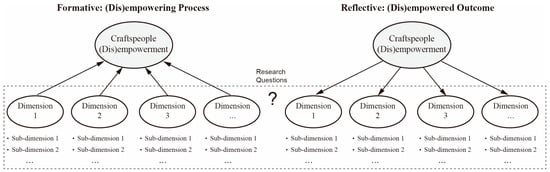
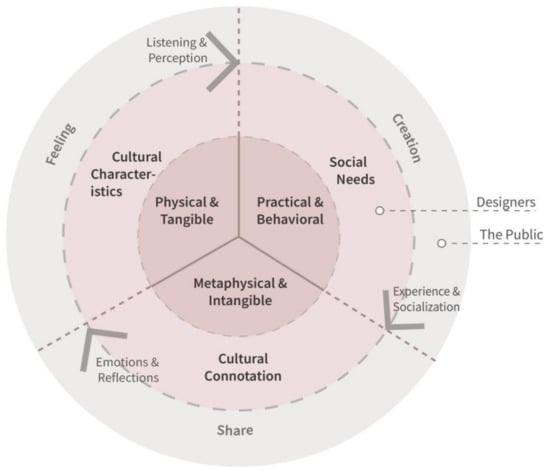
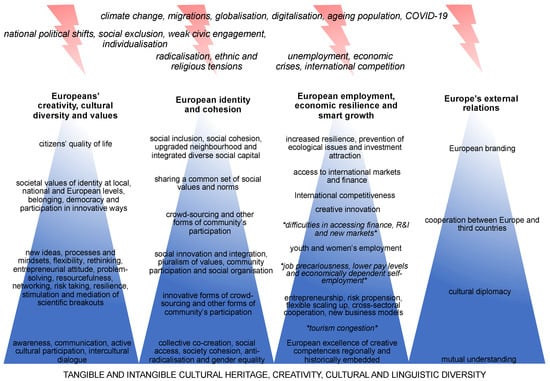
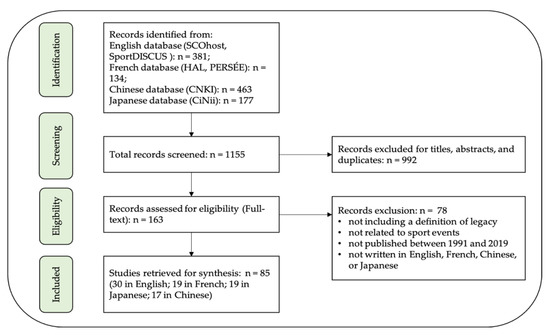
Cultural Crossovers and Social Sustainability
A topical collection in Sustainability (ISSN 2071-1050). This collection belongs to the section "Tourism, Culture, and Heritage".
Viewed by 113639Editor
2. RLL Department, Harvard University Cambridge MA, Boylston Hall, Cambridge, MA 02138, USA
3. FBK-IRVAPP, Via S. Croce 77, 38122 Trento, Italy
Interests: cultural economics and policy; behavioral science and public policy; evolutionary game theory and social behavior; social cognition; social neuroscience and economics; computational social sciences
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
The New Agenda for Culture published in May 2018 by the European Commission embraces an innovative approach to the role of culture in the creation of social and economic value. In particular, it recognizes the importance of the relation between cultural production and participation, on the one side, and health and wellbeing, social cohesion, and innovation, on the other. Moreover, the Agenda also contemplates the possibility of other, significant possible forms of cultural crossovers that are not explicitly mentioned in the Agenda. Possible examples are environmental sustainability and education and lifelong learning, among many.
In the recent past, the interdependence between culture and other social and economic spheres like the ones mentioned above has been mainly conceptualized in terms of spillovers, namely unintentional, unplanned effects of cultural production and participation. By reasoning in terms of crossovers, the attention is shifted toward more intentional and planned contaminations, in order to fully internalize and integrate the potential of culture in fostering social and economic change for the pursuit of the socially relevant goals of human development, economic prosperity, and social cohesiveness.
This Special Issue welcomes theoretical and empirical contributions that aim at providing deeper insights on all aspects of cultural crossovers, be they the ones explicitly mentioned in the New Agenda for Culture or different ones, and on their relationship with social sustainability goals, for instance in terms of inclusive societies, human development, intercultural dialogue, and so on. Empirical analyses of case studies at the regional, national, and international levels are especially welcome. In addition, theoretical models providing sound mathematical modeling of such processes are of interest, as well as papers reporting results from projects funded by relevant European programs, such as Creative Europe or Horizon are. However, the geographical scope of the Special Issue is global, and contributions regarding case studies and policy issues from both inside and outside the EU will be equally relevant and welcome.
Dr. Pier Luigi Sacco
Collection Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Sustainability is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2400 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- cultural crossovers
- social sustainability
- culture, health, and wellbeing
- culture and social cohesion
- culture and innovation
- culture and environmental sustainability