Impact of COVID-19 on the Environment, Energy and Economics (Closed)
A topical collection in Sustainability (ISSN 2071-1050). This collection belongs to the section "Environmental Sustainability and Applications".
Viewed by 67537Editor
Interests: energy economics; climate change; environmental sustainability; environmental economics; health economics and renewable energy
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
The COVID-19 (Novel Coronavirus—Sars-Cov-2) pandemic has been declared a global pandemic by the World Health Organization due to its devastating impact on humanity. The institution of lockdown across countries is reported to have hampered several facets of life, ranging from waste management to economic development, energy consumption, and the environment. Thus, prompt discussions from the scientific community would be helpful in the fight against the virus. In line with the SDGs and the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, we invite papers on the following topics:
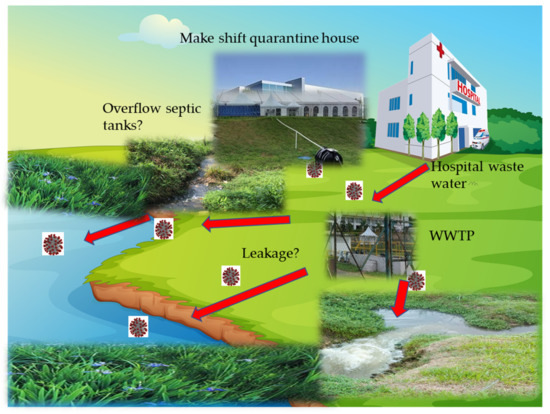
1) Chemicals—waste management—water and sanitation and COVID-19;
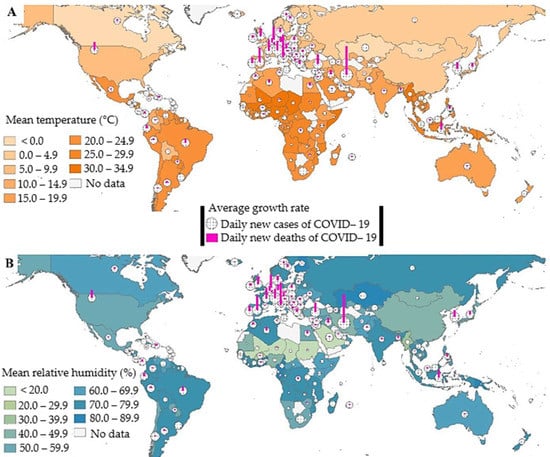
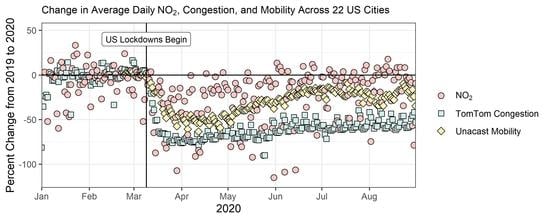
2) COVID-19 and the environment: transmission via surfaces, air, water, soil—detection of COVID-19 virus—the impact of environmental factors on transmission, survival, and infectivity such as wetness, dryness, temperature, relative humidity, sunlight, and air pollution (particulates, bioaerosol);
3) COVID-19 and oceans and blue economy—biodiversity and wildlife;
4) COVID-19 and economic growth, green recovery/greening economies;
5) Effective containment and preventive options and strategies for present and future spread, i.e., face masks, hand wash, disinfection technologies in public places and healthcare facilities;
6) Forecasting short- and long-term impact of the COVID-19 pandemic owing to current intervention and preventive measures.
Dr. Samuel Asumadu-Sarkodie
Guest Editor
References
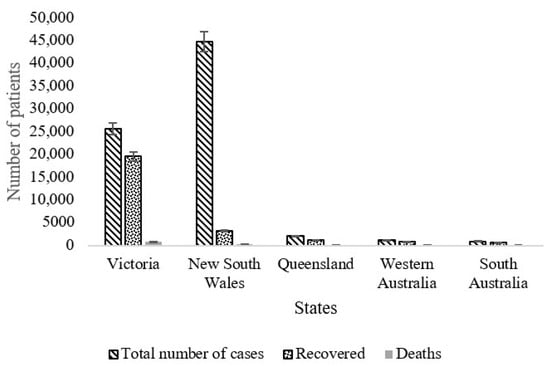
- Sarkodie, S. A., & Owusu, P. A. (2020). Impact of meteorological factors on COVID-19 pandemic: Evidence from top 20 countries with confirmed cases. Environmental Research, 110101.
- Sarkodie, S. A., & Owusu, P. A. (2020). Investigating the cases of novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19) in China using dynamic statistical techniques. Heliyon, e03747.
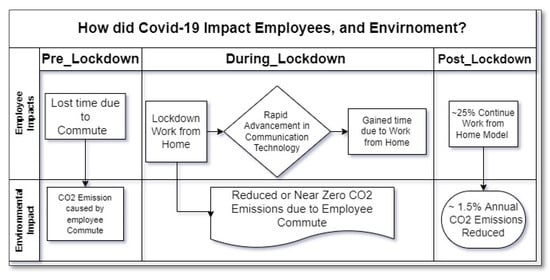
- Sarkodie, S. A., & Owusu, P. A. (2020). Impact of COVID-19 pandemic on waste management. Environment, development and sustainability, 1-10.
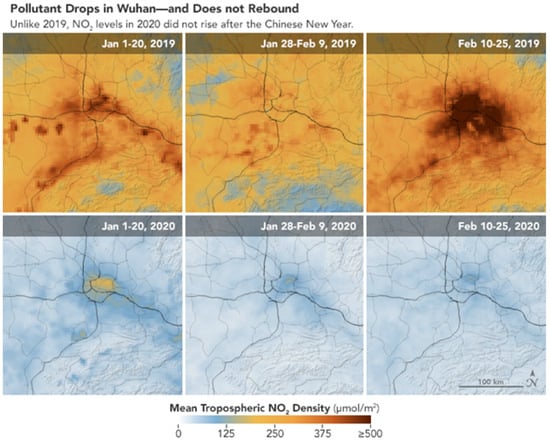
- Sarkodie, S. A., & Owusu, P. A. (2020). Global assessment of environment, health and economic impact of the novel coronavirus (COVID-19). Environment, Development and Sustainability, 1-11.
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Sustainability is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2400 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- transmission modes of COVID-19
- detection of COVID-19
- COVID-19 and waste management
- COVID-19 and weather
- COVID-19 and temperature
- COVID-19 and economics
- COVID-19 and finance
- COVID-19 and environment
- COVID-19 and air pollution