such as the turbine and absorbers, for modification to improve the cost-effectiveness of the system.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
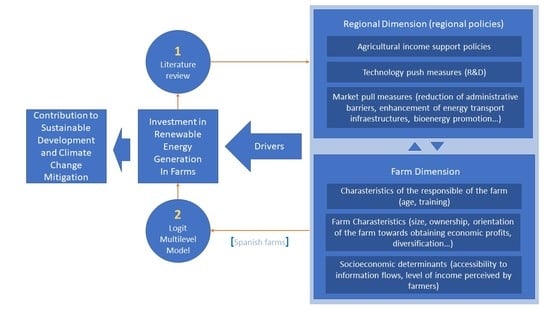
The Role of Regional Determinants in the Deployment of Renewable Energy in Farms. The Case of Spain
by
María J. Ruiz-Fuensanta, María-Jesús Gutiérrez-Pedrero and Miguel-Ángel Tarancón
Cited by 6 | Viewed by 2494
Abstract
We provide a multilevel logit model based on panel data which allows a capturing of the determinants of investment in their capacity for generating renewable energy in farms. As a novelty, we focus on regional determinants in order to assess the role of
[...] Read more.
We provide a multilevel logit model based on panel data which allows a capturing of the determinants of investment in their capacity for generating renewable energy in farms. As a novelty, we focus on regional determinants in order to assess the role of the regional dimension in making decisions by farmers about whether or not to invest in renewable energy generation. The relevance of this territorial/regional dimension acquires even greater significance in countries with a high degree of administrative decentralization, as is the case in Spain; where energy legislation gives a central role to regional governments in aspects related to the promotion of renewable energy sources. Multilevel analysis allows us to evaluate together both dimensions: Individual and regional. The results highlight the importance of the R & D investment carried out in regions, as well as the fact that there is an environment that favors the diffusion of renewable energies into the territory. Other variables, such as the level of agricultural income or regional energy intensity, do not seem to have significant relevance in the light of these results.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
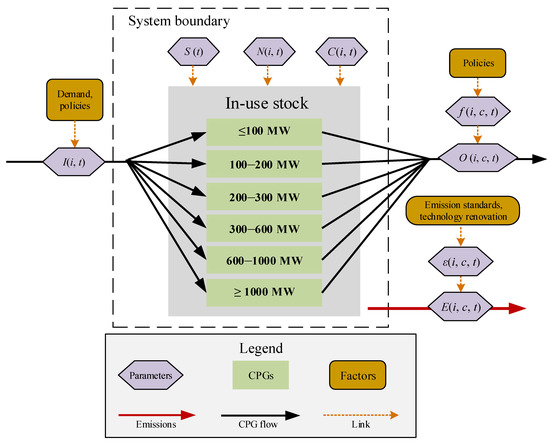
Environmental Benefits of Stock Evolution of Coal-Fired Power Generators in China
by
Fangyi Li, Zhaoyang Ye, Xilin Xiao and Dawei Ma
Viewed by 2328
Abstract
The evolution of in-use coal-fired power generators (CPGs) in China has been impelled by a series of policies called
Developing Large Units and Suppressing Small Ones in recent decades. However, it remains highly uncertain about the contribution of the evolution on air pollution
[...] Read more.
The evolution of in-use coal-fired power generators (CPGs) in China has been impelled by a series of policies called
Developing Large Units and Suppressing Small Ones in recent decades. However, it remains highly uncertain about the contribution of the evolution on air pollution reductions at different stages. Models used to assess the effects of CPGs’ evolution often do not account for the different boundary conditions related to units composition and age structure of the existing CPGs, and lifetime expectancy, which hinders effective strategy development and realistic target setting. This study employs a dynamic Type-Cohort-Time (TCT) stock-driven model and Logarithmic Mean Divisia Index (LMDI) technique, to investigate the structural evolution of China’s CPGs as well as its environmental effects from 1980 to 2050. We consider generator-specific characteristics, lifetime-related issues and alternative techniques in the historical and scenario analysis. The main results are as follows: the environmental benefits of structural evolution were limited, compared with the changes in emission coefficient due to technical renovation. However, scenario analysis indicates that structural adjustment by elimination of outdated CPGs and construction of new ones in future will undertake emission reduction commitments, since the potentials of other approaches decrease. Uncertainty analysis further demonstrates that promoting elimination of small CPGs and substituting them with renewable energy will bring more emission reductions. The key findings can support policy-making on elimination, construction, and emissions abatement of CPGs.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
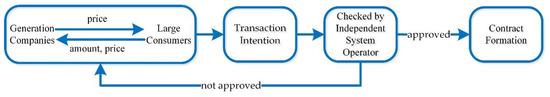
An Agent-Based Two-Stage Trading Model for Direct Electricity Procurement of Large Consumers
by
Jian Zhang, Yanan Zheng, Mingtao Yao, Huiji Wang and Zhaoguang Hu
Cited by 5 | Viewed by 2141
Abstract
Many electricity markets around the world are still at developmental and transitional stages. To complete the transition and achieve the key objectives of perfect market design, designers often choose direct electricity procurement of large consumers (LCs) as a pilot. The trading mechanism is
[...] Read more.
Many electricity markets around the world are still at developmental and transitional stages. To complete the transition and achieve the key objectives of perfect market design, designers often choose direct electricity procurement of large consumers (LCs) as a pilot. The trading mechanism is critical because it lays the foundation for the exploration of formulating a trading model and the succeeding solution; however, the existing trading mechanisms of direct electricity procurement struggle to cope with new challenges that electric power systems are facing. This paper proposes a novel two-stage trading mechanism, considering both the fairness and efficiency of direct electricity procurement. Based on the proposed trading mechanism, an agent-based trading model with multiple participants is developed. The simulation results of the transactions between LCs and generation companies (GenCos) illustrate the feasibility and effectiveness of the proposed mechanism. With this mechanism, LCs and GenCos will have more choices in the trading process and can benefit from the reduction of the average market price. The two-stage trading model provides a new choice for market designers and participants of direct electricity procurement.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
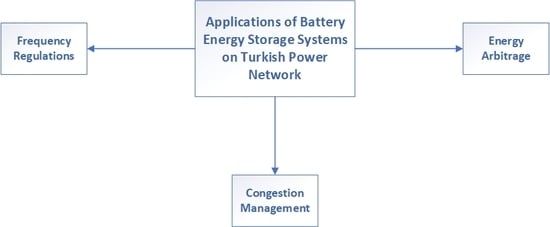
Assessment of Battery Storage Technologies for a Turkish Power Network
by
Mustafa Cagatay Kocer, Ceyhun Cengiz, Mehmet Gezer, Doruk Gunes, Mehmet Aytac Cinar, Bora Alboyaci and Ahmet Onen
Cited by 25 | Viewed by 7967
Abstract
Population growth has brought an increase in energy demand and cost that has a meaningful impact on personal and government expenses. In this respect, governments attach importance to investments in renewable energy resources (RER), which are a sustainable and clean energy source. However,
[...] Read more.
Population growth has brought an increase in energy demand and cost that has a meaningful impact on personal and government expenses. In this respect, governments attach importance to investments in renewable energy resources (RER), which are a sustainable and clean energy source. However, the unpredictable characteristics of RER are a major problem for these clean sources and RER need auxiliary assets. Battery energy storage systems (BESS) are one of the promising solutions for these issues. Due to the high investment cost of BESS, governments act cautiously about accepting and implementing BESS in their power network. Recently, with the improvement of technology, the cost of BESS has been reduced, and therefore battery technologies have begun to be applied to conventional systems. In this study, first, we will review and discuss the current globally state-of-the-art BESS and their applications. Later, attention will be turned to a country-specific study for Turkey.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Thermodynamic and Exergoeconomic Analyses of a Novel Combined Cycle Comprised of Vapor-Compression Refrigeration and Organic Rankine Cycles
by
Nima Javanshir, S. M. Seyed Mahmoudi and Marc A. Rosen
Cited by 30 | Viewed by 3685
Abstract
In this study, a cooling/power cogeneration cycle consisting of vapor-compression refrigeration and organic Rankine cycles is proposed and investigated. Utilizing geothermal water as a low-temperature heat source, various operating fluids, including R134a, R22, and R143a, are considered for the system to study their
[...] Read more.
In this study, a cooling/power cogeneration cycle consisting of vapor-compression refrigeration and organic Rankine cycles is proposed and investigated. Utilizing geothermal water as a low-temperature heat source, various operating fluids, including R134a, R22, and R143a, are considered for the system to study their effects on cycle performance. The proposed cycle is modeled and evaluated from thermodynamic and thermoeconomic viewpoints by the Engineering Equation Solver (EES) software. Thermodynamic properties as well as exergy cost rates for each stream are found separately. Using R143a as the working fluid, thermal and exergy efficiencies of 27.2% and 57.9%, respectively, are obtained for the cycle. Additionally, the total product unit cost is found to be 60.7 $/GJ. A parametric study is carried out to determine the effects of several parameters, such as turbine inlet pressure, condenser temperature and pressure, boiler inlet air temperature, and pinch-point temperature difference, on the cycle performance. The latter is characterized by such parameters as thermal and exergy efficiencies, refrigeration capacity, produced net power rate, exergy destruction rate, and the production unit cost rates. The results indicate that the system using R134a exhibits the lowest thermal and exergy efficiencies among other working fluids, while the systems using R22 and R143a exhibit the highest energy and exergy efficiencies, respectively. The boiler and turbine contribute the most to the total exergy destruction rate.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
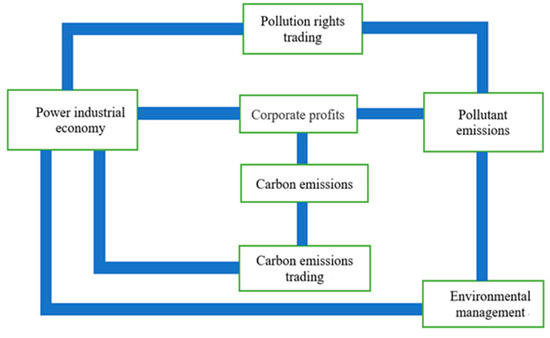
Open AccessArticle
The Integrated Effect of Carbon Emissions Trading and Pollution Rights Trading for Power Enterprises—A Case Study of Chongqing
by
Shengxian Ge, Xianyu Yu, Dequn Zhou and Xiuzhi Sang
Cited by 8 | Viewed by 3782
Abstract
To control growing environmental problems, the pollution rights trading (PRT) center was established in Jiaxing in 2007, and China officially joined the carbon emission reduction market (NCET) in 2011. Since power enterprises are the main participants in the NCET market and PRT market,
[...] Read more.
To control growing environmental problems, the pollution rights trading (PRT) center was established in Jiaxing in 2007, and China officially joined the carbon emission reduction market (NCET) in 2011. Since power enterprises are the main participants in the NCET market and PRT market, the integrated effect of the NCET market and PRT market on power enterprise profit and the regional environment is one of the major issues that needs to be taken into consideration. Based on system dynamics (SD) theory, we propose an NCET-PRT simulation model for power enterprises in Chongqing. Through analyzing parameters of carbon trading price, free ratio, and emission trading prices, 12 different simulation scenarios are configured for sensitivity analysis. Based on the simulation results, the following observations can be obtained: (1) NCET and PRT can effectively promote the performance of enterprises’ carbon emissions reduction and regional pollutant emission reduction but will have a minor negative impact on the industrial economy at the same time; (2) The trading mechanism is interactive; if the carbon emissions trading (NCET) mechanism is implemented separately, the emission of pollutants will be reduced significantly. However, the implementation of pollution rights trading (PRT) alone cannot significantly reduce CO
2 emissions; (3) At an appropriate level, NCET and PRT can be enhanced to achieve a maximum emissions reduction effect at a minimum economic cost.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
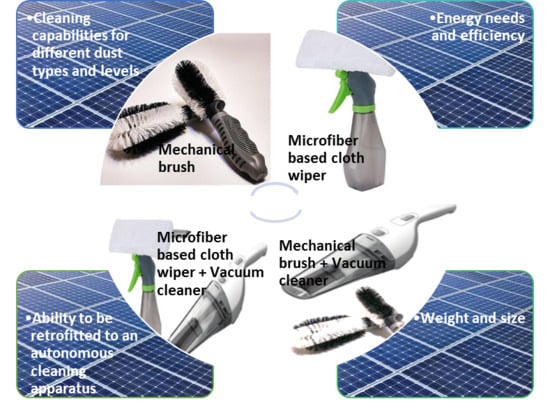
Open AccessArticle
Assessment of Various Dry Photovoltaic Cleaning Techniques and Frequencies on the Power Output of CdTe-Type Modules in Dusty Environments
by
Mohammed Al-Housani, Yusuf Bicer and Muammer Koç
Cited by 57 | Viewed by 5799
Abstract
This study presents the conditions and results of experimental investigations on various photovoltaic (PV) module cleaning methods and the effects on the performance of cadmium-telluride CdTe-type photovoltaic (PV) modules located in Doha, Qatar. The study aims to find the optimum cleaning technique and
[...] Read more.
This study presents the conditions and results of experimental investigations on various photovoltaic (PV) module cleaning methods and the effects on the performance of cadmium-telluride CdTe-type photovoltaic (PV) modules located in Doha, Qatar. The study aims to find the optimum cleaning technique and frequency based on cleaning performance and cost. PV modules are in a dusty and rocky area in the western part of Doha, Qatar within the north campus of Education City. Maximum power point tracking (MPPT) technology is employed for five different PV modules. The results show that microfiber-based wiper along with microfiber & vacuum cleaner are the most effective cleaning methods with about 6% improvement for the weekly period compared to the control panel among the considered methods. However, due to the increased cost of adding a vacuum cleaner, the microfiber-based wiper is the most efficient method when both cost and improvement rates are considered. In addition, the most efficient cleaning frequency (among daily, weekly and monthly) is found to be the weekly cleaning under the tested climate conditions.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
An Economic Analysis of Demand Side Management Considering Interruptible Load and Renewable Energy Integration: A Case Study of Freetown Sierra Leone
by
Abdul Conteh, Mohammed Elsayed Lotfy, Kiptoo Mark Kipngetich, Tomonobu Senjyu, Paras Mandal and Shantanu Chakraborty
Cited by 21 | Viewed by 6582
Abstract
Like in most developing countries, meeting the load demand and reduction in transmission grid bottlenecks remains a significant challenge for the power sector in Sierra Leone. In recent years, research attention has shifted to demand response (DR) programs geared towards improving the supply
[...] Read more.
Like in most developing countries, meeting the load demand and reduction in transmission grid bottlenecks remains a significant challenge for the power sector in Sierra Leone. In recent years, research attention has shifted to demand response (DR) programs geared towards improving the supply availability and quality of energy markets in developed countries. However, very few studies have discussed the implementation of suitable DR programs for developing countries, especially when utilizing renewable energy (RE) resources. In this paper, using the Freetown’s peak load demand data and the price elasticity concept, the interruptible demand response (DR) program has been considered for maximum demand index (MDI) customers. Economic analysis of the energy consumption, customer incentives, benefits, penalties and the impact on the load demand are analyzed, with optimally designed energy management for grid-integrated battery energy storage system (BESS) and photovoltaic (PV)-hybrid system using the genetic algorithm (GA). Five scenarios are considered to confirm the effectiveness and robustness of the proposed scheme. The results show the economic superiority of the proposed DR program’s approach for both customers and supplier benefits. Moreover, RE inclusion proved to be a practical approach over the project lifespan, compared to the diesel generation alternative.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
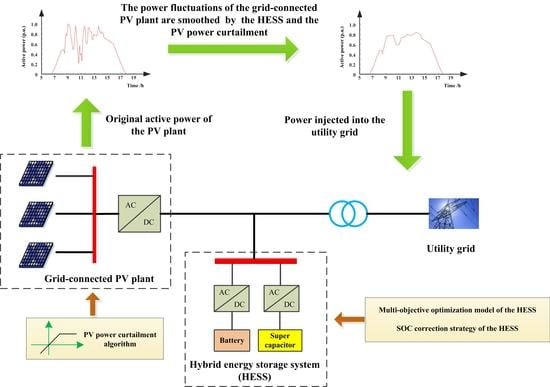
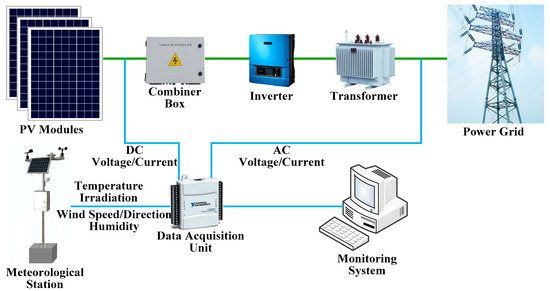
Control Strategy of a Hybrid Energy Storage System to Smooth Photovoltaic Power Fluctuations Considering Photovoltaic Output Power Curtailment
by
Wei Ma, Wei Wang, Xuezhi Wu, Ruonan Hu, Fen Tang and Weige Zhang
Cited by 45 | Viewed by 5222
Abstract
The power fluctuations of grid-connected photovoltaic (PV) systems have negative impacts on the power quality and stability of the utility grid. In this study, the combinations of a battery/supercapacitor hybrid energy storage system (HESS) and the PV power curtailment are used to smooth
[...] Read more.
The power fluctuations of grid-connected photovoltaic (PV) systems have negative impacts on the power quality and stability of the utility grid. In this study, the combinations of a battery/supercapacitor hybrid energy storage system (HESS) and the PV power curtailment are used to smooth PV power fluctuations. A PV power curtailment algorithm is developed to limit PV power when power fluctuation exceeds the power capacity of the HESS. A multi-objective optimization model is established to dispatch the HESS power, considering energy losses and the state of charge (SOC) of the supercapacitor. To prevent the SOCs of the HESS from approaching their lower limits, a SOC correction strategy is proposed to correct the SOCs of the HESS. Moreover, this paper also investigates the performances (such as the smoothing effects, losses and lifetime of energy storage, and system net profits) of two different smoothing strategies, including the method of using the HESS and the proposed strategy. Finally, numerous simulations are carried out based on data obtained from a 750 kWp PV plant. Simulation results indicate that the proposed method is more economical and can effectively smooth power fluctuations compared with the method of using the HESS.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessEditor’s ChoiceArticle
A Multi-Criteria Decision Maker for Grid-Connected Hybrid Renewable Energy Systems Selection Using Multi-Objective Particle Swarm Optimization
by
David Abdul Konneh, Harun Or Rashid Howlader, Ryuto Shigenobu, Tomonobu Senjyu, Shantanu Chakraborty and Narayanan Krishna
Cited by 43 | Viewed by 6295
Abstract
Combating climate change issues resulting from excessive use of fossil fuels comes with huge initial costs, thereby posing difficult challenges for the least developed countries in Sub-Saharan Africa (SSA) to invest in renewable energy alternatives, especially with rapid industrialization. However, designing renewable energy
[...] Read more.
Combating climate change issues resulting from excessive use of fossil fuels comes with huge initial costs, thereby posing difficult challenges for the least developed countries in Sub-Saharan Africa (SSA) to invest in renewable energy alternatives, especially with rapid industrialization. However, designing renewable energy systems usually hinges on different economic and environmental criteria. This paper used the Multi-Objective Particle Swarm Optimization (MOPSO) technique to optimally size ten grid-connected hybrid blocks selected amongst Photo-Voltaic (PV) panels, onshore wind turbines, biomass combustion plant using sugarcane bagasse, Battery Energy Storage System (BESS), and Diesel Generation (DG) system as backup power, to reduce the supply deficit in Sierra Leone. Resource assessment using well-known methods was done for PV, wind, and biomass for proposed plant sites in Kabala District in Northern and Kenema District in Southern Sierra Leone. Long term analysis was done for the ten hybrid blocks projected over 20 years whilst ensuring the following objectives: minimizing the Deficiency of Power Supply Probability (DPSP), Diesel Energy Fraction (DEF), Life Cycle Costs (LCC), and carbon dioxide (CO
) emissions. Capacity factors of
and
obtained for PV and wind, respectively, indicate that Kabala district is the most feasible location for PV and wind farm installations. The optimum results obtained are compared across selected blocks for DPSP values of 0–50% to determine the most economical and environmentally friendly alternative that policy makers in Sierra Leone and the region could apply to similar cases.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
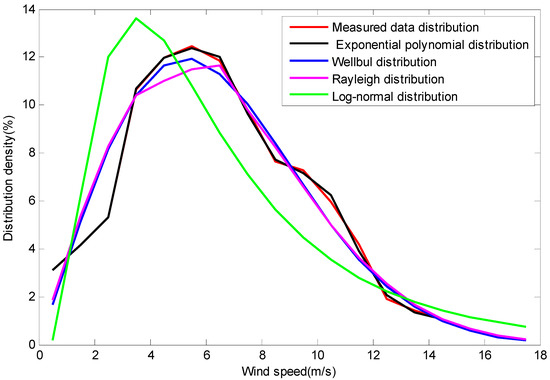
Frequency Distribution Model of Wind Speed Based on the Exponential Polynomial for Wind Farms
by
Lingzhi Wang, Jun Liu and Fucai Qian
Cited by 7 | Viewed by 4327
Abstract
This study introduces and analyses existing models of wind speed frequency distribution in wind farms, such as the Weibull distribution model, the Rayleigh distribution model, and the lognormal distribution model. Inspired by the shortcomings of these models, we propose a distribution model based
[...] Read more.
This study introduces and analyses existing models of wind speed frequency distribution in wind farms, such as the Weibull distribution model, the Rayleigh distribution model, and the lognormal distribution model. Inspired by the shortcomings of these models, we propose a distribution model based on an exponential polynomial, which can describe the actual wind speed frequency distribution. The fitting error of other common distribution models is too large at zero or low wind speeds. The proposed model can solve this problem. The exponential polynomial distribution model can fit multimodal distribution wind speed data as well as unimodal distribution wind speed data. We used the linear-least-squares method to acquire the parameters for the distribution model. Finally, we carried out contrast simulation experiments to validate the effectiveness and advantages of the proposed distribution model.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
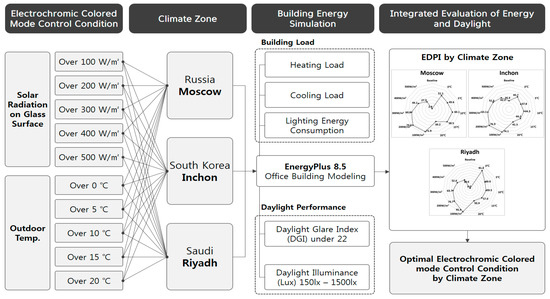
Evaluation of Building Energy and Daylight Performance of Electrochromic Glazing for Optimal Control in Three Different Climate Zones
by
Myunghwan Oh, Minsu Jang, Jaesik Moon and Seungjun Roh
Cited by 17 | Viewed by 4368
Abstract
The objective of this paper is to analyze the control conditions of the transmittance rate, and determine the conditions that are most optimal with respect to building energy and daylight performance in three climate conditions: Riyadh, Saudi Arabia (hot climate); Inchon, South Korea
[...] Read more.
The objective of this paper is to analyze the control conditions of the transmittance rate, and determine the conditions that are most optimal with respect to building energy and daylight performance in three climate conditions: Riyadh, Saudi Arabia (hot climate); Inchon, South Korea (hot and cold climate); and Moscow, Russia (cold climate). The analysis was based on the electrochromic glass developed by a research team. Electrochromic glass is a next generation solar control glass that can control the transmittance of the glass itself. Therefore, proper control methods are essential for rational use of this electrochromic glass. To properly control electrochromic glass, daylight performance must be considered, along with building energy (heating, cooling, and lighting). If only building energy is considered, transmittance needs to be lowered during the summer season and increased during the winter season. Controlling electrochromic glass transmittance with such a method would not improve the satisfaction of users and occupants of a building due to the resulting glare. In addition to energy reduction, the basic function of solar control glass is to prevent glare. Therefore, in this study, we develop the Energy and Daylight Performance Index (EDPI) using, to evaluate the combined building energy and daylight performance and deduce the optimal control method for electrochromic glass. In addition, optimal control conditions for the three different climatic regions were obtained. Limitations of this study were that the scope was restricted to the eastern climate region, and that the building analysis model was limited to one climate region. It is expected that the optimal control method could be used as an initial database in the development of a electrochromic glass control system.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
An Optimal Load Disaggregation Method Based on Power Consumption Pattern for Low Sampling Data
by
Huijuan Wang, Wenrong Yang, Tingyu Chen and Qingxin Yang
Cited by 11 | Viewed by 3657
Abstract
In recent years, Smart Grids have been developing globally. Since smart meters only acquire low-frequency data, non-intrusive load monitoring technology using the signature extracted from high-frequency data needs an additional measurement device to be installed, so it is not suitable for promotion to
[...] Read more.
In recent years, Smart Grids have been developing globally. Since smart meters only acquire low-frequency data, non-intrusive load monitoring technology using the signature extracted from high-frequency data needs an additional measurement device to be installed, so it is not suitable for promotion to the smart grid environment. However, methods using low-frequency features are poorly-suited when several appliances are switched on at the same time, or devices with similar power values are used. In response to these problems, this paper proposes a load disaggregation method based on the power consumption patterns of appliances, combining an improved mathematical optimization model and optimized bird swarm algorithm (OBSA) for load disaggregation. Experiments show that the method can effectively identify the operating states of appliances, and deal with situations in which multiple instruments have similar power characteristics or are simultaneously switching. The performance comparison proves that the improved model is more efficient than the traditional active and reactive power (PQ) optimization model in load disaggregation performance and computation time, and also verifies the robustness of the proposed method and the convergence of OBSA. As an inexpensive method without extra measurement hardware installed, the process is suitable for large-scale applications in smart grids.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
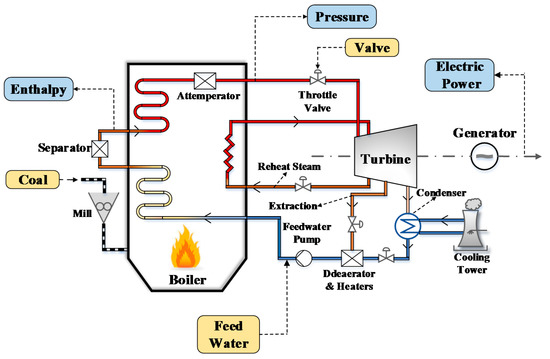
A Sustainable Power Plant Control Strategy Based on Fuzzy Extended State Observer and Predictive Control
by
Chen Chen, Lei Pan, Shanjian Liu, Li Sun and Kwang Y. Lee
Cited by 9 | Viewed by 3454
Abstract
The control of an ultra-supercritical (USC) boiler–turbine power plant is critical in maintaining the safety of the sustainable power grid. However, it is challenging due to the internal nonlinearity, hard manipulation constraints, and widespread uncertainties. To this end, a fuzzy extended state observer
[...] Read more.
The control of an ultra-supercritical (USC) boiler–turbine power plant is critical in maintaining the safety of the sustainable power grid. However, it is challenging due to the internal nonlinearity, hard manipulation constraints, and widespread uncertainties. To this end, a fuzzy extended state observer (FESO)-based stable fuzzy predictive control (SFPC) approach is developed in this paper. First, the control difficulties of the USC boiler–turbine unit are analyzed. Then, based on a Takagi–Sugeno (T–S) fuzzy model, a new FESO is developed for nonlinear systems to achieve a more precise observation performance. The gain of FESO is determined by solving a series of linear matrix inequalities, while guaranteeing the stability of FESO. Then, by combining the proposed FESO with the SFPC, an integrated FESO–SFPC algorithm is devised. The disturbance rejection ability of the FESO–SFPC algorithm is analyzed theoretically. Simulation results on a 1000 MW USC boiler–turbine power plant model further validate the effectiveness of the proposed method.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
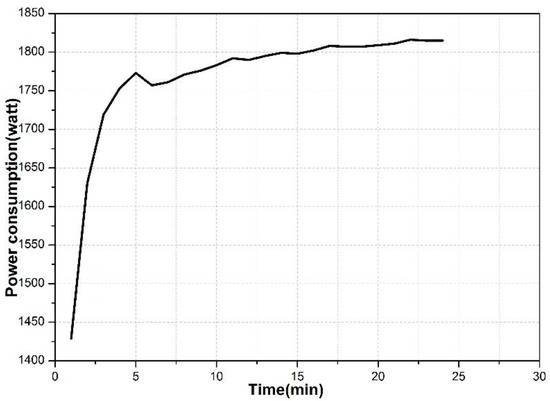
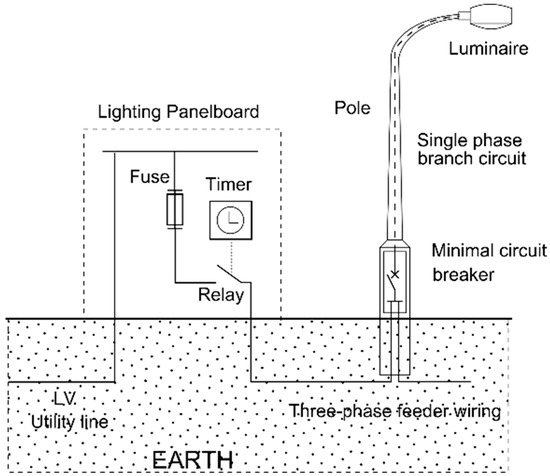
The Active Power Losses in the Road Lighting Installation with Dimmable LED Luminaires
by
Roman Sikora, Przemysław Markiewicz and Wiesława Pabjańczyk
Cited by 8 | Viewed by 3005
Abstract
In accordance with the requirements of PN EN 13201-5 standard for road lighting installation, energy performance indicators should be descripted. In order to calculate energy performance indicators, it is necessary to know the active power of the road lighting system. The above standard
[...] Read more.
In accordance with the requirements of PN EN 13201-5 standard for road lighting installation, energy performance indicators should be descripted. In order to calculate energy performance indicators, it is necessary to know the active power of the road lighting system. The above standard does not specify whether active power losses should be taken into account in calculations. The main purpose of the article is to estimate the active power losses in the road lighting installation. The article presents methods for calculating active power losses, taking into account losses in all main elements of the installation. The obtained calculation results show the relationship between active power losses and the power of luminaires, their number and spacing between poles. Calculations of active power losses were made for single-phase and three-phase installations. The active power losses in a three-phase system do not exceed 1.5% and in a single-phase installation they may be greater than 7%. Therefore, in order to obtain exact values of energy performance indicators (and also predict electricity consumption), active power losses should be taken into account in calculations. In addition, a comparative analysis of the effect of luminaires dimming and active power losses on annual CO
2 emissions was made. Not taking into account the active power losses in the calculation of the lighting installation’s power, for single-phase installations in particular, understates the calculated value of CO
2 emissions by more than 6%.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
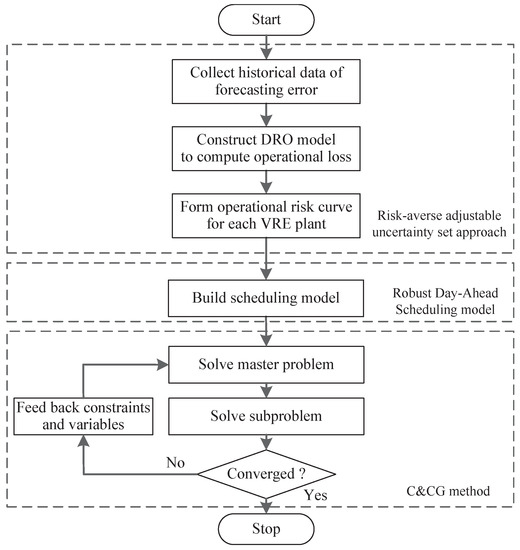
Robust Day-Ahead Scheduling of Electricity and Natural Gas Systems via a Risk-Averse Adjustable Uncertainty Set Approach
by
Li Yao, Xiuli Wang, Tao Qian, Shixiong Qi and Chengzhi Zhu
Cited by 9 | Viewed by 2854
Abstract
The requirement for energy sustainability drives the development of renewable energy technologies and gas-fired power generation. The increasing installation of gas-fired units significantly intensifies the interdependency between the electricity system and natural gas system. The joint scheduling of electricity and natural gas systems
[...] Read more.
The requirement for energy sustainability drives the development of renewable energy technologies and gas-fired power generation. The increasing installation of gas-fired units significantly intensifies the interdependency between the electricity system and natural gas system. The joint scheduling of electricity and natural gas systems has become an attractive option for improving energy efficiency. This paper proposes a robust day-ahead scheduling model for electricity and natural gas system, which minimizes the total cost including fuel cost, spinning reserve cost and cost of operational risk while ensuring the feasibility for all scenarios within the uncertainty set. Different from the conventional robust optimization with predefined uncertainty set, a new approach with risk-averse adjustable uncertainty set is proposed in this paper to mitigate the conservatism. Furthermore, the Wasserstein–Moment metric is applied to construct ambiguity sets for computing operational risk. The proposed scheduling model is solved by the column-and-constraint generation method. The effectiveness of the proposed approach is tested on a 6-bus test system and a 118-bus system.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Resource Assessment and Techno-Economic Analysis of a Grid-Connected Solar PV-Wind Hybrid System for Different Locations in Saudi Arabia
by
Yahya Z. Alharthi, Mahbube K. Siddiki and Ghulam M. Chaudhry
Cited by 65 | Viewed by 7149
Abstract
The economic growth and demographic progression in Saudi Arabia increased spending on the development of conventional power plants to meet the national energy demand. The conventional generation and continued use of fossil fuels as the main source of electricity will raise the operational
[...] Read more.
The economic growth and demographic progression in Saudi Arabia increased spending on the development of conventional power plants to meet the national energy demand. The conventional generation and continued use of fossil fuels as the main source of electricity will raise the operational environmental impact of electricity generation. Therefore, using different renewable energy sources might be a solution to this issue. In this study, a grid-connected solar PV-wind hybrid energy system has been designed considering an average community load demand of 15,000 kWh/day and a peak load of 2395 kW. HOMER software is used to assess the potential of renewable energy resources and perform the technical and economic analyses of the grid-connected hybrid system. The meteorological data was collected from the Renewable Resources Atlas developed by the King Abdullah City of Atomic and Renewable Energy (KACARE). Four different cities in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, namely, the cities of Riyadh, Hafar Albatin, Sharurah, and Yanbu were selected to do the analyses. The simulation results show that the proposed system is economically and environmentally feasible at Yanbu city. The system at this city has the lowest net present cost (NPC) and levelized the cost of energy (LCOE), highest total energy that can be sold to the grid, as well as the lowest CO
2 emissions due to a highly renewable energy penetration. This grid-connected hybrid system with the proposed configuration is applicable for similar meteorological and environmental conditions in the region, and around the world. Reduction of some greenhouse gasses as well as the reduction of energy costs are main contributors of this research.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Decomposition Analysis in Electricity Sector Output from Carbon Emissions in China
by
Xue-Ting Jiang, Min Su and Rongrong Li
Cited by 8 | Viewed by 3195
Abstract
Carbon emissions from China’s electricity sector account for about one-seventh of the global carbon dioxide emissions, or half of China’s carbon dioxide emissions. A better understanding of the relationship between CO
2 emissions and electric output would help develop and adjust carbon emission
[...] Read more.
Carbon emissions from China’s electricity sector account for about one-seventh of the global carbon dioxide emissions, or half of China’s carbon dioxide emissions. A better understanding of the relationship between CO
2 emissions and electric output would help develop and adjust carbon emission mitigation strategies for China’s electricity sector. Thus, we applied the electricity elasticity of carbon emissions to a decoupling index that we combined with advanced multilevel Logarithmic Mean Divisia Index tools in order to test the carbon emission response to the electric output and the main drivers. Then, we proposed a comparative decoupling stability analysis method. The results show that the electric output effect played the most significant role in increasing CO
2 emissions from China’s electric sector. Also, “relative decoupling” was the main state during the study period (1991–2012). Moreover, the electricity elasticity of CO
2 emissions had a better performance regarding stability in the analysis of China’s electricity output.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Effects of Market Reform on Facility Investment in Electric Power Industry: Panel Data Analysis of 27 Countries
by
Juyong Lee, Youngsang Cho, Yoonmo Koo and Chansoo Park
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 3423
Abstract
In this study, we analyzed the effects of electricity market reform on investment in generation facilities. We used the data of 27 OECD member countries and considered ownership structure, horizontal and vertical unbundling, change of transaction method, and government regulation as explanatory variables
[...] Read more.
In this study, we analyzed the effects of electricity market reform on investment in generation facilities. We used the data of 27 OECD member countries and considered ownership structure, horizontal and vertical unbundling, change of transaction method, and government regulation as explanatory variables for market reform. We used four regression models, in which we examined the effects of market reform on the capacity of generation facilities, supply reserve ratio, total investment, and base-load share, respectively. For each panel regression model, we performed a Hausman test to identify the model between random effect and fixed effect. Based on the estimation results, we found that electricity market reform has a negative effect on generation facilities in most countries. Both privatization and regulation have negative impacts on the generation facility and base-load share. On the other hand, the level of liberalization of transactions have positive effects on the generation facility, supply reserve ratio, and base-load share. The empirical analysis also showed that horizontal unbundling does not have a meaningful effect on investment, but vertical unbundling contributes to increasing the supply reserve ratio.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
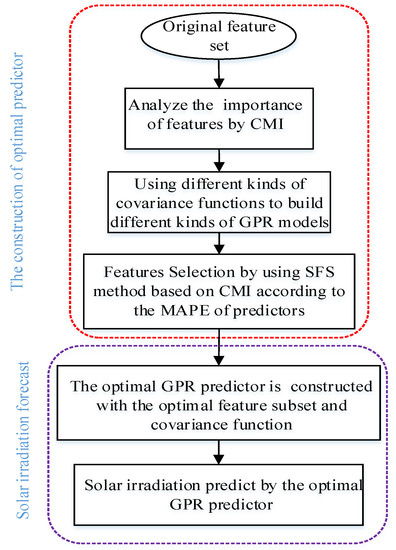
Low Redundancy Feature Selection of Short Term Solar Irradiance Prediction Using Conditional Mutual Information and Gauss Process Regression
by
Nantian Huang, Ruiqing Li, Lin Lin, Zhiyong Yu and Guowei Cai
Cited by 11 | Viewed by 3264
Abstract
Solar irradiation is influenced by many meteorological features, which results in a complex structure meaning its prediction has low efficiency and accuracy. The existing prediction methods are focused on analyzing the correlation between features and irradiation to reduce model complexity but they do
[...] Read more.
Solar irradiation is influenced by many meteorological features, which results in a complex structure meaning its prediction has low efficiency and accuracy. The existing prediction methods are focused on analyzing the correlation between features and irradiation to reduce model complexity but they do not account for redundant analysis in feature subset. In order to reduce the information redundancy in the feature set and improve prediction accuracy, a novel feature selection method for short-term irradiation prediction based on Conditional Mutual Information (CMI) and Gaussian Process Regression (GPR) is proposed. Firstly, the CMI values of different features are calculated to evaluate correlation and redundant information between features in the feature subsets. Secondly, GPR with a stable prediction performance and adaptively determined hyper parameters is used as the predictor. The optimal feature subset and the GPR covariance function can be selected using Sequential Forward Selection (SFS). Finally, an optimal predictor is determined by the minimum prediction error and the prediction of solar irradiation is carried out by the determined predictor. The experimental results show that CMI-GPR
AEK has the highest prediction accuracy with the optimal feature set has low dimension, which is 4.33% lower in MAPE than the predictor without feature selection, although both of them have an optimal kernel function. The CMI-GPR
AEK is less complicated for the predictor and there is less redundancy between features in the model with the dimension of the optimal feature set is only 14.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Electricity as a Cooking Means in Nepal—A Modelling Tool Approach
by
Ramchandra Bhandari and Surendra Pandit
Cited by 26 | Viewed by 8184
Abstract
Cooking energy has an important role in energy demand of Nepal. Over the last decade, import of Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG) has increased by 3.3 times as an alternate cooking fuel to kerosene and firewood. The growing subsidy burden to endorse modern fuel
[...] Read more.
Cooking energy has an important role in energy demand of Nepal. Over the last decade, import of Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG) has increased by 3.3 times as an alternate cooking fuel to kerosene and firewood. The growing subsidy burden to endorse modern fuel switching from traditional energy sources and high import of LPG are challenges for sustainability and energy security. This paper analyzes the future residential cooking energy demand and its environmental and economic impacts from 2015 to 2035 using a Long-range Energy Alternative Planning System (LEAP) tool. In 2035, the LPG demand for cooking is projected to be 26.5 million GJ, 16.3 million GJ, 45.2 million GJ and 58.2 million GJ for business as usual (BAU), low growth rate (LGR), medium growth rate (MGR) and high growth rate (HGR) scenarios, respectively. To substitute LPG with electricity in the cooking sector by 2035, an additional 1207 MW, 734 MW, 2055 MW and 2626 MW hydropower installation is required for BAU, LGR, MGR and HGR scenarios, respectively. In the MGR scenario, substituting LPG with electricity could save from $21.8 million (2016) to $70.8 million (2035) each year, which could be used to develop large-scale hydropower projects in the long term.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Restoration of an Active MV Distribution Grid with a Battery ESS: A Real Case Study
by
Matteo Manganelli, Mario Nicodemo, Luigi D’Orazio, Laura Pimpinella and Maria Carmen Falvo
Cited by 8 | Viewed by 4358
Abstract
In order to improve power system operation, Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESSs) have been installed in high voltage/medium voltage stations by Distribution System Operators (DSOs) around the world. Support for restoration of MV distribution networks after a blackout or HV interruption is among
[...] Read more.
In order to improve power system operation, Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESSs) have been installed in high voltage/medium voltage stations by Distribution System Operators (DSOs) around the world. Support for restoration of MV distribution networks after a blackout or HV interruption is among the possible new functionalities of BESSs. With the aim to improve quality of service, the present paper investigates whether a BESS, installed in the HV/MV substation, can improve the restoration process indicators of a distribution grid. As a case study, an actual active distribution network of
e-distribuzione, the main Italian DSO, has been explored. The existing network is located in central Italy. It supplies two municipalities of approximately 10,000 inhabitants and includes renewable generation plants. Several configurations are considered, based on: the state of the grid at blackout time; the BESS state of charge; and the involvement of Dispersed Generation (DG) in the restoration process. Three restoration plans (RPs) have been defined, involving the BESS alone, or in coordination with DG. A MATLAB
®/Simulink
® program has been designed to simulate the restoration process in each configuration and restoration plan. The results show that the BESS improves restoration process quality indicators in different simulated configurations, allowing the operation in controlled island mode of parts of distribution grids, during interruptions or blackout conditions. The defined restoration plans set the priority and the sequence of controlled island operations of parts of the grid to ensure a safe and better restoration. In conclusion, the results demonstrate that a BESS can be a valuable element towards an improved restoration procedure.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
The Evolution of Renewable Energy Price Policies Based on Improved Bass Model: A System Dynamics (SD) Analysis
by
Xin-gang Zhao, Yu-zhuo Zhang and Yan-bin Li
Cited by 10 | Viewed by 3973
Abstract
Many countries in the world have implemented many price support policies to promote the development of renewable energy, and there are evolutionary processes between different policies at different stages of national development. Existing literature has less research on the internal mechanism and alternative
[...] Read more.
Many countries in the world have implemented many price support policies to promote the development of renewable energy, and there are evolutionary processes between different policies at different stages of national development. Existing literature has less research on the internal mechanism and alternative process of renewable energy price policies’ evolution process. In view of this, this paper innovatively introduces the classic model of innovation diffusion theory, the Bass model, into the renewable energy price mechanism, and improves it on the basis of the traditional Bass model, and then proposes a system dynamics (SD) simulation based on the improved Bass model to study the evolution process of the renewable energy price policies. This paper mainly studies the evolution process of the policies from feed-in tariff (FIT) to renewable portfolio standard (RPS), and takes China’s wind power industry as an example to simulate the model. The results show that FIT can effectively and quickly evolve to RPS based on the internal influence of the interaction among power generation enterprises and the external influence of government behaviors. All the power generation enterprises will implement RPS, and the amount of green power enterprises eventually grows steadily and slowly. In addition, increasing the decline rate of FIT subsidy and RPS unit fine can effectively promote the evolution of RPS policy, and also improve the amount of green power enterprises and the activity of the tradable green certificates (TGC) trading market.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
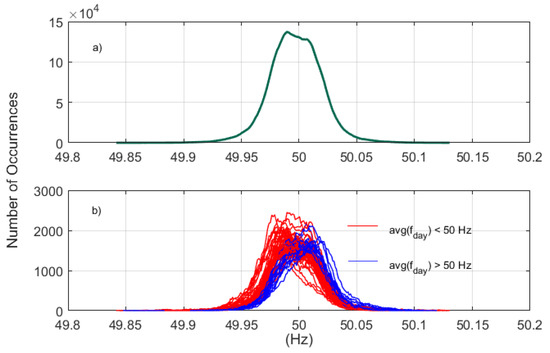
Impact of Asynchronous Renewable Generation Infeed on Grid Frequency: Analysis Based on Synchrophasor Measurements
by
Evangelia Xypolytou, Wolfgang Gawlik, Tanja Zseby and Joachim Fabini
Cited by 7 | Viewed by 4040
Abstract
The increasing power in-feed of Non-Synchronous Renewable Energy Sources (NS-RES) in the grid has raised concerns about the frequency stability. The volatile RES power output and absence of inertia in many types of NS-RES affect the balance between power consumption and production. Therefore,
[...] Read more.
The increasing power in-feed of Non-Synchronous Renewable Energy Sources (NS-RES) in the grid has raised concerns about the frequency stability. The volatile RES power output and absence of inertia in many types of NS-RES affect the balance between power consumption and production. Therefore, the dynamics of the power grid frequency become more complex. Extreme grid frequency deviations and fast variations can lead to partitioning and load shedding in the case of under-frequency. In the case of over-frequency, it can lead to overloading, voltage collapse and blackouts. The Rate of Change of Frequency (RoCoF) reflects an aspect of the stability status of the grid and therefore its analysis with regard to Non-Synchronous Instant Penetration (NSIP) is of great importance. In this work, two months of high-resolution frequency synchrophasor measurements during 18 January 2018–18 March 2018 recorded in Austria were analyzed to investigate the impact of NS-RES on the frequency. The correlation of RoCoF with the NSIP in Austria and Germany and with the frequency deviation were examined. It was observed that with a maximum NSIP share up to
of the total power generation in these two countries, there was no critical increase of RoCoF or abnormal frequency deviation in the power grid.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Cross-Subsidies and Government Transfers: Impacts on Electricity Service Quality in Colombia
by
Fan Li, Wenche Wang and Zelong Yi
Cited by 8 | Viewed by 3744
Abstract
An affordable and reliable supply of electricity service is essential to encourage sustainable social development in developing countries. Colombia uses cross-subsidies to prompt electricity usage for poor households. This raises the issue of whether charging lower prices to poor households, while boosting their
[...] Read more.
An affordable and reliable supply of electricity service is essential to encourage sustainable social development in developing countries. Colombia uses cross-subsidies to prompt electricity usage for poor households. This raises the issue of whether charging lower prices to poor households, while boosting their consumption, induces utilities to lower the quality of service received by them. This paper uses unique databases and examines how underfunded cross-subsidies affect perceived electricity service quality across consumer groups. Results indicate that when facing financial deficits, utilities provide lower perceived service quality to subsidized consumers than to residents paying surcharges. The difference in perceived quality across consumer groups is reduced by an increase in the amount of (external) government transfers. To prompt electricity consumption by the poor, the Colombian government should fund subsidies, strengthen quality regulation, and increase the transparency and reliability of government transfers.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
An Electricity Price Forecasting Model by Hybrid Structured Deep Neural Networks
by
Ping-Huan Kuo and Chiou-Jye Huang
Cited by 128 | Viewed by 9428
Abstract
Electricity price is a key influencer in the electricity market. Electricity market trades by each participant are based on electricity price. The electricity price adjusted with the change in supply and demand relationship can reflect the real value of electricity in the transaction
[...] Read more.
Electricity price is a key influencer in the electricity market. Electricity market trades by each participant are based on electricity price. The electricity price adjusted with the change in supply and demand relationship can reflect the real value of electricity in the transaction process. However, for the power generating party, bidding strategy determines the level of profit, and the accurate prediction of electricity price could make it possible to determine a more accurate bidding price. This cannot only reduce transaction risk, but also seize opportunities in the electricity market. In order to effectively estimate electricity price, this paper proposes an electricity price forecasting system based on the combination of 2 deep neural networks, the Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) and the Long Short Term Memory (LSTM). In order to compare the overall performance of each algorithm, the Mean Absolute Error (MAE) and Root-Mean-Square error (RMSE) evaluating measures were applied in the experiments of this paper. Experiment results show that compared with other traditional machine learning methods, the prediction performance of the estimating model proposed in this paper is proven to be the best. By combining the CNN and LSTM models, the feasibility and practicality of electricity price prediction is also confirmed in this paper.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Public Willingness to Pay for Increasing Photovoltaic Power Generation: The Case of Korea
by
Min-Kyu Lee, Ju-Hee Kim and Seung-Hoon Yoo
Cited by 11 | Viewed by 3122
Abstract
Renewable energy receives particular attention in Korea because of concerns about climate change and scarce traditional energy resources. The government plans to enhance photovoltaic (PV) power’s share of total power generation from 0.5% in 2014 to 10.1% in 2029. The present study tries
[...] Read more.
Renewable energy receives particular attention in Korea because of concerns about climate change and scarce traditional energy resources. The government plans to enhance photovoltaic (PV) power’s share of total power generation from 0.5% in 2014 to 10.1% in 2029. The present study tries to look into the public willingness to pay (WTP) for increasing PV power generation, applying the contingent valuation approach. A survey of 1000 interviewees was carried out in Korea. The observations of the WTP responses were gathered using a dichotomous choice question and analyzed employing the mixture model. The mean household WTP estimate is obtained as KRW 2183 (USD 1.9) per month, which possesses statistical significance. The total yearly WTP expanded to the population is worth KRW 476.9 billion (USD 423.1 million). These values can provide a useful basis for policy-making and decision-making about the economic feasibility of increasing PV power generation.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Optimal Locating of Electric Vehicle Charging Stations by Application of Genetic Algorithm
by
Milad Akbari, Morris Brenna and Michela Longo
Cited by 47 | Viewed by 7700
Abstract
The advent of alternative vehicle technologies such as Electrical Vehicles (EVs) is an efficient effort to reduce the emission of carbon oxides and nitrogen oxides. Ironically, EVs poses concerns related to vehicle recharging and management. Due to the significance of charging station infrastructure,
[...] Read more.
The advent of alternative vehicle technologies such as Electrical Vehicles (EVs) is an efficient effort to reduce the emission of carbon oxides and nitrogen oxides. Ironically, EVs poses concerns related to vehicle recharging and management. Due to the significance of charging station infrastructure, electric vehicles’ charging stations deployment is investigated in this work. Its aim is to consider several limitations such as the power of charging station, the average time needed for each recharge, and traveling distance per day. Initially, a mathematical formulation of the problem is framed. Then, this problem is optimized by application of Genetic Algorithm (GA), with the objective to calculate the necessary number of charging stations then finding the best positions to locate them to satisfy the clients demand.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
A DSM Test Case Applied on an End-to-End System, from Consumer to Energy Provider
by
Nikoleta Andreadou, Yannis Soupionis, Fausto Bonavitacola and Giuseppe Prettico
Cited by 7 | Viewed by 3701
Abstract
Current decarbonisation goals have, in recent years, led to a tremendous increase in electricity production generated from intermittent Renewable Energy Sources. Despite their contribution to reducing society’s carbon dioxide (CO
2) emissions they have been responsible for numerous challenges that the current
[...] Read more.
Current decarbonisation goals have, in recent years, led to a tremendous increase in electricity production generated from intermittent Renewable Energy Sources. Despite their contribution to reducing society’s carbon dioxide (CO
2) emissions they have been responsible for numerous challenges that the current electricity grid has to cope with. Flexibility has become a key mechanism to help in mitigating them. Real-time informed consumers can offer the needed flexibility through modifying their behaviour or by engaging with Demand Side Management (DSM) programs. The latter requires the intervention of several actors and levels of communication management which makes this task difficult from an implementation perspective. With this aim we built and tested a small scale system in our lab which represents a real end-to-end system from the consumer to the energy provider. We programmed the system according to the Object Identification System (OBIS) specification to obtain consumers’ consumption through smart meters with high frequency (one minute). This allows remote control of their appliances in order to reduce the total neighbourhood consumption during critical time periods of the day (peak time). These results and the realisation of a realistic end-to-end system open the way to more complex tests and particularly to the possibility of benchmarking them with other lab tests.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
A Hybrid Online Forecasting Model for Ultrashort-Term Photovoltaic Power Generation
by
Fei Mei, Yi Pan, Kedong Zhu and Jianyong Zheng
Cited by 26 | Viewed by 3877
Abstract
A hybrid photovoltaic (PV) forecasting model is proposed for the ultrashort-term prediction of PV output. The model contains two parts: offline modeling and online forecasting. The offline module uses historical monitoring data to establish a weather type classification model and PV output regression
[...] Read more.
A hybrid photovoltaic (PV) forecasting model is proposed for the ultrashort-term prediction of PV output. The model contains two parts: offline modeling and online forecasting. The offline module uses historical monitoring data to establish a weather type classification model and PV output regression submodels. The online module uses real-time monitoring data for weather type identification on target days and the forecasting of irradiation intensity and temperature time series. The appropriate regression submodel can be selected based on the subsequent results, and the ultrashort-term real-time forecasting of PV output can be performed over a short time scale. The model incorporates power generation and historical meteorological data from the PV station and is suitable for practical engineering applications. In addition to the irradiation intensity and temperature, other factors related to photovoltaic output are evaluated; however, they are excluded from the model for simplicity and efficiency. The performance of the model is verified by practical modeling analysis.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Optimal Placement and Sizing of PV-STATCOM in Power Systems Using Empirical Data and Adaptive Particle Swarm Optimization
by
Reza Sirjani
Cited by 22 | Viewed by 4784
Abstract
Solar energy is a source of free, clean energy which avoids the destructive effects on the environment that have long been caused by power generation. Solar energy technology rivals fossil fuels, and its development has increased recently. Photovoltaic (PV) solar farms can only
[...] Read more.
Solar energy is a source of free, clean energy which avoids the destructive effects on the environment that have long been caused by power generation. Solar energy technology rivals fossil fuels, and its development has increased recently. Photovoltaic (PV) solar farms can only produce active power during the day, while at night, they are completely idle. At the same time, though, active power should be supported by reactive power. Reactive power compensation in power systems improves power quality and stability. The use during the night of a PV solar farm inverter as a static synchronous compensator (or PV-STATCOM device) has recently been proposed which can improve system performance and increase the utility of a PV solar farm. In this paper, a method for optimal PV-STATCOM placement and sizing is proposed using empirical data. Considering the objectives of power loss and cost minimization as well as voltage improvement, two sub-problems of placement and sizing, respectively, are solved by a power loss index and adaptive particle swarm optimization (APSO). Test results show that APSO not only performs better in finding optimal solutions but also converges faster compared with bee colony optimization (BCO) and lightening search algorithm (LSA). Installation of a PV solar farm, STATCOM, and PV-STATCOM in a system are each evaluated in terms of efficiency and cost.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
A Statistical Tool to Detect and Locate Abnormal Operating Conditions in Photovoltaic Systems
by
Silvano Vergura
Cited by 7 | Viewed by 3163
Abstract
The paper is focused on the energy performance of the photovoltaic systems constituted by several arrays. The main idea is to compare the statistical distributions of the energy dataset of the arrays. For small-medium-size photovoltaic plant, the environmental conditions affect equally all the
[...] Read more.
The paper is focused on the energy performance of the photovoltaic systems constituted by several arrays. The main idea is to compare the statistical distributions of the energy dataset of the arrays. For small-medium-size photovoltaic plant, the environmental conditions affect equally all the arrays, so the comparative procedure is independent from the solar radiation and the cell temperature; therefore, it can also be applied to a photovoltaic plant not equipped by a weather station. If the procedure is iterated and new energy data are added at each new run, the analysis becomes cumulative and allows following the trend of some benchmarks. The methodology is based on an algorithm, which suggests the user, step by step, the suitable statistical tool to use. The first one is the Hartigan’s dip test that is able to discriminate the unimodal distribution from the multimodal one. This stage is very important to decide whether a parametric test can be used or not, because the parametric tests—based on known distributions—are usually more performing than the nonparametric ones. The procedure is effective in detecting and locating abnormal operating conditions, before they become failures. A case study is proposed, based on a real operating photovoltaic plant. Three periods are separately analyzed: one month, six months, and one year.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Comparative Study of Frequency Converters for Doubly Fed Induction Machines
by
Tarek Nahdi and Dusan Maga
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 3752
Abstract
The efficient utilization of energy sources seems to be one of the most challenging problems for designers and scientists alike. This challenge particularly applies to power electronics, where the increasing value of energy density leads to demands for optimization processes and better exploitation
[...] Read more.
The efficient utilization of energy sources seems to be one of the most challenging problems for designers and scientists alike. This challenge particularly applies to power electronics, where the increasing value of energy density leads to demands for optimization processes and better exploitation (and distribution) of available power sources. As a result, the implementation of frequency-controlled systems is more often in the spotlight. The systems with doubly fed induction machines and a frequency converter in the rotor circuit are typical representatives of these demands. In a wide spectrum of power electronic systems, frequency converters are often used that have a constant current, a diode rectifier, and a thyristor inverter. This article provides a novel approach to modeling methodology, and presents a unique comparison of four different frequency converter schemes that are connected to a doubly fed induction machine. This article presents the modeling methodology itself, as well as the results based on an asynchronous generator motor fed by different frequency converters, a spectral analysis of the output voltage of the used frequency converters, and a comparison of the different technologies. Based on the above, this paper recommends the use of a multistage-multilevel frequency converter scheme.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Why the Wind Curtailment of Northwest China Remains High
by
Guoliang Luo, Erli Dan, Xiaochun Zhang and Yiwei Guo
Cited by 31 | Viewed by 7348
Abstract
The total grid-connected installed capacity of wind power in northwest China has grown from 16,260 MW in 2013 to 43,290 MW in 2016; an increase of 88.7% each year. However, this region has suffered from increasingly serious wind curtailment since 2014, and the
[...] Read more.
The total grid-connected installed capacity of wind power in northwest China has grown from 16,260 MW in 2013 to 43,290 MW in 2016; an increase of 88.7% each year. However, this region has suffered from increasingly serious wind curtailment since 2014, and the wind curtailment amount accounts for nearly a half of China’s total. The wind curtailment rate of Gansu Province, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region and Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region in this area has increased and remains high. This paper constructs an analytical model to explore the reasons of the high wind curtailment of these three provinces from the four aspects of the wind power supply capacity, demand, grid transmission capacity, power system flexibility and market mechanism and laws. The results show that the relationship between the wind energy distribution and supply and the local load is incompatible, which is the source causing the high wind curtailment in northwest China. On the one hand, the game between the local government and developers has driven the development of wind power bases. On the other hand, the electricity sector is growing slowly and oversupply of electricity is seen in many areas of China. The wind power grid of northwest China not only faces limit of grid transmission capacity, but also constraint of insufficient flexibility of the electricity system. Presently, China has not set up a market mechanism and subsidy mechanism for the peak load adjustment, thus the thermal power companies lack motivation to voluntarily adjust the peak load. Moreover, the regional segregation and market barriers are also obstacles for the wind power outward transmission.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Optimal Power Scheduling for a Medium Voltage AC/DC Hybrid Distribution Network
by
Zhenshan Zhu, Dichen Liu, Qingfen Liao, Fei Tang, Jun Jason Zhang and Huaiguang Jiang
Cited by 30 | Viewed by 4761
Abstract
With the great increase of renewable generation as well as the DC loads in the distribution network; DC distribution technology is receiving more attention; since the DC distribution network can improve operating efficiency and power quality by reducing the energy conversion stages. This
[...] Read more.
With the great increase of renewable generation as well as the DC loads in the distribution network; DC distribution technology is receiving more attention; since the DC distribution network can improve operating efficiency and power quality by reducing the energy conversion stages. This paper presents a new architecture for the medium voltage AC/DC hybrid distribution network; where the AC and DC subgrids are looped by normally closed AC soft open point (ACSOP) and DC soft open point (DCSOP); respectively. The proposed AC/DC hybrid distribution systems contain renewable generation (i.e., wind power and photovoltaic (PV) generation); energy storage systems (ESSs); soft open points (SOPs); and both AC and DC flexible demands. An energy management strategy for the hybrid system is presented based on the dynamic optimal power flow (DOPF) method. The main objective of the proposed power scheduling strategy is to minimize the operating cost and reduce the curtailment of renewable generation while meeting operational and technical constraints. The proposed approach is verified in five scenarios. The five scenarios are classified as pure AC system; hybrid AC/DC system; hybrid system with interlinking converter; hybrid system with DC flexible demand; and hybrid system with SOPs. Results show that the proposed scheduling method can successfully dispatch the controllable elements; and that the presented architecture for the AC/DC hybrid distribution system is beneficial for reducing operating cost and renewable generation curtailment.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Wind Power Development and Energy Storage under China’s Electricity Market Reform—A Case Study of Fujian Province
by
Dunguo Mou
Cited by 8 | Viewed by 4053
Abstract
This paper, based on the Fujian provincial 500 kV grid and part of the 220 kV grid and the key power plants, including hydro, coal, nuclear, gas, wind and pumping and storage hydro powers (PSHP) connected to the grid, constructs an independent electricity
[...] Read more.
This paper, based on the Fujian provincial 500 kV grid and part of the 220 kV grid and the key power plants, including hydro, coal, nuclear, gas, wind and pumping and storage hydro powers (PSHP) connected to the grid, constructs an independent electricity market model. Using data that are very close to reality about coal fired power production costs, along with data about power plants’ technical constraints, this paper studies the effect of wind power on Fujian’s provincial electricity market. Firstly, the paper analyzes the relationship between wind speed and wind power output and the effects of short-term power output fluctuation on frequency modulation and voltage regulation. Secondly, under supposition of the production costs following quadratic functions, the paper analyzes the effects of changes in wind power output on the electricity supply costs under optimal power flow. Thirdly, using the bidding model in the Australian Electricity Market Operator for reference and supposing that, in a competitive market, coal fired power plants can bid 6 price bands according to their capacity, the paper analyzes effects of wind power on electricity prices under optimal power flow, the stabilizing effects of PSHP and the minimum PSHP capacity needed to stabilize the electricity market. Finally, using a daily load curve, this paper simulates the electricity prices’ fluctuation under optimal power flow and PSHP’s stabilizing effect. The results show that, although PSHP has a large external social welfare effect, it can hardly make a profit. In the end, this paper puts forward some policy suggestions for Fujian province’s wind and nuclear power development, PSHP construction and electricity market development.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
GMDH-Based Semi-Supervised Feature Selection for Electricity Load Classification Forecasting
by
Lintao Yang, Honggeng Yang and Haitao Liu
Cited by 15 | Viewed by 3936
Abstract
With the development of smart power grids, communication network technology and sensor technology, there has been an exponential growth in complex electricity load data. Irregular electricity load fluctuations caused by the weather and holiday factors disrupt the daily operation of the power companies.
[...] Read more.
With the development of smart power grids, communication network technology and sensor technology, there has been an exponential growth in complex electricity load data. Irregular electricity load fluctuations caused by the weather and holiday factors disrupt the daily operation of the power companies. To deal with these challenges, this paper investigates a day-ahead electricity peak load interval forecasting problem. It transforms the conventional continuous forecasting problem into a novel interval forecasting problem, and then further converts the interval forecasting problem into the classification forecasting problem. In addition, an indicator system influencing the electricity load is established from three dimensions, namely the load series, calendar data, and weather data. A semi-supervised feature selection algorithm is proposed to address an electricity load classification forecasting issue based on the group method of data handling (GMDH) technology. The proposed algorithm consists of three main stages: (1) training the basic classifier; (2) selectively marking the most suitable samples from the unclassified label data, and adding them to an initial training set; and (3) training the classification models on the final training set and classifying the test samples. An empirical analysis of electricity load dataset from four Chinese cities is conducted. Results show that the proposed model can address the electricity load classification forecasting problem more efficiently and effectively than the FW-Semi FS (forward semi-supervised feature selection) and GMDH-U (GMDH-based semi-supervised feature selection for customer classification) models.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
A Stochastic Optimization Model for Carbon Mitigation Path under Demand Uncertainty of the Power Sector in Shenzhen, China
by
Guangxiao Hu, Xiaoming Ma and Junping Ji
Viewed by 3414
Abstract
In order to solve problems caused by climate change, countries around the world should work together to reduce GHG (greenhouse gas) emissions, especially CO
2 emissions. Power demand takes up the largest proportion of final energy demand in China, so the key to
[...] Read more.
In order to solve problems caused by climate change, countries around the world should work together to reduce GHG (greenhouse gas) emissions, especially CO
2 emissions. Power demand takes up the largest proportion of final energy demand in China, so the key to achieve its goal of energy-saving and emission reduction is to reduce the carbon emissions in the power sector. Taking Shenzhen as an example, this paper proposed a stochastic optimization model incorporating power demand uncertainty to plan the carbon mitigation path of power sector between 2015 and 2030. The results show that, in order to achieve the optimal path in Shenzhen’s power sector, the carbon mitigation technologies of existing coal and gas-fired power plants will be 100% implemented. Two-thirds and remaining one-third of coal-fired power plant capacities are going to be decommissioned in 2023 and 2028, respectively. Gas-fired power, distributed photovoltaic power, waste-to-energy power and CCHP (Combined Cooling, Heating, and Power) are going to expand their capacities gradually.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures